World
Abidjan-Lagos Corridor Highway Under Construction
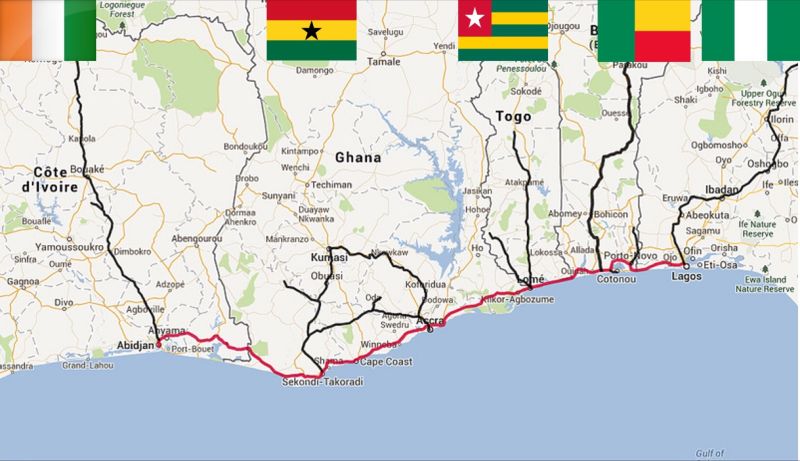
By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
Never underestimate the power of the Economic Community of West Africa States (ECOWAS), also known as CEDEAO in French and Portuguese, created on 28th May 1975 as a regional political and economic union bringing together fifteen (15) countries of West Africa. Per the date of its establishment, this so-called regional bloc marks its 50th year in 2025, a significant historical celebration.
Considered one of the pillar regional blocs of the continent-wide African Economic Community (AEC), ECOWAS generally has its primary common goal of working consistently towards achieving, what is first referred to, as “collective self-sufficiency” for its member states by creating a single large trade bloc by building a full economic and trading union. Additionally, ECOWAS aims to raise the living standards of an estimated population of over 425 million people and to promote economic development based on the principles of interdependence, solidarity, and cooperation.
Until writing this article, ECOWAS has frequently been discussing and reviewing the Abidjan-Lagos Corridor Highway Development Project, one single regional infrastructure project these several years. It has shown its total commitment to looking for funding while billions have been siphoned by leaders into foreign banks. African leaders are quick negotiating and paying for foreign military weapons but are grossly unsuccessful in soliciting similar assistance from these external partners to invest in infrastructure development such as the Abidjan-Lagos Corridor Highway Development Project.
West African Highway Launched in 2017
The construction of this proposed grandiose West African highway has its chequered history. The proposed project was successfully launched in 2017, and since then it has had a series of high-powered meetings and conferences, technical studies have been conducted, and the construction to its feasibility and practical operationalization. The Abidjan-Lagos highway, the six-lane dual carriage highway, is estimated at $15.1 billion.
On resource mobilization, it was explicitly noted that ECOWAS had adopted a new regulatory framework on the Public Private Partnership (PPP) – an incentive for the entry of the private sector in large investments like the nature of this project. The African Development Bank (AfDB) on behalf of the development partners offered its assurance for unwavering commitment to the realization of the highway.
Akinwunmi Adesina, President of the African Development Bank (AfDB) has several times highlighted the importance of the Abidjan-Lagos highway as an infrastructure project in West Africa that would ease the free movement of people, goods and services, generate social and economic activities, and ultimately promote cross-border trade within the region, its economic viability and enormous potentials especially now that African Union looks to implement the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA). Noticeably, Africa has long been considered a frontier for manufacturing, technology, for food production. Africa is getting ready for business, it is busily building the world’s largest single market of 1.4 billion people.
Special Meetings and Technical Consultations
Several meetings upon meetings and meetings have been held since the project was proposed in 2017. Since 2017, paid meetings have been held, and experts have been paid. The latest of such a paid meeting was held on November 10-11, 2024. This roundtable was initiated following the instructions given to the ECOWAS Commission. Late September 2024, such a roundtable meeting was held in Abidjan, the capital city of Côte d’Ivoire, under the auspices of the Commission of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), the African Development Bank (AfDB) and the ECOWAS Bank for Investment and Development (EBID).
The highway corridor is calculated to be approximately 1,080 km long. It will connect some of the largest and most economically dynamic cities Abidjan, Accra, Cotonou, Lomé and Lagos while covering a large proportion of West Africa’s population. It will also link very vibrant seaports in West Africa. In addition, it will serve all the landlocked ECOWAS member-states, for example, Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger in the region. Nearly 40 million people are estimated to be living along the Abidjan-Lagos corridor while 47 million people travel along the axis every year. These are expected to be direct beneficiaries of the development of the project touted to be a real backbone of trade in the region.
According to official documents, this highway project falls in line with the key objectives of the ECOWAS Vision 2050, including (i) facilitating the movement of people and goods, and (ii) accelerating trade and transport, regional and international, improving road infrastructure. It is eventually expected that the transport corridor will be transformed into a development corridor to stimulate investment, sustainable development and poverty reduction within the entire region.
West African Highway and AfCFTA
The focal point of controversy and debate, these several years, are centred on the mechanism of financing, and the state-of-the-art management of this new mega-highway – from planning through practical construction to its final commissioning, ready for cutting-edge usage by the transport industry. The idea of prioritizing highway innovation, signalling a bold leap in West Africa’s transportation infrastructure, is its recognizable potential transformative impact. Simply intended to improve and facilitate the movement of services, goods and people across the region. The Abidjan-Lagos Highway highlights its potential to enhance regional connectivity and drive economic growth, especially with the establishment of the African Continental Free Trade (AfCFTA), the ambitious flagship of the African Union (AU).
According to ECOWAS’ latest document issued after their two-day special meeting held on November 11 in Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, “experts have lauded findings of the study which has among others, unveiled a potential $6.8 billion investment prepared and ready to be implemented to unlock economic growth and enhance the viability of the proposed highway.” The overall objective is to identify and unlock the inherent and latent economic potential (short, medium and long-term) and commercial viability of economic and industrial value chain projects. These economic projects, once implemented, will also generate trade volumes and traffic to augment the viability of the highway.
The final draft reports were issued after groups revisited (that was not the first time) several tolled bridges and roads in Abidjan for knowledge and experience sharing strategy envisaged for the Abidjan-Lagos Highway. At the end of the exercise, the study report (re)validated commitment to unlock the inherent and latent economic potential of the highway construction and estimated $6.8 billion in potential investment in the region.
Final Construction Still Out of Sight
For the past few years, significant attention has been drawn by the widely publicized announcement of securing enough funds from African banks and external sources for the construction of this regional highway which could become a cornerstone, and the public narrative of achievement by ECOWAS, which marks its 50th year in 2025. However, transport industry analysts, researchers and experts have already cast serious doubts and skyline scepticism if ECOWAS could live up to this onerous task. Grandiose ceremony-infested ECOWAS future task of achieving its primary target of constructing a ‘speed-highway’ remains an eternal dream. Noticeably, ECOWAS has little to celebrate, except its existence by name, (the golden jubilee) at its 50th year in May 2025. At least, Africans will rather jubilate over the authenticity of reforming and transforming the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS).
World
Online African Women Conference: From Adaptation in Russia to Issues of Health and Spirituality

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
Women, generally, are fighting for their own empowerment in society. Gender equality dominates their activities, flexing their feminine muscles for higher positions, with men, in diverse professional aspects, including politics and entrepreneurial spheres of activity.
Such consistent struggle was backed by a collective declaration, worldwide observing March 8 as International Women’s Day. Until today, March 8 commemorates women’s fight for equality and liberation along with the women’s rights movement. In addition, the March 8 celebration focuses on issues such as gender equality, reproductive rights, and violence and abuse against women.
On the eve of March 8, the Cameroonian Diaspora (Diaspocam) and the “African Business Club” together with Russian women’s organisations, held a special online conference under the theme: “How to Succeed as a Woman in Russia”, which brought together over a hundred participants from different regions, including Africa.
The discussion was dedicated to the challenges of adaptation, career prospects, health, and spiritual security of a fast-growing number of young African women living in the Russian Federation. The conference was moderated by Louis Gouend, a specialist in business communications between Russia and Africa, President of the African Business Club, and an expert of the Council of Russia-Africa Cooperation under the State Duma, lower chamber of Russian legislators.
Louis Gouend congratulated the women participants while extending to them good health, wisdom, and new achievements. The main goal of the conference was to create a space of trust and exchange views on the full spectrum of women’s multidisciplinary approach to questions.
On adaptation and legislation: Alina Andrukh, Director of the International Department, spoke on the topic “Global Adaptation of Foreign Citizens in Russia.” She thoroughly examined educational trajectories for women, employment opportunities, and new legislative realities that foreign women need to consider when building a career in the Russian Federation.
The speaker further placed special emphasis on how to avoid getting into trouble, complying with Russian laws, and protecting one’s rights.
Health Without Barriers and Support Centres: One of the most anticipated speeches was given by Ekaterina Glok, a midwife by profession. In her presentation on “The Health of an African Woman in Russia,” she touched upon the delicate topics of reproductive and sexual health. The expert gave practical advice on how to overcome the language barrier and shyness when visiting a gynaecologist, and explained the specifics of the Russian healthcare system for foreign patients.
Ekaterina, however, reminded the women of the importance of regular medical check-ups: visiting a doctor, at least, once a year is necessary even in the absence of complaints. She informed the participants about the existence of support centres for women and single mothers, where they can turn to in difficult life situations. Additionally, the speaker announced her upcoming working missions in the Republic of Cameroon, planned for May 2026, and gave many practical tips on maintaining women’s health.
Social and Cultural Challenges – Warning About Dangers: An important block of questions concerning safety and conscious motherhood was highlighted by Mme Zima épouse Ndong Toung Celestine Charlotte, Cultural Advisor at the Embassy of Cameroon. She had a frank conversation, warning the girls about scammers and dishonest individuals offering attractive working conditions, behind which often lie indecent earnings and dangerous situations.
The Advisor reminded that for those who came to Russia to study, education should remain their main priority. She urged lady students to be vigilant, not to give in to dubious offers, and to postpone questions of pregnancy and starting a family to a later period, after completing their studies. She touched upon the legal and moral aspects of unwanted pregnancy, calling on the girls to engage in conscious life planning.
Economic Independence and Earning Opportunities: Luciana Tchami, a member of the executive bureau of Diaspocam, a non-profit social organisation, presented a report on “Women’s Capabilities: Professions and Part-Time Jobs for Young Women in Russia.” She gave examples of successful strategies for earning money and building a career within the conditions of the Russian labour market that are accessible to foreign students and young professionals.
The speaker detailed specific areas of work: young women can take short-term training courses and work in beauty salons (manicure, pedicure); many cafes and restaurants offer convenient part-time jobs. Luciana also mentioned specialised websites with attractive conditions for job seekers and opportunities for remote work: becoming a freelancer and helping with tasks online, for online stores, and in other areas.
Spiritual Support: A Reminder of a Woman’s Value. The conference concluded with Pastor Gustave Mbeng, responsible for charity at Diaspocam. His prayer-speech was dedicated to women’s rights and spiritual awakening. As a pastor, Mbeng reminded the participants that woman is the last and most ideal creation of God, perfect in all parameters of the universe. He emphasised that women are more beautiful and harmonious than men, and urged the girls to take care of themselves and not to distance themselves from God, so that there would be fewer difficulties and questions in life.
Pastor Gustave further paid special attention to the theme of preserving life. He took a stand against abortion, reminding that every child is a creation of God, and in the eyes of the Almighty, there is no such concept as abortion. If pregnancy does occur, it is important to preserve the child’s life and trust in God’s providence.
Technical organisation, moderation, translation and coordination of the conference were provided by Iness Zengue Abeng, President of the Association of International Students “Russia-Africa,” and Belle-Grâce Euphrasie, Dean, who acted as interpreter during the online event.
Conclusion and Future Plans: At the end, Louis Gouend extended gratitude to all participants, speakers, and presenters for the warm and trusting atmosphere.
The conference was held in an open dialogue format on the”Yandex Telemost” platform, which allowed women from different parts of Russia to ask questions live and receive moral support. Following the meeting, the organisers decided to hold such an online gathering, including organising a series of meetings not only for women but also for foreigners living in Russia.
The topics of future conferences will aim at education, open discussions, and debate on issues important for Africans in the Russian Federation: knowing one’s rights, being able to avoid unpleasant situations, behaving correctly in difficult life circumstances, and preserving cultural and spiritual identity.
Until now, prejudice and reactionary attitudes have denied full-fledged civic rights to millions of women, who are considered as workers, mothers, family partners, and citizens worldwide. Nevertheless, International Women’s Day, with its chequered history, is a public holiday in several countries. The United Nations observes the holiday in connection with a particular issue, campaign, or theme in women’s rights across the world.
World
Beijing Readies to Hand Over New ECOWAS Building Complex

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
Beijing’s decades-long policy decision to expand Chinese presence in Africa has, largely, transcended into gifting buildings. The African Union and Africa’s CDC to Zimbabwe’s parliamentary village, Ghana’s Foreign Ministry headquarters, and Egypt’s sports stadium, among many others, are classic examples. Following all these, China will hand over the new headquarters of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) in mid-March 2026.
Since the turn of the 21st century, China has risen to become Africa’s geopolitical partner, addressing concrete infrastructural projects across the continent. As is well-known, Beijing does so, with the sole aim of spending thousands of dollars to gain strategic control of the continent’s critical resources.
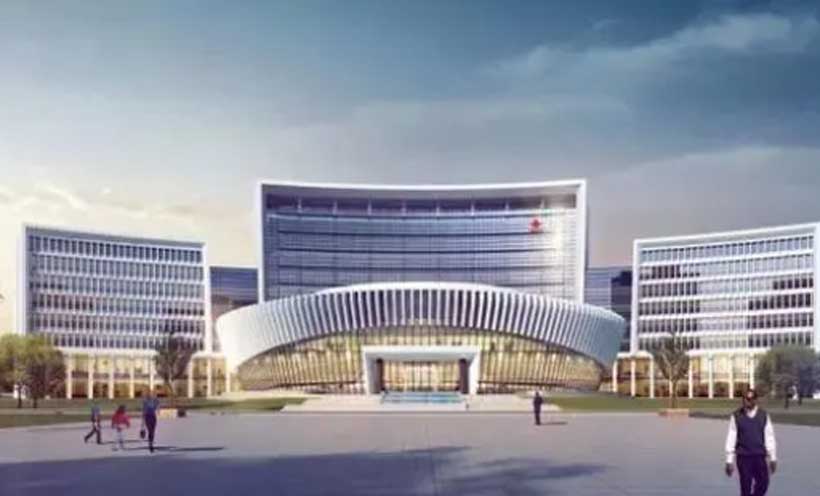
In an official news release, the regional bloc’s president, Dr Omar Alieu Touray, said that the new headquarters complex in Abuja, Nigeria, which will house the Commission, Parliament, and Court of Justice of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), will be operational in March 2026.
Built on a 7-hectare site along the road to Abuja airport, the building is currently completed. Known as the ‘Eye of West Africa,’ the new ECOWAS headquarters complex is entirely funded and built by the People’s Republic of China through the China International Development Cooperation Agency (China Aid).
It is a modern and functional administrative building, designed to meet the needs of the West African organisation. It will provide services to create a favourable working environment for the community’s staff members. The new complex comprises a main administrative building with three restaurants/cafeterias, banking rooms, a crèche, a gym, and three blocks containing 899 workstations: block A (central) has 11 floors, and blocks B and C have eight floors each.
It also includes a multipurpose building with security facilities, shops, a water tank, and archive rooms, as well as car parks with a total capacity of 702 parking spaces, a 720-seat auditorium, two committee rooms, a conference room, an equipment room, guard posts, and a helipad.
The new ECOWAS headquarters complex is seen as a symbol of the strengthening cooperation between China and the regional organisation. It is part of a technical and institutional partnership aimed at further supporting ECOWAS’ operational capacities, as well as part of ongoing cooperation between the two parties.
Accordingly, the headquarters complex will enable greater operational efficiency, reduced costs, and increased staff productivity. ECOWAS has expressed deep gratitude and sincere appreciation to China for its commitment and support to the regional organisation through the construction, seen as a ‘symbol of Beijing’s steadfast commitment to West African integration.’
World
Iranian Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei Dies After Air Strikes

By Dipo Olowookere
Iranian Supreme Leader, Mr Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, has died after coordinated airstrikes carried out by the United States and Israel on Tehran on Saturday morning.
His death was confirmed on Sunday morning by Iranian state media, which also disclosed that his daughter and grandchild were among those killed in the bombardment, which destroyed his compound.
Mr Khamenei was killed during a meeting with top leaders of the Middle East country yesterday, including the Defence Minister Amir Nasirzadeh and Revolutionary Guard commander Mohammad Pakpour, who reportedly died too.
His elimination has sparked mixed reactions, with some Iranians on the streets celebrating his demise, and others condemning the joint air strikes.
The President of the United States, Mr Donald Trump, described the late Iranian leader as “one of the most evil people in history,” expressing satisfaction at the action, which he said was “successful,” as it represented justice for both Iranians and Americans.
Meanwhile, Tehran has vowed to further respond to the attacks after initially firing missiles at six neighbours, including Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, UAE, Bahrain, and Jordan.
Flight operations in the region have been disrupted because of the retaliatory action of Iran over the weekend, though most of the missiles were intercepted.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn





















