Media OutReach
SMART launches new research group WISDOM to pioneer technologies that will help machines “see” like humans

- Multi-million-dollar, three-and-a-half-year programme to advance Singapore’s optoelectronics and photonics capabilities and semiconductor industry, which generated over S$133 billion in 2023 and accounts for approximately 7% of Singapore’s GDP
- Bringing together over 20 Singapore and US-based researchers, this is the first time a programme will study the combination of three integral components: optics, optoelectronics and electronics
- WISDOM supports Singapore’s Future of Microelectronics (FME) national initiative, and has key partnerships with leading research institutions including the National Semiconductor Translation and Innovation Centre (NSTIC)
- The IRG’s research endeavours are expected to benefit industries such as automotive, consumer electronics, healthcare, and space travel and sample collection – including applications in autonomous driving, augmented reality, robotics and high-speed data communication
SINGAPORE – Media OutReach Newswire – 7 May 2025 – Imagine creating 3D-sensing technologies so lightweight, compact and high-performance that they could take us to planets beyond Mars. The Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART), Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s (MIT) research enterprise in Singapore, has launched a new interdisciplinary research group (IRG) focused on developing next-generation 3D-sensing technologies for practical use across industries such as automotive, consumer electronics, aerospace and healthcare, among others.
Jointly led by faculty from MIT and Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore), the Wafer-scale Integrated Sensing Devices based on Optoelectronic Metasurfaces (WISDOM) IRG will focus on developing ultra-thin, scalable sensing devices – systems that allow machines such as autonomous vehicles and robots to perceive depth, shape and spatial detail safely and with more versatility, much like human vision.
3-Dimensional (3D) sensing is essential for many modern applications, from autonomous vehicles and robotics to augmented reality and medical diagnostics. However, current systems still fall short of human-like perception capabilities, which pose limitations such as contextual unawareness and decision errors.
Today’s optical systems are also often bulky, expensive and difficult to mass-produce due to reliance on complex components and manual assembly. While new materials called optoelectronic metasurfaces — which are ultra-thin and can control light in powerful new ways — show great potential, it has been difficult so far to turn them into practical, widely used products, due to challenges in how these materials are combined with other technologies and manufactured at large scale.
SMART WISDOM will be helmed by Co-Lead Principal Investigators Prof Juejun Hu, Professor of Materials Science and Engineering at MIT, and Prof Tan Chuan-Seng, Professor of Electronic Engineering at the School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering at NTU Singapore.
“What makes me really excited about WISDOM is that we’re putting together pieces that haven’t been combined before – to benefit a ton of industries and use cases. For example, think how a super light and powerful LiDAR system could make trips to planets beyond Mars a reality. It’s like having a whole new set of eyes for exploration, and about making the seemingly impossible, possible,” said Prof Juejun Hu, Co-Lead Principal Investigator, WISDOM.
Combining expertise from five leading institutions
SMART brings together top researchers from leading institutions in the United States and Singapore, including MIT, NTU Singapore, National University of Singapore (NUS), Stanford University and University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC), to redefine how optical metasurfaces are designed, integrated and manufactured.
This multi-million, multi-year effort, supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) Singapore under its Campus for Research Excellence and Technological Enterprise (CREATE) programme, brings together leading experts across disciplines in photonics, materials science and semiconductor engineering to position Singapore at the forefront of global innovation in sensing technologies and advanced manufacturing.
World-first approach to pioneering 3D-sensing and next-generation applications
WISDOM will capitalise on wafer-scale integration using standard silicon complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) processes to revolutionise how meta-optical systems are produced. This is the first time a programme is put together to study the combination of these three separate elements: optical metasurfaces, optoelectronic devices with a focus on light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and vertical surface emitting laser arrays (VCSELs); and silicon CMOS electronics.
At the heart of WISDOM’s pioneering research is their world-first approach that integrates the three elements into a wafer-scale platform. This tri-element integration seeks to unlock entirely new functionalities in optical metasurface technology, enabling next-generation sensing systems with multi-modal illumination and detection, advanced displays with built-in high-speed communication, and biomedical devices with versatile light sources for diagnostics and therapeutics.
“The launch of WISDOM marks an exciting chapter in SMART’s and MIT’s long legacy in Singapore – bringing together the best in their fields from US, Singapore and the region for interdisciplinary research and collaboration to drive world-class research and innovation with commercial and societal impact for Singapore and beyond. The first-of-its-kind research will pioneer groundbreaking advancements for next-generation sensing systems, enabling transformative solutions across industries such as automotive, healthcare, aerospace and consumer electronics,” said Bruce Tidor, Chief Executive Officer and Director (Interim), SMART.
WISDOM’s inaugural project aims to develop a high-performance, metasurface-enabled LiDAR prototype, addressing key challenges in scalability, integration and performance. By combining metasurface optics, optoelectronic devices, and CMOS electronics on a single silicon substrate, WISDOM seeks to redefine the capabilities of LiDAR systems. This innovation promises to enhance detection accuracy, extend range and field-of-view, and reduce motion artifacts, with transformative implications for industries such as automotive, healthcare, robotics and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). Beyond improving safety in autonomous vehicles and navigation in drones, it also opens doors to revolutionary applications like glasses-free 3D displays and high-speed optical communication, laying the groundwork for smarter, more efficient technologies that will shape the future.
“WISDOM represents a paradigm shift in how meta-optical systems are integrated – from discrete assembly to wafer-scale packaging. Even at the research stage, we have a clear objective to bring our innovations to market and societal impact – enabling transformative sensing technologies for mass-market applications. WISDOM is designed to streamline manufacturing by eliminating costly and intricate die-to-die assembly, significantly improving throughput,” said MIT Prof Hu Juejun.
“By combining NTU’s two decades of expertise in electronics engineering and wafer packaging with MIT’s strengths in optical systems, we aim to create a new platform for large-scale manufacturing of optical metasurfaces using industry-standard CMOS processes. NTU is known for translating fundamental research into real-world technologies, and this collaboration builds on that strength. Ranked top in the world for Electrical and Electronic Engineering1, we are well-placed to deliver innovations that are both scalable and commercially viable, while also training the next generation of engineers to lead in areas like Augmented Reality, robotics and consumer technology,” said NTU Prof Tan Chuan-Seng.
As MIT’s research enterprise in Singapore, SMART is dedicated to driving innovation that powers future industries and transforms global technological landscapes. WISDOM adds on to SMART’s continuing commitment to advancing cutting-edge and translational research in fields such as artificial intelligence, agriculture, antimicrobial resistance, cell therapy and more. In addition to advancing scientific understanding, the IRG’s work is expected to contribute to intellectual property development, technology licensing, and the creation of Singapore research spin-offs and startups in related industries.
Hashtag: #SMART
The issuer is solely responsible for the content of this announcement.
About Wafer-scale Integrated Sensing Devices based on Optoelectronic Metasurfaces (WISDOM)
WISDOM is an interdisciplinary research group (IRG) launched in April 2025 by SMART, MIT’s research enterprise in Singapore. WISDOM is the first research and industry endeavour to study and integrate optical metasurfaces, light emitting diodes (LEDs) and vertical surface emitting laser arrays (VCSELs), and complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) electronics for industry and commercial application. By developing innovative 3D-sensing technologies that enhance system performance, scalability and cost efficiency, WISDOM aims to revolutionise optoelectronics and photonics, and address key challenges in semiconductor manufacturing and other key industries. These 3D-sensing technologies will deliver impactful advancements that drive progress in sensor innovation while fostering opportunities for commercial applications and societal benefits in Singapore and globally.
About Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART) [新加坡-麻省理工学院科研中心]
Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (![]() SMART) is MIT’s Research Enterprise in Singapore, established by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in partnership with the National Research Foundation of Singapore (NRF) since 2007. SMART is the first entity in the Campus for Research Excellence and Technological Enterprise (
SMART) is MIT’s Research Enterprise in Singapore, established by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in partnership with the National Research Foundation of Singapore (NRF) since 2007. SMART is the first entity in the Campus for Research Excellence and Technological Enterprise (![]() CREATE) developed by NRF. SMART serves as an intellectual and innovation hub for research interactions between MIT and Singapore. Cutting-edge research projects in areas of interest to both Singapore and MIT are undertaken at SMART. SMART currently comprises an
CREATE) developed by NRF. SMART serves as an intellectual and innovation hub for research interactions between MIT and Singapore. Cutting-edge research projects in areas of interest to both Singapore and MIT are undertaken at SMART. SMART currently comprises an ![]() Innovation Centre and five Interdisciplinary Research Groups (IRGs): Antimicrobial Resistance (
Innovation Centre and five Interdisciplinary Research Groups (IRGs): Antimicrobial Resistance (![]() AMR), Critical Analytics for Manufacturing Personalized-Medicine (
AMR), Critical Analytics for Manufacturing Personalized-Medicine (![]() CAMP), Disruptive & Sustainable Technologies for Agricultural Precision (
CAMP), Disruptive & Sustainable Technologies for Agricultural Precision (![]() DiSTAP), Mens, Manus and Machina (
DiSTAP), Mens, Manus and Machina (![]() M3S), and Wafer-scale Integrated Sensing Devices based on Optoelectronic Metasurfaces (WISDOM).
M3S), and Wafer-scale Integrated Sensing Devices based on Optoelectronic Metasurfaces (WISDOM).
SMART research is funded by the National Research Foundation Singapore under the CREATE programme.
For more information, please visit ![]() http://smart.mit.edu
http://smart.mit.edu
Media OutReach
Money20/20 Asia Report: APAC Fintech Ecosystem Shifts from Experimentation to Scale as AI and Digital Assets Drive Regional Leadership
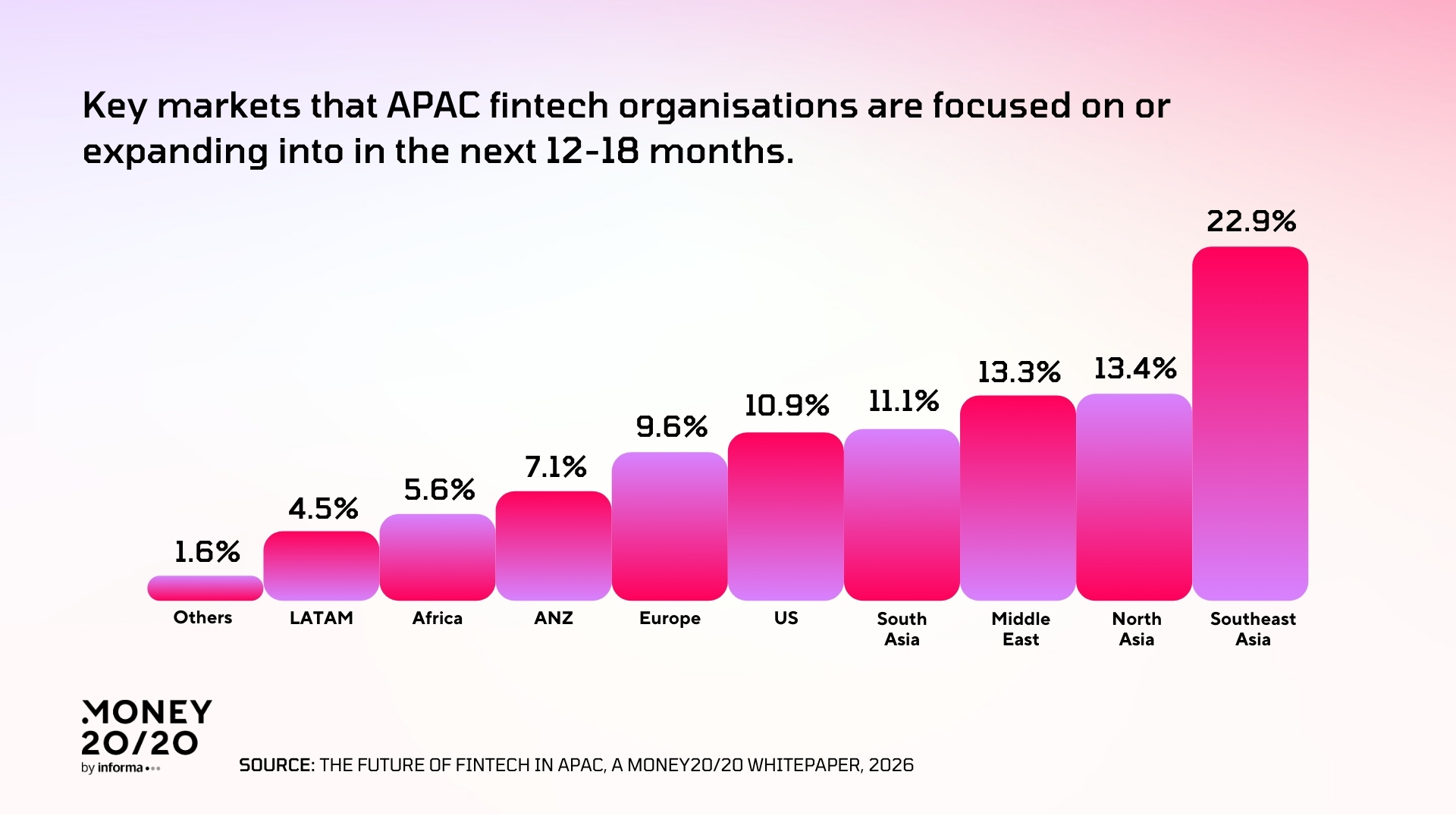
Based on insights from over 130 senior fintech leaders, the report highlights an industry moving beyond pilot programs toward enterprise-scale solutions that prioritize collaboration, digital trust, and financial inclusion as core business imperatives for 2026.
Key Findings
- 22.9% of respondents identify the region as their primary growth target, underscoring its continued dominance as the region’s growth engine.
- 90.6% of executives say social good initiatives are now embedded in corporate strategy — confirming impact has become a commercial imperative.
- 61.2% of organizations have already adopted AI or machine learning.
- New frameworks in Singapore, Hong Kong, and Japan are driving institutional adoption of stablecoins and tokenized assets.
- 63.5% of leaders cite fraud prevention as their highest operational priority.
“APAC is no longer experimenting — it’s executing,” said Ian Fong, VP of Content at Money20/20 Asia. “The region is building financial infrastructure that is faster, safer, and more inclusive than ever before. What happens here will influence the future of money globally.”
Digital Trust Becomes the New Currency
With digital adoption accelerating, 63.5% of leaders identify fraud prevention as their top priority. Regulators and industry players are now pivoting toward real-time risk intelligence and AI-driven security.
“The speed of digital adoption in APAC has outpaced traditional fraud models,” said Justin Lie, Founder & CEO of SHIELD. “What we’re seeing now is a shift toward real-time, device-level intelligence that operates silently in the background. Trust is the new currency of digital finance, and the companies that embed it in every interaction while delivering a frictionless experience will define the future of the industry.”
Stablecoins Move into Mainstream Financial Infrastructure
Institutional engagement with stablecoins and tokenized financial instruments has grown significantly, supported by clearer regulatory frameworks emerging across Singapore, Hong Kong, and Japan.
“Across Asia, stablecoins are already embedded in real economic activity from payments and cross-border settlements to treasury optimization,” said Yam Ki Chan, Vice President, Asia Pacific at Circle. “The region is demonstrating how digital assets can scale within financial systems, and the next phase is about interoperability and the development of an economic operating system for the internet”.
Digital Lending Expands Financial Access
The report highlights 72.9% of respondents believe SME-tailored fintech solutions are key to APAC’s economic growth, signaling a widening opportunity for inclusive financial innovation.
“Financial inclusion isn’t achieved by simply putting products online — it requires building for the realities of everyday consumers,” said Moritz Gastl, General Manager of Tala Philippines. “In markets like the Philippines, trust, transparency, and flexibility matter just as much as credit scoring. Digital lending works when it empowers people, not when it replicates old systems with new interfaces.”
Looking Ahead: Collaboration Will Define the Next Decade
As AI scales, payment rails interconnect, and digital assets enter regulated markets, APAC is emerging as a global blueprint for future financial systems.
“The next wave of fintech innovation will be defined by how well we balance technological advancement with social impact,” added Fong. “APAC markets are proving that financial innovation and inclusion can advance together.”
The Future of Fintech in APAC report can be downloaded HERE.
Hashtag: #Money20/20
The issuer is solely responsible for the content of this announcement.
Media OutReach
Huawei Highlights Digital Inclusion and Conservation Tech as AI Use Accelerates

About 80 guests attended the first day’s forum at the Leonardo Royal Hotel Barcelona Fira. In remarks published by Huawei, Yang Chaobin, CEO of Huawei ICT BG, said the digital divide “seems to be widening further” even as AI accelerates. “High-speed networks and robust computing facilities are essential foundations for an inclusive and sustainable AI era,” he said.

The International Telecommunication Union estimates about 2.2 billion people were still offline in 2025. Dr. Cosmas Zavazava, director of the ITU’s Telecommunication Development Bureau, said inclusion must be treated as a prerequisite for the AI era.
“AI must strengthen meaningful connectivity and support inclusive digital transformation. This requires responsible AI governance, investment in local talent and content, and capacity building, particularly for young girls, women, indigenous communities and marginalized groups.”
Huawei said it has fulfilled a commitment under the ITU Partner2Connect Digital Coalition to help expand connectivity in remote regions. By the end of 2025, the company said its initiatives had supported digital access for 170 million people in rural and underserved areas across more than 80 countries. In a Huawei news release, Jeff Wang, president of Huawei Public Affairs and Communications, said: “To bridge the digital skills gap, Huawei works closely with governments and partners to enhance digital access, deliver skills training, and advance STEM education for underserved communities.”
On March 2, the focus shifted to conservation with a visit to Spain’s Natural Park of Sant Llorenç del Munt i l’Obac. Here, digital monitoring tools are being used to support biodiversity protection, including efforts to safeguard the endangered Bonelli’s eagle alongside better managing potential impacts from outdoor activities like climbing on rock-dwelling birds and caving on protected bat species. The project forms part of the Tech4Nature initiative, developed with the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) to support digital tools in protected areas across 11 countries.
Sònia Llobet, the park’s director, said the project is helping managers balance visitor access with nature protection.
“As park managers, our challenge is how to make visitor access compatible with the conservation of this natural space,” she said. “This project is helping us answer some of the questions we face in balancing tourism and environmental protection.”
Hashtag: #Huawei
The issuer is solely responsible for the content of this announcement.
Media OutReach
Correcting and Replacing: Infinix NOTE 60 Ultra Ushers in New Premium Era

Thanks to powerful partnerships with industry leaders, NOTE 60 Ultra represents Infinix’s boldest entry in the flagship tier, debuting in Barcelona during MWC 2026
BARCELONA, SPAIN – Media OutReach Newswire – 5 March 2026 – Infinix is cementing its status within the premium smartphone segment in a bold new way with NOTE 60 Ultra, its landmark flagship debuting in Barcelona during Mobile World Congress 2026.
Co-developed with Italian automotive and design legend Pininfarina, NOTE 60 Ultra’s design is driven by an emotion-led aesthetic inspired by super cars. Beneath its bold design lies a fully realized flagship experience, integrating breakthrough in-house innovations with best-in-class partner technologies. A professional-grade 200MP ultra-high-definition imaging system, built-in multi-country satellite communication connectivity, and immersive audio precision-tuned by SOUND BY JBL come together to challenge expectations in the premium segment.
Supercar Design DNA in a Flagship, Shaped by Pininfarina
In the premium segment, the design language is a device’s opening statement. A user’s perception at first glance is shaped by aesthetics, long before a single specification is considered.
Drawing inspiration from the aerodynamic philosophy and pioneering spirit of high-performance sports cars, Infinix, in partnership with Pininfarina, takes a radical departure in sculpting a flagship. What stands out immediately is what’s missing: the camera bump. As premium handsets adopt larger sensors, they often sacrifice form with increasingly protruding camera modules.
True to the sports car heritage, NOTE 60 Ultra introduces a fully integrated, single-body rear: the Aluminum Unibody Design. At the heart of this craftsmanship is the World’s 1st Uni-Chassis Cam Module, formed a single, continuous sheet of CORNING® GORILLA® GLASS VICTUS that virtually conceals the presence of the camera. Much like a supercar sculpted for low-drag, the rear design maintains a smooth, uninterrupted silhouette. This also ensures a natural in-hand feel and unobtrusively slips into any pocket, while reinforcing the phone’s durability and structural integrity.
Paying homage to Italian cultural and racing heritage, NOTE 60 Ultra arrives in four striking colorways: Torino Black, Monza Red, Amalfi Blue, and Roma Silver. Each hue draws inspiration from the most iconic scenes and legends of Italy’s motorsport and cultural history, capturing the spirit of speed, lifestyle, and emotional beauty.
Just as a supercar announces its ignition through sound and light, NOTE 60 Ultra mirrors the ritual. A Floating Taillight signature spans the rear, illuminating as the device powers on. And as a final nod to automotive heritage, NOTE 60 Ultra features an Active Matrix Display reminiscent of a supercar dashboard at startup. Concealed within the rear surface, the hidden display lights up to reveal notifications, expressive icons, or a pixel-style virtual companion.
Dual Flagship Cameras for Detail, Zoom, and True-to-Life Imaging
Although discreet at first glance, Infinix makes no concessions on camera performance and earmarks a new era for Infinix’s imaging capability. Delivering performance on par with industry-leading standards, Infinix’s Dual Flagship Imaging Architecture marks several brand-first breakthroughs and improvements across three dimensions, reinforcing its position as a signature offering.
Under the hood, it’s clear that NOTE 60 Ultra refuses to settle for less. Discreetly integrated within the Uni-Chassis Cam Module is a powerful triple-camera array. Anchored by a next-generation 200MP Samsung ISOCELL HPE sensor, NOTE 60 Ultra delivers ultra-high-definition clarity. And ensuring flagship-grade versatility across focal lengths, the phone is complemented by a 50MP Samsung ISOCELL JN5 periscope telephoto lens and a 112° ultra-wide lens.
However, hardware alone does not define the full experience. For the first time, Infinix supports the XDR display standard with Ultra HDR Capture. Powered by a proprietary XDR Image Engine, Infinix’s advanced system delivers a superior dynamic range, ideal for true-to-life photos of bright lights at night or breathtaking sunset scenes.
The result is exceptional resolution that sets a higher bar for precise framing in daylight or after dark, while faithfully preserving details often lost in standard photography. Whether exploring daytime cityscapes or distant horizons, NOTE 60 Ultra excels with its advanced optical‑to‑digital zoom performance. Crisp, detailed shots are captured across a versatile zoom range, from a 2× optical crop and native 3.5× optical zoom to a 7× lossless digital zoom, extending up to 100× for extreme distances.
Expansive Satellite Calling and Messaging Coverage
Beyond what meets the eye, NOTE 60 Ultra carries a more subtle capability designed to accompany the user’s ambition, as far as and wherever the road leads. NOTE 60 Ultra is the first¹ to introduce dual-way satellite calling with expansive global coverage across a far greater number of countries¹. Powered by two-way messaging and calling beyond traditional terrestrial networks, NOTE 60 Ultra offers an added peace of mind whether navigating remote terrain beyond cellular coverage or facing large-scale network disruptions. The device bridges regional connectivity gaps to maintain communication and enables emergency location sharing when it matters most.
Ultra-Fast, Enduring Functionalities for an All-Around Flagship Experience
NOTE 60 Ultra combines category-leading performance and enduring power to support multi-sensory entertainment without interruption. Complementing this, its latest user experience delivers forward-looking innovations and AI-driven optimizations, making it more accessible and seamless for everyday use.
Impressively, Infinix debuted the Proprietary Battery Self-Healing Technology. Despite featuring a massive 7000mAh silicon-carbon battery within a slim, lightweight frame, NOTE 60 Ultra is engineered to restore up to 1%² of battery health every 200 charge cycles. Complementing this breakthrough, NOTE 60 Ultra supports wired 100W All-Around Fast Charge and 50W wireless charging, achieving a full charge from 1% to 100%² in only 48 minutes through a wired connection.
Even with a massive battery, Infinix pulls out all the stops to optimize for both speed and energy management. Featuring a 4nm all-big-core MediaTek Dimensity 8400 Ultimate chipset together with Infinix’s self-developed performance engine, NOTE 60 Ultra achieves up to 25%² faster multitasking, accelerated app responsiveness, and sustained smoothness.
NOTE 60 Ultra excels in its class with a captivating, 1.5K Ultra HDR cinematic display. Delivering fluid 144Hz responsiveness and exceptional 4500-nit peak brightness, visuals remain vibrant across most lighting conditions. Even in motion, intelligent predictive stabilization minimizes motion sickness, whether watching a film or playing games from within a car. And just as a high-performance vehicle demands calibrated acoustics, NOTE 60 Ultra doesn’t settle for less. It delivers high-fidelity audio through a stereo system with SOUND BY JBL, completing a truly compelling entertainment experience.
The NOTE 60 Ultra’s optimized performance enables its intelligent AI features to run fluidly and efficiently with minimal battery drain. Its integrated AI ecosystem focuses on practical daily-enhancing functions, including real-time vitals tracking via Advanced Health Monitor, personalized file organization and an adaptive AI-powered knowledge base, all evolving with user preferences. These AI capabilities are seamlessly woven into GlowSpace, a new interface debuting on XOS 16.³ Powered by Android 16, GlowSpace introduces a fully reimagined UI centered on fluid motion and luminous details that animate with every interaction.
Through co-engineering with leading technology and innovation partners, Infinix has aligned NOTE 60 Ultra around a unified vision of excellence. The outcome is a benchmark-setting flagship defined not by spectacle, but by deeply integrated and purposeful engineering, inside-out.
Product availability
NOTE 60 Ultra comes with a promise of 3 years of major OS updates and 5 years of security patches.
NOTE 60 Ultra is available in four colors: Torino Black, Monza Red, Amalfi Blue, and Roma Silver.
It will be available in two variants: 12GB + 256GB, 12GB + 512GB, with built-in eSIM⁴.
NOTE 60 Ultra comes with a deluxe gift box with automotive-inspired display stand design. A Supercar-Inspired MagCharge Base in Zinc Alloy, a Kevlar-Pattern MagPad, a Custom Kevlar MagCase, and a Track-Edition SIM Ejector Pin are included in the gift box.
Disclaimer
¹As of launch, this device is the first commercially available smartphone to support two‑way satellite calling across multiple countries. Feature availability, supported regions and coverage are subject to local certification, network deployment and market conditions.
²All data comes from Infinix laboratories. The testing data may vary slightly between different test versions and testing environments.
³The specific XOS upgrade plan for each model will be announced separately. Please note that availability of this upgrade may be limited in certain countries.
⁴eSIM availability is carrier and region-dependent; it may not be supported in all countries.
Hashtag: #Infinix
The issuer is solely responsible for the content of this announcement.
About Infinix
Established in 2013, Infinix is an innovation-driven brand dedicated to delivering cutting-edge technology, bold design, and outstanding performance. The brand provides smart, enjoyable mobile experiences that enhance everyday life. Beyond smartphones, Infinix has expanded its portfolio to include TWS earbuds, smartwatches, laptops, tablets, smart TVs, and more—building a comprehensive ecosystem of smart devices. Currently, Infinix products are available in over 70 countries and regions worldwide, including Africa, Latin America, the Middle East, South Asia, and Southeast Asia.
For more information, please visit: ![]() http://www.infinixmobility.com/
http://www.infinixmobility.com/
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn












