General
How Machine Learning Can Speed Up Regression Testing and Improve Accuracy
Modern software releases move fast, and manual regression testing often slows teams down. Machine learning helps automate repetitive checks, cut testing time, and reduce human error. It speeds up regression testing by predicting which test cases matter most and improves accuracy by detecting defects that manual testing can miss.
By analyzing past results and application changes, machine learning models identify high-risk areas that need attention. They can also update test scripts automatically and flag false positives before they waste valuable time. The process transforms quality assurance from a time-heavy step into an intelligent, data-driven practice.
As the discussion continues, the focus will shift to how specific machine learning techniques accelerate regression testing and how these models raise accuracy through smarter decision-making. Understanding these methods helps teams deliver better software faster and with greater confidence.
Machine Learning Approaches for Accelerating Regression Testing
Machine learning models now play a key role in improving test speed, accuracy, and adaptability. They help teams predict risk, focus on high-impact areas, and maintain large test suites with less manual input. Machine learning models now play a key role in improving test speed, accuracy, and adaptability. By analyzing past test data and application changes, these models help identify the most critical areas for testing, ensuring a more targeted approach. By prioritizing high-risk areas, machine learning-driven testing explained by Functionize allows teams to streamline their testing efforts, reducing unnecessary tests and focusing on what matters most. Compared to traditional manual testing, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error, machine learning models can quickly identify patterns and potential issues that might otherwise go unnoticed. While automated testing tools can speed up the process, machine learning-driven approaches offer a more intelligent, data-driven way to improve both speed and accuracy. As these models continuously learn from new data, they adapt to changes in the application, further refining their predictions.
Automated Test Case Prioritization and Selection
Automating test case selection saves time and helps quality teams focus on changes that matter most. Machine learning models analyze historical data such as past defects, code changes, and execution logs to determine which tests have the highest chance of catching new issues. This allows testers to run fewer but more meaningful tests.
Predictive algorithms can rank test cases by likelihood of failure or business impact. For instance, a model might use data on recent commits or modules with high defect density to reorder the suite. Teams then gain faster feedback without running every test after each build.
By pairing historical analytics with real-time signals, this approach reduces test redundancy while keeping accuracy high. It supports continuous delivery pipelines that require quick cycle times and minimal rework.
AI-Powered Test Suite Maintenance and Self-Healing Scripts
Maintenance creates major delays in large regression cycles. As interfaces or code structures evolve, older scripted tests often stop working. Machine learning can fix this problem by enabling self-healing test logic. It learns from element attributes, layout changes, and user flows to adjust tests automatically.
This approach reduces manual effort, since a tester does not need to rewrite scripts after each UI update. Modern tools track patterns across thousands of interface elements and use visual recognition to identify what changed in the application.
By adapting on its own, the system keeps tests useful through many software updates. The result is less downtime and fewer false failures, even as products shift between releases.
Optimizing Test Coverage and Efficiency with Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics models find gaps in existing tests and highlight areas that may need more coverage. This process often uses code churn data, historical defect rates, and user interaction logs to show where defects are most likely to appear. Teams then direct testing resources to those higher-risk areas.
These analytics can also help balance test distribution. For example, low-risk components might need only lightweight checks, while high-impact modules receive deeper testing.
Applying predictive insights helps achieve both higher coverage and faster delivery. It also allows early detection of potential stability issues before they reach production, reducing overall costs and improving test efficiency across each release cycle.
Improving Regression Test Accuracy with Machine Learning Models
Machine learning models can increase regression test accuracy by predicting which test cases matter most, identifying fault patterns in code, and reducing the time needed to verify new changes. Effective use of data preparation, model selection, and evaluation leads to stronger predictions and fewer missed defects.
Model Selection and Evaluation for Test Prediction
Choosing the right regression model defines how well predictions match real test outcomes. Models such as linear regression, random forest, support vector regression, and gradient boosting each handle data relationships differently. A good approach is to begin with a baseline model to compare performance across several algorithms.
Teams often use scikit-learn tools like RandomForestRegressor, GradientBoostingRegressor, and Ridge to predict regression test results. Selecting models with strong generalization avoids wasted computing time. Cross-validation, especially k-fold cross-validation, helps confirm performance consistency across datasets.
Evaluation metrics such as mean squared error (MSE), root mean squared error (RMSE), and R² (coefficient of determination) measure predictive accuracy. Lower MSE or RMSE values indicate better alignment between predictions and test outcomes. Using multiple metrics gives a balanced view of model performance.
Feature Engineering and Data Preparation for Reliable Outputs
Accurate results depend on clean and well-prepared data. Exploratory data analysis (EDA) helps detect outliers, missing values, or strong correlations that may distort predictions. Columns can be transformed using feature scaling, standardization through StandardScaler, or one-hot encoding for categorical variables.
Data normalization keeps all features within a similar scale, which prevents large-value features from dominating the model. Missing values can be filled with methods like SimpleImputer, improving input consistency. Feature selection or recursive feature elimination (RFE) can remove unnecessary inputs that lower performance.
Balanced and properly formatted input data allows regression models to identify true patterns in software behavior. A clear data structure reduces noise in predictions and increases confidence in each result.
Preventing Overfitting and Ensuring Model Strength
Models that perform too well on training data may fail with new code changes. Overfitting often occurs when the model captures random noise instead of meaningful test patterns. Careful cross-validation and hyperparameter tuning help control this issue.
Regularization techniques such as Lasso regression and Ridge regression limit unnecessary complexity by applying penalties to large coefficients. This keeps predictions stable across updates. GridSearchCV in scikit-learn can systematically test combinations of regularization strengths to find balanced settings.
Ensemble methods like bagging, random forest, or gradient boosting (XGBoost) combine multiple predictors to increase stability. These approaches average out errors across models and reduce sensitivity to specific data conditions. A consistent evaluation process helps maintain long-term predictive accuracy in regression testing pipelines.
Conclusion
Machine learning allows teams to speed up regression testing by analyzing test results and predicting which areas of code need the most attention. This targeted approach cuts down on repetitive test runs and saves time. As a result, test cycles move faster without losing accuracy.
AI-based tools also make test scripts adapt automatically to software updates. That reduces manual maintenance and helps keep test cases relevant. By using data-driven insights, teams can focus on the most important test cases instead of running thousands that add little value.
The technology also improves defect detection. For example, algorithms can separate real failures from false positives, so testers can act on genuine issues more quickly. The process becomes more efficient and dependable.
In summary, machine learning makes regression testing faster, smarter, and more precise. It allows development teams to maintain software quality while releasing updates at a steady pace.
General
Tinubu Tasks Acting IGP Disu to Restore Peace, Strengthen Security Nationwide
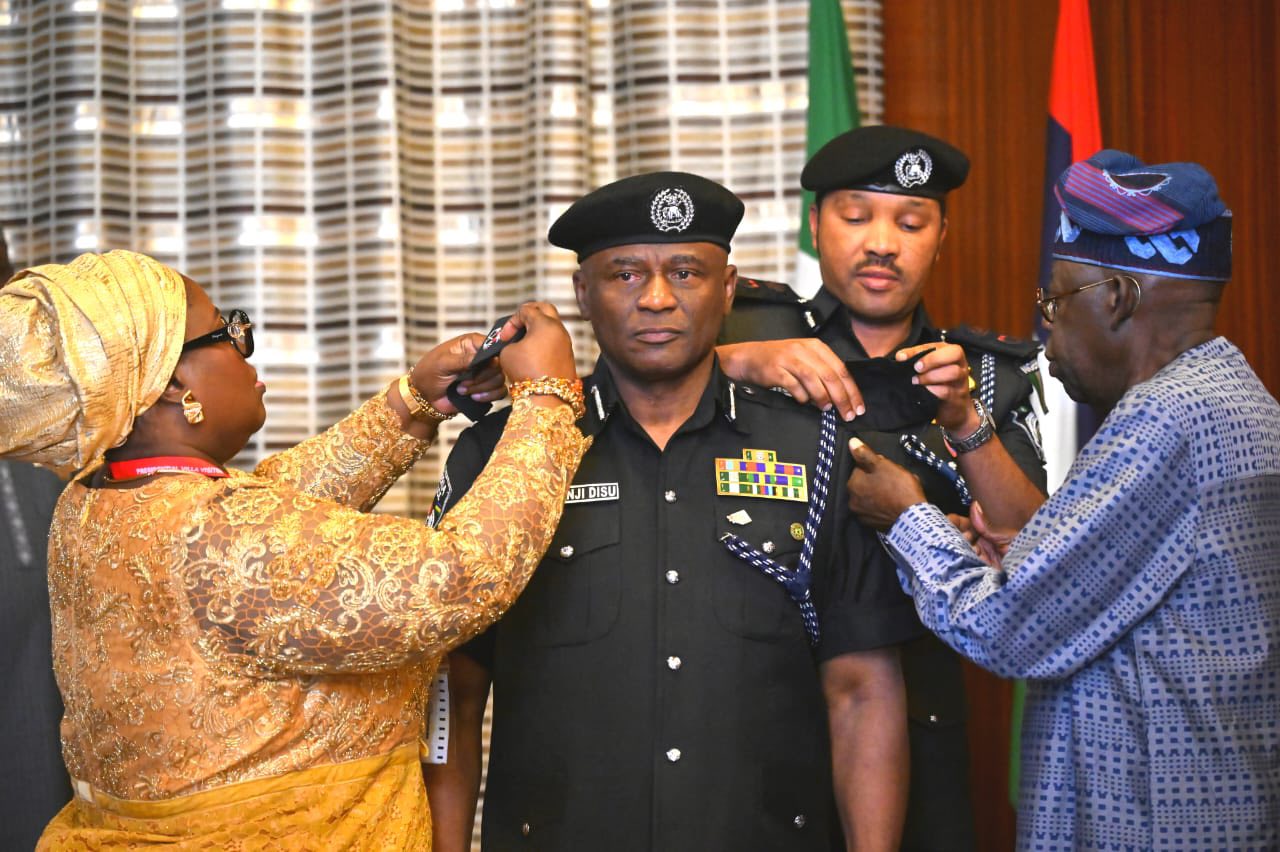

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
The acting Inspector-General of Police (IGP), Mr Tunji Disu, has been charged to do everything within his powers to restore peace and strengthen security across the nation.
This task was given to the new police chief by President Bola Tinubu after being decorated at the State House in Abuja on Wednesday.
Mr Disu was chosen to succeed Mr Kayode Egbetokun on Tuesday. His appointment is expected to be approved by the Nigeria Police Council and confirmed by the Senate next week.
President Tinubu described Mr Disu’s appointment as coming at a critical moment, urging him to rebuild public confidence in the police’s capacity to do their job in collaboration with other security forces.
“I made this decision for you to assume this responsibility. I know your record. I saw the dedication you exhibited while you were in Lagos when I was governor,” the President said.
“Lead firmly but fairly, demand professionalism at every level and ensure that the safety of lives and property remains our highest priority. It’s a daunting challenge. I know you can do it. You have my word, you have my full support,” he added.
Mr Tinubu urged him to advance the security pillars of his administration’s Renewed Hope Agenda. He expressed confidence in the Acting IGP’s discipline, operational experience and leadership capacity.
“Nigeria is challenged with banditry, terrorism and other criminal activities. You will be part of the thinking and innovation to overcome them,” the President said, reaffirming his belief that Nigeria would prevail under a committed leadership.
The President also paid tribute to Mr Egbetokun, who was present with his spouse, saying, “We are a grateful nation. Nigeria appreciates your contribution to maintaining law and order.”
He urged Egbetokun to be ready to offer useful advice to his successor and wished him and his family peace, good health and success in future endeavours, noting,
“You have not succeeded without a good successor. His success will also be part of your legacy.”
Mr Tinubu urged all security stakeholders to work collectively to safeguard lives and property during this critical period.
General
Real Estate Sector Now Safe Haven for Fraudsters—EFCC

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
The chairman of the Economic and Financial Crimes Commission (EFCC), Mr Ola Olukoyede, has lamented how “people now defraud the government and individuals and invest in real estate.”
He raised this concern when he received the executives of the Association of Real Estate and Property Managers (AREAPM) in Edo State on Wednesday.
The EFCC chief, represented by the acting Zonal Director and Deputy Commander of the Commission, Mr Sa’ad Hanafi Sa’ad, warned real estate managers against money laundering.
“We have noted with grave concern that fraudsters are laundering money and hiding proceeds of crime through real estate and property. People now defraud the government and individuals and invest in real estate,” he stated.
He noted that the agency would continue to discharge its statutory mandate of bringing those who seek to circumvent the system to book.
“As a commission, we recognise the role of Real Estate and Property Managers. Property Managers are designated non-financial businesses and professions.
“So, we expect them to be professionals and uphold the relevant rules and regulations in the discharge of their duties,” he stated, adding that, “The commission will apply the laws when there is a breach of relevant rules and regulations.”
He assured the AREAPM executives of the organisation’s willingness to collaborate with them in dealing with fraud and criminality in the sector.
“We have a unit, the Land and Property Fraud Section, which attends to issues in that regard. So, when you have challenges, you can report to us,” he stated.
In his remarks, the chairman of AREAPM in Edo State, Mr Akpesiri Michael Egbonoje, stated that the essence of the visit was to seek areas of collaboration with the commission and work out ways of combating real estate financial crimes and fraud in the state.
“Part of our strategy is to familiarise ourselves with law enforcement agencies in the state and seek for collaborative relationships. As a body, we cannot do it alone; we need help in the areas of financial crimes.
“We have tried to sanitise the space, but we realised that your agency is at the apex when it comes to dealing with financial crimes.
“We believe that structured collaboration between AREARM and the EFCC will promote financial transparency, investor confidence, and accountability within the real estate sector.”
General
Coroner’s Court Fixes April 14 for Inquiry into Death of Chimamanda Adichie’s Son

By Adedapo Adesanya
The Coroner’s Court sitting at the Yaba Magistrate Court has announced April 14, 2026, for the commencement of an inquiry into the death of 21-month-old Nkanu Nnamdi Esege, son of renowned Nigerian author Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie and Dr Ivara Esege.
Magistrate Atinuke Adetunji fixed the date on Wednesday when the matter came up before the court.
The twin child, Nkanu, died on January 7, 2026, after receiving care at Atlantis Hospital and undergoing medical procedures at Euracare Multi-Specialist Hospital in Lagos.
The child was initially admitted to Atlantis Hospital in Lagos for what was described as a worsening but initially mild illness.
The family had sought initial care as arrangements were being made to transfer him to Johns Hopkins Hospital in the United States. Atlantis referred him to Euracare for pre-flight diagnostic procedures, including an MRI, lumbar puncture, and insertion of a central line.
However, the child passed away following the procedures.
His parents have alleged medical negligence and professional misconduct in connection with his death.
According to a leaked internal message sent privately to family members and close friends at the time, Ms Adichie blamed the staff of Euracare Multi-Specialist Hospital, located in Victoria Island, Lagos, for causing the demise of the lad.
“My son would be alive today if not for an incident at Euracare Hospital on January 6th,” she wrote in a broadcast message confirmed later on.
“We have now heard about two previous cases of this same anesthesiologist overdosing children. Why did Euracare allow him to keep working? This must never happen to another child,” she also wrote in the lengthy message.
The 48-year-old writer had her first child, a daughter, in 2016. In 2024, her twin boys were born using a surrogate.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn












