Economy
Demand And Supply Zone Trading: A Comprehensive Overview From Experts
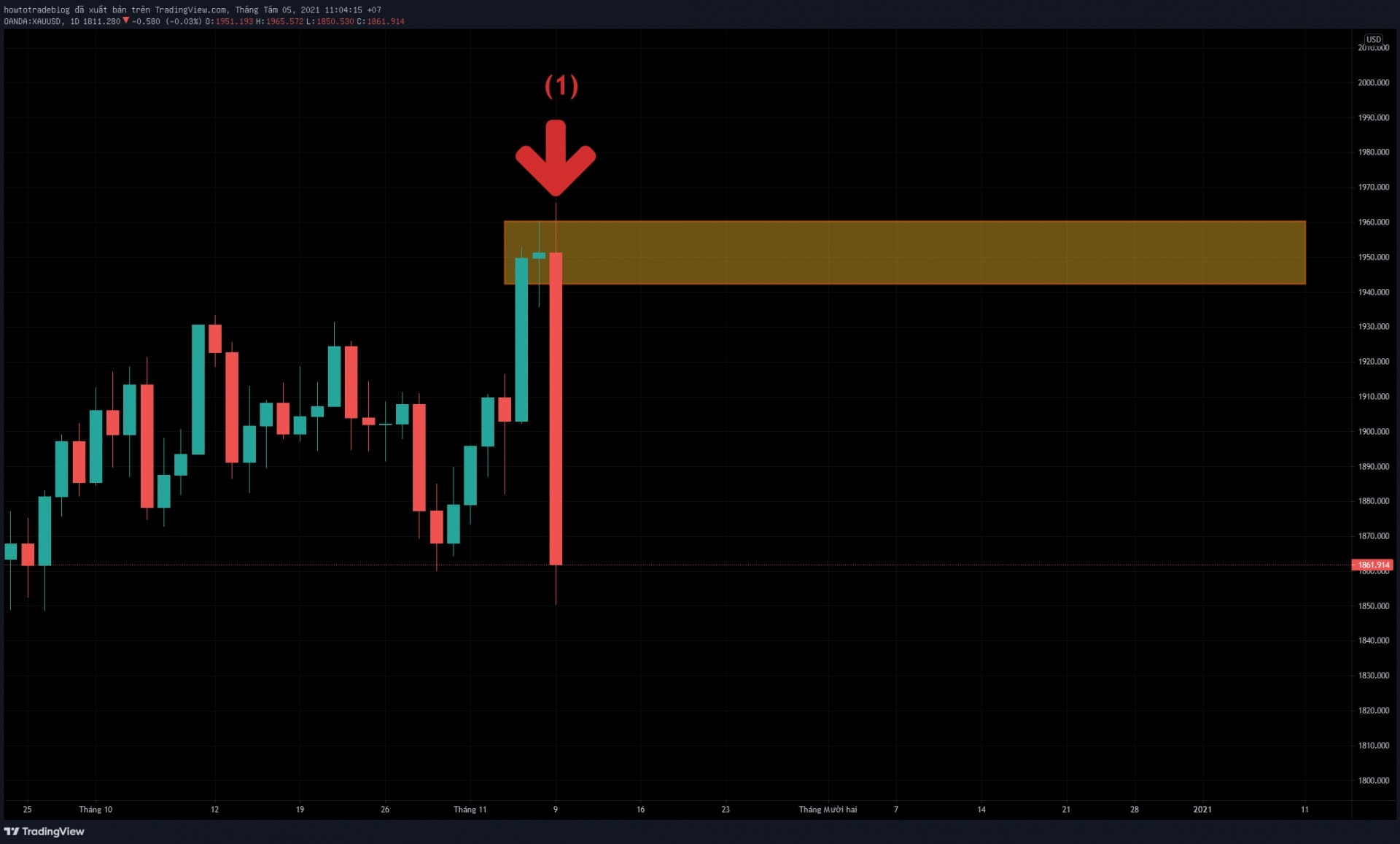
Traders Union (TU) experts know that supply and demand rules control all markets. When traders trade, they usually use technical signals to find out if there is more supply or demand. In this guide, the analysts will delve into the world of supply and demand zones and explore their significance in trading. But before you dive in, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamentals.
What you should know about supply and demand zones
The guidance from TU’s analysts provides insight into the crucial aspects of demand and supply zone trading. It is important to understand these zones:
- Supply Zone – this is where traders commonly opt to sell, and it typically lies above the current price. When the price reaches a well-established supply level, it triggers the completion of unsold sell orders, frequently resulting in a downward price movement.
- Demand Zone – conversely, the demand zone serves as the go-to area for traders looking to buy. It’s situated below the current price, attracting many buyers who are prepared with purchase orders at that specific level. Recognizing a demand zone is a key skill in trading.
These insights provide a solid foundation for traders to comprehend how supply and demand zones operate in the dynamic world of trading.
Advantages & disadvantages of supply and demand trading
Let’s check out the good and not-so-good sides of these approaches, according to analysts at Traders Union.
Advantages:
- Easy to understand
Supply and demand trading is simple and makes sense. It’s about how prices are set when supply and demand meet.
- Works everywhere
This idea fits any market where stuff is bought and sold, making it a useful strategy for all traders.
- Can predict future prices
Supply and demand zones often hint at where prices might go next, helping traders make predictions.
- Clear risk and reward
These zones show when to enter, exit, and set goals, which helps manage risks and rewards.
Disadvantages:
- Not always clear
Figuring out supply and demand zones can vary between traders, making it a bit unclear sometimes.
- Might miss small moves
Sometimes, small price changes in these zones can give wrong signals, making traders enter or exit trades too early.
- Looks back in time
Supply and demand zones are based on past data, so they might not always predict future prices accurately.
- Needs patience
This method often means waiting for prices to hit the right zones, which can be tough when the market is calm.
Recommendations for beginners
Supply and demand are big deals in Forex trading. TU’s experts have five tips to help beginners like you:
- Combine with technical analysis
Just knowing supply and demand isn’t enough. You should also learn technical stuff like chart patterns and indicators. This helps you understand how the market might react to supply and demand.
- Risk management
Be smart about risks. Don’t bet too much money on one trade, usually no more than 1-2% of your total. This way, you can handle losses without emptying your account and get better over time.
- Spot big differences
Look for big differences between supply and demand. These can hint at potential trades. Find places where prices have shot up or down quickly.
- Use longer time frames
If you’re starting out, use longer charts like daily or weekly. They show the market better and aren’t as noisy as shorter ones.
- Confirm with indicators
While supply and demand are important, you can use other indicators for extra certainty. Things like volume indicators, RSI, or moving averages can back up your supply and demand ideas.
Conclusion
Understanding supply and demand is essential in the world of trading, and the Traders Union has provided valuable insights into these fundamental principles. While supply and demand trading offers simplicity, universality, predictive potential, and clear risk-reward management, it does come with challenges, including subjectivity, potential for missed signals, reliance on historical data, and the need for patience.
Economy
Oil Slumps 11% as Trump Signals Resolution of Iran War

By Adedapo Adesanya
Oil plunged by more than 11 per cent on Tuesday after the market held onto comments by US President Donald Trump about a quick end to the war with Iran that has disrupted global crude flows.
Brent futures fell $11.16 or 11 per cent to $87.80 a barrel, and the US West Texas Intermediate (WTI) crude settled at $83.45 a barrel, down $11.32 or 11.9 per cent. This was the steepest percentage drop of any session since 2022.
The American president, in an interview on Monday, said he thought the war against Iran was “very complete” and the US was “very far ahead” of his initial four- to five-week estimated time frame.
The market also followed US Energy Secretary Chris Wright, who wrote on X that the American military had facilitated a shipment of oil out of the Strait of Hormuz.
However, it was reported later that Iran has begun laying naval mines in the strategically vital strait, through which 20 per cent of crude flows pass.
Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), now sharing control of the strait with the regular navy, has a range of asymmetric capabilities, including scattered mine-laying craft, explosive-laden boats and shore-based missile batteries, giving it the ability to create a complex array of threats to passing vessels.
Disruptions in Hormuz have already had significant ripple effects as tanker traffic through the strait has plummeted with shipping companies avoiding the area and insurers hiking premiums amid risk, and analysts warn that prolonged disruption could trigger one of the largest energy shocks in decades.
It was also reported that President Trump was considering easing oil sanctions on Russia related to its war in Ukraine, and releasing emergency crude stockpiles to help curb spiking prices.
Market analysts noted that nearly 1.9 million barrels per day of crude refining capacity in the Gulf has been shut in due to the US-Israeli war on Iran.
Seeking to calm down soaring oil prices, G7 finance ministers have discussed a possible joint release of strategic petroleum reserves, up to potentially 400 million barrels. This will be facilitated by the International Energy Agency (IEA).
The American Petroleum Institute (API) estimated that crude oil inventories in the United States fell by 1.7 million barrels in the week ending March 6, after adding 5.6 million barrels in the week prior. Official data from the US Energy Information Administration (EIA) will be released later on Wednesday.
Economy
NNPC Gets Approval for $20bn Final Investment Decision on Bonga Deepwater Project

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
A targeted fiscal incentive designed to unlock the long-awaited Final Investment Decision (FID) on the Bonga Southwest Aparo (BSWA) deepwater project has been approved by President Bola Tinubu.
The approval followed months of intensive technical and commercial negotiations involving the Nigerian National Petroleum Company (NNPC) Limited as the concessionaire, the Nigeria Revenue Service (NRS), the Special Adviser to the President on Energy, Olu Verheijen, and the chief executive of Shell, Mr Wael Sawan.
In a statement signed on Tuesday by the Chief Corporate Communications Officer of NNPC, Mr Andy Odeh, it was disclosed that the project is estimated to attract about $20 billion in Foreign Direct Investment and position Nigeria for a new era of deepwater production.
It was said that it has the potential to attract strategic investments and accelerate sustainable economic growth, adding that it signals renewed confidence in Nigeria’s policy direction and its resolve to translate reform momentum into tangible investment outcomes.
The chief executive of NNPC, Mr Bashir Bayo Ojulari, said, “This approval is a testament to the President’s leadership, NNPC’s disciplined execution and our ability to structure complex, bankable transactions that deliver value for Nigeria.
“For nearly two decades, the Bonga Southwest project remained stalled. Today, under President Tinubu’s reform-driven leadership and through NNPC’s sustained advocacy, we have broken that logjam. This is what partnership, persistence, and policy clarity can achieve.”
“This milestone further affirms NNPC’s commitment, under the President’s leadership, to unlocking Nigeria’s vast energy potential through partnerships, disciplined innovation and execution excellence,” he further stated.
The Bonga Southwest project will be the first FID on a Nigeria deepwater Production Sharing Contract asset since 2008, re-establishing Nigeria as a premier deepwater investment destination.
The fiscal package approved by President Tinubu includes an enhanced Production Tax Credit and resolution of the 2021 dispute settlement agreement, creating a competitive framework that balances national value with investor returns.
The Bonga Southwest Aparo project, operated by Shell with all IOCs in Nigeria as partners, will create over 5,000 direct and indirect jobs, and deliver 150,000 barrels per day of crude oil and 140 million standard cubic feet per day of gas upon completion.
NNPC Limited, as concessionaire, worked closely with SNEPCo and the broader contractor party to develop alternative fiscal solutions that address structural constraints while protecting Nigeria’s long-term interests.
Economy
Nigeria Posts N5.17trn Surplus as Trade Value Falls to N36.02trn in Q1 2025
By Adedapo Adesanya
Nigeria recorded a trade surplus of N5.17 trillion in the first quarter of 2025, according to the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) in its latest Foreign Trade in Goods Statistics report.
This affirmed that the country’s exports rose faster than imports for yet another quarter.
The report showed that the country’s total merchandise trade stood at N36.02 trillion in the period under review, higher than the N33.93 trillion recorded in the corresponding period of 2024 by 6.19 per cent, but lower than the N36.60 trillion achieved in the previous quarter by 1.58 per cent.
Total exports were valued at N20.60 trillion, accounting for 57.18 per cent of total trade. This represents a 7.42 per cent increase from ₦19.18 trillion recorded in the first quarter of 2024 and 2.92 per cent higher than the N20.01 trillion posted in the fourth quarter of 2024.
Meanwhile, imports came in at N15.43 trillion during the period, 4.59 per cent more than the N14.75 trillion recorded in the corresponding quarter of 2024, but 7.02 per cent lower than the N16.59 trillion of the preceding quarter.
The NBS report showed that Nigeria’s export trade continued to be dominated by crude oil, which was valued at N12.96 trillion and accounted for about 62.89 per cent of total exports, while non-crude oil exports were valued at N7.64 trillion, representing 37.11 per cent of total exports, and non-oil products contributed N3.17 trillion or 15.38 per cent of the export value.
The NBS noted that India, the Netherlands, the United States, France and Spain were Nigeria’s major export partners during the quarter.
On the import side, China remained Nigeria’s largest trading partner, followed by India, the United States, the Netherlands and the United Arab Emirates.
Major commodities exported during the period included crude oil, liquefied natural gas, petroleum gases, urea and cocoa beans, while key imports included gas oil, motor spirit, crude petroleum oils, cane sugar for refining and durum wheat.
The stats office added that the country’s positive trade balance rose by more than 50 per cent compared with the previous quarter, reflecting a stronger export performance
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn





















