Technology
Nigeria’s Battle Against Cybercrime: Are You Safe?

Cybercrime is nothing new in Nigeria. Part of youth culture for decades, criminal enterprises have spread across the country.
In 2020, Nigeria ranked 16th highest in the world for international cybercrimes, by the FBI. However, Nigeria ranked 47th on the Global Cybersecurity Index, showing a vast disparity between the volume of cybercrime, and the effectiveness of Nigeria’s cybersecurity.
To understand this divide, it’s important to understand where cybercrime originated in the country.
Let’s investigate…
A brief history of cybercrime in Nigeria
The roots of cybercrime culture in Nigeria date as far back as the 1980s. In those early days, Nigerian youth mainly perpetrated cybercrime through email scams.
Known colloquially as the “yahoo yahoo” business, “yahoo boys” use social engineering tactics to con their victims into sending them money. The fraudsters often use emotional pressure points or promises of high returns.
The Nigerian government took a blow in 2020 when hacker collective Anonymous declared cyberwar against them. They hacked the database of the Central Bank of Nigeria and police websites on behalf of the #ENDSARS movement.
Biggest threats to Nigeria’s cybersecurity
The landscape of global cyber threats shifts regularly. However, recent years have shown a rise in the popularity of certain types of cybercrime in Nigeria.
Social engineering tactics
Arguably the oldest cybercrime in Nigeria, social engineering continues to be a favourite of Nigerian cybercriminals. These tactics often include heartfelt backstories, pleas for help, and the promise of love, or return on investment — all via email.
These tactics play on victims’ emotions and vulnerabilities. Those who’ve been successful with these scams live frivolous lifestyles. “Yahoo boys” with fancy cars and clothes have also become role models for young people desiring the same lifestyle.
Phishing websites
Chances are you’ve ended up on a site like this before. Sometimes they pose as legitimate sites but are almost always just an attempt to collect data, or install viruses. Phishing sites are hugely popular in Nigeria as it goes hand in hand with email scams.
You only need to click on a dangerous link before a fraudster can view your data. This is where using a VPN for PC is essential. Virtual Private Networks (VPN) hide your browsing and location data from malicious phishing websites.
Insider collaboration
A significant area of concern for Nigerian businesses is insider collaboration. This occurs between criminals and employees. Fraudsters have often sent out open requests for anyone willing to cause damage to their employer for payment.
This is quite hard to track too, as hackers use valid credentials to access secure networks. Keeping logs of activities within the network can help to find leaks. This can also help to spot malicious activity in the future.
Cybersecurity vulnerabilities of third parties
One of the biggest concerns for Nigerian businesses is the security of third parties. Even if your business is a fortress, a poorly protected third-party can bring the castle tumbling down.
This is especially troubling to Nigerian businesses operating globally. More third parties mean more vulnerabilities. Only work with trusted clients and expand the scope of your cybersecurity to those you work with.
Deepfake technology
A hot-button issue in Nigeria at the moment, deepfake fraud is more common than ever. Deepfake technology is the life-like reanimation of an individual’s face, meaning you can make anyone say anything.
Unfortunately, deep-fake is only getting better. In 2018, Nigerian President Muhammadu Buhari was featured in a deepfake video. The video became so viral that the President was prompted to make a statement dismissing the video as a fake.
How Nigeria is fighting back
Policing against cybercrime in Nigeria has been inadequate for decades. Only recently has the government declared significant steps in its plan to fight the rising issue of cybercrime.
Nigeria introduces the National Cybersecurity Policy and Strategy (NCPS)
In 2021, Nigeria implemented the NCPS, which indicated cybercrime as a leading threat to Nigeria and its economy. The NCPS represents an attempt to safeguard Nigeria’s digital economy, by strengthening the country’s legal and regulatory framework.
Also ongoing is the development of the National Cybersecurity Coordination Centre (NCCC). The NCCC would ensure clear communication and a well-developed response to cybercrime across Nigeria.
Efforts like these are projected to boost cyber protections and cybersecurity awareness. While work is still ongoing, the future of cybersecurity in Nigeria looks bright.
Conclusion
Although it has been a mainstay for years, cybercrime is now starting to be taken seriously in Nigeria.
Being uncontrolled for so long, cybercrime has been able to grow steadily.
By embracing modern cybersecurity practices, Nigeria might finally rid itself of its unwanted cybercriminal image.
Technology
Capillary Technologies Acquires SessionM from Mastercard

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
A software product company established in 2012, Capillary Technologies India Limited, has acquired the customer engagement and loyalty company, SessionM, from Mastercard.
This followed a definitive agreement signed by the global leader in AI-powered customer loyalty and engagement solutions with the renowned digital payments firm.
The acquisition of SessionM is the latest in a series of strategic moves by Capillary, following its successful listing on the Indian Stock Exchange in November 2025.
With SessionM in its portfolio, Capillary reinforces its position as a global leader in enterprise loyalty, offering a leading platform to the world’s most sophisticated enterprise brands.
Mastercard has identified Capillary Technologies—consistently recognised as a Leader in The Forrester Wave as the ideal partner to lead SessionM into its next era of growth.
As part of the agreement, a specialised team within SessionM will transition to Capillary, ensuring that the platform’s deep technical expertise is preserved.
SessionM’s esteemed global customer base—which includes Fortune 500 retailers, airlines, and CPG brands—will continue to receive the same high-calibre support and service they experienced before the acquisition.
“M&A has been a key growth strategy for Capillary over the years, and as a public company, we are delivering on that promise to our shareholders and the market.
“By bringing SessionM into our portfolio, we are not just expanding our footprint across the globe; we are further strengthening our loyalty capabilities to deliver one of the industry’s most comprehensive offerings.
“Our mission remains to provide enterprises across industries with specialised, AI-native loyalty technology solutions,” the chief executive of Capillary Technologies, Aneesh Reddy, commented.
Technology
Emergent Ventures, Others Invest $2.2m in Potpie
By Dipo Olowookere
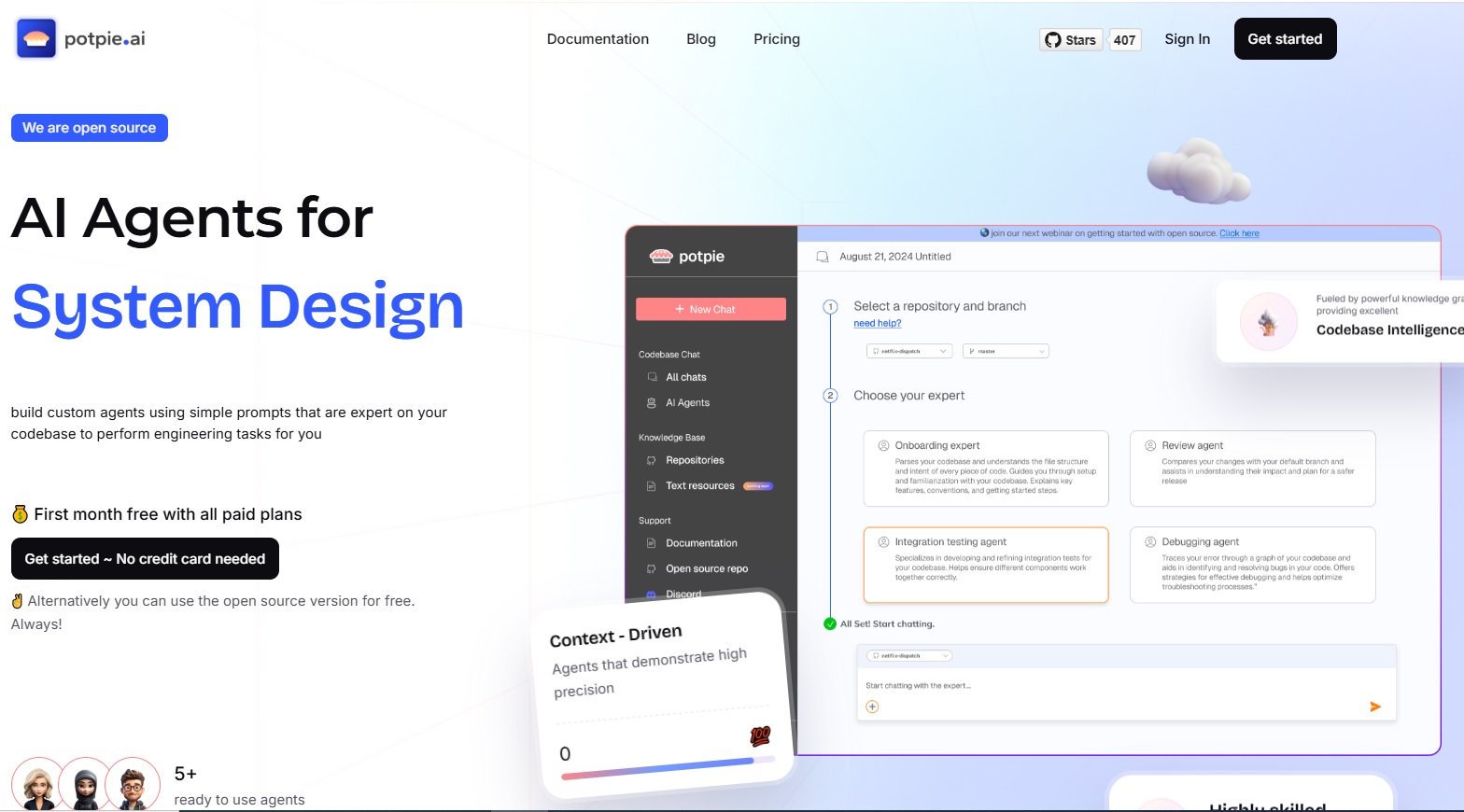
About $2.2 million pre-seed round to help engineering teams unify context across their entire stack and make AI agents genuinely useful in complex software environments has been announced by Potpie.
Potpie was established by Aditi Kothari and Dhiren Mathur, who were determined to unify context across the entire engineering stack and enabling spec driven development.
As generative AI adoption accelerates, most tools focus on surface-level code generation while ignoring the deeper problem of context.
Large language models are powerful, but without access to system-level understanding, tooling history, and architectural intent, they struggle in real production environments.
Traditional approaches rely on senior engineers to manually hold this context together, a model that breaks down at scale and fails when AI agents are introduced.
The platform enables teams to automate high-impact and non-trivial use cases across the software development lifecycle, like debugging cross-service failures, maintaining and writing end-to-end tests, blast radius detection and system design.
It is designed for enterprise companies with large and complex codebases, starting at around one million lines of code and scaling to hundreds of millions.
Rather than acting as another coding assistant, Potpie builds a graphical representation of software systems, infers behaviour and patterns across modules, and creates structured artefacts that allow agents to operate consistently and safely.
A statement made available to Business Post on Monday revealed that the funding support came from Emergent Ventures, All In Capital, DeVC and Point One Capital.
The capital will be used to support early enterprise deployments, expand the engineering team, and continue building Potpie’s core context and agent infrastructure, it was disclosed.
“As AI makes code generation easier, the real challenge shifts to reasoning across massive, interconnected systems. Potpie is our answer to that shift, an ontology-first layer that helps enterprises truly understand and manage their software,” Kothari was quoted as saying in the disclosure.
A Managing Partner at Emergent Ventures, Anupam Rastogi, said, “In large enterprises, the real challenge is not generating code, it is understanding the system deeply enough to change it safely.
“Potpie’s ontology-first architecture, combined with rigorous context curation and spec-driven development, creates a structured model of the entire engineering ecosystem. This allows AI agents to reason across services, dependencies, tickets, and production signals with the clarity of a senior engineer. That is what makes Potpie uniquely capable of solving complex RCA, impact analysis, and high-risk feature work even in codebases exceeding 50 million lines.”
Technology
Expert Reveals Top Cyber Threats Organisations Will Encounter in 2026

By Adedapo Adesanya
Organisations in 2026 face a cybersecurity landscape markedly different from previous years, driven by rapid artificial intelligence adoption, entrenched remote work models, and increasingly interconnected digital systems, with experts warning that these shifts have expanded attack surfaces faster than many security teams can effectively monitor.
According to the World Economic Forum’s Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2026, AI-related vulnerabilities now rank among the most urgent concerns, with 87 per cent of cybersecurity professionals worldwide highlighting them as a top risk.
In a note shared with Business Post, Mr Danny Mitchell, Cybersecurity Writer at Heimdal, said artificial intelligence presents a “category shift” in cyber risk.
“Attackers are manipulating the logic systems that increasingly run critical business processes,” he explained, noting that AI models controlling loan decisions or infrastructure have become high-value targets. Machine learning systems can be poisoned with corrupted training data or manipulated through adversarial inputs, often without immediate detection.
Mr Mitchell also warned that AI-powered phishing and fraud are growing more sophisticated. Deepfake technology and advanced language models now produce convincing emails, voice calls and videos that evade traditional detection.
“The sophistication of modern phishing means organisations can no longer rely solely on employee awareness training,” he said, urging multi-channel verification for sensitive transactions.
Supply chain vulnerabilities remain another major threat. Modern software ecosystems rely on numerous vendors and open-source components, each representing a potential entry point.
“Most organisations lack complete visibility into their software supply chain,” Mr Mitchell said, adding that attackers frequently exploit trusted vendors or update mechanisms to bypass perimeter defences.
Meanwhile, unpatched software vulnerabilities continue to expose organisations to risk, as attackers use automated tools to scan for weaknesses within hours of public disclosure. Legacy systems and critical infrastructure are especially difficult to secure.
Ransomware operations have also evolved, with criminals spending weeks inside networks before launching attacks.
“Modern ransomware operations function like businesses,” Mitchell observed, employing double extortion tactics to maximise pressure on victims.
Mr Mitchell concluded that the common thread across 2026 threats is complexity, noting that organisations need to abandon the idea that they can defend against everything equally, as this approach spreads resources too thin and leaves critical assets exposed.
“You cannot protect what you don’t know exists,” he said, urging organisations to prioritise visibility, map dependencies, and focus resources on the most critical assets.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn

















