General
Lawmakers Must Not Spend N110bn on Cars, Palliatives—SERAP

By Adedapo Adesanya
Socio-Economic Rights and Accountability Project (SERAP) has advised the Senate President, Mr Godswill Akpabio, and Speaker of the House of Representatives, Mr Tajudeen Abbas, to halt plans to spend N40 billion on 465 exotic and bulletproof cars for members and principal officials and N70 billion as palliatives for new members.
In the letter dated July 15, 2023, signed by SERAP deputy director, Mr Kolawole Oluwadare, the organisation said, “This travesty and apparent conflicts of interest and self-dealing by members of the National Assembly must stop.”
SERAP also urged them to “repeal the 2022 Supplementary Appropriation Act to reduce the budget for the National Assembly by N110 billion, reflect the current economic realities in the country and address the impact of the removal of fuel subsidy on the over 137 million poor Nigerians.”
It asked the parliament to “request President Bola Tinubu to present a fresh supplementary appropriation bill, to redirect the N110 billion to address the situation of the over 20 million out-of-school children in Nigeria, for the approval of the National Assembly.”
“While N70 billion ‘support allowance’ is budgeted for 306 new lawmakers, only N500 billion worth of palliatives is budgeted for 12 million poor Nigerians. N40 billion is also allocated to buy 465 Sports Utility Vehicles (SUVs) and bulletproof cars for members and principal officials,” the group stated.
SERAP said, “It is a fundamental breach of their fiduciary duties for members of the National Assembly to arbitrarily increase their own budget and to use the budget as a tool to satisfy the lifestyle of lawmakers.”
“It is a grave violation of the public trust and constitutional oath of office for members of the National Assembly to unjustifiably increase their own budget at a time when over 137 million poor Nigerians are living in extreme poverty exacerbated by the removal of fuel subsidy.
“We would be grateful if the recommended measures are taken within seven days of the receipt and/or publication of this letter. If we have not heard from you by then, SERAP shall take all appropriate legal actions to compel you and the National Assembly to comply with our request in the public interest.
“Rather than exercising their constitutional and oversight functions to pursue the public interest by considering bills to improve the conditions of the over 137 million poor Nigerians who are facing the impact of the removal of fuel subsidy, the lawmakers seem to be looking after themselves.
“According to reports, no fewer than 107 units of the 2023 model of the Toyota Landcruiser and 358 units of the 2023 model of Toyota Prado would be bought for the use of members of the Senate and the House of Representatives, respectively.
“The planned purchase is different from the official bulletproof vehicles expected to be purchased for the four presiding officers of the National Assembly.
“The proposed spending of N110 billion by members of the National Assembly is apparently on top of the N281 billion already provided for the lawmakers in the 2023 National Assembly budget. The proposed spending is also different from the N30.17 billion budgeted for the ‘inauguration expenses’ for new members.
“SERAP is concerned that the budget for the National Assembly may further be increased as members are reportedly demanding an upward review of their salaries and allowances purportedly to offset the impact of the removal of fuel subsidy.
“Section 14(2)(b) of the Nigerian Constitution of 1999 [as amended] provides that, ‘the security and welfare of the people shall be the primary purpose of government.
“Under Section 16(1)(a)(b), the National Assembly has the obligations to ‘harness the resources of the nation and promote national prosperity and an efficient, a dynamic and self-reliant economy’, and to ‘secure the maximum welfare, freedom and happiness of every citizen.’
“Section 18 of the Constitution of Nigeria provides, among others, that: ‘Government shall direct its policy towards ensuring that there are equal and adequate educational opportunities at all levels. Government shall strive to eradicate illiteracy, and to this end, Government shall provide (a) free, compulsory, and universal primary education.
“The Compulsory, Free Universal Basic Education Act also provides in Section 2(1) that, ‘Every Government in Nigeria shall provide free, compulsory and Universal basic education for every child of primary and junior secondary, school-age,” it said.
It warned that “The proposed spending of N110 billion by members of the National Assembly is a fundamental breach of the Nigerian Constitution and the country’s international human rights obligations.
“Nigerians have a right to honest and faithful performance by their public officials, including lawmakers, as public officials owe a fiduciary duty to the general citizenry.
“Cutting the N110 billion from the budget of the National Assembly would be entirely consistent with your constitutional oath of office, and the letter and spirit of the Nigerian Constitution, as it would promote efficient, honest, and legal spending of public money.
“The problem of out-of-school children has continued to have catastrophic effects on the lives of millions of children, their families, and communities.
“By being out of school, these Nigerian children have been exposed to real danger, violence, and even untimely death. Redirecting the proposed spending of N110 billion to address the situation of over 20 million out-of-school children across the country would improve access of Nigerian children to quality education.
“Education is both a human right in itself and an indispensable means of realizing other human rights. As an empowerment right, education is the primary vehicle by which economically and socially marginalized adults and children can lift themselves out of poverty and obtain the means to participate fully in their communities.
“Under international law, states are required to progressively implement socio-economic rights, including the right to quality education commensurate with the level of resources available. Gross misallocation of resources to the detriment of the enjoyment of the right to quality education can constitute a human rights violation.”
General
IBEDC Promises Stability, Growth After Board Restructuring

By Adedapo Adesanya
The Ibadan Electricity Distribution Company (IBEDC) has announced the reconstitution of its board following the resignation of three nominees of the Asset Management Corporation of Nigeria (AMCON), promising growth and stability.
Earlier this week, the disco, which serves Oyo, Ogun, Osun and Kwara States, as well as parts of Ekiti, Kogi and Niger States, unveiled its new board led by the new chairman, Mr Tunde J. Afolabi.
The newly constituted board include Mr Ayodeji Ariyo Gbeleyi, with Mr Michael I. Magaji as Alternate Director; Mr Taiwo Afolabi; Professor Oladapo Afolabi; Mr Tunde Fayinka; Mr Oluwaseyi Akinwale and Mr Adeolu Ijose.
According to the chairman, the emergence of a new core investor and the reconstituted board marks a significant milestone in the company’s corporate journey and signals a renewed strategic direction focused on stability, continuity and sustainable growth.
“This transition represents renewal, not rupture. It represents investment, not instability. It represents partnership, not division. Our goal is to strengthen governance, enhance operational performance, deepen capital investment and deliver improved service to customers across our franchise areas,” he added.
Mr Afolabi, while addressing customers directly, assured them that there would be no avoidable service disruptions as a result of the transition, stating that all IBEDC offices will remain open, while field operations will continue uninterrupted.
“The new core investor has committed to sustained capital investments in feeder rehabilitation and expansion, transformer upgrades and replacements, injection substation improvements, and the replacement of obsolete network components,” he stated.
He added that IBEDC plans to accelerate the integration of advanced digital and operational technologies, disclosing that these include enhanced outage management systems, strengthened billing platforms, expanded smart metering deployment, and digitised customer engagement channels aimed at improving transparency and service responsiveness.
On workforce stability, the chairman emphasised that there will be no job losses as a direct result of the transition, noting that the board, under his leadership, is committed to employee welfare, improved work tools, modern safety equipment, and technology upgrades to support field efficiency, while maintaining high performance standards.
Mr Afolabi also pledged proactive and structured engagement with regulators, including the Nigerian Electricity Regulatory Commission (NERC) and the Nigerian Electricity Management Services Agency (NEMSA), underscoring its commitment to full regulatory compliance, strengthened governance frameworks, transparency and accountability.
Furthermore, he reaffirmed the commitment of the distribution company to structured and timely payment cycles for vendors and suppliers, recognising their critical role in maintaining network stability.
With the new board in place, he insisted that IBEDC is poised to deepen operational excellence, strengthen financial sustainability, and position itself firmly on the path to becoming Nigeria’s leading power distribution company—powering progress across its franchise with unity, confidence and innovation.
Established in November 2013 following Nigeria’s power sector privatisation, IBEDC operates the largest distribution network serving the highest customer population within Nigeria’s electricity distribution landscape.
General
Eyesan Promises Enhanced Transparency, Digital Transformation at NUPRC

By Adedapo Adesanya
The chief executive of the Nigerian Upstream Petroleum Regulatory Commission (NUPRC), Mrs Oritsemeyiwa Eyesan, has promised to enhance transparency and ensure that the NUPRC’s internal communications are fully digital.
Mrs Eyesan said this when the Executive Secretary of the Nigeria Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative (NEITI), Mr Musa Adar, visited the commission’s corporate headquarters in Abuja.
“We have set for ourselves a 60-day programme to digitise our interactions and communications within the commission. I can assure you that once we get to day 60, there will be no paper trail within the Commission. All our transmissions will be electronic, which also means speed is assured. It means we will be able to trace where we have hiccups,” Mr Eyesan said.
The NUPRC boss said digitising processes often leads to better results, like the enforcement of payments of royalties.
“I can tell you without a shadow of doubt that for royalty payments, the default rate was enormous prior to 2025 when the Commission went live on the system. Now, compliance has improved,” Mrs Eyesan said.
The NUPRC boss sought a deepened relationship with NEITI, which will foster transparency, especially amid the 2025 Licensing Round.
In his remarks, the NEITI’s scribe said there was a need for the NUPRC to carry the agency along in its operations as this would not only enhance transparency but also deepen investor confidence.
Mr Adar also urged the commission to be firm on oil companies that run afoul of the Petroleum Industry Act.
Speaking on the Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative, Mr Adar asked that the NUPRC actively participate in the 2026 EITI flagship conference, which will provide the Commission with better insights into the standards that guide EITI implementation.
The NEITI boss also sought support from the Commission in the area of data sharing, which will enhance the operations of the agency.
“We are here to seek understanding, and we must collaborate,” Mr Adar said.
General
Tinubu Tasks Acting IGP Disu to Restore Peace, Strengthen Security Nationwide
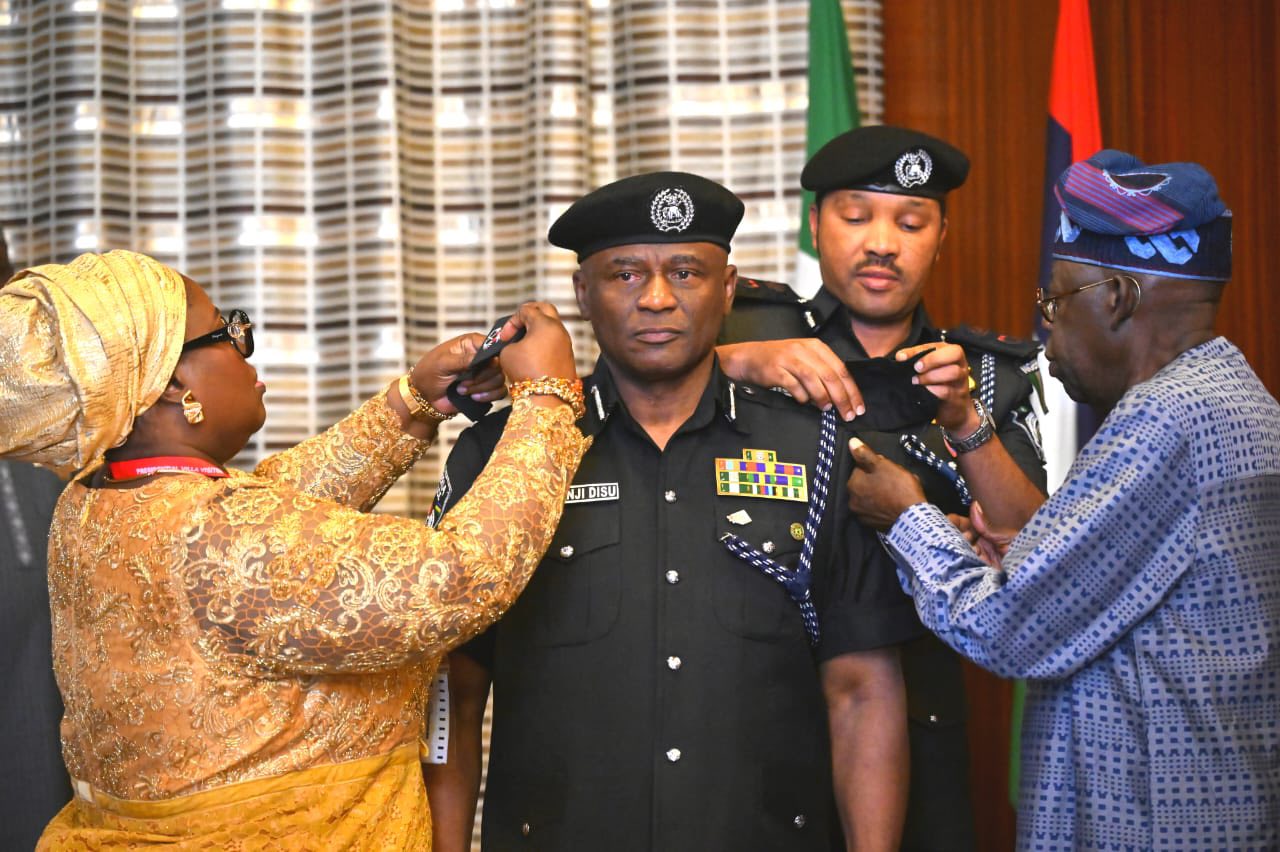

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
The acting Inspector-General of Police (IGP), Mr Tunji Disu, has been charged to do everything within his powers to restore peace and strengthen security across the nation.
This task was given to the new police chief by President Bola Tinubu after being decorated at the State House in Abuja on Wednesday.
Mr Disu was chosen to succeed Mr Kayode Egbetokun on Tuesday. His appointment is expected to be approved by the Nigeria Police Council and confirmed by the Senate next week.
President Tinubu described Mr Disu’s appointment as coming at a critical moment, urging him to rebuild public confidence in the police’s capacity to do their job in collaboration with other security forces.
“I made this decision for you to assume this responsibility. I know your record. I saw the dedication you exhibited while you were in Lagos when I was governor,” the President said.
“Lead firmly but fairly, demand professionalism at every level and ensure that the safety of lives and property remains our highest priority. It’s a daunting challenge. I know you can do it. You have my word, you have my full support,” he added.
Mr Tinubu urged him to advance the security pillars of his administration’s Renewed Hope Agenda. He expressed confidence in the Acting IGP’s discipline, operational experience and leadership capacity.
“Nigeria is challenged with banditry, terrorism and other criminal activities. You will be part of the thinking and innovation to overcome them,” the President said, reaffirming his belief that Nigeria would prevail under a committed leadership.
The President also paid tribute to Mr Egbetokun, who was present with his spouse, saying, “We are a grateful nation. Nigeria appreciates your contribution to maintaining law and order.”
He urged Egbetokun to be ready to offer useful advice to his successor and wished him and his family peace, good health and success in future endeavours, noting,
“You have not succeeded without a good successor. His success will also be part of your legacy.”
Mr Tinubu urged all security stakeholders to work collectively to safeguard lives and property during this critical period.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn