Health
Russian COVID-19 Vaccines Disappear from Africa’s Radar
By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
Until recently, Africa has not been high on Russia’s policy agenda. African leaders have to understand that Russia, for the past three decades, Africa was at the bottom of its policy agenda. After the end of the Soviet era, Russia has focused broadly on the United States and Europe, dreaming of becoming part of Europe, part of the configuration of the Global North. The low economic presence of Russia from 1991 until 2019 was a testament to the fact that Africa was at the bottom of its priority list. Of course, the October 2019 summit was symbolic, but after that, Russia has left most of the bilateral agreements undelivered across Africa.
With its “special military operation” on Ukraine that necessitated the imposition of stringent sanctions from the United States, European Union and their allies, the United Nations Security Council, mounting pressure on Russia since February 24 2022, pushes Russia to begin soliciting aggressively for support in Africa. Last July, in an article posted to its official website, Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov wrote: “The development of a comprehensive partnership with African countries remains among top priorities of Russia’s foreign policy; Moscow is open to its further build-up multifaceted relations with Africa.”
In his Op-Ed article, Lavrov argues: “We have been rebuilding our positions for many years now. The Africans are reciprocating. They are interested in having us. It is good to see that our African friends have a similar understanding with Russia.” Lavrov, however, informed about broadening African issues “in the new version of Russia’s Foreign Policy Concept against the background of the waning of the Western direction” and this will objectively increase the share of the African direction in the work of the Foreign Ministry.
Lavrov consistently displays his passion for historical references. Soviet support for struggles for political independence and against colonialism should be laid to rest in the archives. The best way to fight neo-colonialism is to demonstrate by investing in those competitive sectors and depart away from hyperbolic rhetoric on an endless list of sectors. In practical terms, we rather face today’s development challenges and what is in store for the future generation. Africa today does not need anti-Western slogans; Africa simply needs external players who would passionately and genuinely invest in the critical economic sectors. The fundamental fact is that Africa is making efforts to transform its economy to create employment, modern agriculture, and industrialize the continent, especially with the introduction of the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA).
Despite criticisms, China has built an exemplary distinctive economic power in Africa. Besides China, Africa is largely benefiting from the European Union and Western aid flows and economic and trade ties. Compared, Russia plays very little role in Africa’s infrastructure, agriculture and industry and makes little effort to leverage the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA). Our monitoring shows that the Russian business community hardly pays attention to the significance of the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), which provides a unique and valuable platform for businesses to access an integrated African market of over 1.3 billion people.
Lavrov’s efforts toward building non-Western ties in these crucial times are highly commendable, especially with Africa. But, the highly respected Minister easily and most times forgot the fact that during these two-three years of a global pandemic, the coronavirus that engulfed the planet, in every corner of the world, Africa was desperately looking for vaccines. Health authorities are still warning that Covid-19 has not been completely faced throughout the world.
Quartz, a reputable global media, reported early this year that “as of the end of 2022, about a quarter of the population of African countries has been fully vaccinated against Covid-19, according to the latest figures shared by Africa CDC. The coverage varies drastically depending on the country. In Liberia, for instance, nearly 80% of the population is fully vaccinated, while only 34% is in neighbouring Sierra Leone. Congo, Sudan, Senegal, and Madagascar all have vaccination rates below 10%.
In his briefing, Ouma said the target for Africa remains to vaccinate 70% of the population. That goal, however, was set by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the overall population. These numbers are about to change – and not because of an increase in vaccinations. Africa CDC acting director Ahmed Ogwell Ouma announced in a video briefing on December 22 that it will modify the way it reports vaccination rates. Rather than reporting coverage of the overall population, it will only report vaccinations of the eligible populations aged 12 or more.
Due to delays in international vaccine deliveries, Africa lags behind the rest of the world in Covid vaccination rates and is the only continent where less than 50% of the population is fully vaccinated. Currently, just more than 800 million doses of vaccines have been administered in Africa, or 80% of the total received. About a third of the vaccinations have been made with Johnson & Johnson’s vaccine, followed by Pfizer (22%), AstraZeneca (17%), China’s Sinopharm (15%) and Sinovac (7%).
Several reports monitored by this author show that Russia has played a minimal role in the entire health sector in Africa. With the Covid-19 vaccination, Russia randomly sprinkled a few thousand as humanitarian assistance among its “Soviet friends”, including Egypt, Ethiopia, Guinea, Angola, Mozambique, Zimbabwe and South Africa. Nevertheless, the worse was Russia’s sudden failure to supply the 300 million vaccines through the African Union (AU), especially during the times of health crisis.
An authoritative policy report presented in November 2021 titled ‘Situation Analytical Report’ and prepared by 25 Russian policy experts headed by Sergei A. Karaganov noted explicitly the failure to supply Sputnik vaccines to the African Union. The report criticized Russia’s current policy and lukewarm approach towards Africa.
“In several ways, Russia’s possibilities are overestimated both publicly and in closed negotiations. The supply of Russian-made vaccines to Africa is an example. Having concluded contracts for the supply of Sputnik V to a number of African states, Russian suppliers failed to meet contractual obligations on time,” says the report in part.
The coronavirus outbreak a pandemic on March 11, 2020. Worth noting that Russia claims that it was the first to find a coronavirus cure. The World Health Organization (WHO), until today, has not certified Russia’s vaccines, though. On the other hand, all the vaccines that have been registered in Russia – Sputnik V, Sputnik Light, CoviVac and EpiVacCorona – are produced in large quantities by Russian pharmaceutical companies and are currently used for vaccination.
Director of the Gamaleya National Research Centre for Epidemiology and Microbiology Alexander Gintsburg has several times highlighted aspects of vaccine production and marketing. He noted to raise the attractiveness of the vaccines on foreign markets, including countries in the Middle East, Africa and Latin America.
The Russian Direct Investment Fund, tasked to engage in marketing the vaccines abroad, got messed up, especially in Africa. Of course, it took steps and speedily registered the vaccines in more than 20 African countries but terribly failed on delivery deadlines. Worse was the Russian Direct Investment Fund supplied, at exorbitant prices, through middlemen in the Arab Emirates to a number of African countries. Russia’s Foreign Ministry has, however, held a series of African Foreign Ministers during this Covid-19 period and desperate moment reiterated to assist with direct supplies to Africa. That is Russia, considered a reliable partner for Africa.
The above thoughts on the part of the Covid-19 business offered the reasons why Russia absolutely refused to join and be part of the Covax facility, which acts as a global collective bargaining initiative to secure vaccine doses for countries who signed up, including those are self-financing their purchases, as well as assistance from donors for poorer developing countries. The first vaccines purchased through Covax were indeed destined to reach Africa. That was, monitored by this author, some 88.7 million doses of the AstraZeneca and Pfizer vaccines distributed to 47 countries, including Africa, during the first half of 2021. This same year, during the virtual meeting of G7 leaders, the European Union announced it had donated a further 500 million euros to the COVAX program. The World Bank also committed $12 billion as concessional loans to assist African countries in accessing foreign vaccines.
That is not all from several reports monitored. In April 2022, writing under the headline: “How Russia’s Hollow Humanitarian Hurt Its Vaccine Diplomacy in Africa,” – the co-authors, Matthew T. Page and Paul Stronski, both noted in 2020 that Russia touted deliveries of medical and protective supplies to several African countries, while the Russian-developed Sputnik V vaccine offered hopes that African countries would soon be able to launch large-scale immunization drives. Russian efforts to promote Sputnik V in Africa have floundered for a variety of reasons, including regulatory worries, production and logistical shortfalls, bureaucratic inertia, and even sticker shock. There is, however, another key factor behind Moscow’s failed vaccine diplomacy: its traditionally diminutive post-Soviet development presence on the continent.
Compared to Australia, Canada, the European Union, Japan, the United Kingdom, the United States, and even many foundations, Russia has provided a tiny share of international development assistance to African countries since the end of the Cold War. Unlike India and Cuba, it has provided scanty medical assistance to – or investment in – African countries.
Suppose Russia wants to be influential on the continent. In that case, African political and economic leaders should demand more of Moscow, not simply settle for the symbolic diplomatic engagements or agreements at which the Russian leadership excels. Indeed, Africa has not ranked high on the Russian foreign policy agenda for much of the past three decades, getting barely a mention in the country’s key security documents except as either a partner in an emerging multipolar world or a source of instability.
Indeed the time has come for African leaders to rally together to ensure that no effort is spared in facilitating and supporting the building of large-scale vaccine manufacturing capacity on the continent. The African Vaccine Manufacturing Summit held in April 2021 was an encouraging start. Focus needs to be on developing real vaccine R&D capacity, which must necessarily lead to health products. This requires substantial investment and a long-term commitment. In a similar vein, under the aegis of the African Union, leaders have to begin looking for inside solutions rather than base hopes on these geopolitical games, great external powers seeking only support for their peculiar or parochial interests.
Understandably, while making efforts to maintain and expand its presence in Africa, Russia simply lacks the capability to deliver on its various promises in Africa. Surely, African countries have to begin to re-evaluate their relationship with Russia. African leaders should not expect anything tangible from meetings, conferences and summits. Since the first Russia-Africa summit held in 2019, very little has been achieved. Given the stringent sanctions imposed following Putin’s invasion of neighbouring Ukraine, it is even more improbable that Moscow would commit adequate financial resources to invest in economic sectors.
In stark contrast to key global players, for instance, the United States, China and the European Union and many others, Russia obviously has limitations. Notwithstanding that, for Russia to regain a part of its Soviet-era influence, it has to address its policy approach, this time trying to shift towards new paradigms – implementing some of the decade-old pledges and promises, and those bilateral agreements; secondly to promote development-oriented policies and how to make these strategic efforts more practical, more consistent, more effective and most admirably result-oriented with African countries.
Health
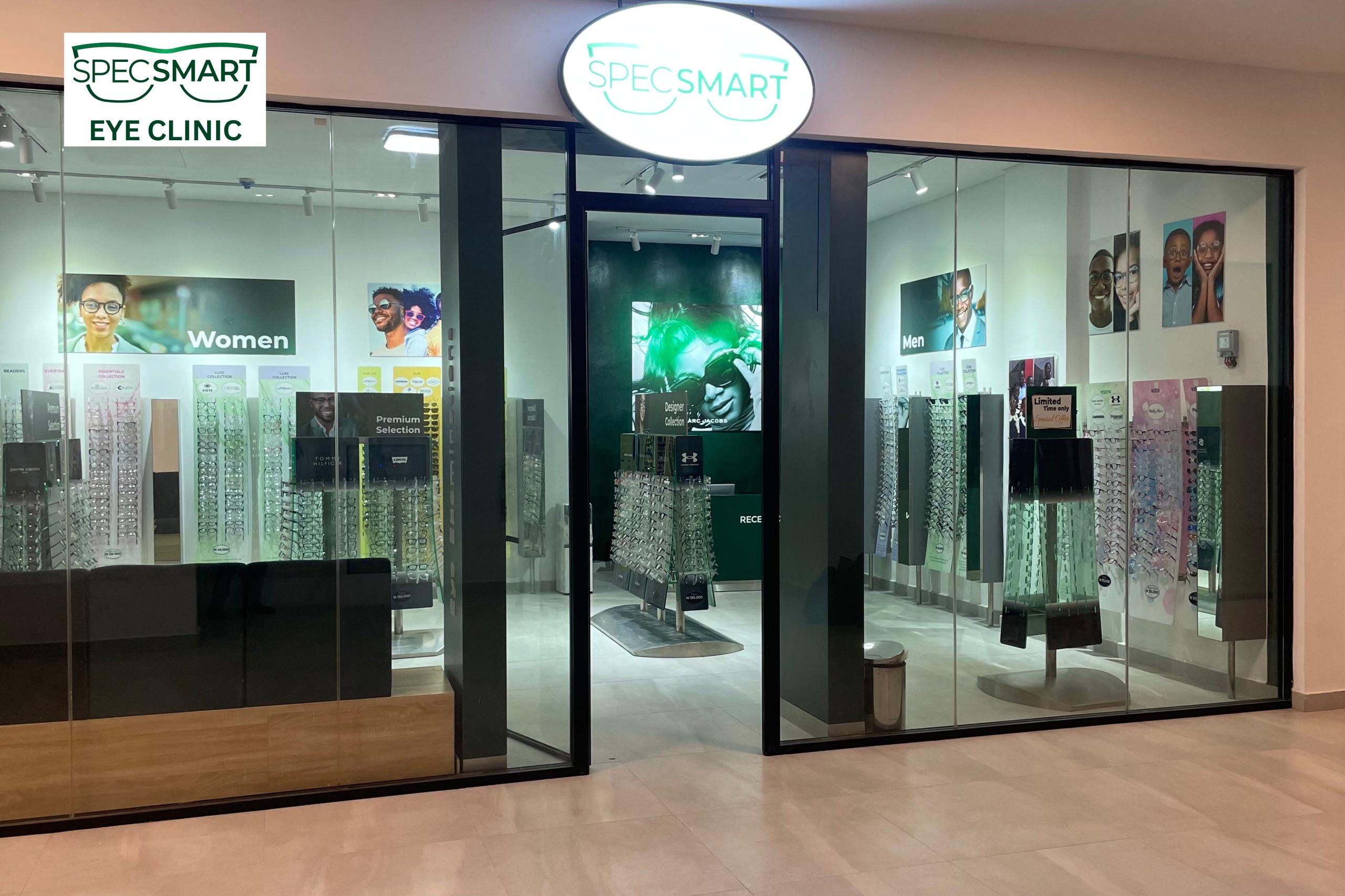
SpecSMART Eye Clinic Takes Affordable, Quality Care to Ikeja, Environs

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
The dream of residents of Ikeja and its environs enjoying affordable and quality care has now become a reality as a result of the opening of a new branch of SpecSMART Eye Clinic in the Opebi area of the capital of Lagos State.
SpecSMART Eye Clinic, a leading provider of optometry services in Lagos, commenced operations in Nigeria’s commercial capital in 2022.
Since then, it has been offering top-notch eye care to residents of the metropolis, especially those living on the Island. It has built a strong reputation for delivering high-quality primary eye care and optical products.
However, to extend its services to Lagosians living on the Mainland, it has now opened a new branch in Ikeja, reinforcing its commitment to providing accessible, affordable eye care to a wider community.
Business Post gathered that the clinic’s state-of-the-art services are supported by a team of skilled optometrists and opticians, utilizing cutting-edge digital equipment.
The new Ikeja location will offer a wide range of services, including Automated Eye Examinations using advanced digital equipment for precise diagnosis and personalized care.
In addition, clients will enjoy on-the-spot lens glazing for single vision, bifocals, and varifocals, with additional lens coatings, with services to be rendered seven days a week from 9 am to 9 pm on Mondays to Saturdays, and on Sundays and public holidays from 10 am 7 pm.
Also, the clinic has over 950 frames, ranging from affordable home brands to premium designer options, priced from N18,000, and has flexible appointment scheduling with 24-hour online booking via SpecSMART’s website.
The facility has partnerships with leading HMO providers in the country and offers glaucoma management and other essential eye health services.
According to the company, its introductory packages start from N30,000 and include consultation, frame, and single-vision lenses.
“With the opening of our Ikeja branch, we are ready to serve more individuals who need accessible, cost-effective, and reliable eye care.
“Our aim is to create a positive impact in Nigeria’s optometry sector by combining advanced technology with a patient-centred approach,” the Practice Head and Medical Director of SpecSMART, Dr Adaeze Nwoko, stated.

Health
FG Begins Vaccination Against Mpox in FCT, Six States

By Adedapo Adesanya
The Federal Ministry of Health and Social Welfare through the National Primary Health Care Development Agency (NPHCDA) has commenced the vaccination against Monkeypox, now known as Mpox.
Business Post reports that Bayelsa, Rivers, Cross River, Akwa Ibom, Enugu, Benue, and the Federal Capital Territory, were selected as pilot states for the vaccination.
An average of 631 persons are expected to be vaccinated across the seven states with two doses of the Mpox vaccine. A buffer for 50 persons will be kept at the national in case of an upsurge in other states.
NPHCDA in a statement posted on its verified X account confirmed the exercise, stressing that the vaccination will help to protect communities and safeguarding health of the people.
In a related development, according to the latest update by the Nigeria Centre for Disease Control (NCDC), there are 1,442 suspected cases of Mpox from 36 states and the Federal Capital Territory, while the number of confirmed cases of the infection was 118 from 28 states and the FCT.
“To prevent the spread of Mpox, we strongly advise the public to avoid contact with animals that may carry the virus, including sick or dead animals in affected areas, avoid handling materials that have been in contact with infected animals, limit unnecessary physical contact with individuals who are infected, practice frequent handwashing with soap and water, and ensure that animal food products are thoroughly cooked before eating.
“It’s also important to use protective clothing and gloves when handling sick animals or their tissues. Similarly, health workers are advised to follow standard safety protocols including droplet precautions when treating patients, use protective equipment including masks, gloves, and gowns, during patient care, and be vigilant for symptoms of Mpox, especially fever and rash, among other measures.”
Health
AXA Mansard Health Partners LUTH in Blood Donation Drive

By Aduragbemi Omiyale
Over 250 pints of blood have been donated by AXA Mansard Health to the Lagos University Teaching Hospital (LUTH), Idi Araba.
The blood was donated by more than 100 employees of the leading health insurance company in Nigeria through its volunteering programme tagged AXA Hearts in Action.
The initiative is part of the company’s blood donation drive aimed at contributing to positive societal and environmental impacts through employee volunteering, and expertise related financial support and in-kind donations.
According to the Chief Client Officer of AXA Mansard, Ms Rashidat Adebisi, “Through the AHIA, our employees do not just give time to great causes; we work together for a better future.”
“We share our time, knowledge and expertise as a people with a shared purpose of acting for human progress by protecting what matters through initiatives like this,” she added.
Ms Adebisi said the blood drive is a shining example of the philosophy in action, where collective contributions serve as a reminder that true impact often involves giving more than just money. It’s about putting one’s heart in action – an idea embedded in AXA’s corporate culture.
On his part, the chief executive of AXA Mansard Health Limited, Mr Tope Adeniyi, said with hospitals frequently experiencing blood shortages, events like these serve as a lifeline for patients in need.
“We are proud to contribute to the local healthcare sector and provide much-needed support to hospitals such as LUTH, ensuring that they have resources essential to saving lives,” he added.
Also commenting, the Head of Corporate Services and Public Relations at LUTH, Omolola Olubukunola Fakeye, thanked the firm for the “generous support,” which has made a “meaningful difference to our blood bank and ultimately to the lives of patients.”
“Blood donations are invaluable in many critical treatments, and initiatives like AXA Mansard’s blood drive bring immense relief to healthcare system.
“We are sincerely grateful for this partnership and the dedication of AXA Mansard’s employees,” Fakeye stated.
AXA Hearts in Action operates globally, she urging AXA employees everywhere to engage with and give back to their communities.
Through diverse projects – from health initiatives like this blood drive and medical outreaches to environmental efforts like the AXA Week for Good “Trash-to-Treasure” waste management project – AXA staff have opportunities to make a lasting difference on issues that matter.
For AXA Mansard, every act of social service brings them closer to the communities they serve, helping build a world where giving back is not only about charity but about lasting, positive change.
-

 Feature/OPED5 years ago
Feature/OPED5 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism8 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz2 years ago
Showbiz2 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking6 years ago
Banking6 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy2 years ago
Economy2 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking2 years ago
Banking2 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports2 years ago
Sports2 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn
-

 Technology4 years ago
Technology4 years agoHow To Link Your MTN, Airtel, Glo, 9mobile Lines to NIN
























