Technology
Buhari Inaugurates Council to Boost Digital Economy, e-Government

By Adedapo Adesanya
President Muhammadu Buhari has inaugurated the Presidential Council on Digital Economy and e-Government, promising that his administration will continue to take advantage of digital technologies to transform every sector of the economy.
At the event on Friday in Abuja, the President directed the Minister of Communications and Digital Economy, Mr Isa Pantami, to chair the council on his behalf and give regular updates.
He tasked members of the council to work towards further strengthening the capacity of government to develop, adopt and deploy digital technologies to make government more efficient and transparent, thereby improving Nigeria’s global standing in the ease of doing business index.
Mr Buhari noted that the organisation, whose members have been arrived at after a painstaking and thorough process, would provide the oversight needed to bring about a veritable structure for accelerating achievements in the digital economy and in the implementation of e-government in the country.
He enjoined every member of the council to consider the task as a national assignment and justify the trust reposed in their ability to support and significantly enhance the digital transformation of Nigeria.
“I launched the National Digital Economy Policy and Strategy (NDEPS) on the 28th of November, 2019, and expanded the mandate of the then Ministry of Communications to include Digital Economy.
“The implementation of that policy and mandate has enabled us to achieve significant progress and record a number of unprecedented achievements.
“The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the global economy showed that the steps we took in developing and implementing NDEPS were indeed timely.
“For example, the Information and Communications Technology sector was the fastest growing sector in both the fourth quarter of 2020 and the entire year 2020, based on the Report by the National Bureau of Statistics.
“The sector’s 14.7 per cent double-digit growth rate was instrumental in supporting our country to exit the recession triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic, far earlier than predicted by experts.
“The significant contribution of 17.92 per cent by the ICT sector to our GDP in the second quarter of 2021 is another example of the important impact of the digital economy on the overall economy.
“In the same vein, the growth of our digital economy sector enabled us to cope with the effect of the lock-down as both activities of the government and private sector, as well as educational activities, were able to move to online platforms,” he said.
Furthermore, Mr Buhari expressed delight that the approval of the National Policy on Virtual Engagements for Federal Public Institutions had helped to formalise government online meetings.
According to him, statutory meetings like the Federal Executive Council (FEC), Council of State, and other meetings can now effectively and legally take place online.
He added that Nigeria’s progress in e-governance had been noted by the international community, eliciting recognition from international stakeholders, including the appointment of the Minister of Communications and Digital Economy as the Chairman of the 2022 Forum of the highly regarded World Summit of the Information Society.
While congratulating the minister, the president acknowledged that the ministry has partnered with the Korea International Cooperation Agency to develop a National e-government Master Plan, approved by FEC in August 2019.
The President listed benefits from the partnership, including “the training of over 1,400 Nigerian public servants in both Nigeria and South Korea on e-governance; the launching of an E-Government Training Centre handed over to the Federal Government in November 2019, and the signing off of Phase II of the e-government Project – Project for Building Foundations Towards Digital Governance in Nigeria (2020-2026).”
On his part, Mr Pantami noted that NDEPS launched in 2019, made provision for the establishment of the Presidential Council to coordinate the development of an indigenous digital economy.
While describing the implementation of NDEPS for a digital Nigeria as very successful, the minister said in the last two years, the sector had provided ICT intervention to no fewer than 1,667 institutions at the federal and sub-national levels.
He stated that the recent auctioning of spectrums by the ministry generated over 400 per cent of revenue to the federal government coffers while two virtual institutions established by the government had trained some 500,000 Nigerians on digital and emerging technologies.
The 27-man committee chaired by Pantami on behalf of the president has the following members: Boss Mustapha, Secretary to the Government of the Federation; Governor Inuwa Yahaya of Gombe State; Governor Nasir El-Rufai of Kaduna State; Governor Abdullahi Sule of Nasarawa State; Governor Godwin Obaseki of Edo; Governor Babajide Sanwo-Olu of Lagos State and Senator Hope Uzodinma, Governor of Imo.
Others are Dr Zainab Ahmed, Minister of Finance, Budget and National Planning; Adeniyi Adebayo, Minister of Industry, Trade and Investment; Dr Folasade Yemi-Esan, Head of Civil Service of the Federation; and Prof. Umar Danbatta, Executive Vice Chairman/CEO Nigerian Communications Commission.
Prof. M.B. Abubakar, Managing Director/CEO, Galaxy Backbone Limited; Dr Abimbola Alale, Managing Director/CEO, Nigerian Communications Satellite Limited; and Aliyu Aziz, Director General/CEO, National Identity Management Commission, are also members of the council.
Also on the committee are Mr Oswald Guobadia, Senior Special Assistant, (Digital Transformation) to the President; Olufemi Olufeko, Director, e-Government Dept, Federal Ministry of Communications and Digital Economy; A.B. Okauru, Director General, Nigeria Governors Forum; Prof. Simon Sodiya, President Nigeria Computer Society; and Gbenga Adebayo, Chairman, Association of Licensed Telecommunications Operators of Nigeria (ALTON).
Other members are Prof. Kabiru Bala, representative of the academia and Vice-Chancellor, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria; Prof. Nnenna Oti, representative of the academia and Vice-Chancellor, Federal University of Technology, Owerri; and Mr Kashifu Abdullahi, Secretary and the Director-General/CEO, National Information Technology Development Agency (NITDA).
Mr Sungil Son, Country Director (KOICA); Dr Olufemi Adeluyi, Technical Assistant (Research & Development) to Minister of Communication & Digital Economy; and Abubakar Dahiru, Special Assistant (Cyber Security & Digital Identity) to the Minister are also members of the committee.
Technology
Telecom Operators to Issue 14-Day Notice Before SIM Disconnection

By Adedapo Adesanya
Telecommunications operators in Nigeria will now be required to give subscribers a minimum of 14 days’ notice before deactivating their SIM cards over inactivity or post-paid churn, following a fresh proposal by the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC).
The proposal is contained in a consultation paper, signed by the Executive Vice Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of the NCC, Mr Aminu Maida, and titled Stakeholders Consultation Process for the Telecoms Identity Risks Management Platform, dated February 26, 2026, and published on the Commission’s website.
Under the proposed amendments to the Quality-of-Service (QoS) Business Rules, the Commission said operators must notify affected subscribers ahead of any planned churn.
“Prior to churning of a post-paid line, the Operator shall send a notification to the affected subscriber through an alternative line or an email on the pending churning of his line,” the document stated.
It added that “this notification shall be sent at least 14 days before the final date for the churn of the number.”
A similar provision was proposed for prepaid subscribers. According to the Commission, operators must equally notify prepaid customers via an alternative line or email at least 14 days before the final churn date.
Currently, under Section 2.3.1 of the QoS Business Rules, a subscriber’s line may be deactivated if it has not been used for six months for a revenue-generating event. If the inactivity persists for another six months, the subscriber risks losing the number entirely, except in cases of proven network-related faults.
The new proposal is part of a broader regulatory review tied to the rollout of the Telecoms Identity Risk Management System (TIRMS), a cross-sector platform designed to curb fraud linked to recycled, swapped and barred mobile numbers.
The NCC explained in the background section of the paper that TIRMS is a secure, regulatory-backed platform that helps prevent fraud stemming from churned, swapped, barred Mobile Station International Subscriber Directory Numbers in Nigeria.
It said this platform will provide a uniform approach for all sectors in relation to the integrity and utilisation of registered MSISDNs on the Nigerian Communications network.
In addition to the 14-day notice requirement, the Commission also proposed that operators must submit details of all churned numbers to TIRMS within seven days of completing the churn process, strengthening oversight and accountability in the system.
The consultation process, which the Commission said is in line with Section 58 of the Nigerian Communications Act 2003, will remain open for 21 days from the date of publication. Stakeholders are expected to submit their comments on or before March 20, 2026.
Technology
Silverbird Honours Interswitch’s Elegbe for Nigeria’s Digital Payments Revolution

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
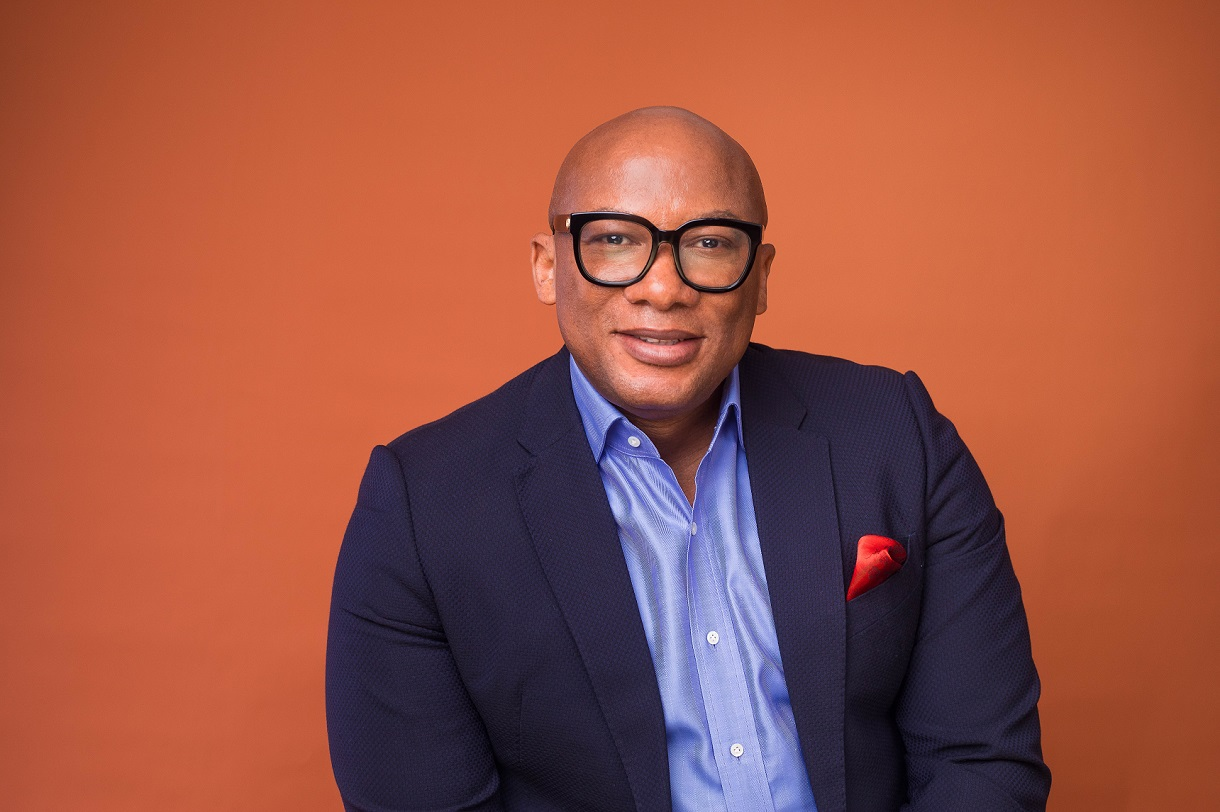
The founder of Interswitch, Mr Mitchell Elegbe, has been honoured for pioneering Nigeria’s digital payments revolution.
At a ceremony in Lagos on Sunday, March 1, 2026, he was bestowed with the 2025 Silverbird Special Achievement Award for shaping Africa’s financial ecosystem.
The Silverbird Special Achievement Award recognises individuals whose innovation, vision, and sustained impact have left an indelible mark on society.
Mr Elegbe described the award as both humbling and symbolic of a broader journey, saying, “This honour represents far more than a personal milestone. It reflects the courage of a team that believed, long before it was fashionable, that Nigeria and Africa could build world-class financial infrastructure.”
“When we started Interswitch, we were driven by a simple but powerful idea that technology could democratise access, unlock opportunity, and enable commerce at scale.
“This recognition by Silverbird strengthens our resolve to continue building systems that empower businesses, support governments, and expand inclusion across the continent,” he said when he received the accolade at the Silverbird Man of the Year Awards ceremony attended by several other dignitaries, whose leadership and contributions continue to shape national development and industry transformation.
In 2002, Mr Elegbe established Interswitch after he was inspired by a bold conviction that technology could fundamentally redefine how value moves within and across economies.
Under his leadership, the company has evolved into one of Africa’s foremost integrated payments and digital commerce companies, powering financial transactions for governments, banks, businesses, and millions of consumers.
Today, much of Nigeria’s electronic payments ecosystem traces its foundational architecture to the systems and rails established under his leadership.
“Mitchell’s journey is inseparable from Nigeria’s digital payments evolution. His foresight and resilience helped establish foundational infrastructure at a time when the ecosystem was still nascent.
“This recognition affirms not only his personal legacy, but the broader impact of Interswitch in enabling commerce and strengthening financial systems across Africa,” the Executive Vice President and Group Marketing and Communications for Interswitch, Ms Cherry Eromosele, commented.
Technology
SERAP Seeks FCCPC Probe into Big Tech’s Impact on Nigeria’s Digital Economy

By Adedapo Adesanya
The Socio-Economic Rights and Accountability Project (SERAP) has called on the Federal Competition and Consumer Protection Commission (FCCPC) to urgently investigate major global technology companies over alleged abuses affecting Nigeria’s digital economy, media freedom, privacy rights and democratic integrity.
In a complaint addressed to the chief executive of FCCPC, Mr Tunji Bello, the group accused Google, Meta (Facebook), Apple, Microsoft (Bing), X, TikTok, Amazon and YouTube of deploying opaque algorithms and leveraging market dominance in ways that allegedly undermine Nigerian media organisations, businesses, and citizens’ rights.
The complaint, signed by SERAP Deputy Director, Mr Kolawole Oluwadare, urged the commission to take measures necessary to urgently prevent further unfair market practices, algorithmic influence, consumer harm and abuses of media freedom, freedom of expression, privacy, and access to information.”
SERAP also asked the FCCPC to convene a public hearing to investigate allegations of algorithmic discrimination, data exploitation, revenue diversion, and anti-competitive conduct involving the tech giants.
According to the organisation, dominant digital platforms now act as private gatekeepers of Nigeria’s information and business ecosystem, wielding enormous influence over public discourse and market competition without sufficient transparency or regulatory oversight.
“Millions of Nigerians rely on these platforms for news, information and business opportunities,” SERAP stated, warning that opaque algorithms and offshore revenue extraction models pose both economic and human rights concerns.
The group argued that the alleged practices threaten media plurality, consumer protection, privacy rights, and the integrity of Nigeria’s forthcoming elections.
SERAP pointed to actions taken by the South African Competition Commission, which investigated Google over alleged bias against local media content, adding that the South African probe reportedly resulted in measures including algorithmic transparency requirements, compliance monitoring and financial remedies.
SERAP urged the FCCPC to take similar steps to safeguard Nigerian media and businesses.
The organisation maintained that if established, the allegations could amount to violations of Sections 17 and 18 of the Federal Competition and Consumer Protection Act (FCCPA), which prohibit abuse of market dominance and anti-competitive conduct.
SERAP stressed that the FCCPC has statutory authority to investigate and sanction conduct that substantially prevents, restricts or distorts competition in Nigeria.
It also warned that failure by the Commission to act promptly could prompt the organisation to pursue legal action to compel regulatory intervention.
Citing concerns reportedly raised by the Nigerian Press Organisation (NPO), SERAP said big tech companies have fundamentally altered Nigeria’s information environment, creating what it described as a structural imbalance of power that threatens the sustainability of professional journalism.
Among the allegations listed are: Algorithms controlled outside Nigeria determining content visibility, monetisation of Nigerian news content without proportionate reinvestment, offshore extraction of advertising revenues, limited discoverability of Nigerian websites and platforms, and lack of transparency in ranking and recommendation systems.
SERAP argued that declining revenues in the Nigerian media industry have led to shrinking newsrooms, closure of bureaus, and the emergence of news deserts, weakening journalism’s constitutional role in democratic accountability.
The organisation further warned that algorithmic opacity and data-driven micro-targeting could influence voter exposure to information ahead of Nigeria’s forthcoming elections, raising concerns about electoral fairness and transparency.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn