Technology
16.8 million Nigerians are Cyberattacked through Ad-supported Apps

A multinational cybersecurity business named Kaspersky conducted a study on the threat environment in a few African nations, recording over 28 million malware assaults and 102 million potentially undesirable apps in the smartphones of numerous people in Kenya, South Africa, and Nigeria.
According to a statement made by Kaspersky, the proliferation of PUAs and hacks occurred over a seven-month period.
According to the cybersecurity and antivirus company, a PUA is any software that a user did not choose to install on their device. The ad-supported software is one example of such a program (or adware).
These are pieces of software that show unsolicited adverts on computers. When they infect mobile devices, they are referred to as malware. Pornware is a type of PUA that shows pornographic content on devices.
Some PUAs are lawfully designed applications, however, they may be exploited to pose unique risks to users, such as the distribution of harmful software such as spyware, viruses, or other malware. Cybercriminals may purposefully conceal malware into PUAs, advertising websites, or supporting software.
According to the cybersecurity firm, not only are PUAs growing more widespread, but they are also more effective than traditional malicious software. Researchers have found that attacks on PUAs users occur four times more frequently than attacks on traditional malicious software.
For example, if over 16.8 million PUAs were detected in Nigeria over a seven-month period, 3.8 million malware assaults were also revealed to have occurred more than four times in the nation over that same period of time.
“The reason ‘grey zone’ software is becoming more popular is that it is more difficult to detect at first and that if the program is identified, its designers will not be deemed hackers “explained Kaspersky security expert Denis Parinov. “The issue with them is that consumers are not always aware that they agreed to the installation of such apps on their device, and in some situations, such apps are abused or used as a cover for malware downloads.”
In South Africa, around 10 million malicious software assaults were detected, and 43 million Puas were discovered throughout the review period. According to Kaspersky, internet users in Kenya face greater threats, with over 14 million malicious software discovered, and 43 million PUAs identified.
These kinds of cyberattacks were also popular in Kenya but were largely carried out by unlicensed and dishonest financial institutions.
Because of this, many people who wanted to get involved in trading started to search Capex Broker review, in order to find out whether or not a certain broker was among the scam financial companies and were licensed or not, as everyone who advertised something online was thought to be a fake.
However, it is also perilous for Nigeria since the potential harm these assaults might inflict on the local digital realm is tremendous.
Potentially unwanted apps (PUAs) are apps that are not dangerous in and of themselves. However, they typically have a detrimental impact on user experience. Adware, for example, floods user devices with advertisements; aggressive monetization software spreads unwanted paid offers; and downloaders may install other apps on the device, including harmful ones.
The researchers discovered that PUAs infect users nearly four times more frequently than regular malware when computing interim findings of threat landscape activity in African countries. They also eventually reach more people: for example, in South Africa, the virus would target 415,000 people in seven months, whereas PUA would target 736,000.
This specific danger, according to Geoffrey Cleaves, Head of Secure-D at Upstream, preys on the most susceptible.
“The fact that the virus is pre-installed on smartphones purchased in their millions by normally low-income households tells you all you need to know about what the business is now up against,” according to him.
According to Kaspersky’s research, three out of every ten devices are in danger of having undeletable applications on their phones, making them an ideal target for dangerous malware.
According to the Interpol Cybercrime COVID-19 Impact, phishing is the most serious concern worldwide, followed by malware and ransomware, harmful sites, and fake news. According to the research, the COVID-19-related attacks were mostly social engineering attempts.
Malware and adware may infiltrate devices in two ways. Freeware can install malicious software or advertising applications on a device.
Shareware is software that is shared for the purpose of the trial, whereas freeware is software that may be used for free. Users can obtain adware on their devices by visiting infected websites, which results in the download and installation of software that is never used.
PUA may be used to steal money from unknowing users in addition to spamming your device. According to the paper, PUA programs are not often deemed harmful in and of themselves. However, they typically have a detrimental impact on user experience.
Adware, for example, floods the user’s device with advertisements; aggressive monetization software spreads unrequested paid offers; and downloaders may install other, often harmful, apps on the device.
Technology
Interswitch Technovation 4.0 Hackathon Winners Share N10m

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
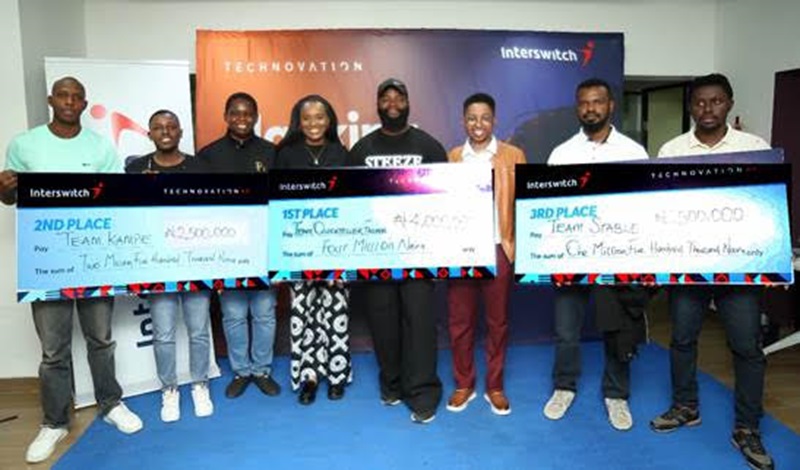
The winners of the Technovation 4.0 Hackathon, themed The Wicked Hackathon, organised by Interswitch, have been given N10 million in cash prizes for their efforts.
At the one-day finale event, which took place on Wednesday, March 4, 2026, at the Interswitch Innovation Lab and Co-Working Space, the money was shared among the top teams whose innovative solutions stood out during the rigorous multiple phases of the competition.
Team Quickteller Fashion emerged as the overall winner, securing the grand prize of N4 million for a solution that impressed judges with its originality, practicality, and strong strategic relevance. Team Kampe claimed second position with N2.5 million, while Team Stable placed third, receiving N1.5 million. Up to N300,000 worth of cash prizes were also awarded to the fourth, fifth and sixth qualifying teams.
For nine months, cross-functional teams from across the organisation collaborated to conceptualise, validate, develop, and refine solutions, moving from raw ideas to minimum viable products (MVPs) with ready-to-market potential and deployment across the business.
The atmosphere at the grand finale reflected that of preparation and anticipation as the top 9 teams presented their innovations through live demonstrations and detailed pitches, fielding questions from a distinguished panel of judges before the top three winners were selected. Each presentation highlighted rigorous validation processes, thoughtful market considerations, and a strong emphasis on measurable impact.
While many of the solutions remain confidential due to their strategic relevance, the diversity and depth of ideas showcased during the hackathon’s final underscored the organisation’s growing culture of intrapreneurship and structured innovation. The projects illustrated how technology-driven thinking can unlock efficiencies, strengthen operational capabilities, and open new pathways for growth across the digital payments and commerce ecosystem.
“Technovation continues to reflect who we are as an organisation, bold, forward-thinking, and deeply committed to building impactful solutions from within. Over the years, we have seen ideas conceived during this programme evolve into meaningful capabilities that strengthen our ecosystem.
“The passion, discipline, and ingenuity demonstrated by our teams this year reinforce our belief in the power of African innovation to solve complex challenges and shape the future of technology on the continent,” the Chief Innovation Officer for Interswitch, Ms Adaobi Okerekeocha, stated.
Technology
Google Introduces Yorùbá, Hausa Language Support for AI Search Features
By Modupe Gbadeyanka
The language support for its AI Search features has been expanded by Google, with the inclusion of Yoruba and Hausa in Nigeria.
This is part of a broader effort to make AI more inclusive across the continent, with support now extending to a total of 13 African languages.
Under the AI Overviews and AI Mode, speakers of both Nigerian languages can utilise AI-powered Search experiences in their mother tongue for quick summaries and conversational exploration.
This means existing AI features in Google Search are now accessible to people like the student in Kano asking a question in Hausa, and the trader in Ibadan seeking advice in Yorùbá.
By addressing language barriers, this update ensures that technology reflects the identity and culture of the people it serves. With this expansion, more people can now use AI Mode to ask complex questions in their preferred language, while exploring the web more deeply and naturally through text or voice.
The 13 languages now supported across Africa include Afrikaans, Akan, Amharic, Hausa, Kinyarwanda, Afaan Oromoo, Somali, Sesotho, Kiswahili, Setswana, Wolof, Yorùbá, and isiZulu.
These languages were chosen based on the vibrant search activity across the continent, ensuring that our AI experiences reach the communities that need them most.
Commenting on the development, the Communications and Public Affairs Manager for Google in West Africa, Taiwo Kola-Ogunlade, said, “Building a truly global Search goes far beyond translation — it requires a nuanced understanding of local information.
“With the advanced multimodal and reasoning capabilities of our custom version of Gemini in Search, we’ve made huge strides in language understanding, so our most advanced AI search capabilities are locally relevant and useful in each new language we support.
“This is about ensuring Nigerians can converse with Search in their mother tongues, making information more helpful for everyone.”
To use AI Overviews and AI Mode in the local language, users must open the Google app on an Android or iOS device, or via the Web. They are required to tap on AI Mode within the Search experience. Thereafter, they can type or speak the question in their preferred language, such as Hausa or Yorùbá, and let the AI guide the journey.
Technology
Telecom Operators to Issue 14-Day Notice Before SIM Disconnection

By Adedapo Adesanya
Telecommunications operators in Nigeria will now be required to give subscribers a minimum of 14 days’ notice before deactivating their SIM cards over inactivity or post-paid churn, following a fresh proposal by the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC).
The proposal is contained in a consultation paper, signed by the Executive Vice Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of the NCC, Mr Aminu Maida, and titled Stakeholders Consultation Process for the Telecoms Identity Risks Management Platform, dated February 26, 2026, and published on the Commission’s website.
Under the proposed amendments to the Quality-of-Service (QoS) Business Rules, the Commission said operators must notify affected subscribers ahead of any planned churn.
“Prior to churning of a post-paid line, the Operator shall send a notification to the affected subscriber through an alternative line or an email on the pending churning of his line,” the document stated.
It added that “this notification shall be sent at least 14 days before the final date for the churn of the number.”
A similar provision was proposed for prepaid subscribers. According to the Commission, operators must equally notify prepaid customers via an alternative line or email at least 14 days before the final churn date.
Currently, under Section 2.3.1 of the QoS Business Rules, a subscriber’s line may be deactivated if it has not been used for six months for a revenue-generating event. If the inactivity persists for another six months, the subscriber risks losing the number entirely, except in cases of proven network-related faults.
The new proposal is part of a broader regulatory review tied to the rollout of the Telecoms Identity Risk Management System (TIRMS), a cross-sector platform designed to curb fraud linked to recycled, swapped and barred mobile numbers.
The NCC explained in the background section of the paper that TIRMS is a secure, regulatory-backed platform that helps prevent fraud stemming from churned, swapped, barred Mobile Station International Subscriber Directory Numbers in Nigeria.
It said this platform will provide a uniform approach for all sectors in relation to the integrity and utilisation of registered MSISDNs on the Nigerian Communications network.
In addition to the 14-day notice requirement, the Commission also proposed that operators must submit details of all churned numbers to TIRMS within seven days of completing the churn process, strengthening oversight and accountability in the system.
The consultation process, which the Commission said is in line with Section 58 of the Nigerian Communications Act 2003, will remain open for 21 days from the date of publication. Stakeholders are expected to submit their comments on or before March 20, 2026.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn












