World
Russia Lacks Professionals To Pursue Its Policy Goals in Africa

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
Understandably more than three decades after the Soviet collapse, Russia has few well-trained multipolar-oriented specialists and professionals to work seriously on its diverse policy goals in Africa.
As simple as the narratives in several reports, Russians have bitterly complained of an acute shortage of policy leaders with the necessary adequate knowledge and expertise who could advance efforts at directing, coordinating and monitoring purpose-driven action plans and deliver impact at a scale expected in Africa.
With the rapidly-evolving multipolar world, the increasing competitiveness for influence and the need to reinforce cooperation between the government and business sectors, Russia has to focus on its agenda and take suitable strategies for implementing policy-set goals in Africa. Perhaps now, Russians are acknowledging their existing weaknesses. Complaints of inadequate professional staff in several reports could be interpreted as poor performance and as a cover-up for its policy pitfalls in Africa.
On the other hand, Russia has so many reputable educational institutions graduating thousands of candidates yearly. The Russian Diplomatic Academy, Moscow State University’s Institute of Oriental and African Studies, Moscow State Institute of International Relations (MGIMO), Russian University of Peoples’ Friendship, St. Petersburg State University, the Institute for African Studies, et cetera. Suppose Russian officials still maintain there is a lack of professionals. In that case, it must be due to poor planning, poor vision and poor coordinating efforts between state institutions of government and educational centres, as pointed out in a policy report in November 2021.
That report, titled – ‘Situation Analytical Report’ – was prepared by 25 policy experts headed by Professor Sergei A. Karaganov, Dean and Academic Supervisor of the Faculty of World Economy and International Relations of the National Research University’s Higher School of Economics (HSE University). Karaganov is also the Honorary Chairman of the Presidium of the Council on Foreign and Defence Policy.
The report was very critical of Russia’s current policy towards Africa. It indicated inconsistency in policy implementation and further underlined the fact that has been few definitive results from various efforts in dealing with African countries. It says in part: “Apart from the absence of a public strategy for the continent, there is a shortage of qualified personnel, the lack of coordination among various state and para-state institutions working with Africa.”
Last December, Interfax News Agency reported that the Russian Science and Higher Education Ministry was preparing new educational programmes for developing countries within the context of the emerging multipolar world. Since the Soviet collapse, Russia has trained graduates and professionals for the past three decades in many of its institutes and universities in the Russian Federation.
“The challenge is the transformation of the system of international relations and the re-focusing of educational and scientific flows to the East and the South. We realize that this turn requires a substantial number of competent professionals, so we are preparing a new educational and scientific programme called Oriental and African Studies,” Russian Science and Higher Education Minister Valery Falkov said during Government Hour in the Federation Council.
“We need specialists who are not just fluent in languages of the regions and have a profound knowledge of their history and culture but who are also proficient in economic and geopolitical matters,” he said at the Federation Council, the Upper Chamber of Parliament.
Russian International Affairs Council, a non-government organization and policy think tank, also published an opinion article authored by Kirill Babaev, Director of the Institute of Far Eastern Studies of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Professor at the Financial University. He made an excellent analysis of the relations between Russia and Africa.
The article highlighted future perspectives and successes in building political dialogues during the previous years. On the other hand, he exposes for serious consideration by authorities some existing obstacles and weaknesses.
He wrote that Russia’s return to Africa had been discussed in the media and at various levels of power for two decades. That the African elites, especially those who studied at Soviet institutes and universities, still have memories of the struggle for the political freedom of Africa. During the Soviet times, at the height of fighting against Western colonialism, there were economic offerings of the Soviet era.
However, all these cards are a matter of the past, while in the present, it has been difficult for Russia to offer Africa anything of value that could compete with large-scale Western investment or Chinese infrastructure projects, he wrote in his article.
Today the situation has changed radically, according to his assessment. He pointed out the challenges Russia faces, one of them being “an immense lack of personnel for successful work in Africa”, and further suggested the necessity of putting together a distinctive group of experienced professionals and specialists to work on practical, consistent and effective policy challenges as well as geopolitical tasks with African countries.
In an insightful long-ranging conversation in April 2022, the newly appointed Rector of the Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia, Oleg Yastrebov, told me that his university was established back in 1960; it primarily provided higher education to Third World students during the Soviet days. Many students, especially from developing countries, still come to this popular university from Latin America, Asia and Africa. It is Russia’s most multidisciplinary university, which boasts the largest number of foreign students and offers various academic disciplines.
Without mincing words, the youth is the future. The whole development and technological progress depend on them – the present young generation learning to become professional leaders in various fields and get equipped with the necessary skills that help them to acquire the knowledge of communication internationally.
“We are the most international, the most multidisciplinary and the friendliest university in Russia. It has the strongest language school. By studying languages, students receive an extra diploma as a translator. A student can choose from 12 foreign languages to study: European, Oriental or Russian as a foreign language,” he told me authoritatively.
He unreservedly argued that the university staff and academic teams provide the necessary knowledge and cutting-edge skills for young aspiring leaders from 160 countries, and that makes the university first-class among many others in the Russian Federation. The countries include those in Europe, Asia and the Middle East, Africa and Latin America.
The Institute for African Studies under the Russian Academy of Sciences was founded in 1959. Since then, it has undergone various changes and carried out huge scientific research on Africa. It has nearly a hundred staff including well-experienced researchers, academic fellows and specialists on various African issues and directions.
Professor Dmitri Bondarenko, Deputy Director of the Institute for African Studies (IAS), told me during discussions, just before the first Russia-Africa summit and precisely the 60th anniversary of the IAS, that state institutions and business companies seek the Institute’s consultancy services more and more often nowadays. In particular, the Institute played an important role in the preparation of the first Russia-Africa summit held in October 2019.
“The situation has been changing during the last few years. Today the importance of Africa for Russia in different respects, including political and economic, is recognized by the state, and the Russian Foreign Ministry and other state institutions dealing with Russia-African relations in various spheres, ask us for our expert advice on different points quite often,” said Bondarenko.
According to him, the situation now is much better for African studies than for a long time before. In particular, today, there are much more opportunities for doing fieldwork in Africa. Russian Africanists and their work are becoming better known in the global Africanist community. Quite a lot of junior researchers join the academy nowadays. In an assessment, African studies in Russia are on the right road to broadening international cooperation with Africanists worldwide.
Unlike the United States and Europe, Russia has poor relations with its trained African professionals and African specialists who graduated from Soviet and Russian educational establishments. Without a doubt, some of them could serve as bridges between Russia and Africa. Why not? At the U.S.-Africa Leaders Summit, there was an explicit indication to engage African professionals in the entire structure in the process of re-setting relations and moving it to the next stage. That is an irreversibly strong positive step.
Are Russia-Africa relations truly based on long-standing traditions of friendship and solidarity created by the Soviet Union? Is forging closer relations within their agreed framework to continue coordinating positions on platforms? Why are Russians complaining? Have they already trashed the joint declaration adopted, after the first summit, on the key areas of Russian-African cooperation or will it be considered only as an important historical document in the State Archival Library of Vladimir Lenin?
The accelerated development of human resource potential is inextricably linked to economic development. The 21st century has heralded the rise of the knowledge economy, and Russia really needs people who will be able to make vital contributions to tackling social and economic challenges facing Africa. Of course, the Soviet Union made an invaluable contribution to developing the scientific and educational potential of a number of African countries.
Obviously, Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov has reminded several times that Africa is Russia’s priority, especially during this emerging democratic polycentric world order. There should have been well-coordinated efforts toward working with graduates trained in Russian institutions and an integrated manner of working closely with African specialists in opening up practically a new page in the history of Russia’s relations with Africa.
World
Russia Expands Military-Technical Cooperation With African Partners

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
Despite geopolitical complexities, tensions and pressure, Russia’s military arms and weaponry sales earned approximately $15 billion at the closure of 2025, according to Kremlin report. At the regular session, chaired by Russian President Vladimir Putin on Jan. 30, the Commission on Military and Technical Cooperation with Foreign Countries analyzed the results of its work for 2025, and defined plans for the future.
It was noted that the system of military-technical cooperation continued to operate in difficult conditions, and with increased pressure from the Western countries to block business relations with Russia. The meeting, however, admitted that export contracts have generally performed sustainably. Russian military products were exported to more than 30 countries last year, and the amount of foreign exchange exceeded $15 billion.
Such results provide an additional opportunity to direct funds to the modernization of OPC enterprises, to the expansion of their production capacities, and to advanced research. It is also important that at these enterprises a significant volume of products is civilian products.
The Russian system of military-technical cooperation has not only demonstrated effectiveness and high resilience, but has created fundamental structures, which allow to significantly expand the “geography” of supplies of products of military purpose and, thus strengthen the position of Russia’s leader and employer advanced weapons systems – proven, tested in real combat conditions.
Thanks to the employees of the Federal Service for Military Technical Cooperation and Rosoboronexport, the staff of OPC enterprises for their good faith. Within the framework of the new federal project “Development of military-technical cooperation of Russia with foreign countries” for the period 2026-2028, additional measures of support are introduced. Further effective use of existing financial and other support mechanisms and instruments is extremely important because the volumes of military exports in accordance with the 2026 plan.
Special attention would be paid to the expansion of military-technological cooperation and partnerships, with 14 states already implementing or in development more than 340 such projects.
Future plans will allow to improve the characteristics of existing weapons and equipment and to develop new promising models, including those in demand on global markets, among other issues – the development of strategic areas of military-technical cooperation, and above all, with partners on the CIS and the CSTO. This is one of the priority tasks to strengthen both bilateral and multilateral relations, ensuring stability and security in Eurasia.
From January 2026, Russia chairs the CSTO, and this requires working systematically with partners, including comprehensive approaches to expanding military-technical relations. New prospects open up for deepening military-technical cooperation and with countries in other regions, including with states on the African continent. Russia has been historically strong and trusting relationships with African countries. In different years even the USSR, and then Russia supplied African countries with a significant amount of weapons and military equipment, trained specialists on their production, operation, repair, as well as military personnel.
Today, despite pressure from the West, African partners express readiness to expand relations with Russia in the military and military-technical fields. It is not only about increasing supplies of Russian military exports, but also about the purchase of other weapons, other materials and products. Russia has undertaken comprehensive maintenance of previously delivered equipment, organization of licensed production of Russian military products and some other important issues. In general, African countries are sufficient for consideration today.
World
Trump Picks Kevin Warsh to Succeed Jerome Powell as Federal Reserve Chair

By Adedapo Adesanya
President Donald Trump has named Mr Kevin Warsh as the successor to Mr Jerome Powell as the Federal Reserve chair, ending a prolonged odyssey that has seen unprecedented turmoil around the central bank.
The decision culminates a process that officially began last summer but started much earlier than that, with President Trump launching a criticism against the Powell-led US central bank almost since he took the job in 2018.
“I have known Kevin for a long period of time, and have no doubt that he will go down as one of the GREAT Fed Chairmen, maybe the best,” Mr Trump said in a Truth Social post announcing the selection.
US analysts noted that the 55-year old appear not to ripple market because of his previous experience at the apex bank as Governor, with others saying he wouldn’t always do the bidding of the American president.
If approved by the US Senate, Mr Warsh will take over the position in May, when Mr Powell’s term expires.
Despite having argued for reductions recently, “Warsh has a long hawkish history that markets have not forgotten,” one analyst told Bloomberg.
President Trump has castigated Mr Powell for not lowering interest rates more quickly. His administration also launched a criminal investigation of Powell and the Federal Reserve earlier this month, which led Mr Powell to issue an extraordinary rebuke of President Trump’s efforts to politicize the independent central bank.
World
BRICS Agenda, United States Global Dominance and Africa’s Development Priorities
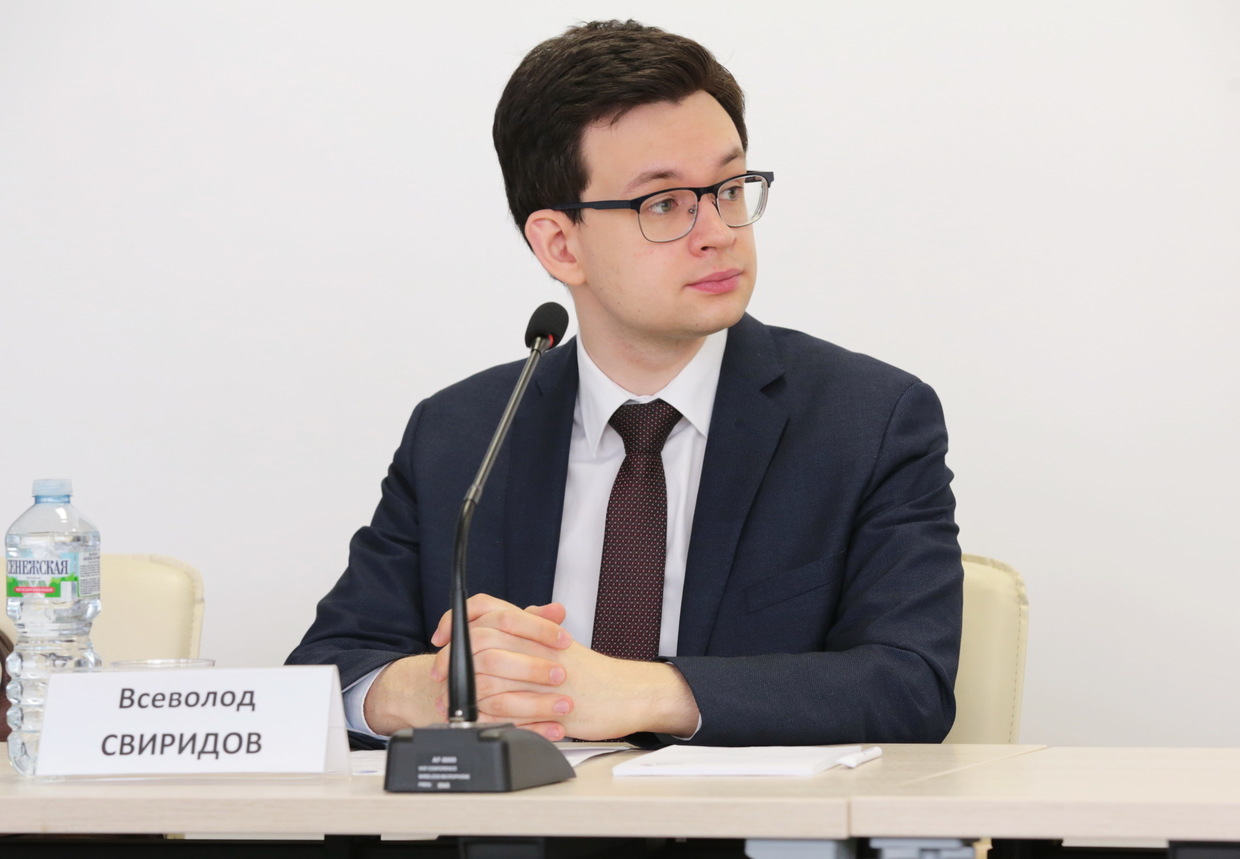

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
Donald Trump has been leading the United States as its president since January 2025. Washington’s priority is to Make America Great Again (MAGA). Trump’s tariffs have rippled many economies from Latin America through Asian region to the continent of Africa. Trump’s Davos speech has explicitly revealed building a ‘new world order’ based on dominance rather than trust. He has also initiated whirlwind steps to annex Greenland, while further created the Board of Peace, aimed at helping end the two-year war between Israel and Hamas in Gaza and to oversee reconstruction. Trump is handling the three-year old Russia-Ukraine crisis, and other deep-seated religious and ethnic conflicts in Africa.
These emerging trends, at least in a considerable short term, are influencing BRICS which has increased its geopolitical importance, and focusing on uniting the countries in the Global East and Global South. From historical records, BRICS, described as non-western organization, and is loosing its coherence primarily due to differences in geopolitical interests and multinational alignments, and of course, a number of members face threats from the United States while there are variations of approach to the emerging worldwide perceptions.
In this conversation, deputy director of the Center for African Studies at Moscow’s National Research University High School of Economics (HSE), Vsevolod Sviridov, expresses his opinions focusing on BRICS agenda under India’s presidency, South Africa’s G20 chairmanship in 2024, and genegrally putting Africa’s development priorities within the context of emerging trends. Here are the interview excerpts:
What is the likely impact of Washington’s geopolitics and its foreign policy on BRICS?
From my perspective, the current Venezuela-U.S. confrontation, especially Washington’s tightened leverage over Venezuelan oil revenue flows and the knock-on effects for Chinese interests, will be read inside BRICS as a reminder that sovereign resources can still be constrained by financial chokepoints and sanctions politics. This does not automatically translate into BRICS taking Venezuela’s side, but it does strengthen the bloc’s long-running argument for more resilient South-South trade settlement, diversified energy chains, and financing instruments that reduce exposure to coercive measures, because many African and other developing economies face similar vulnerabilities around commodities, shipping, insurance, and correspondent banking. At the same time, BRICS’ expansion makes consensus harder: several members maintain significant ties with the U.S., so the most likely impact is a technocratic push rather than a loud political campaign.
And highlighting, specifically, the position of BRICS members (South Africa, Ethiopia and Egypt, as well as its partnering African States (Nigeria and Uganda)?
Venezuela crisis urges African members to demand that BRICS deliver usable financial and trade tools. For South Africa, Ethiopia, and Egypt, the Venezuela case is more about the precedent: how quickly external pressure can reshape a country’s fiscal room, debt dynamics, and even investor perceptions when energy revenues and sanctions compliance collide. South Africa will likely argue that BRICS should prioritize investment, industrialization, and trade facilitation. Ethiopia and Egypt, both debt-sensitive and searching for FDI, will be especially attentive to anything that helps de-risk financing, while avoiding steps that could trigger secondary-sanctions anxieties or scare off diversified investors.
Would the latest geopolitical developments ultimately shape the agenda for BRICS 2026 under India’s presidency?
India’s 2026 chairmanship is already framed around “Resilience, Innovation, Cooperation and Sustainability,” and Venezuela’s shock (paired with broader sanction/market-volatility lessons) will likely sharpen the resilience part. From an African perspective, that is an opportunity: South Africa, Ethiopia, and Egypt can press India to translate the theme into deliverables that matter on the ground: food and fertilizer stability, affordable energy access, infrastructure funding. India, in turn, has incentives to keep BRICS focused on economic problem-solving rather than becoming hostage to any single flashpoint. So the Venezuela episode may function as a cautionary case study that accelerates practical cooperation where African members have the most to gain. And I would add: the BRICS agenda will become increasingly Africa-centered simply because Africa’s weight globally is rising, and recent summit discussions have repeatedly highlighted African participation as a core Global South vector. South Africa’s G20 chairmanship last year explicitly framed around putting Africa’s development priorities high on the agenda, further proves this point.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism9 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn