Feature/OPED
Access Bank and the Rebirth of the National Theatre: Revitalising Nigeria’s Cultural Future
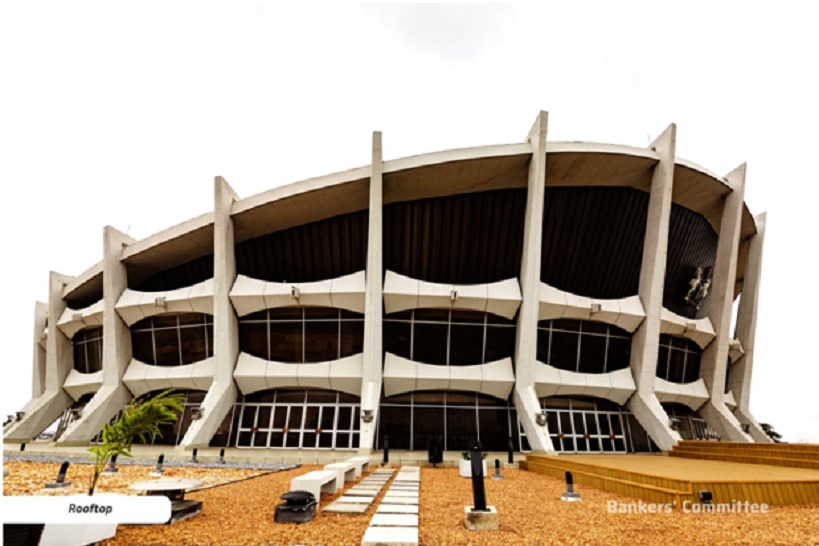

When the National Theatre Lagos first opened ahead of FESTAC ’77, an architectural marvel,a symbol of the cultural soul of a nation ready to introduce its artistic brilliance to the world. Modelled after the Varna Palace of Culture and Sports in Bulgaria and constructed between 1973 and 1976, the National Theatre was designed as an emblem of Nigeria’s ambition to be Africa’s cultural capital. Its 5,000-seat main hall, festival arena, exhibition spaces, and state-of-the-art acoustics made it one of the most sophisticated performance complexes on the continent.
Throughout the 1970s and 1980s, the Theatre became home to Nigeria’s most iconic productions, from Hubert Ogunde’s epic plays to international dance festivals, orchestral performances, film premieres, and global conferences. It was a beacon for African creativity, a place where culture, identity, music, and storytelling came alive. But by the early 2000s, the Theatre, though heavy with cultural memory, had fallen into disrepair. Years of inadequate maintenance, stalled concession agreements, and structural depreciation left the building struggling to meet modern technical and creative demands. The symbol of national pride had become a shadow of its past promise.
Recognising the scale of cultural loss and the opportunity embedded within it, the Bankers’ Committee, with Access Bank playing a pivotal role, initiated the largest cultural infrastructure revitalisation project in contemporary Nigeria. The decision was both strategic and patriotic: Nigeria’s creative industry, now contributing significantly to GDP through film, fashion, music, design, cultural tourism, and digital content, urgently needed a modern, centralised hub that could support global-standard production and creative entrepreneurship. Reviving the National Theatre would not only restore a national icon but also stimulate job creation, attract international collaborations, and reposition Lagos as a premier African creative economy hub.
The renewal of the National Theatre is therefore more than a restoration project; it is anecessary economic intervention, a cultural renaissance, and a visionary step toward building a more inclusive and future-ready Nigeria. And for Access Bank, supporting this transformation is a natural continuation of a long, deliberate commitment to art, culture, and creative empowerment.
Access Bank’s Legacy of Championing the Creative Economy
Well before Nigeria’s creative industry gained global recognition, Access Bank had positioned itself as a cultural investor and ecosystem builder. For over a decade, the Bank has supported transformational initiatives across music, visual arts, fashion, film, sustainability, and youth development.
Access Bank has helped spotlight emerging and established African artists on a global stage through partnerships and collaborations with platforms like ART X. The annual fair, now one of Africa’s most influential contemporary art events, has benefitted immensely from the Bank’s commitment to nurturing young talent, commissioning bold projects, and providing a meeting point for creators, collectors, and global art enthusiasts.
In film and entertainment, Access Bank has backed festivals, documentaries, youth-focused storytelling, and creative incubators, recognising that Nigeria’s cultural exports are among its most powerful global assets. Across literature, community theatre, design, and public art, the Access brand remains synonymous with innovation, creativity, and cultural elevation. The revival of the National Theatre is thus an extension of this commitment.
A Cultural Renaissance Rooted in National Development
The National Theatre project is designed as a two-phase undertaking. Phase One, already significantly advanced, focuses on restoring the original theatre structure. This includes upgrading the main stage, cinema halls, exhibition spaces, lighting systems, acoustics, seating, ventilation, and accessibility infrastructure. The goal is to return the iconic building to world-class functionality while preserving its historic architecture.
Phase Two introduces a modern Creative Industries Park, a multi-purpose development designed to house film production studios, music recording labs, fashion houses, IT and gaming centers, photography studios, coworking spaces, and training academies. This innovation hub is expected to host thousands of young creators annually, enabling them to produce, learn, collaborate, and scale ideas into globally competitive businesses.
With Access Bank’s involvement through the Bankers’ Committee, the project has attracted international partnerships, institutional investors, technical specialists, and creative collaborators. It is poised to become one of the most significant cultural and economic catalysts in West Africa.
In a world where creative exports have become a major source of national influence, from Nollywood films to Afrobeats, digital arts to global fashion, infrastructure is destiny. Nigeria’s young creators generate some of the world’s most consumed cultural content, yet the ecosystem has lacked the physical and institutional support systems needed to harness that potential fully.
The revitalised National Theatre is therefore a launchpad for Nigeria’s next creative era.
With Access Bank’s long-standing commitment to empowering Africa’s creative industries, the revival blends heritage with innovation, history with ambition, and art with economic development.
From art fairs to creative hubs, sustainability initiatives to youth empowerment, Access Bank continues to champion platforms that inspire, educate, and elevate communities across the country.
By supporting the transformation of the National Theatre, the Bank has once again placed itself at the heart of Nigeria’s cultural renewal, bridging past and future, preserving heritage, and building an ecosystem where creativity can thrive without limits.
Feature/OPED
History is Watching: Tinubu’s Moment to Rescue Nigeria’s Stolen Future

By Blaise Udunze
Governance is not complicated. It is about people and the resources entrusted to serve them. When resources are managed wisely, the people prosper, and prosperity spreads. Mismanage them, and poverty multiplies. Nigeria’s tragedy is not scarcity. It is stewardship.
For decades, Nigeria, described as Africa’s largest oil producer, has earned hundreds of billions of dollars, yet remains home to some of the world’s poorest citizens. That contradiction is not accidental. It is systemic. It reflects policy distortion, institutional weakness, and a culture of impunity that has too often treated public wealth as political spoils rather than a national trust.
The Abuja-based Independent Media and Policy Initiative (IMPI) recently captured this paradox bluntly by saying, Nigeria’s poverty crisis is not the result of inadequate resources, but of persistent failure to manage them prudently and sustainably. It described the crisis as a “self-inflicted economic malady.” That phrase should trouble every public official.
Between 1980 and 2015, Nigeria rode multiple oil booms. Instead of converting windfalls into diversified productivity, the country succumbed to what economists call the Dutch disease. Oil revenues surged. The naira appreciated. Imports became cheaper. Domestic production became uncompetitive. Agriculture declined. Manufacturing withered.
IMPI’s analysis shows that between 1980 and 1986, exchange rate appreciation crippled local industries and turned Nigeria from a major agricultural exporter into a net food importer. Cocoa, palm oil, and rubber, once pillars of export strength, gave way to dependency. A parallel distortion emerged, the so-called “Nigerian disease.” Rural labour migrated to cities in search of oil-fueled wage spikes. Farming declined. Food insecurity deepened, which has continued to linger each day. Over-mechanised and poorly coordinated agricultural investments, uncompleted irrigation projects, and subsidies skewed toward politically connected elites widened inequality. Oil wealth created the wrong impression of prosperity while hollowing out the economy’s productive core.
Former Vice President Yemi Osinbajo once framed the issue plainly: Nigeria’s challenge is not geographical restructuring but resource management and service delivery. After decades of vast oil earnings, the uncomfortable question remains. Where is the infrastructure?
If mismanagement were purely historical, recovery might simply require time and discipline. But the problem is not confined to the past, and this is because between 2010 and 2026, an estimated $214 billion, roughly N300 trillion, has been flagged as missing, diverted, unrecovered, irregularly spent, or trapped in non-transparent fiscal structures. These figures reveal that they are not speculative but arise from audit reports, legislative investigations, civil society litigation, and investigative findings across administrations.
The oil sector alone provides sobering examples. In 2014, unremitted oil revenues triggered national outrage. Years later, audit queries continue to trail the Nigerian National Petroleum Company Limited. The names of institutions change. The pattern persists. The Central Bank of Nigeria has also faced audit alarms over trillions in unremitted surpluses and questionable intervention facilities. Auditor-General has flagged failures to remit operating surpluses into the Consolidated Revenue Fund, alongside hundreds of billions allegedly disbursed to unidentified beneficiaries under intervention schemes, which is alarming and a common fraudulent practice.
Across ministries, departments, and agencies, trillions have been cited in unsupported expenditures, unremitted taxes, procurement irregularities, and statutory liabilities left unrecovered. The institutions differ. The language of audit reports varies. The years change. The pattern does not.
A natural occurrence, which is the plain truth, and unarguably, is that when electricity funds disappear, the grid collapses. Also, when agricultural loans remain unrecovered, food prices surge. The same goes when social investment programmes stall due to bureaucratic lack of transparency; the vulnerable remain exposed. Nigeria borrows not only because revenue is insufficient but because leakage is persistent.
The 2026 fiscal projections sharpen the dilemma. This has continued to raise concern as seen in the proposed N58.47 trillion budget, which carries a N25.91 trillion deficit, with N15.9 trillion allocated to debt servicing. What signifies a systemic failure is that nearly half of the projected federal revenue will service past loans before development priorities are funded. The truth be told, borrowing is not inherently destructive. Economies such as the United States deploy deficit financing strategically to expand productivity. The difference lies in what the borrowing finances.
To date, Nigeria’s deficits are increasingly funded by recurrent obligations rather than productivity-enhancing infrastructure. This is why Nigeria’s domestic borrowing persistently crowds out private-sector credit, driving up interest rates and stifling enterprise. Time after time, the nation has continued to witness how weak revenue mobilisation, overt oil dependence, and institutional inefficiencies compound the strain, and for these reasons, public debt is projected to has surpass N177.14 trillion by the end of 2026, which is driven by the budget deficit in 2026 Appropriation Bill.
Based on what is obtainable in other advance country, debt becomes sustainable only when borrowed funds are channeled into growth-enhancing investments, institutions ensure transparency and value for money, and economic expansion outpaces debt accumulation. When these conditions weaken, deficits evolve into a fiscal trap.
Despite some of the challenges occasioned by mismanaged resources and leakages, policymakers project cautious optimism. The Central Bank forecasts GDP growth of approximately 4.49 percent, moderating inflation, and foreign reserves exceeding $50 billion. On paper, stability appears to be returning. But stability is not prosperity.
Take, for instance, between 2006 and 2014, Nigeria recorded average GDP growth rates of six to seven percent, peaking near eight percent. Yet poverty remained stubbornly high, judging by the lived experience of the populace. This shows that growth without inclusion is only an arithmetic, not development. Today, households confront elevated food prices despite the report that food inflation fell from 29.63 per cent in January 2025 to 8.89 per cent in January 2026, energy costs, and unemployment. Yes, one may say that the exchange-rate unification and fuel subsidy removal were economically rational reforms. However, without aggressive domestic production expansion and credible social safety nets, adjustment costs fall heavily on citizens.
The concept of the “resource curse,” coined by Professor Richard Auty, explains why resource-rich nations often experience weaker institutions and lower long-term growth than resource-poor peers. Nigeria truly exemplifies that irony. Yet the curse is not inevitable. This is because countries such as Norway and Botswana transformed natural resource wealth into long-term prosperity through disciplined institutions, sovereign wealth management, and uncompromising transparency, which happens to be foreign to Nigeria’s system. The difference was not geology. It was governance.
Former President Olusegun Obasanjo has never been quite over resource plundering as he lamented that Nigeria has squandered divine gifts. The same lies with the former Minister George Akume, who warned that no nation grows if a quarter of its resources are consistently mismanaged. The former Anambra governor, Peter Obi, observed bluntly that wealth cannot be entrusted to those without integrity. The United Nations is also amongst those who have repeatedly warned that mismanaged natural resources fuel instability and conflict. Where institutions are weak, resource wealth becomes combustible. Nigeria has navigated that edge for decades.
Nigeria does not suffer from a shortage of reform announcements. It suffers from a gap between announcement and enforcement. The Treasury Single Account was designed to consolidate public funds under constitutional oversight. Yet significant funds have periodically remained outside complete transparency. The problem is that audit findings often accumulate without visible recovery, prosecution, or systemic reform.
The reality is that if every naira saved from subsidy reform is not transparently reinvested in infrastructure, healthcare, education, and productivity, public trust will erode further. If intervention facilities are not tracked and repaid, agriculture will stagnate. If oil revenues are not fully remitted and independently audited, diversification will remain rhetorical, just as they have defined the system today. What will definitely propel a change when visible enforcement, recoveries, prosecutions, and institutional strengthening must replace quiet reports and circular memos.
President Bola Ahmed Tinubu stands at a consequential intersection due to the critical issues unfolding. His administration has initiated painful but necessary reforms in the areas of fuel subsidy removal, exchange-rate unification, and fiscal restructuring. One stands to say that these measures aim to restore macroeconomic order. But for a fact, macroeconomic stability is a foundation, not a destination. His presidency will either mark the beginning of Nigeria’s fiscal rescue or consolidate a system that mortgages tomorrow to survive today.
Human capital cannot remain peripheral. Education aligned with labour-market needs, vocational capacity, healthcare access, and social protection are economic multiplier, not welfare indulgences. Capital expenditure must prioritise integrated infrastructure like power transmission, logistics corridors, and digital connectivity, that unlocks productivity. Every earned naira must enter the Federation Account transparently. Every statutory surplus must be constitutionally remitted. Every diversion must carry a consequence.
One thing that must be understood today is that Nigeria’s future will not be determined solely by oil output or GDP growth percentages. It will be determined by whether resources translate into reliable electricity, functioning roads, expanding industries, competitive exports, and rising household incomes. A nation can borrow to build bridges. Or it can borrow to pay salaries. The former compounds growth. The latter compounds debt.
If deficits translate into visible infrastructure, industrial expansion, thriving private enterprise, and strengthened revenue generation, history will record this era as a bold recalibration. If not, it will be remembered as deferred reckoning.
Nigeria has been wealthy for decades. What it has lacked is disciplined guardianship of that wealth. End the era of systemic leakage and institutional silence, or preside over its continuation. The choice is stark but clear. The point is, this is not just about one leader’s legacy; it is about the future of over 200 million Nigerians and generations.
And for nearly 200 million Nigerians, the outcome will define not just a presidency, but a generation.
Blaise, a journalist and PR professional, writes from Lagos and can be reached via: bl***********@***il.com
Feature/OPED
How Christians Can Stay Connected to Their Faith During This Lenten Period

It’s that time of year again, when Christians come together in fasting and prayer. Whether observing the traditional Lent or entering a focused period of reflection, it’s a chance to connect more deeply with God, and for many, this season even sets the tone for the year ahead.
Of course, staying focused isn’t always easy. Life has a way of throwing distractions your way, a nosy neighbour, a bus driver who refuses to give you your change, or that colleague testing your patience. Keeping your peace takes intention, and turning off the noise and staying on course requires an act of devotion.
Fasting is meant to create a quiet space in your life, but if that space isn’t filled with something meaningful, old habits can creep back in. Sustaining that focus requires reinforcement beyond physical gatherings, and one way to do so is to tune in to faith-based programming to remain spiritually aligned throughout the period and beyond.
On GOtv, Christian channels such as Dove TV channel 113, Faith TV and Trace Gospel provide sermons, worship experiences and teachings that echo what is being practised in churches across the country.
From intentional conversations on Faith TV on GOtv channel 110 to true worship on Trace Gospel on channel 47, these channels provide nurturing content rooted in biblical teaching, worship, and life application. Viewers are met with inspiring sermons, reflections on scripture, and worship sessions that help form a rhythm of devotion. During fasting periods, this kind of consistent spiritual input becomes a source of encouragement, helping believers stay anchored in prayer and mindful of God’s presence throughout their daily routines.
To catch all these channels and more, simply subscribe, upgrade, or reconnect by downloading the MyGOtv App or dialling *288#. You can also stream anytime with the GOtv Stream App.
Plus, with the We Got You offer, available until 28th February 2026, subscribers automatically upgrade to the next package at no extra cost, giving you access to more channels this season.
Feature/OPED
Turning Stolen Hardware into a Data Dead-End

By Apu Pavithran
In Johannesburg, the “city of gold,” the most valuable resource being mined isn’t underground; it’s in the pockets of your employees.
With an average of 189 cellphones reported stolen daily in South Africa, Gauteng province has become the hub of a growing enterprise risk landscape.
For IT leaders across the continent, a “lost phone” is rarely a matter of a misplaced device. It is frequently the result of a coordinated “snatch and grab,” where the hardware is incidental, and corporate data is the true objective.
Industry reports show that 68% of company-owned device breaches stem from lost or stolen hardware. In this context, treating mobile security as a “nice-to-have” insurance policy is no longer an option. It must function as an operational control designed for inevitability.
In the City of Gold, Data Is the Real Prize
When a fintech agent’s device vanishes, the $300 handset cost is a rounding error. The real exposure lies in what that device represents: authorised access to enterprise systems, financial tools, customer data, and internal networks.
Attackers typically pursue one of two outcomes: a quick wipe for resale on the secondary market or, far more dangerously, a deep dive into corporate apps to extract liquid assets or sellable data.
Clearly, many organisations operate under the dangerous assumption that default manufacturer security is sufficient. In reality, a PIN or fingerprint is a flimsy barrier if a device is misconfigured or snatched while unlocked. Once an attacker gets in, they aren’t just holding a phone; they are holding the keys to copy data, reset passwords, or even access admin tools.
The risk intensifies when identity-verification systems are tied directly to the compromised device. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), widely regarded as a gold standard, can become a vulnerability if the authentication factor and the primary access point reside on the same compromised device. In such cases, the attacker may not just have a phone; they now have a valid digital identity.
The exposure does not end at authentication. It expands with the structure of the modern workforce.
65% of African SMEs and startups now operate distributed teams. The Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) culture has left many IT departments blind to the health of their fleet, as personal devices may be outdated or jailbroken without any easy way to know.
Device theft is not new in Africa. High-profile incidents, including stolen government hardware, reinforce a simple truth: physical loss is inevitable. The real measure of resilience is whether that loss has any residual value. You may not stop the theft. But you can eliminate the reward.
Theft Is Inevitable, Exposure is Not
If theft cannot always be prevented, systems must be designed so that stolen devices yield nothing of consequence. This shift requires structured, automated controls designed to contain risk the moment loss occurs.
Develop an Incident Response Plan (IRP)
The moment a device is reported missing, predefined actions should trigger automatically: access revocation, session termination, credential reset and remote lock or wipe.
However, such technical playbooks are only as fast as the people who trigger them. Employees must be trained as the first line of defence —not just in the use of strong PINs and biometrics, but in the critical culture of immediate reporting. In high-risk environments, containment windows are measured in minutes, not hours.
Audit and Monitor the Fleet Regularly
Control begins with visibility. Without a continuous, comprehensive audit, IT teams are left responding to incidents after damage has occurred.
Opting for tools like Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) allows IT teams to spot subtle, suspicious activities or unusual access attempts that signal a compromised device.
Review Device Security Policies
Security controls must be enforced at the management layer, not left to user discretion. Encryption, patch updates and screen-lock policies should be mandatory across corporate devices.
In BYOD environments, ownership-aware policies are essential. Corporate data must remain governed by enterprise controls regardless of device ownership.
Decouple Identity from the Device
Legacy SMS-based authentication models introduce avoidable risk when the authentication channel resides on the compromised handset. Stronger identity models, including hardware tokens, reduce this dependency.
At the same time, native anti-theft features introduced by Apple and Google, such as behavioural theft detection and enforced security delays, add valuable defensive layers. These controls should be embedded into enterprise baselines rather than treated as optional enhancements.
When Stolen Hardware Becomes Worthless
With POPIA penalties now reaching up to R10 million or a decade of imprisonment for serious data loss offences, the Information Regulator has made one thing clear: liability is strict, and the financial fallout is absolute. Yet, a PwC survey reveals a staggering gap: only 28% of South African organisations are prioritising proactive security over reactive firefighting.
At the same time, the continent is battling a massive cybersecurity skills shortage. Enterprises simply do not have the boots on the ground to manually patch every vulnerability or chase every “lost” terminal. In this climate, the only viable path is to automate the defence of your data.
Modern mobile device management (MDM) platforms provide this automation layer.
In field operations, “where” is the first indicator of “what.” If a tablet assigned to a Cape Town district suddenly pings on a highway heading out of the city, you don’t need a notification an hour later—you need an immediate response. An effective MDM system offers geofencing capabilities, automatically triggering a remote lock when devices breach predefined zones.
On Supervised iOS and Android Enterprise devices, enforced Factory Reset Protection (FRP) ensures that even after a forced wipe, the device cannot be reactivated without organisational credentials, eliminating resale value.
For BYOD environments, we cannot ignore the fear that corporate oversight equates to a digital invasion of personal lives. However, containerization through managed Work Profiles creates a secure boundary between corporate and personal data. This enables selective wipe capabilities, removing enterprise assets without intruding on personal privacy.
When integrated with identity providers, device posture and user identity can be evaluated together through multi-condition compliance rules. Access can then be granted, restricted, or revoked based on real-time risk signals.
Platforms built around unified endpoint management and identity integration enable this model of control. At Hexnode, this convergence of device governance and identity enforcement forms the foundation of a proactive security mandate. It transforms mobile fleets from distributed risk points into centrally controlled assets.
In high-risk environments, security cannot be passive. The goal is not recovery. It is irrelevant, ensuring that once a device leaves authorised hands, it holds no data, no identity leverage, and no operational value.
Apu Pavithran is the CEO and founder of Hexnode
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn