Health
Where Are The 3.5m Nigerians Infected With HIV/AIDS?


By Dimos Sakellaridis
The intention of the title is not to scare or stigmatize any reader but to generate an intelligent discussion about the scourge of HIV/AIDS in Nigeria.
In a country of 189 million people, 3.5 million may seem like an insignificant number. However, I know of some countries with population less than 3.5 million people and I cannot imagine what the future of such a country would look like if all their citizens were infected with HIV/AIDS.
The picture of such an imagination would be a monumental tragedy of devastating proportions! Horrendous statistics in Nigeria pegs the HIV/AIDS infected population at 3.5 million and either way you look at it, it is no mean figure.
HIV is spread when blood, semen, or vaginal fluids from an infected person enter another person’s body, usually through sexual contact, from sharing needles when injecting drugs, or from mother to baby during birth.
Many reasons have been adduced for the increasing scourge. One of the top reasons is poor needle and condom use.
In the current harrowing economy, sexual pleasure will be a top recreational activity and that possibly means increased unprotected sex for individuals seeking short term pleasure to long-term economic struggles.
If such a large number of Nigerians are infected with HIV/AIDS according to National Agency for the Control of AIDS (NACA), then a larger population of Nigerians must be interacting with them one way or the other.
Some of the 3.5 million may be married to someone or be related to another as son, daughter, cousin, in-law, brother, sister, niece, nephew, aunt or uncle. The infected ones may be relating to other people as friends, neighbours, customers, clients or colleagues. One way or the other, we are all connected to them.
Some others tragically may be relating to these infected ones as sèxual partners. When you look at 3.5 million holistically, then you realize that it is not a strange distant figure in another city or territory.
It is very close to home and that is scary! If these infected people are Nigerians, then other Nigerians are connected to them one way or the other. So, when experts advise individuals to stay safe especially in sexual relationships, sharp people are smart to listen and adhere.
In retrospection, I am positive that if any of these individuals were infected through unprotected intercourse, they would wish they had done something differently. By something, I mean use a condom every time they had sèx.
So many people find condom use boring. Others believe that condom use gets in the way of full sèxual pleasure or excitement. I understand their reservations especially if they have never heard of the Fiesta Premium condoms available in 12 different variants of colours, textures, shapes, flavours, thickness and sizes, so that individuals can enjoy a different, exciting and pleasurable experience every time they have sèx.
Fiesta condoms puts the ‘F’ in Fun and is backed by DKT Nigeria’s symbols of excellence; ‘Effective, Safe, Affordable and Quality’ (ESAQ).
Fiesta premium Condoms are great choice because they can prevent both pregnancy and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), so whenever you use Fiesta condoms, you get double protection combined with pleasure every time.
I have heard of so many reasons behind people not using condoms. Top on the list is condoms reduce pleasure. I believe this reason is given because they don’t know about Fiesta Ultra-Thin brand that is as close to skin as you get without that “rubber” taste that can be a real turn off.
When another person says using condom is boring, it is because they have not used the Fiesta dotted condom with more than 500 pleasure dots on the surface to increase stimulation for both partners or the Fiesta ribbed condom with more than 50 pleasure rings to increase stimulation for both partners.
A favourite with Nigerian men is the Fiesta Original Black (a.k.a. Baba dudu) condoms which are gently lubricated, black condoms to increase pleasure for you and your partner and give you a real ‘Black man’s condom experience’.
There is even a Fiesta Glow condoms popularly called ochu uzo (Pathfinder) because it is luminous and glows in the dark even defying power failure to find its target.
Sèx does not have to be risky and dangerous especially where there is the grave potential that one’s sèxual partner may already be infected with HIV/AIDS. Condom use must be encouraged.
Fiesta Premium condoms distributed nationwide by DKT Nigeria have twelve exciting variants including stimulating variants enhanced with chocolates, strawberries and Prolong for extended phantasmagoric levels of pleasure.
The number of ladies engaged in commercial sex workers may increase because the challenging economy could push many promising young girls into the tackiness of prostitution.
Many of them would choose the horrendous career path unaware of the tragedies that are embedded within especially the risk of sexually transmitted diseases and death! It is very unfortunate. But that is the plain truth.
Women and young girls suffering under the agony of poverty may soon choose the ‘easy’ way out through prostitution and they may not know that they can even protect themselves although in very unpalatable profession.
These women or girls are related to people. They have families and friends who may not be aware that they are related to a person within the enemy lines of infection with HIV/AIDS.
This is a tragedy especially when you imagine the number of people living with HIV/AIDS in Nigeria. This is not to stigmatize the PLWHA but any population of people living with HIV/AIDS should be treated with the utmost importance especially as the global community celebrates World AIDS Day on December 1st, 2016.
I am positive that engaging in positive sèxual behaviours including the use of condoms to prevent STDs will greatly reduce the increasing scourge of HIV/AIDS in Nigeria.
If awareness can be created to alter behavior change, I am positive that the scourge of HIV/AIDS can be stemmed on several fronts especially the youths who are the major victims of the scourge.
Dimos Sakellaridis is the Country Director of DKT International Nigeria.
Health
Union Disrupts NAFDAC Operations in Lagos Over Sachet Alcohol Ban

By Adedapo Adesanya
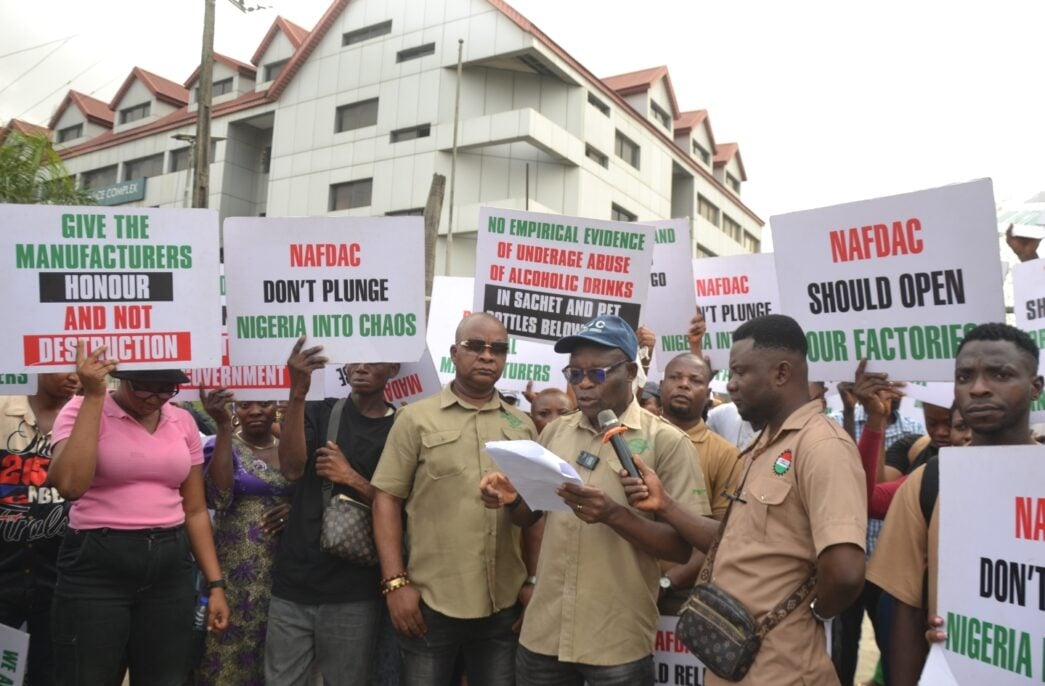
Members of the National Union of Food, Beverage and Tobacco Employees protested at the Lagos office of the National Agency for Food and Drug Administration and Control (NAFDAC), disrupting operations in reaction to the ban on sachet alcohol.
The protesting union members barricaded the agency’s premises in Isolo, meaning staff who arrived early to resume duty were forced to remain outside the complex.
Recall that NAFDAC has continued the ban on alcoholic beverages sold in sachets and PET bottles below 200 millilitres, despite calls from certain quarters, including the picketers.
The union is demanding the immediate unsealing of affected factories and production lines, warning that sustained enforcement of the policy could trigger significant economic consequences across the industry.
It is the second time this month that union members disrupted the Lagos NAFDAC office over what they described as the agency’s refusal to comply with an alleged federal government directive to suspend enforcement of the ban on the production and sale of alcoholic beverages in sachets.
The union claimed that directives had been issued by the Office of the Secretary to the Government of the Federation and the Office of the National Security Adviser, calling for the suspension of enforcement and the reopening of sealed production lines.
However, NAFDAC dismissed the claims, maintaining that it had not received any official instruction from the Federal Government to halt enforcement of the ban on sachet and PET-bottled alcohol.
Meanwhile, police officers were later seen at the NAFDAC Isolo premises, which dispersed the blockade to allow NAFDAC staff back into the premises.
Representatives of the Director-General of NAFDAC later engaged the protesting union in talks, but the meeting ended without resolution as demonstrators insisted their agitation would continue.
Union leaders presented their concerns during closed-door discussions with a director within the agency and the Special Assistant to the Director-General. However, no agreement was reached.
The protesters are urging NAFDAC to reconsider what they describe as the strict enforcement of the ban on sachet alcohol. Instead, they want the agency to focus on regulating access to such products, particularly by restricting sales to minors, while intensifying public enlightenment campaigns on responsible consumption.
Despite this, protesters say they will not stop until their demands are addressed.
Health
Modern Veterinary Clinics For Advanced Pet Care

As companion animals live longer and owners expect more from routine care, modern veterinary clinics have evolved into centers offering advanced diagnostics, specialty surgery, and integrative therapies. For busy professionals juggling work, travel, and online business demands, knowing which clinic delivers comprehensive care is essential. Frisco vet services illustrate how these modern practices combine cutting-edge technology, multidisciplinary expertise, and client-focused workflows. This article outlines the infrastructure, service offerings, and decision criteria that indicate a clinic capable of providing contemporary, evidence-based care while keeping visits efficient and stress-free for both pets and owners.
What Defines A Modern Veterinary Clinic
A modern veterinary clinic is defined less by a single piece of equipment and more by an integrated approach that combines up‑to‑date technology, specialized staff, and clinic design that prioritizes safety and comfort. These clinics treat animals with complex conditions, run efficient workflows, and communicate transparently with owners.
Key Infrastructure And Technology Investments
Contemporary clinics invest strategically in diagnostic and treatment modalities that materially change outcomes: digital radiography for rapid imaging, in‑house laboratories for same‑day blood work, ultrasound for real‑time organ assessment, and advanced surgical suites with anesthesia monitoring. Investment also includes infection‑control systems, reliable HVAC, and sterilization equipment. These capital decisions reduce turnaround time for diagnoses and support complex procedures that previously required referral.
Staffing, Specialization, And Continuing Education
Staffing reflects clinical ambition: veterinarians with specialty training (DACVS, DACVIM, DACVECC), certified veterinary technicians, and support staff trained in low‑stress handling. Modern clinics often host visiting specialists or maintain referral relationships with tertiary centers. Importantly, clinics that prioritize continuing education schedule regular training, subscribe to current literature, and engage in case reviews, actions that keep protocols current and improve outcomes.
Clinic Design For Safety, Flow, And Comfort
Design matters. Logical patient flow minimizes cross‑contamination and stress: separate entrances for healthy and sick patients, dedicated isolation wards, and distinct surgical zones. Comfortable client areas, clear signage, and private consultation rooms improve communication and compliance. For pets, non‑slip surfaces, quiet recovery areas, and pheromone‑friendly environments reduce anxiety, which in turn improves diagnostic accuracy and post‑procedure recovery.
Advanced Diagnostic Capabilities
Diagnostics are the backbone of modern pet care. Faster, more precise tests enable tailored treatment plans and earlier interventions.
Advanced Imaging: Digital X‑Ray, Ultrasound, CT, And MRI
Digital X‑ray provides high‑resolution images with immediate availability and easier sharing for remote consults. Ultrasound is indispensable for soft‑tissue evaluation and guided biopsies. CT and MRI, once exclusive to academic centers, are now present in many referral clinics, allowing detailed assessment of complex fractures, thoracic disease, neurologic conditions, and staging of cancer. Image quality and interpretation, often augmented by teleradiology, lead to more confident surgical planning and prognostication.
Laboratory, Point‑Of‑Care Testing, And Genomic Diagnostics
In‑house labs produce same‑day CBCs, chemistry panels, and cytology, accelerating decision‑making. Point‑of‑care tests for infectious agents, endocrine disorders, and clotting function add convenience without sacrificing reliability. Genomic diagnostics, from breed‑specific risk panels to tumor genomics, are increasingly accessible, enabling targeted therapies and risk stratification for hereditary conditions.
How Diagnostics Inform Preventive Care And Personalized Medicine
Diagnostics underpin preventive medicine: heartworm antigen tests, thyroid screening, and wellness blood panels reveal problems before clinical signs appear. Personalized medicine emerges when diagnostics inform individualized vaccination schedules, dietary plans, or monitoring frequency. The result: care that reduces emergency visits and improves long‑term quality of life.
State‑Of‑The‑Art Surgical And Interventional Services
Surgery in modern clinics spans routine spays and neuters to complex orthopedic reconstructions and image‑guided interventions.
Minimally Invasive, Laser, And Image‑Guided Procedures
Minimally invasive techniques, arthroscopy, laparoscopy, and endoscopy, reduce pain, shorten hospital stays, and speed return to function. Laser surgery provides precision and reduced bleeding for soft‑tissue procedures. Image‑guided interventions, such as CT‑guided biopsies or fluoroscopy for foreign body retrieval, allow targeted treatments that were once riskier or impossible.
Anesthesia, Pain Management, And Perioperative Safety
Anesthesia protocols are more nuanced today: individualized drug selection, multimodal analgesia, regional blocks, and continuous monitoring (ECG, capnography, pulse oximetry) improve safety. Preoperative assessment, including risk stratification and optimization of comorbidities, reduces complications. Recovery protocols emphasize early mobilization and aggressive pain control to prevent chronic pain syndromes.
Postoperative Rehabilitation And Recovery Protocols
Rehabilitation is an expected component of surgical care. Physical therapy, hydrotherapy, and tailored exercise plans reduce muscle atrophy and improve joint function. Clinics often provide home‑care instructions and scheduled reassessments to track progress and adjust protocols. These programs turn good surgical outcomes into durable functional gains.
Petfolk Veterinary & Urgent Care – Frisco
Advanced Therapeutics And Specialty Treatments
Beyond diagnostics and surgery, modern clinics deliver advanced therapeutics that extend and improve life quality.
Regenerative Medicine: Stem Cells And PRP
Regenerative modalities like mesenchymal stem cell therapy and platelet‑rich plasma (PRP) injections aim to stimulate healing in tendon, ligament, and osteoarthritic conditions. While still an evolving field, controlled studies and clinical experience show promising functional improvements for select patients. Clinics offering these therapies combine careful case selection with measurable outcome tracking.
Oncology, Neurology, Cardiology, And Other Specialties
Specialty services allow complex, multidisciplinary care. Veterinary oncologists provide staging, chemotherapy, and radiation planning: neurologists manage seizure disorders and spinal disease: cardiologists use echocardiography and interventional procedures for congenital heart defects. Integration with imaging and lab diagnostics enables cohesive care pathways that mirror human tertiary centers.
Integrative Therapies: Physical Rehab, Acupuncture, And Nutrition
Integrative care recognizes the value of adjunctive treatments. Acupuncture and targeted nutrition plans complement medical therapy for chronic pain and mobility issues. Nutritional counseling, including therapeutic diets for renal, cardiac, or dermatologic disease, is standard in clinics focused on long‑term outcomes.
Improving Pet And Client Experience With Technology
Technology enhances both clinical care and client experience, especially for owners who need efficient, transparent services.
Telemedicine, Remote Monitoring, And Virtual Follow‑Ups
Telemedicine extends access for triage, follow‑ups, and behavioral consultations. Remote monitoring devices, activity trackers, continuous glucose monitors, and wearable ECGs, provide objective data between visits. Virtual follow‑ups reduce travel burdens and let clinicians adjust care in real time, improving adherence and satisfaction.
Electronic Medical Records, Client Portals, And Scheduling Tools
Electronic medical records (EMRs) streamline documentation and support coordinated care. Client portals give owners access to vaccination histories, lab results, and discharge instructions. Integrated scheduling and automated reminders decrease no‑shows and improve preventive care compliance, a benefit both to clinics and busy clients.
Pain Management, Behavior‑Based Care, And Low‑Stress Handling
Client experience is inseparable from pet comfort. Modern clinics train staff in low‑stress handling techniques and behavior‑based protocols that reduce fear and aggression. Transparent pain‑management plans, clear cost estimates, and follow‑up communications foster trust and better outcomes.
How To Choose The Right Modern Clinic For Your Pet
Choosing a clinic requires practical criteria and an understanding of trade‑offs between convenience, specialization, and cost.
Questions To Ask: Credentials, Equipment, And Outcomes
Prospective clients should ask about specialist credentials, the availability of imaging and lab services, and the clinic’s approach to anesthesia and pain control. Request examples of similar cases and expected outcomes. A clinic that welcomes such questions is often more transparent and results‑oriented.
Cost, Insurance, And Referral Pathways
Advanced care carries higher costs. Discuss fee structures, payment options, and whether the clinic works with pet insurance. Understand referral pathways: does the clinic refer to or host board‑certified specialists? Clear referral and co‑management policies indicate maturity and a networked approach to care.
Evaluating Reviews, Accreditation, And Collaboration With Primary Vets
Look for consistent reviews that mention communication, follow‑up, and outcomes rather than isolated flashy cases. Accreditation (AAHA in the U.S.) or affiliation with universities can signal adherence to higher standards. Finally, the best specialty clinics collaborate with primary care veterinarians, ensuring continuity rather than competition.
Conclusion
Modern veterinary clinics for advanced pet care combine technology, specialization, and thoughtful design to deliver better diagnostic accuracy, safer surgeries, and more personalized therapies. Pet owners benefit when clinics pair capabilities with clear communication, transparent costs, and collaborative care models. For professionals, including small business owners and busy entrepreneurs who value efficient, outcome‑driven services, selecting a clinic that integrates advanced diagnostics, robust perioperative care, and client‑centric technology yields the best chance for sustained pet health. As veterinary medicine continues to mirror human healthcare in capability and complexity, informed choices and trusted partnerships between owners and clinics will determine the real value of those advances.
Health
Oyo Seals Ar-Rahmon Khabul Herbal Over Health Concerns

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
An Ibadan-based herbal company, Ar-Rahmon Khabul Herbal Nigeria Limited, has been sealed by the Oyo State Rule of Law Enforcement Authority (OYRLEA).
The state government, in a statement signed on Friday by the Commissioner for Information, Mr Dotun Oyelade, revealed that the herbal firm was shut down due to environmental violations and public health concerns.
The leader of OYRLEA, Mrs Aderonke Aderemi, explained that the action was taken after multiple petitions from residents alleging persistent offensive odour and health challenges linked to the company’s operations.
She noted that the state government swung into action “to protect public health, preserve environmental standards, and enforce regulatory compliance across the state.”
It was gathered that investigations identified tobacco leaf as a major component in its production process, generating a strong, putrid odour deemed hazardous to residents and capable of posing serious health risks to the surrounding community.
“Joint inspections by officials revealed that the company operates a herbal production facility within a densely populated residential area, in clear violation of environmental and public health standards,” the statement said, adding that further findings from the inspection include the emission of harmful and toxic gaseous substances into the atmosphere, the discharge of wastewater into a nearby community water body, the installation of a chimney deemed too short and directly facing residential buildings, and the accumulation of solid waste within the premises despite claims of engaging a waste contractor, among others.
Prior to the enforcement action, the agency had issued an abatement notice directing the company to cease operations and relocate within 21 days in accordance with the Oyo State Environmental, Sanitation and Waste Control Regulations.
OYRLEA, along with the agencies that carried out the enforcement, reiterates that air pollution, hazardous waste discharge, and improper waste management are violations of environmental laws.
Mrs Aderemi reaffirmed OYRLEA’s commitment to sustained monitoring and enforcement to ensure a safe and healthy environment for all residents.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn