Economy
Nigeria, 4 Others Ban ‘Dirty’ Fuels From Europe


By Dipo Olowookere
Five West African countries, including Nigeria, have decided to ban ‘dirty’ fuels from Europe, which are believed to contain higher sulphur levels.
This comes in response to concerns over vehicle emissions and in an effort to bring safer, cleaner air to more than 250 million people in the region, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) said.
According to UNEP, last week, Nigeria, Benin, Togo, Ghana, and Côte d’Ivoire introduced strict standards that will ensure cleaner, low sulphur diesel fuels, and better emissions standards, thus effectively cutting off Europe’s West African market.
Earlier this year, a report by the non-governmental organization Public Eye exposed how European trading companies are exploiting weak regulatory standards in West African countries, thus allowing fuels with sulphur levels that are up to 300 times higher than those permitted in Europe.
“West Africa is sending a strong message that it is no longer accepting dirty fuels from Europe,” said Mr Erik Solheim, head of UNEP. “Their decision to set strict new standards for cleaner, safer fuels and advanced vehicle emissions standards shows they are placing the health of their people first.”
He hailed the move as an example for other countries, noting that air pollution kills millions annually.
“We need to ensure that all countries urgently introduce cleaner fuels and vehicles to help reduce the shocking statistics,” stated Mr Solheim.
In addition to new fuel standards, the group of West African countries has agreed to upgrade their own public and private refineries to meet the same higher standards by 2020.
UN Environment has been working with countries in West Africa to develop policies and standards that will stop the import of fuels with dangerously high levels of sulphur, as well as to introduce cleaner fuels and vehicles. Reducing such emissions around the world is essential to ensure levels of urban air pollution and climate emissions come down.
Combining low-sulphur fuels with advanced vehicle standards can lead to as much as a 90 per cent reduction in harmful emissions.
According to Nigeria’s Environment Minister, Mrs Amina Mohamed, “for 20 years, Nigeria has not been able to address the vehicle pollution crisis due to the poor fuels we have been importing. Today we are taking a huge leap forward: limiting sulphur in fuels from 3,000 parts per million to 50 parts per million. This will result in major air quality benefits in our cities and will allow us to set modern vehicle standards.”
Mrs Mohamed will meet with Lilianne Ploumen, Dutch Minister of Foreign Trade and Development Cooperation, in Hague, in order to take stock of the progress being made to improve the quality of fuels that have been exported from Dutch ports to countries in West Africa, as The Netherlands produces many of the exported dirty fuels.
“The recent report from the NGO Public Eye made abundantly clear that coordinated action is needed to stop the practice of exporting dirty fuels to West Africa. I am very pleased West African governments quickly decided to introduce standards that will help accessing European standard quality fuels. Their people deserve cleaner air, better health, and a cleaner environment. I commend UN Environment for their excellent work,” announced Minister Ploumen.
UNEP hosts the Secretariat of the Partnership for Clean Fuels and Vehicles (PCFV), a global public-private partnership that supports a shift to cleaner fuels and vehicles worldwide. When PCFV began its work in 2005, not a single low or middle income country used low sulphur fuels. Today, 23 countries have made that shift. Another 40 are on their way to doing the same.
In addition, UNEP is hosting the Climate and Clean Air Coalition, which recently adopted a global strategy for moving the world to clean, low-sulphur fuels and advanced emissions standards. Experts estimate that this measure will save an annual 100,000 premature deaths by 2030.
Economy
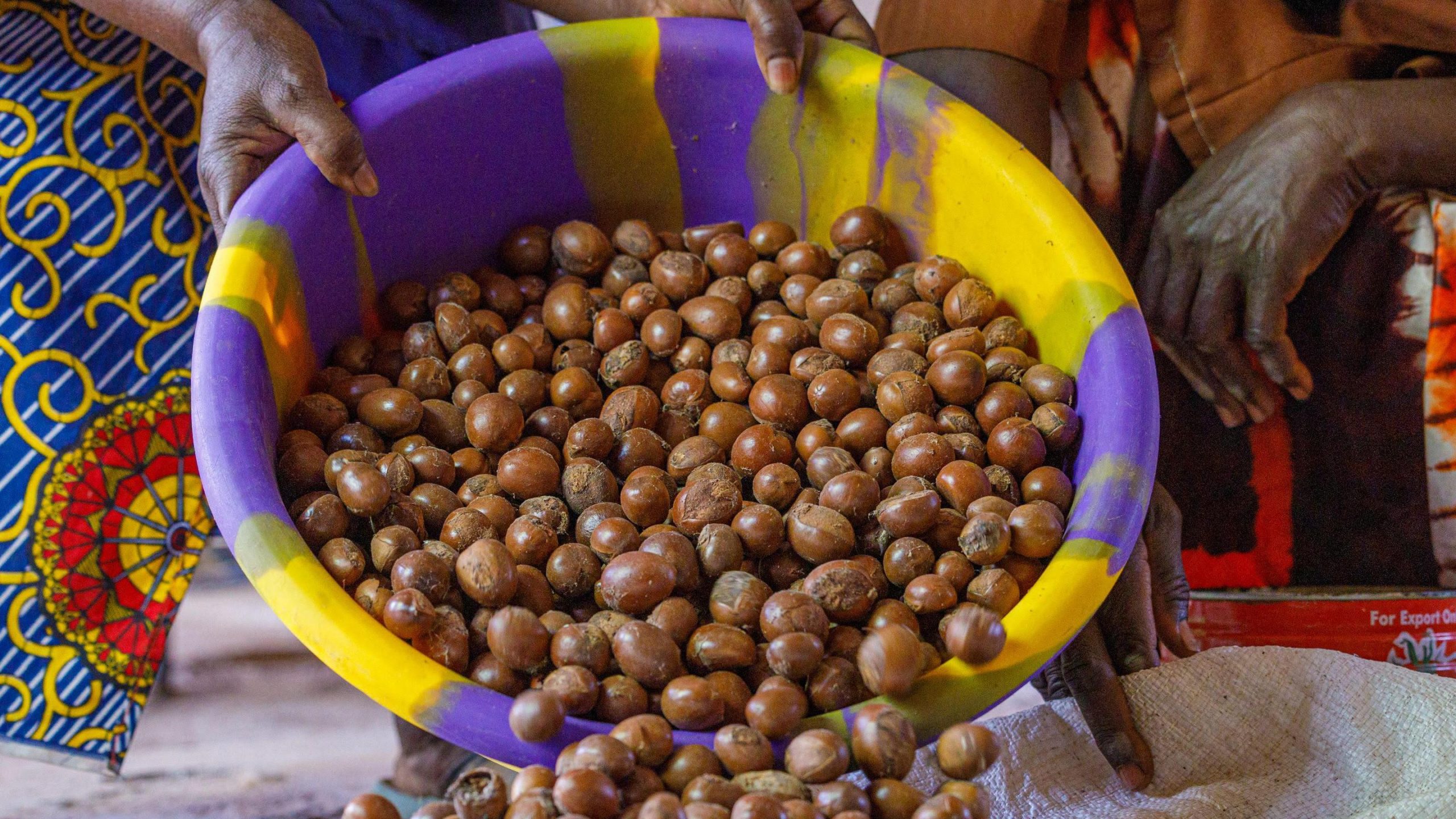
Tinubu Okays Extension of Ban on Raw Shea Nut Export by One Year

By Aduragbemi Omiyale
The ban on the export of raw shea nuts from Nigeria has been extended by one year by President Bola Tinubu.
A statement from the Special Adviser to the President on Information and Strategy, Mr Bayo Onanuga, on Wednesday disclosed that the ban is now till February 25, 2027.
It was emphasised that this decision underscores the administration’s commitment to advancing industrial development, strengthening domestic value addition, and supporting the objectives of the Renewed Hope Agenda.
The ban aims to deepen processing capacity within Nigeria, enhance livelihoods in shea-producing communities, and promote the growth of Nigerian exports anchored on value-added products, the statement noted.
To further these objectives, President Tinubu has authorised the two Ministers of the Federal Ministry of Industry, Trade and Investment, and the Presidential Food Security Coordination Unit (PFSCU), to coordinate the implementation of a unified, evidence-based national framework that aligns industrialisation, trade, and investment priorities across the shea nut value chain.
He also approved the adoption of an export framework established by the Nigerian Commodity Exchange (NCX) and the withdrawal of all waivers allowing the direct export of raw shea nuts.
The President directed that any excess supply of raw shea nuts should be exported exclusively through the NCX framework, in accordance with the approved guidelines.
Additionally, he directed the Federal Ministry of Finance to provide access to a dedicated NESS Support Window to enable the Federal Ministry of Industry, Trade and Investment to pilot a Livelihood Finance Mechanism to strengthen production and processing capacity.
Shea nuts, the oil-rich fruits from the shea tree common in the Savanna belt of Nigeria, are the raw material for shea butter, renowned for its moisturising, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. The extracted butter is a principal ingredient in cosmetics for skin and hair, as well as in edible cooking oil. The Federal Government encourages processing shea nuts into butter locally, as butter fetches between 10 and 20 times the price of the raw nuts.
The federal government said it remains committed to policies that promote inclusive growth, local manufacturing and position Nigeria as a competitive participant in global agricultural value chains.
Economy
NASD Bourse Rebounds as Unlisted Security Index Rises 1.27%

By Adedapo Adesanya
The NASD Over-the-Counter (OTC) Securities Exchange expanded for the first session this week by 1.27 per cent on Wednesday, February 25.
This lifted the NASD Unlisted Security Index (NSI) above 4,000 points, with a 50.45-point addition to close at 4,025.25 points compared with the previous day’s 3,974.80 points, as the market capitalisation added N30.19 billion to close at N2.408 trillion versus Tuesday’s N2.378 trillion.
At the trading session, FrieslandCampina Wamco Nigeria Plc grew by N5.00 to trade at N100.00 per share compared with the previous day’s N95.00 per share, Central Securities Clearing System (CSCS) Plc improved by N4.18 to sell at N70.00 per unit versus N65.82 per unit, and First Trust Mortgage Bank Plc increased by 14 Kobo to trade at N1.59 per share compared with the previous day’s N1.45 per share.
However, the share price of Geo-Fluids Plc depreciated by 27 Kobo at midweek to close at N3.27 per unit, in contrast to the N3.30 per unit it was transacted a day earlier.
At the midweek session, the volume of securities went down by 25.3 per cent to 8.7 million units from 11.6 million units, the value of securities decreased by 92.5 per cent to N80.7 million from N1.2 billion, and the number of deals slipped by 33.3 per cent to 32 deals from the preceding session’s 48 deals.
At the close of business, CSCS Plc remained the most traded stock by value on a year-to-date basis with 34.1 million units exchanged for N2.0 billion, trailed by Okitipupa Plc with 6.3 million units traded for N1.1 billion, and Geo-Fluids Plc with 122.0 million units valued at N478.0 million.
Resourcery Plc ended the trading session as the most traded stock by volume on a year-to-date basis with 1.05 billion units valued at N408.7 million, followed by Geo-Fluids Plc with 122.0 million units sold for N478.0 million, and CSCS Plc with 34.1 million units worth N2.0 billion.
Economy
Investors Lose N73bn as Bears Tighten Grip on Stock Exchange

By Dipo Olowookere
The bears consolidated their dominance on the Nigerian Exchange (NGX) Limited on Wednesday, inflicting an additional 0.09 per cent cut on the market.
At midweek, the market capitalisation of the domestic stock exchange went down by N73 billion to N124.754 trillion from the preceding day’s N124.827 trillion, and the All-Share Index (ASI) slipped by 114.32 points to 194,370.20 points from 194,484.52 points.
A look at the sectoral performance showed that only the consumer goods index closed in green, gaining 1.19 per cent due to buying pressure.
However, sustained profit-taking weakened the insurance space by 3.79 per cent, the banking index slumped by 2.07 per cent, the energy counter went down by 0.24 per cent, and the industrial goods sector shrank by 0.22 per cent.
Business Post reports that 25 equities ended on the gainers’ chart, and 54 equities finished on the losers’ table, representing a negative market breadth index and weak investor sentiment.
RT Briscoe lost 10.00 per cent to sell for N10.35, ABC Transport crashed by 10.00 per cent to N6.75, SAHCO depreciated by 9.98 per cent to N139.35, Haldane McCall gave up 9.93 per cent to trade at N3.99, and Vitafoam Nigeria decreased by 9.93 per cent to N112.50.
Conversely, Jaiz Bank gained 9.95 per cent to settle at N14.03, Okomu Oil appreciated by 9.93 per cent to N1,765.00, Trans-nationwide Express chalked up 9.77 per cent to close at N2.36, Fortis Global Insurance moved up by 9.72 per cent to 79 Kobo, and Champion Breweries rose by 5.39 per cent to N17.60.
Yesterday, 1.4 billion shares worth N46.2 billion were transacted in 70,222 deals compared with the 1.1 billion shares valued at N53.4 billion traded in 72,218 deals a day earlier, implying a rise in the trading volume by 27.27 per cent, and a decline in the trading value and number of deals by 13.48 per cent and 2.76 per cent, respectively.
Fortis Global Insurance ended the session as the busiest stock after trading 193.7 million units for N152.7 million, Zenith Bank transacted 120.7 million units worth N11.1 billion, Japaul exchanged 114.8 million units valued at N407.0 million, Ellah Lakes sold 98.4 million units worth N999.2 million, and Access Holdings traded 63.1 million units valued at N1.7 billion.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn