General
The Challenges Of Dredging In Nigeria And Specifically In Africa

Introduction
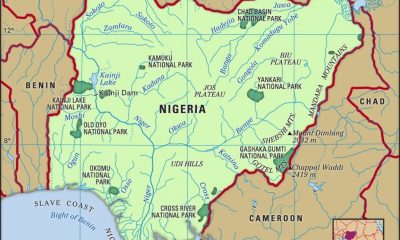
Dredging plays a vital role in shaping economic and environmental outcomes across many African nations. In Nigeria, a country defined by its vast waterways, complex delta systems, and dense coastal regions, dredging has become more than a necessity—it’s a core infrastructure activity. However, despite its importance, dredging in Nigeria faces several challenges that are deeply rooted in geographical, regulatory, and economic complexities.
A Growing Need for Dredging
Nigeria’s rivers and coastline have long served as important transportation and economic corridors. However, with increased siltation, encroaching sandbars, and sediment build-up, vital routes have become less navigable. As a result, dredging is frequently required for river dredging operations, port access, and flood management. Additionally, the continuous need for coastal erosion control is pushing both public and private stakeholders to invest in long-term dredging strategies.
Unfortunately, the regional challenges across Africa make consistent progress difficult.
Environmental and Regulatory Hurdles
One of the primary issues facing dredging in Nigeria is regulatory inconsistency. Multiple layers of local, state, and federal governance often result in conflicting permits, unclear environmental impact standards, and delayed approvals. These delays are especially critical when dealing with waterway infrastructure development, which requires timely intervention to prevent disruptions in transportation and trade.
Furthermore, environmental concerns—such as disturbance to aquatic ecosystems, resettlement of nearby communities, and improper disposal of dredged materials—must be addressed with sensitive planning and oversight. Without clear environmental frameworks, these concerns can result in halted projects or long-term ecological damage.
Infrastructure and Equipment Gaps
Dredging projects in Africa, particularly in Nigeria, are often hindered by a lack of modern equipment and trained personnel. Many small operators rely on outdated or makeshift dredging machines that are inefficient and prone to breakdowns. This gap is particularly evident in more remote or underfunded regions where access to quality dredging tools and support is limited.
Dredge Flow continues to advocate for partnerships that bring in more sustainable equipment and technical expertise into local markets. The goal is not only to improve project efficiency but also to increase safety and long-term results.
Socio-Economic Factors
The intersection of dredging with socio-economic development cannot be overlooked. On the one hand, dredging stimulates job creation and enables trade by maintaining waterways. On the other hand, unregulated dredging practices can lead to land disputes, environmental degradation, and the displacement of communities. Balancing these outcomes is one of the more delicate challenges in regions already affected by limited infrastructure and governance gaps.
Moreover, due to Nigeria’s urban expansion and land reclamation initiatives, the demand for dredged sand has skyrocketed. This creates incentives for illegal dredging, which further complicates oversight and disrupts river dredging operations intended for legitimate infrastructure development.
Regional Differences in Africa
While dredging in Nigeria faces its localized challenges, other African nations also struggle with similar yet context-specific issues. In East Africa, for example, fluctuating lake levels and sedimentation affect inland port operations. In West Africa, rising sea levels have accelerated the need for coastal erosion control, particularly in countries like Ghana and Sierra Leone.
These shared challenges highlight the need for collaborative efforts, shared technologies, and investment in capacity building across the continent.
The Way Forward
Despite these obstacles, opportunities for improvement remain. By investing in modern dredging technology and skilled labor, Nigeria and its neighbors can better tackle both routine and emergency projects. Creating unified regulatory frameworks and enforcing strict environmental standards will help ensure that waterway infrastructure development is sustainable and community-friendly.
Additionally, incorporating local expertise and involving affected communities in decision-making processes can lead to better project outcomes and reduced conflict. Through these efforts, dredging can serve as a foundation for environmental resilience, economic growth, and regional cooperation.
Conclusion
To overcome these regional challenges, Dredge Flow offers tailored dredging operations and solutions designed for the unique conditions of Nigeria and broader African waterways. By combining durable dredging equipment with on-ground expertise, we help streamline river dredging operations, improve coastal erosion control, and support sustainable waterway infrastructure development. Our goal is to provide cost-effective, long-term dredging strategies that enable governments and private sectors to maintain safe, navigable, and environmentally stable water bodies across the continent.
General
Discos Restore Power Supply After First National Grid Collapse of 2026

By Adedapo Adesanya
Gradual electricity restoration has began across the nation after the country’s national grid recorded its first collapse in 2026 on Friday.
The first collapse in 2026 on January 23 came after a similar incident on December 29, 2025, which had caused widespread power outages across the country.
The prevalent grid collapse in the country has been attributed to a combination of technical faults, inadequate maintenance of transmission lines, and fluctuations in generation capacity.
Earlier today, electricity generation dropped sharply from over 4,500 megawatts to as low as 24 megawatts as of 1:30 pm.
Checks showed that all 23 power generation plants connected to the grid reportedly lost output during the incident, resulting in zero power allocation to each of the 11 electricity distribution companies from Lagos to Kano to Abuja.
Officials of the Transmission Company of Nigeria (TCN) had yet to issue a detailed statement at the time of filing this report by 4:40 p.m.
However, a notice from Abuja Electric Distribution Company (AEDC) to customers noted that “gradual restoration of supply” has commenced.
In Lagos State, several streets in the Orelope area of Alimosho Local Government also reported power restoration.
General
Google Search Shows Nigerians Prioritizing Ambition, Self-Growth in 2026

By Aduragbemi Omiyale
A Google Search report has revealed that Nigerians are deploying the platform to make findings on how to get better in 2026 so as to navigate the year seamlessly.
Data showed that in the first two weeks of January, there has been a 40 per cent spike in searches related to self-improvement, entrepreneurial growth and “becoming better” as they search for the tools needed to succeed in every area of life.
A few of the most searches on Google by Nigerians this year have been Starting a blog, Launching a podcast, How to start a business, and Opening a YouTube channel, among others.
For example, How to start a business emerged as the top-searched how to start query this month, seeing a significant 80 per cent increase as Nigerians look to build new ventures and drive economic opportunity.
Investing in the Better Me
Personal growth is a top priority for Nigerians this year, with searches for how to be a good/better person increasing by 20 per cent. This desire for improvement extends into the heart of the home and community, with people searching for ways to be better partners, husbands, wives, and listeners.
A Healthy Start to 2026
Well-being is at the forefront of the national conversation. Nigerians are forming new habits to stay energized, with searches for how to eat healthy and healthy diet rising by 40 per cent. Mental wellness is also gaining momentum, as searches for “how to meditate” spiked by 40 per cent during the same period.
The Quest for Mastery
Whether it is professional development or personal hobbies, the quest for mastery is on. Top mind for many are searches on how to improve communication skills, memory, and even English proficiency. In the world of leisure and skill-based learning, Nigerians are looking to get better at everything from chess and running to singing and even Fortnite.
“These trends are a powerful reflection of Nigeria’s collective ambition and our shared desire to grow.
“We see Search as a cultural mirror that captures the pulse of the nation, and remain committed to ensuring our tools, from Search to Gemini, provide the relevant and helpful insights Nigerians need to navigate their daily journeys and build a more prosperous future,” the Communications and Public Affairs Manager for Google West Africa, Mr Taiwo Kola-Ogunlade, said.
The full list of Searches is below.
|
Top “how to be a better…” searches |
Top “how to improve…” searches |
|
1. How to be a better person 2. How to be a better lover 3. How to be a better girlfriend 4. How to be a better boyfriend 5. How to be a better husband 6. How to become a better writer 7. How to become a better singer 8. How to be a better wife 9. How to be a better kisser 10. How to be a better listener |
1. How to improve English 2. How to improve memory 3. How to improve credit score 4. How to improve communication skills 5. How to improve handwriting 6. How to improve eyesight 7. How to improve posture 8. How to improve gut health 9. How to improve concentration 10. How to improve circulation |
|
Top “how to get better at…” searches |
Top “how to start…” searches |
|
1. How to get better at Fortnite 2. How to get better at chess 3. How to get better at basketball 4. How to get better at warding League 5. How to get better at singing 6. How to get better at drawing 7. How to get better at pull ups 8. How to get better at math 9. How to get better at running 10. How to get better at soccer |
1. How to start a business 2. How to start a blog 3. How to start a conversation 4. How to start a podcast 5. How to start a YouTube channel 6. How to start running 7. How to start an essay 8. How to start a speech 9. How to stop worrying and start living 10. How to start a letter |
General
Cloover Secures $1.2bn to Build AI Operating System for Energy Independence

By Dipo Olowookere
About $1.222 billion in both equity financing and debt facility has been secured by a pan-European platform building an operating system for energy independence, Cloover.
The company, established in 2023 by Jodok Betschart, Peder Broms and Valentin Gönczy, recently received $22 million in Series A equity funding and a $1.2 billion loan to enable it build Artificial Intelligence (AI) operating system for its operations.
The globe is racing to secure its energy future as electricity demand rises, grids come under pressure, and households face growing uncertainty over costs and supply.
At the same time, demand for decentralized energy solutions like solar, batteries, heat pumps, and EV charging is surging. The missing piece has been infrastructure that can deliver these systems at scale.
Cloover is building the digital nervous system of the distributed energy economy. Its AI-powered platform integrates workflow management, financing, procurement, and energy optimization into one seamless operating system. It automates complex workflows, detects risks early, and empowers data-driven decisions from the first customer leading to long-term energy-management through Cloover’s EMS and dynamic tariffs.
Further, Cloover’s AI Finance co-pilot helps SME installers solve capital flow challenges along the whole value chain and improve liquidity to enable faster growth. By replacing disconnected tools and slow financing processes with one integrated system, Cloover enables installers to close more projects, move faster, and serve a broader customer base.
A statement from the energy firm disclosed that the equity round was led by MMC Ventures and QED Investors, with participation from Lowercarbon Capital, BNVT Capital, Bosch Ventures, Centrotec, and Earthshot Ventures. The debt facility was provided by a leading European bank to fund customer and installer financing on the platform.
Cloover also benefits from a €300 million guarantee from the European Investment Fund, which underpins its financing programs and enables scalable, low-cost capital for the energy transition. In total, Cloover has now raised more than $30 million in equity financing and secured over $1.3 billion in debt.
With the new capital, Cloover will expand into additional European markets and is considering France, Italy, the UK, and Austria, deepen its platform with further AI-driven workflow automation and financing products.
“With this $1.2 billion commitment, we’re enabling households to become energy independent, without the friction of upfront costs or complex loan applications. Our AI operating system connects stakeholders across the value chain and revolutionizes how energy independence becomes the new norm,” the chief executive of Cloover, Mr Betschart said.
Also, the chief product officer at Cloover, Valentin Gönczy, said, “Cloover is not just about financing – we’re building the backbone for energy independence. We are creating the Shopify of Energy: a platform that equips manufacturers, installers, households, and investors with the tools to grow, collaborate, and deliver distributed energy at scale.”
The General Partner at MMC Ventures, Oliver Richards, while commenting, said, “Cloover is tackling one of the largest and most structurally important opportunities in the European energy transition.
“What truly sets them apart is execution: in 2025 the team delivered outstanding commercial progress while building the foundations of a scalable platform business. Jodok, Peder and Valentin have assembled an exceptional team with deep expertise across energy, software, and credit, and we’re excited to back them as they scale Cloover into a category-defining company.”
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism9 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn