Health
WHO Supports Nigeria, 4 Others to Fight Lassa Fever Outbreaks

By Dipo Olowookere
With five countries in Western Africa reporting outbreaks of Lassa fever, the World Health Organization (WHO) has scaled up its efforts to support the region’s response to the disease.
While these outbreaks are occurring during the Lassa fever season in countries where the disease is endemic, the speed of escalation is of concern.
The largest outbreak thus far has affected 16 states in Nigeria. The Nigeria Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) declared an outbreak of Lassa fever on 22 January 2019. The 213 confirmed cases to date, including 42 deaths, mark a significant increase – already a third of the total cases for all of last year, when Nigeria experienced its worst outbreak of Lassa fever. Four health workers have been infected so far in this latest outbreak.
In Nigeria, WHO is scaling up its efforts to support the Federal authorities, NCDC and the affected Nigerian states in responding to the outbreak.
An important focus is on early detection and confirmation of suspected cases, providing optimal supportive care and ensuring infection prevention and control measures in designated health care facilities in the affected states.
WHO has intensified its technical assistance and is supporting coordination, enhanced surveillance, epidemiological analysis and risk communication. WHO is also mobilizing experts to support case management and infection prevention and control.
A total of 12 cases have been confirmed to date in Benin, Guinea, Liberia and Togo, including two deaths, with more suspected cases being investigated. WHO is assisting health authorities in these countries with contact tracing and providing medical and non-medical supplies and technical and financial resources as needed for case management, risk communication and logistics.
“We are concerned by the high number of cases so early in the Lassa fever season, which is expected to last another four more months,” said Dr Ibrahima Socé Fall, Regional Emergencies Director at WHO Regional Office for Africa. “WHO is working with the health authorities in the five-affected countries to ensure health workers have the capacity to detect cases and we are monitoring the regional spread of the disease.”
WHO has set up a regional coordination mechanism for countries to report any suspected case of Lassa fever to expedite the flow of timely information and to assess the situation, recommend actions and help organize assistance. WHO has also reached out to the six other at-risk countries – Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Ghana, Mali, Niger and Sierra Leone – and is supporting prevention and readiness activities as needed.
“WHO continues to advise all countries in the Lassa fever belt to enhance their preparedness and response capacities, especially for early case detection, laboratory confirmation, case management under recommended barrier nursing, risk communication and community engagement,” said Dr Fall.
Lassa fever is an acute viral haemorrhagic illness that occurs predominantly in West Africa, after human exposure to the urine or faeces of infected Mastomys rats. More than 80% of Lassa fever cases are rodent-to-human transmission. Person-to-person transmission occurs in both community and health-care settings.
Prevention of Lassa fever relies on promoting good “community hygiene” to discourage rodents from entering homes by storing grain and other foodstuffs in rodent-proof containers, disposing of garbage far from the home, maintaining clean households, keeping cats and the safe handling of anyone who may have died of the disease.
In health-care settings, health-care workers should always apply standard infection prevention and control precautions when caring for patients.
Health
Chimamanda: MDCN Suspends Euracare Medical Director, Anesthesiologist

By Adedapo Adesanya
The Medical and Dental Practitioners Investigation Panel of the Medical and Dental Council of Nigeria (MDCN) has invoked its order of suspension against the Medical Director of Euracare Multi-Specialist Hospital, Dr Tosin Majekodunmi, and two others, after establishing a prima facie case of medical negligence against them in the management of the late Nkanu Adichie-Esege.
Nkanu, the son of renowned Nigerian author, Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie and Dr Ivara Esege, died on January 7, 2026, after receiving care at Atlantis Hospital and undergoing medical procedures at Euracare Multi-Specialist Hospital in Lagos. He was 21 months old.
Apart from the Medical Director at Euracare, the panel also suspended the anesthesiologist at the same hospital, Dr Titus Ogundare, as well as the Chief Medical Officer at Atlantis Pediatric Hospital, Dr Atinuke Uwajeh.
The trio were suspended from medical practice in Nigeria pending the determination of their case by the Medical and Dental Practitioners Disciplinary Tribunal.
A statement signed by the committee’s secretary, Dr Enejo Abdu, also disclosed it was determining if there is a prima facie case of professional misconduct against 10 other doctors.
These are Dr Adeseye Akinsete, Dr Chidinma Ohagwu, Dr Anthony Ajeh, Dr Amarachi Bayo, and Dr Nkechi Peji. Others are Dr Olaoye Oludare, Dr Agaja Oyinkansola, Dr Patricia Akintan, Dr Babatunde Bamgboye, and Dr Raji Faidat.
The panel, which also cleared eight other doctors, reached these decisions after considering the complaint against all 21 doctors and reviewing their counter-affidavits, including their oral depositions on oath.
It concluded its investigation at its 25th session held at Excel Hotel & Resort in Abuja on February 17 and 18, 2026.
The 21-month-old child, Nkanu Adichie-Esege, was initially admitted to Atlantis Hospital in Lagos for what was described as a worsening but initially mild illness.
While arrangements were being made to transfer him to Johns Hopkins Hospital in the United States, Atlantis referred him to Euracare for pre-flight diagnostic procedures, including an MRI, lumbar puncture, and insertion of a central line.
However, the child passed following the procedures.
His parents have alleged medical negligence and professional misconduct in connection with his death.
In a legal notice dated January 10, 2026, issued by the law firm led by Kemi Pinheiro (SAN), Ms Adichie and her husband accused Euracare, its anesthesiologist, and other attending medical personnel of breaching the duty of care owed to their son.
The notice stated that the child, born on March 25, 2024, was referred to Euracare on January 6, 2026, for diagnostic and preparatory procedures ahead of an emergency medical evacuation to the United States, where a specialist team was reportedly on standby.
The procedures reportedly included: Echocardiogram, Brain MRI, and insertion of a peripherally inserted central catheter.
Lumbar puncture, Intravenous sedation using propofol was administered.
The parents alleged that the child developed sudden and severe complications while being transported to the cardiac catheterisation laboratory after the MRI.
The development has raised worries and questions about the country’s healthcare.
Health
Nigeria to Receive Breakthrough HIV Prevention Drug Lenacapavir—NACA
By Adedapo Adesanya
The National Agency for the Control of AIDS (NACA) has announced that Nigeria would take delivery of Lenacapavir, a groundbreaking human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) prevention drug that has shown 100 per cent effectiveness in preventing the viral infection in clinical trials.
A short statement released by the Head of Public Relations for NACA, Mrs Toyin Aderibigbe, on Monday said the agency had secured regulatory approval from the National Agency for Food and Drug Administration and Control (NAFDAC).
HIV over time causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDs), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive.
Lenacapavir is an injectable treatment administered twice a year, making it a more convenient alternative to daily oral prevention drugs.
The drug is expected to be available in Nigeria and 119 other low- and middle-income countries at an affordable price of $40 per person annually, thanks to voluntary licensing agreements with generic manufacturers.
“The Government of Nigeria is advancing preparations for the introduction and rollout of Lenacapavir as Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP).
“This is part of the government’s commitment to strengthen HIV prevention and accelerate progress toward epidemic control,” the statement read.
NACA listed some significant milestones achieved, including completion of landscape and readiness assessments across ten states: Akwa Ibom, Anambra, Benue, Cross River, Ebonyi, FCT, Gombe, Kano, Kwara, and Lagos, alongside regulatory approval by NAFDAC.
“The commodities are expected in the country in March 2026,” NACA noted.
Nigeria has approximately 1.9 million people living with HIV, with a national prevalence of 1.3% among adults aged 15-49 years.
The country recorded 74,000 new HIV infections and 51,000 AIDS-related deaths in 2021.
The South-South zone has the highest HIV prevalence at 3.1%, while women aged 15-49 years are more than twice as likely to be living with HIV as men.
Daily oral PrEP has been available in Nigeria since 2016, but uptake varies. Adherence issues like pill fatigue, stigma, limited awareness, and inconsistent access have hindered wider use.
Newer PrEP options include injections that last two or six months, providing an alternative for those who prefer less frequent dosing and may overcome many barriers of daily oral use.
Health
Union Disrupts NAFDAC Operations in Lagos Over Sachet Alcohol Ban

By Adedapo Adesanya
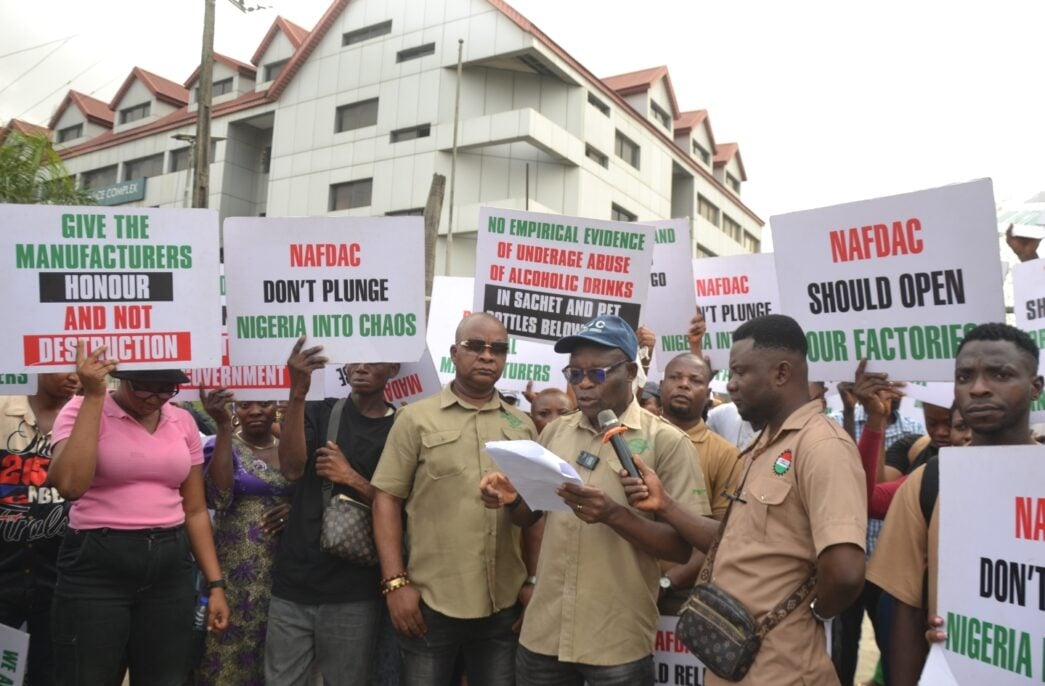
Members of the National Union of Food, Beverage and Tobacco Employees protested at the Lagos office of the National Agency for Food and Drug Administration and Control (NAFDAC), disrupting operations in reaction to the ban on sachet alcohol.
The protesting union members barricaded the agency’s premises in Isolo, meaning staff who arrived early to resume duty were forced to remain outside the complex.
Recall that NAFDAC has continued the ban on alcoholic beverages sold in sachets and PET bottles below 200 millilitres, despite calls from certain quarters, including the picketers.
The union is demanding the immediate unsealing of affected factories and production lines, warning that sustained enforcement of the policy could trigger significant economic consequences across the industry.
It is the second time this month that union members disrupted the Lagos NAFDAC office over what they described as the agency’s refusal to comply with an alleged federal government directive to suspend enforcement of the ban on the production and sale of alcoholic beverages in sachets.
The union claimed that directives had been issued by the Office of the Secretary to the Government of the Federation and the Office of the National Security Adviser, calling for the suspension of enforcement and the reopening of sealed production lines.
However, NAFDAC dismissed the claims, maintaining that it had not received any official instruction from the Federal Government to halt enforcement of the ban on sachet and PET-bottled alcohol.
Meanwhile, police officers were later seen at the NAFDAC Isolo premises, which dispersed the blockade to allow NAFDAC staff back into the premises.
Representatives of the Director-General of NAFDAC later engaged the protesting union in talks, but the meeting ended without resolution as demonstrators insisted their agitation would continue.
Union leaders presented their concerns during closed-door discussions with a director within the agency and the Special Assistant to the Director-General. However, no agreement was reached.
The protesters are urging NAFDAC to reconsider what they describe as the strict enforcement of the ban on sachet alcohol. Instead, they want the agency to focus on regulating access to such products, particularly by restricting sales to minors, while intensifying public enlightenment campaigns on responsible consumption.
Despite this, protesters say they will not stop until their demands are addressed.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn












