General
Nigeria Hunger Crisis Worsens, Hits Lake Chad Basin
By Modupe Gbadeyanka
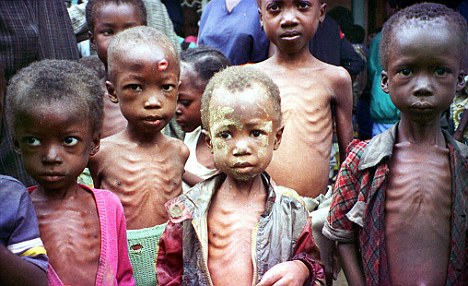
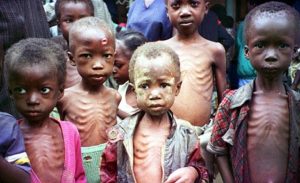
Few days ago, the United Nations’ Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) raised an alarm of food crisis in northeast Nigeria caused by activities of Boko Haram militants.
It warned then that if nothing urgent was done, it could become worse.
However, on Friday, the FAO further warned that the food security situation in Nigeria and the Lake Chad Basin is drastically deteriorating as conflict and instability continue.
The agency has called for swift and decisive action from the international community to protect the livelihoods of millions of families dependent on farming, livestock and fishing for their food and livelihoods.
It said with the next planting season starting in May, and with scarcity of animal fodder and water points during the lean season, it is crucial that crop seeds, tools and livestock support reach families urgently to limit the scope of the deepening crisis that now involves four countries: Cameroon, Chad, Niger and Nigeria.
Some 7.1 million people are now severely food insecure across the four countries. Among them are 515,000 children who are suffering from severe acute malnutrition – a condition which, if untreated, can lead to permanent damage to a child’s development and even death.
FAO is among the UN agencies and governments attending the Oslo Humanitarian Conference today, organized to mobilize international funding for the crisis-struck region, where 80 to 90 percent of people rely on farming, fishing and herding for their livelihoods.
“In the worst-affected areas, famine continues to loom — and millions will remain trapped in cycles of severe hunger if we don’t enable farmers to start cropping now,” said Dominique Burgeon, Director of FAO’s Emergency and Rehabilitation Division, who is representing FAO at the conference. “Our collective efforts cannot be limited to merely avoiding massive famine – they need to allow people to return to a dignified life. And supporting agriculture is the key to both,” he said.
Besides reducing hunger and boosting nutrition, investing in farmers also provides much needed job opportunities that reduce migration and limit the potential for radicalization of unemployed youth, according to Burgeon.
Crisis spilling across borders
Violence related to the armed group Boko Haram in north eastern Nigeria has spilled over to parts of neighbouring countries in the Lake Chad Basin – specifically, Cameroon’s Far North, western Chad and south eastern Niger – with devastating effects on food security and livelihoods.
With the Lake Chad Basin approaching a critical period in the agricultural calendar, FAO is urgently calling for $30 million in immediate emergency support to help farming families in the four countries get ready to plant in the upcoming May planting season and prevent them from slipping into long-term dependency on food aid.
It said a total of $232 million will be needed to secure food production and access to food for three million people in the worst-hit areas over the next three years. The vast majority of the requested funds – some $191 million – is designated for Nigeria, which is bearing the brunt of the crisis.
Violence and displacement drive severe hunger

Violence has driven millions across the four countries from their homes and hampered access to agricultural lands and assets, creating massive humanitarian needs in an area already struggling with food insecurity, poverty and environmental degradation. Host communities, in particular, have been struggling for several years now to feed the displaced as well as their own.
As humanitarian access improves, revealing the magnitude of impact of the conflict, time has come to support both people who remained on their land and those who decide to return to their original livelihoods.
In Borno State alone, the population in crisis, emergency and catastrophe phases of food insecurity (Phases 3 to 5 on the five-tiered scale used by humanitarian agencies) increased from 2 million in August 2016 to 3.3 million in October-December 2016. The worst-affected in this group are not able to feed themselves and have exhausted all resources by selling off their belongings, including seeds, tools and animals. Without intervention, that number is expected to climb to 3.6 million at the height of the lean season in August 2017.
The UN foresees around 120 000 people facing famine conditions in Nigeria. Of this number, the vast majority – some 96 percent — are expected to be in Borno.
Targeting the most vulnerable
Emergency farming assistance must go hand in hand with food assistance for it to be successful throughout the upcoming lean season. To this end, FAO is collaborating with the World Food Programme to ensure vulnerable families — mainly IDPs and host communities — receive food assistance, and at the same time agriculture-based livelihood support in the form of provision of seeds, tools and fertilizer. This way, they will able to restore and protect their livelihoods and farming assets for ongoing food production.
FAO’s long-term strategy for the Lake Chad region puts a special emphasis on supporting refugees, internally displaced families and host communities, as these are the most vulnerable groups in this crisis. Interventions are geared to improving their food security and nutrition and building their resilience so they are better equipped to handle future shocks. In addition, restoring agriculture-based livelihoods will offer a unique opportunity to pave the way to recovery and peace in the affected areas.
The strategy incorporates not only provision of farming and livestock inputs but also technical training, cash transfers, instruction in natural resource management, and support in setting up community-managed funds that can reduce vulnerability to shocks.
General
NISO Attributes Electricity Woes to Inadequate Gas Supply

By Adedapo Adesanya
The Nigerian Independent System Operator (NISO) has attributed the poor power supply facing a considerable number of Nigerians to inadequate gas supply to thermal power plants.
Business Post reports that epileptic power supply has plagued consumers in Lagos, Oyo, Abuja, and Osun, among others, this month, leading to worries. Also, some businesses have recorded losses due to the epileptic power supply in their areas.
In a statement posted on its X handle, NISO disclosed that average available generation on the national grid currently stands at about 4,300 megawatts (MW), with the low output primarily attributed to gas supply constraints.
The system operator noted that thermal power plants, which account for the dominant share of Nigeria’s electricity generation mix, require an estimated 1,629.75 million standard cubic feet (MMSCF) of gas per day to operate at optimal capacity. However, as of February 23, 2026, actual gas supply to the plants was approximately 692.00 MMSCF per day.
The available supply represents less than 43 per cent of the daily gas requirement, resulting in constrained generation output and reduced electricity allocation to Distribution Companies (DisCos).
NISO, which independently manages the nation’s electricity grid, explained that any disruption or limitation in gas supply directly affects available generation capacity and overall grid output, given the heavy reliance on thermal plants.
It added that when total system generation drops significantly, the operator is compelled to implement load shedding across the network while dispatching available energy in line with allocation percentages approved under the Multi-Year Tariff Order (MYTO) framework of the Nigerian Electricity Regulatory Commission (NERC), to maintain grid stability and prevent system disturbances.
While expressing regret over the inconvenience to electricity consumers and market participants, NISO said it is working closely with relevant stakeholders to restore full energy allocation once gas supply improves and generation capacity returns to normal levels.
General
EFCC Re-Arraigns ex-AGF Malami, Wife, Son Over Alleged Money Laundering
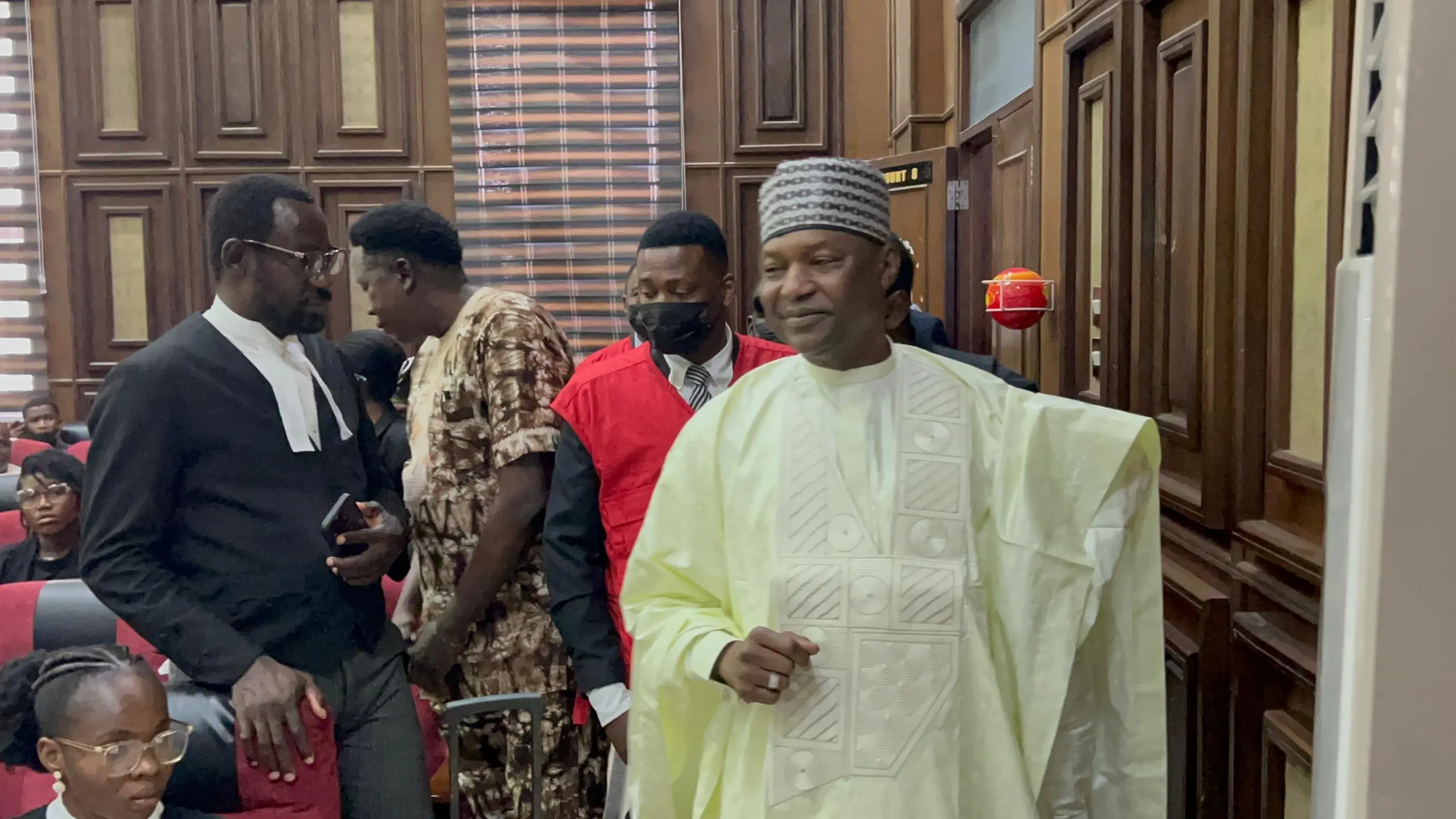

By Adedapo Adesanya
The Economic and Financial Crimes Commission (EFCC) has re-arraigned former Attorney-General of the Federation (AGF), Mr Abubakar Malami (SAN), his wife, Mrs Asabe Bashir, and son, Mr Abdulaziz Malami, on money laundering charges.
They were brought before Justice Joyce Abdulmalik of the Federal High Court in Abuja, following the re-assignment of the case to the new trial judge.
Upon resumed hearing, EFCC’s lawyer, Mr Jibrin Okutepa (SAN), informed the court that the matter was scheduled for defendants’ re-arraignment.
“The matter is coming before your lordship this morning for the very first time. I will be applying for the plea of the defendants to be taken,” he said.
Mr Okutepa equally applied that the sums listed in Counts 11 and 12 be corrected to read N325 million instead of N325 billion for Count 11, and N120 million instead of N120 billion for Count 12.
When it was not opposed by the defence lawyer, Mr Joseph Daudu (SAN), Justice Abdulmalik granted the oral application by Mr Okutepa.
The defendants, however, pleaded not guilty to the 16 counts preferred against them by the anti-graft agency bordering on money laundering.
Justice Obiora Egwuatu had, on February 12, withdrawn from the case shortly after the civil case filed by the EFCC was brought to him.
The case was formerly before Justice Emeka Nwite, who sat as a vacation judge during the Christmas/New Year break.
After the vacation period, the CJ reassigned the cases to Justice Egwuatu, who had now recused himself, before it was reassigned to Justice Abdulmalik.
The former AGF, his wife, and son were earlier arraigned before Justice Nwite on December 30, 2025.
While Malami and his son were remanded at Kuje Correctional Centre, Asabe was remanded at Suleja Correctional Centre before they were admitted to N500 million bail each, on January 7, with two sureties each in the like sum.
General
INEC Shifts 2027 Presidential, N’Assembly Elections to January 16

By Adedapo Adesanya
Nigeria will hold next year’s presidential and National Assembly elections a month earlier than planned, after the Independent National Electoral Commission (INEC) revised the polling schedule.
The elections will be held on January 16, instead of the previously announced date of February 20, INEC said in an X post, signed by Mr Mohammed Kudu Haruna, National Commissioner and Chairman, Information and Voter Education Committee.
There were also changes to the Governorship and State Houses of Assembly elections initially fixed for Saturday, March 6 2027, in line with the Electoral Act, 2022, have now been moved to Saturday, February 6, 2027.
The electoral commission said the changes were caused by the enactment of the Electoral Act, 2026 and the repeal of the Electoral Act, 2022, which introduced adjustments to statutory timelines governing pre-election and electoral activities.
“The Commission reviewed and realigned the schedule to ensure compliance with the new legal framework,” it said.
INEC said party primaries (including resolution of disputes) will commence on April 23, 2026 and end on May 30, 2026, after which Presidential and National Assembly campaigns will begin on August 19, 2026, while Governorship and State Houses of Assembly campaigns will begin on September 9, 2026.
It noted that campaigns will end 24 hours before Election Day, and political parties have been advised to strictly adhere to the timelines.
INEC also stated it will enforce compliance with the law.
The electoral body also rescheduled the Osun Governorship election which was earlier scheduled for Saturday, August 8 2026, by a week to Saturday, August 15, 2026.
INEC noted that some activities regarding the Ekiti and Osun governorship elections have already been conducted, and the remaining activities will be implemented in accordance with the Electoral Act, 2026.
Speaking at a news briefing in Abuja two weeks ago, the chairman of INEC, Mr Joash Amupitan, expressed the readiness of the commission to conduct the polls next year.
The timetable issued by the organisation for the polls at the time came when the federal parliament had yet to transmit the amended electoral bill to President Bola Tinubu for assent.
Later that week, the Senate passed the electoral bill, reducing the notice of elections from 360 days to 180 days, while the transmission of results was mandated with a proviso.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn














