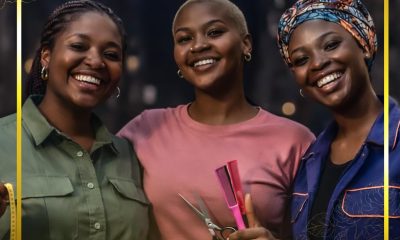Banking
Fitch Affirms Fidelity Bank at ‘B-‘, Gets Positive Reviews

By Dipo Olowookere
Nigerian medium-sized lender, Fidelity Bank Plc, has had its Long-Term Issuer Default Rating (IDR) rating affirmed by Fitch Ratings at ‘B-‘ with the outlook stable.
Fitch said in a statement that the bank’s Viability Rating (VR) has been also affirmed at ‘b-‘ and Support Rating at ‘5’, while its National Ratings were also confirmed.
Fidelity Bank is a financial institution with a market share of around 4%-5% of domestic loans and deposits. Its small franchise limits the size and scope of business it can undertake and the bank has developed a niche focus on selected corporate business sectors and relatively underbanked sectors, such as the financing of SMEs. Fidelity Bank operates solely in Nigeria.
Lending to SMEs in Nigeria requires more flexible underwriting standards to address their limitations and underwriting standards are adapted to meet the needs of the bank’s niche customer base.
Despite a focus on SMEs, Fidelity Bank’s impaired loans/total loans ratios (5.9% at end-September 2017) are broadly in line with the average for rated second-tier Nigerian banks (around 6.5%). Asset quality trends are favourable, reflecting loan restructuring and some recoveries in 2017. The sustainability of this trend will become clear over time.
Fidelity Bank’s earnings and profitability ratios are in line with the sector averages although performance metrics for second-tier banks vary considerably. There were some positive earnings developments in 2017.
Margins are improving, loan impairment charges are reducing as a percentage of pre-impairment operating profit and investments in technology are helping to improve cost/income ratios.
Fidelity Bank’s funding profile is fairly typical of a smaller Nigerian bank. Franchise limitations make deposit collection more difficult and Fidelity’s loans/deposit ratio hovers around 100%. Depositor concentrations are fairly high, with the top 10 deposits typically representing about 13% of total customer deposits. Low-cost demand and savings deposits represent around 75% of customer deposits, which is positive. Naira liquidity ratios are at levels that are marginally above the 30% regulatory minimum.
Access to foreign currency (FC) was particularly tight for Nigerian banks in 2016 but the bank did not delay any payments on its FC trade-related and bank obligations, even at the height of the liquidity squeeze.
The FC liquidity situation eased in Nigeria throughout 2017 and in October Fidelity Bank raised a senior five-year $400 million bond on the international capital markets. This has eased the bank’s FC liquidity position. Funds raised were partly used to repay $256 million of a $300 million Eurobond bond originally maturing in May 2018.
Loan loss cover ratios (68% at end-September 2017) are slightly lower than peer averages (75% – 80%).
Fidelity Bank meets minimum 15% capital ratios requirements, but the bank’s ability to withstand even moderate shocks may be limited considering below average loan-loss cover ratios, high single name concentrations and potential asset-quality deterioration.
Fidelity Bank’s National Long-Term Ratings reflect its creditworthiness relative to the country’s best credit and to peers operating in Nigeria.
Fidelity Bank’s senior unsecured bonds are rated in line with the bank’s IDRs. In our view, the likelihood of default on these notes reflects the likelihood of default of the bank. The Recovery Rating (RR) assigned to these bonds is ‘RR4’, indicting average recovery prospects.
Fitch believes that sovereign support to Nigerian banks cannot be relied on given Nigeria’s (B+/Negative) weak ability to provide support, particularly in FC. In addition, there are no clear messages from the authorities regarding their willingness to support the banking system. Therefore, the Support Rating Floor (SRF) of all Nigerian banks is ‘No Floor’ and all Support Ratings (SR) are ‘5’. This reflects our view that senior creditors cannot rely on receiving full and timely extraordinary support from the Nigerian sovereign if any of the banks become non-viable.
Banking
CIBN to Back ACAMB on Professional Development, Industry Advocacy

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
The Chartered Institute of Bankers of Nigeria (CIBN) has promised to support the ambitious plans of the Association of Corporate and Marketing Professionals in Banks (ACAMB).
At a meeting between the leaderships of the two organisations on Tuesday, the president of CIBN, Professor Pius Deji Olanrewaju, said it was impressed with the capability development and the undergraduate mentorship schemes of ACAMB under its leader, Mr Jide Sipe.
The CIBN chief commended the forward-thinking vision of the group, saying it had raised standards across Nigeria’s banking sector.
“ACAMB’s support has given CIBN and the banking sector brand equity,” he said, praising the association’s record in reputation management. recalling ACAMB’s role in addressing crises within the sector, describing the partnership as strategic and beneficial.
He further pledged support for ACAMB’s 30th anniversary in September 2026, its AGM, and other programmes, including fundraising initiatives.
“I want to assure you that everything you have presented today has been clearly noted and will be acted upon.
“We are fully committed to working closely with you so as to translate these discussions and vision into measurable progress. Our shared goal is to strengthen the sector, protect its reputation, and enhance its public image in a meaningful and lasting way.
“This meeting discussed various initiatives and reforms crucial for the future of our industry, including the need for continuous training and adaptation to new programs,” Mr Olanrewaju stated.
Speaking at the meeting, the president of ACAMB described the visit as a crucial first step in his tenure, aimed at contributing significantly to giving flight to his vision and that of ACAMB.
“When we assumed office, one of the first things we agreed on was the need to visit key stakeholders.
“However, before reaching out more broadly, we felt it was important to begin with our primary constituency and core stakeholders. We want them to understand the direction we are taking and to support the work we are doing, so that ACAMB can achieve greater success than it has in the past.
“We couldn’t have properly started our tenure without this very important meeting with the CIBN,” Mr Sipe stated
He introduced the newly constituted ACAMB Exco, which includes the 2nd Vice President, Morolake Phillip-Ladipo; General Secretary, Olugbenga Owootomo; Assistant General Secretary, Ademola Adeshola; Publicity Secretary, Abiodun Coker; and Executive Secretary, Fadekemi Ajakaiye.
Banking
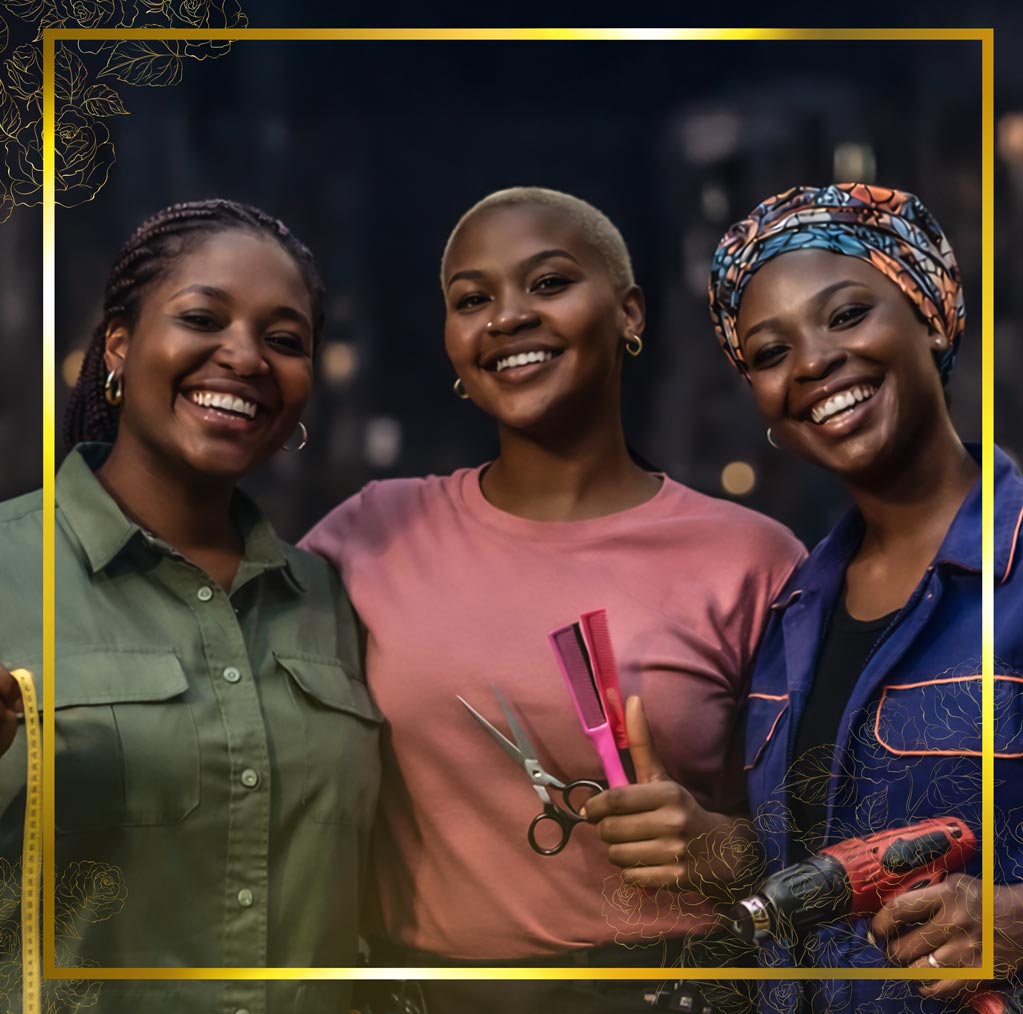
All Set for Second HerFidelity Apprenticeship Programme

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
Registration for the second HerFidelity Apprenticeship Programme (HAP 2.0) organised by Fidelity Bank Plc has commenced.
The Divisional Head of Product Development at Fidelity Bank, Mr Osita Ede, informed newsmen that the initiative was designed to empower women with sustainable entrepreneurship skills.
The lender created the flagship women-empowerment initiative to equip women with practical, income‑generating skills and structured pathways to entrepreneurship.
“HerFidelity Apprenticeship Programme 2.0 reflects our commitment to continuous improvement. Having evaluated feedback from the first edition, we have returned with stronger partnerships and deeper mentorship programmes to ensure that women acquire not just skills, but sustainable economic opportunities,” he said.
“At the heart of the programme is guided, real‑world learning. Participants will undergo intensive apprenticeship training under reputable institutions and industry experts across select fields such as hair styling, shoe making, auto mechatronics, and interior decoration,” Mr Ede added.
He noted that HerFidelity Apprenticeship Programme 2.0 goes beyond skills acquisition by offering participants a wide range of business advisory services. These include business and financial literacy training, mentorship support throughout the apprenticeship journey, access to Fidelity Bank’s women‑focused and SME financial solutions, as well as guidance on business formalisation and growth strategies.
Further emphasising the bank’s vision, Mr Ede said, “By integrating structured mentorship with entrepreneurial development, Fidelity Bank is positioning women not just as trainees, but as future employers, innovators, and economic contributors within their communities. This aligns with our mandate to help individuals grow, businesses thrive, and economies prosper.”
Banking
The Alternative Bank Opens New Branch in Ondo

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
A new branch of The Alternative Bank (AltBank) has been opened in Ondo State as part of the expansion drive of the financial institution.
A statement from the company disclosed that the new branch would support export-oriented agribusinesses through Letters of Credit and commodity-backed trade finance, ensuring that local producers can scale beyond state borders.
For SMEs, the bank is introducing robust payment rails, asset financing for equipment and inventory, and supply chain-backed facilities that strengthen working capital without trapping businesses in interest-based debt cycles.
The Governor of Ondo State, Mr Lucky Aiyedatiwa, represented by his Chief of
Staff, Mr Olusegun Omojuwa, at the commissioning of the branch, underscored the importance of financial institutions in economic development.
“The pivotal role of financial institutions to economic growth and development of any economy cannot be overemphasised. It provides access to capital, supporting small and medium-scale enterprises and encouraging savings.
“Therefore, I have no doubt in my mind that the presence of The Alternative Bank in Ondo State will deepen financial services, create employment opportunities and stimulate economic activities across various sectors,” he said.
In her remarks, the Executive Director for Commercial and Institutional Banking (Lagos and South West) at The Alternative Bank, Mrs Korede Demola-Adeniyi, commended the state government’s leadership and outlined the lender’s long-term vision for Ondo State.
“As Ondo State steps into its next fifty years, and into the future anchored on the sustainable development championed during the recent anniversary celebrations, The Alternative Bank is here to be the financial engine for that vision. We didn’t come to Akure to hang banners. We came to fund work, farms, shops, and factories.”
With Ondo State’s economy anchored largely on agriculture, particularly cocoa production, poultry farming, and other cash crops, alongside a growing SME and trade ecosystem, AltBank is deploying sector-specific financing solutions tailored to these strengths.
For cocoa aggregators, processors and poultry operators, the bank will provide production financing, facility expansion support, machinery lease structures, and structured trade facilities under its joint venture and cost-plus financing models, with transaction cycles of up to 180 days for commodity trades and longer-term structured asset financing for equipment and infrastructure.
The organisation is a notable national non-interest bank with a physical network now surpassing 170 locations, deploying capital to solve real-world challenges through initiatives such as the Mata Zalla project, which saw to the training of hundreds of women as electric tricycle drivers and mechanics.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn