Banking
How Etiebet’s 2016 Letter Offers New Clues to N2.4bn Debt to Access Bank

In a letter dated November 9, 2016 written by former petroleum minister and All Progressive Congress (APC) chieftain, Don Etiebet, in respect of what is turning out to be a messy N2.4 billion indebtedness by an oil and gas company, Top Oil, to Access Bank Plc, appears to offer a new narrative to the dispute.
Writing in his capacity as chairman of Top Oil and Gas Company Limited, the letter shows an admission by Etiebet of the indebtedness and profuse pleading for time to resolve the matter with the principal parties, CASTOIL that appear to have brought the business from Mobil Oil Nigeria Limited, for which Top Oil was hoping to profit from as a third party participant.
However, the Etiebet letter seen by Business A.M. among the documents making the court rounds, also shows while CASTOIL had the direct supply business with Mobil Oil, Top Oil made have found the business very attractive as to take full responsibility of sourcing the funds, hence the Import Finance Facility (IFF) made available to it by the bank for the purpose of importation of Automotive Gas Oil (AGO) for supply to Mobil.
In the letter addressed to “The Manager, Access Bank Plc, Business Banking Division, Chevron Roundabout Branch, Lekki” with the heading, “RE: US$6.3 MILLION OUTSTANDING L/C PAYMENT”, Etiebet refers to the ‘demands’ by the manager for the payment of an outstanding letter of credit (LC) of $6,382,666.00, “which was used to import 10,000MT of AGO to supply Mobil Oil Nigeria Limited from Augusta Energy.”
In what appears to suggest an apology over the situation, Etiebet then wrote: “I regret that this payment is still outstanding till today. The true and correct position is that Top Oil and Gas Development Company Limited (TOPOIL) carried out this contract with a third party, CAST OIL and GAS LIMITED (CASTOIL) which brought the project from Mobil Oil Nigeria Limited. TOPOIL did not deal directly with Mobil Oil as it is common practice in the industry that companies cooperate to execute the project of this nature and share the profit,” Etiebet wrote.
He went on to explain that after an initial payment made by the third party, CASTOIL, the latter failed to make a further payment, suggesting this to be the reason for the delay and failure to redeem the letter of credit sum.
“Unfortunately, after the initial payment of N170,000,000.00 from CASTOIL into TOPOIL account with Access Bank Plc in August 2015 as agreed, CASTOIL failed to make further payments. CASTOIL then request (sic) TOPOIL to give it some time to reconcile certain issues with Mobil Oil and in the process issued TOPOIL a “PAYMENT COMMITMENT” in the sum of N1,321,431,000.00, which is what CASTOIL owed TOPOIL for the L/C at N200/$ at that time plus other costs and to pay up in three instalments by the 31st of August 2015 as per attached CASTOIL letter,” Etiebet, in the letter, also referred to how the Economic and Financial Crimes Commission (EFCC) had become involved, expressing confidence that the money would be paid to TOP OIL for it to settle Access Bank, what it owes it.
The letter further reads: “When the commitment was not honoured, TOPOIL reported the case to the security agencies. In the process of the investigations, CASTOIL entered into another agreement with TOPOIL to pay up by the end of November 2015, with understanding to pay interests and any forex variation from N200/$ to the fx rate at the time of completion of payment. The case is being handled by the EFCC with CASTOIL’s Managing Director, Mr TunjiAmushan being on Administrative Bail with sureties and his International Passport impounded as he reports to the EFCC every Thursday with promises to pay up. EFFCC has assured us that they would recover all the money plus interest and FX variation from him before long plus other sanctions.”
The letter showed that apparently while TOPOIL was trying to resolve whatever difficulties it was having with CASTOIL over the payment it did not inform or carry along with its bankers.
In further demonstration of remorse, therefore, Etiebet then stated in the letter: “I am very sorry that this was not reported to you before now because we thought CASTOIL would pay up as has been promised since last year for us to liquidate the outstanding L/C payment. So I take this opportunity to commit to you that the debts of US$6,382,666 to your bank shall, meanwhile, be paid from alternative sources including profits TOPOIL would be making from its current contracts with NNPC-Retail to supply AGO to Total-Offshore. “With other contracts in the pipeline including the supply of PMS to NNPC-Retail, I hereby give my personal undertaking to pay all the outstanding in the US$6,382,666 within 90 days. I want to let you know that we all in TOPOIL regret this unfortunate situation but thank you so much for your continued understanding and cooperation,” Etiebet concluded his rapprochement to the bank.
Sources close to the situation said nothing came out of the promises made in this 2016 letter as the bank did not receive any payment. The bitter contestation of the indebtedness that is currently going on would shades this profound apologetic and hugely conciliatory position in this letter and raises questions about how things got to this point and what, if any, could be the underlying motive behind a complete repudiation of the debt that in this November 9, 2016 letter was fully admitted. In an advertorial widely published in the media, Obodex Nigeria Limited, a company in which Etiebet has large interest and is chairman, claims that it does not owe any debt to Access Bank, a claim which seems to contradict the November 9, 2016 letter.
FACT SHEET TO POINT OF DISAGREEMENT
On November 21, 2014, Access Bank, following an accepted offer letter to the TOPOIL provides a US$6 million Import Finance Facility (IFF) to facilitate the importation of Automotive Gas Oil (AGO) for supply to Mobil Producing Unlimited by TOPOIL. The facility was tenured for a year with a maximum of 90 (ninety) days circle. In addition to the US$6 million IFF, TOPOIL was also availed a N100 million Revolving Time Loan vide the same offer letter for the purpose of facilitating the payment of Custom duties and other related Logistics.
This was also tenured for 1 (one) year with a maximum of 90 (ninety) days circle. Several Letters of Credit (LCs) were issued on the facilities, but only 1 (one) remained unpaid which is A2015C1091CL. The facts on the stated LC are stated below: In April 2015 TOPOIL submitted a Proforma Invoice valued at $5,802,500.00 and informed Access Bank it had an order from Mobil. Consequently, LC A2015C1091CL was issued in favour of a company called Augusta Energy SA (“Beneficiary”).
Upon presentation of all shipping documents required for this particular LC, funds were remitted by the bank to the beneficiary. In 2016, Access Bank increased the TOPOIL’s IFF from US$6 million to US$12 million and this was communicated to TOPOIL in an offer letter dated January 20, 2016. When the facility was not paid, the chairman of TOPOIL, Don Etiebet wrote to Access Bank in a letter dated November 9, 2016 that the LC was done with a third party known as Cast Oil & Gas Limited and committed to repay the Customer’s indebtedness.
Due to TOPOIL’s failure to repay the sum of US$6,382,665.71 at the expiration of the facility, the said amount was converted into a N2.2 billion Term Loan through an offer letter dated July 4, 2017 and the unutilized sum of US$5,617,334.29 on the US$12million IFF was also converted to a N1,463,000.000.00 Time Loan through the same offer letter. The N1,463,000.000.00 Time Loan was, however, never utilised by the TOPOIL.
Banking
CIBN to Back ACAMB on Professional Development, Industry Advocacy

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
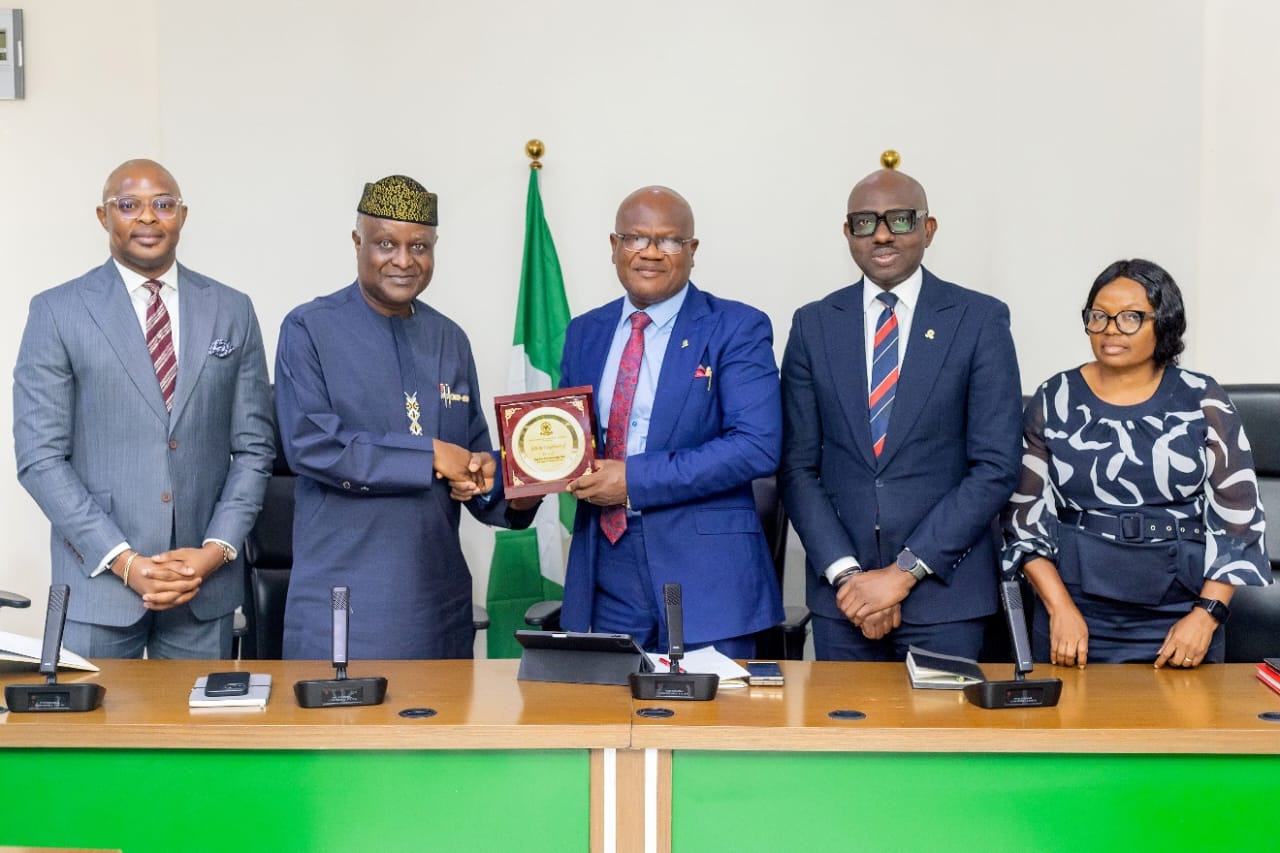
The Chartered Institute of Bankers of Nigeria (CIBN) has promised to support the ambitious plans of the Association of Corporate and Marketing Professionals in Banks (ACAMB).
At a meeting between the leaderships of the two organisations on Tuesday, the president of CIBN, Professor Pius Deji Olanrewaju, said it was impressed with the capability development and the undergraduate mentorship schemes of ACAMB under its leader, Mr Jide Sipe.
The CIBN chief commended the forward-thinking vision of the group, saying it had raised standards across Nigeria’s banking sector.
“ACAMB’s support has given CIBN and the banking sector brand equity,” he said, praising the association’s record in reputation management. recalling ACAMB’s role in addressing crises within the sector, describing the partnership as strategic and beneficial.
He further pledged support for ACAMB’s 30th anniversary in September 2026, its AGM, and other programmes, including fundraising initiatives.
“I want to assure you that everything you have presented today has been clearly noted and will be acted upon.
“We are fully committed to working closely with you so as to translate these discussions and vision into measurable progress. Our shared goal is to strengthen the sector, protect its reputation, and enhance its public image in a meaningful and lasting way.
“This meeting discussed various initiatives and reforms crucial for the future of our industry, including the need for continuous training and adaptation to new programs,” Mr Olanrewaju stated.
Speaking at the meeting, the president of ACAMB described the visit as a crucial first step in his tenure, aimed at contributing significantly to giving flight to his vision and that of ACAMB.
“When we assumed office, one of the first things we agreed on was the need to visit key stakeholders.
“However, before reaching out more broadly, we felt it was important to begin with our primary constituency and core stakeholders. We want them to understand the direction we are taking and to support the work we are doing, so that ACAMB can achieve greater success than it has in the past.
“We couldn’t have properly started our tenure without this very important meeting with the CIBN,” Mr Sipe stated
He introduced the newly constituted ACAMB Exco, which includes the 2nd Vice President, Morolake Phillip-Ladipo; General Secretary, Olugbenga Owootomo; Assistant General Secretary, Ademola Adeshola; Publicity Secretary, Abiodun Coker; and Executive Secretary, Fadekemi Ajakaiye.
Banking
All Set for Second HerFidelity Apprenticeship Programme

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
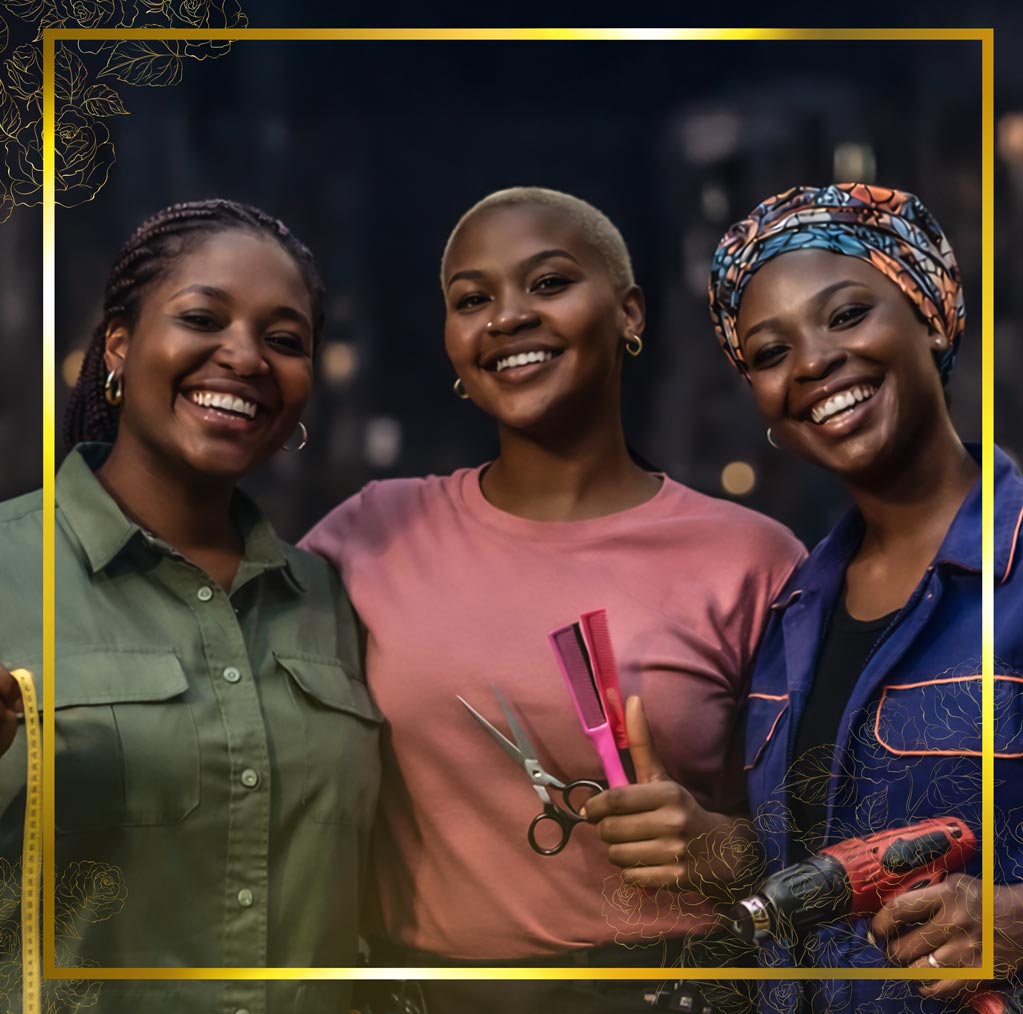
Registration for the second HerFidelity Apprenticeship Programme (HAP 2.0) organised by Fidelity Bank Plc has commenced.
The Divisional Head of Product Development at Fidelity Bank, Mr Osita Ede, informed newsmen that the initiative was designed to empower women with sustainable entrepreneurship skills.
The lender created the flagship women-empowerment initiative to equip women with practical, income‑generating skills and structured pathways to entrepreneurship.
“HerFidelity Apprenticeship Programme 2.0 reflects our commitment to continuous improvement. Having evaluated feedback from the first edition, we have returned with stronger partnerships and deeper mentorship programmes to ensure that women acquire not just skills, but sustainable economic opportunities,” he said.
“At the heart of the programme is guided, real‑world learning. Participants will undergo intensive apprenticeship training under reputable institutions and industry experts across select fields such as hair styling, shoe making, auto mechatronics, and interior decoration,” Mr Ede added.
He noted that HerFidelity Apprenticeship Programme 2.0 goes beyond skills acquisition by offering participants a wide range of business advisory services. These include business and financial literacy training, mentorship support throughout the apprenticeship journey, access to Fidelity Bank’s women‑focused and SME financial solutions, as well as guidance on business formalisation and growth strategies.
Further emphasising the bank’s vision, Mr Ede said, “By integrating structured mentorship with entrepreneurial development, Fidelity Bank is positioning women not just as trainees, but as future employers, innovators, and economic contributors within their communities. This aligns with our mandate to help individuals grow, businesses thrive, and economies prosper.”
Banking
The Alternative Bank Opens New Branch in Ondo

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
A new branch of The Alternative Bank (AltBank) has been opened in Ondo State as part of the expansion drive of the financial institution.
A statement from the company disclosed that the new branch would support export-oriented agribusinesses through Letters of Credit and commodity-backed trade finance, ensuring that local producers can scale beyond state borders.
For SMEs, the bank is introducing robust payment rails, asset financing for equipment and inventory, and supply chain-backed facilities that strengthen working capital without trapping businesses in interest-based debt cycles.
The Governor of Ondo State, Mr Lucky Aiyedatiwa, represented by his Chief of
Staff, Mr Olusegun Omojuwa, at the commissioning of the branch, underscored the importance of financial institutions in economic development.
“The pivotal role of financial institutions to economic growth and development of any economy cannot be overemphasised. It provides access to capital, supporting small and medium-scale enterprises and encouraging savings.
“Therefore, I have no doubt in my mind that the presence of The Alternative Bank in Ondo State will deepen financial services, create employment opportunities and stimulate economic activities across various sectors,” he said.
In her remarks, the Executive Director for Commercial and Institutional Banking (Lagos and South West) at The Alternative Bank, Mrs Korede Demola-Adeniyi, commended the state government’s leadership and outlined the lender’s long-term vision for Ondo State.
“As Ondo State steps into its next fifty years, and into the future anchored on the sustainable development championed during the recent anniversary celebrations, The Alternative Bank is here to be the financial engine for that vision. We didn’t come to Akure to hang banners. We came to fund work, farms, shops, and factories.”
With Ondo State’s economy anchored largely on agriculture, particularly cocoa production, poultry farming, and other cash crops, alongside a growing SME and trade ecosystem, AltBank is deploying sector-specific financing solutions tailored to these strengths.
For cocoa aggregators, processors and poultry operators, the bank will provide production financing, facility expansion support, machinery lease structures, and structured trade facilities under its joint venture and cost-plus financing models, with transaction cycles of up to 180 days for commodity trades and longer-term structured asset financing for equipment and infrastructure.
The organisation is a notable national non-interest bank with a physical network now surpassing 170 locations, deploying capital to solve real-world challenges through initiatives such as the Mata Zalla project, which saw to the training of hundreds of women as electric tricycle drivers and mechanics.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn