World
Extending AGOA Reflects African Exporters Access to US Markets

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
As the geopolitical situation intensifies, with U.S. President Donald Trump imposing huge trade tariffs to either restrict or regulate export transactions to United States, African leaders and entrepreneurs have mounted critical efforts to re-negotiate the extension of the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA), which expires 30th September 2025. Over the past few years, African leaders have been advocating for large-scale structural reforms, financial inadequacies and policy approach by multinational institutions mostly dominated by the United States. Notwithstanding Africa’s huge untapped resources, Africa still looks to United States, multinational financial institutions to savage its economy.
In spite of this consistent criticism over current U.S. policy which has flattened relations with Africa since the ascension of Donald Trump into the White House in Washington, African leaders and exporters are feverishly trying to reaffirm their commitment to deepening their comprehensive strategic trade partnership, desirous to sustain AGOA through which to generate foreign currency incomes to their state coffers. Despite the indelible fact that European and Asian markets are alternatives to explore, African exporters still highly value trade sustainbility with United States. AGOA should promptly be renewed, as it has been the case before, otherwise it would impact so negatively on diverse developments across Africa.
What’s AGOA and Why it Matters for Africa:
AGOA, enacted on 18th May 2000, provides eligible sub-Saharan African countries with duty-free access to the U.S. market, but current due to expire on 30th September 2025. The duty-free access for nearly 40 African countries has boosted development, fostered more equitable and sustainable growth in Africa. By design AGOA is a useful mechanism for improving accessibility to trade competitiveness, connectivity, and productivity. During these past 25 years, AGOA has been the cornerstone of U.S. economic engagement with the countries of sub-Saharan Africa.
In the context of the crucial geopolitical changes, many African leaders, corporate executives, and the business community are still searching for mutually beneficial trade partnerships with United States. With the changing times, Africa is also building its muscles towards a new direction since the introduction of the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), which was officially launched in July 2019. In practical terms, trading started under the AfCFTA from January 2021.
The United States has prioritized the AfCFTA. And AGOA, which offers a trade preference program, perfectly fits into that. It provides duty-free access to the U.S. market for eligible products and trading services from designated sub-Saharan African countries. It was enacted in May 2000 and aims to boost economic growth and development in the region through trade.
Sample Case Studies, Trade Volumes with United States:
U.S. and South Africa signed a Trade and Investment Framework Agreement (TIFA) as far back as in 2012. The trade agreement establishes a forum for consultative discussions, cooperative work, and possible agreements on a wide range of trade issues, with a special focus on customs and trade facilitation, technical barriers to trade, sanitary and phytosanitary (SPS) measures, and trade and investment promotion. South Africa trade summary records show that U.S. goods and services trade with South Africa totaled an estimated $26.2 billion in 2024.
For instance, South African Trade Minister Parks Tau has held several talks, with US Trade Representative Jamieson Greer, these months until September 2025, aimed at maintaining trade relations with United States. South Africa hosts the G20 presidency, and utilizing its G20 presidency as an instrument for negotiating for trade, an opportunity when missed would impavt seriously on South Africa. Many sub-Saharan African countries would face similar fate seriously without AGOA.
With Angola, the first meeting of the United States-Angolan Council on Trade and Investment was held in June 2010 in Luanda. U.S. goods and services trade with Angola totaled an estimated $3.2 billion in 2024. In June 2025, Luanda, capital city of Angola, hosted the U.S.-Africa trade summit. United States has invested in the construction of Lobito highway corridor.
Its neighbouring Central African Republic has U.S. goods and services trade totaled an estimated $74.4 million in 2024. Comparatively, the U.S. goods and services trade with Democratic Republic of Congo totaled an estimated $1.0 billion in 2024, up 8.4 percent ($ 79.1 million) from 2023.
Ethiopia trade summary shows that the U.S. goods and services trade with Ethiopia totaled an estimated $4.3 billion in 2024, up 28.4 percent ($940.2 million) from 2023. Ethiopia has the largest of its citizens in the United States.
In the bid to diversify its economy from its dependence on crude oil, which accounts for nearly all the value of exports, Nigeria strives to build its agricultural, mining, and manufacturing sectors, especially in the automotive assembly, cement, textile, and clothing sectors. This has led to talks and negotiations of trade agreements with United States. Nigeria also has large number of its citizens domicile in America. U.S. goods and services trade with Ghana totaled an estimated $3.8 billion in 2024, while with Nigeria totaled an estimated $13.0 billion in 2024, up 16.5 percent ($1.8 billion) from 2023. With Tanzania, it totaled an estimated $1.4 billion in 2024.
Key features and benefits of AGOA:
It’s worth reiterating here that during these past several years, AGOA has been the cornerstone of U.S. economic engagement with the countries of sub-Saharan Africa. In this case, as AGOA is closely working with the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) Secretariat and with the African Union (AU), trade professionals could primarily leverage various economic sectors and unwaveringly act as bridges between the United States and Africa.
Duty-free Access: AGOA allows eligible products from sub-Saharan African countries to enter the U.S. market without paying tariffs.
Promotion of Economic Growth: The program encourages economic growth by providing incentives for African countries to open their economies and build free markets.
Encouraging Economic Reforms: AGOA encourages economic and political reforms in eligible countries, including the rule of law and market-oriented policies.
Increased Trade and Investment: The program aims to strengthen trade and investment ties between the United States and sub-Saharan Africa.
Economic Growth and Employment Creation: AGOA has been instrumental in creating employment by raising exports. It further encourages raising exports to the United States. In addition, AGOA has helped eligible countries to work towards economic growth across the African continent. It establishes the process of transforming a market-based economy and sets the criteria for diversification and strengthening trade policy interests between the United States and Africa.
Recent Developments: AGOA’s authorization is scheduled to expire in September 2025. The ongoing debates have intensified, with the majority of African leaders calling for its extension. This implies affirmation of United States policy by Africa and its evolving position within the context of multipolarity. The Corporate Council on Africa (CCA) has taken robust steps and adopted a fast-tracking approach to rally African leaders and the U.S. Congress to promptly renew AGOA. The CCA, established in 1993, provides unparalleled access to high-level decision-makers, curated networking opportunities, market intelligence, and a platform to shape policy and drive business.
Arguments for U.S.-Africa As Inseparable Biological Twins:
Besides the indelible benefits of the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA), some African strategists and research analysts indisputably believe that financial remittance flow is definitely one of the surest reliable sources of foreign exchange, depending solely on the dollar currency, to support trade.
In its latest report released in June 2024, the World Bank indicated that, despite the geopolitical uncertainties, instability and challenges, sub-Saharan Africa’s remittance flow reached US$54 billion in 2023. According to World Bank Statistics, remittance inflows to sub-Saharan Africa stood at US$49 billion in 2021.
The U.S.-African Diaspora Factor: Over the years, African leaders have been engaging with their diaspora, especially those excelling in the academia, business, science, technology, engineering, sports and other fields that the continent needs to optimize its diverse potentials and to meet development priorities. These professionals primarily leverage into various sectors, act as bridges between the United States and Africa. Beyond remittances, Africa stands to benefit largely from the input of its diaspora considered as progressive in the United States. Looking ahead for ensuring the trade between the United States and Africa, therefore requires reviewing measures such as trade policy, trade facilitation, productive capacity, trade-related infrastructure, trade finance, trade information and factor-market integration.
In an analytical summary, AGOA is a significant trade policy that has played a crucial role in promoting economic growth and development in sub-Saharan Africa. Beyond that, it is therefore necessary—African leaders, the U.S. government, both U.S. and African trade agencies, the private sector, civil society, and stakeholders—to combine the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) and the Africa Continental Free Trade Agreement (AfCFTA) as the cornerstone in strengthening a new path towards economic partnership with Africa. The logical AGOA extension is unreservedly supported by the African Union (AU) and Regional Economic Blocs. The tremendous growing potential of African Diaspora and its inseparable cultural involvement in trade and economic sectors makes it an imperative life-wire for prompt extension and the sustainability of the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA).
World
Online African Women Conference: From Adaptation in Russia to Issues of Health and Spirituality

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
Women, generally, are fighting for their own empowerment in society. Gender equality dominates their activities, flexing their feminine muscles for higher positions, with men, in diverse professional aspects, including politics and entrepreneurial spheres of activity.
Such consistent struggle was backed by a collective declaration, worldwide observing March 8 as International Women’s Day. Until today, March 8 commemorates women’s fight for equality and liberation along with the women’s rights movement. In addition, the March 8 celebration focuses on issues such as gender equality, reproductive rights, and violence and abuse against women.
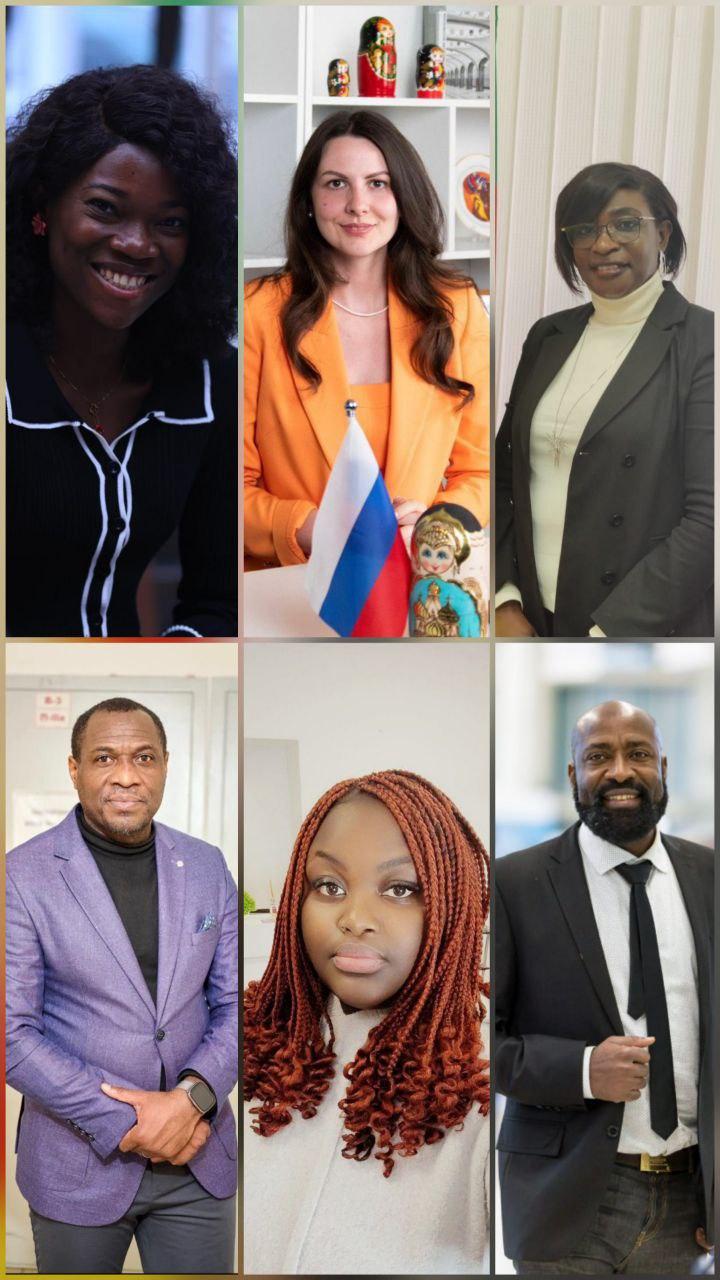
On the eve of March 8, the Cameroonian Diaspora (Diaspocam) and the “African Business Club” together with Russian women’s organisations, held a special online conference under the theme: “How to Succeed as a Woman in Russia”, which brought together over a hundred participants from different regions, including Africa.
The discussion was dedicated to the challenges of adaptation, career prospects, health, and spiritual security of a fast-growing number of young African women living in the Russian Federation. The conference was moderated by Louis Gouend, a specialist in business communications between Russia and Africa, President of the African Business Club, and an expert of the Council of Russia-Africa Cooperation under the State Duma, lower chamber of Russian legislators.
Louis Gouend congratulated the women participants while extending to them good health, wisdom, and new achievements. The main goal of the conference was to create a space of trust and exchange views on the full spectrum of women’s multidisciplinary approach to questions.
On adaptation and legislation: Alina Andrukh, Director of the International Department, spoke on the topic “Global Adaptation of Foreign Citizens in Russia.” She thoroughly examined educational trajectories for women, employment opportunities, and new legislative realities that foreign women need to consider when building a career in the Russian Federation.
The speaker further placed special emphasis on how to avoid getting into trouble, complying with Russian laws, and protecting one’s rights.
Health Without Barriers and Support Centres: One of the most anticipated speeches was given by Ekaterina Glok, a midwife by profession. In her presentation on “The Health of an African Woman in Russia,” she touched upon the delicate topics of reproductive and sexual health. The expert gave practical advice on how to overcome the language barrier and shyness when visiting a gynaecologist, and explained the specifics of the Russian healthcare system for foreign patients.
Ekaterina, however, reminded the women of the importance of regular medical check-ups: visiting a doctor, at least, once a year is necessary even in the absence of complaints. She informed the participants about the existence of support centres for women and single mothers, where they can turn to in difficult life situations. Additionally, the speaker announced her upcoming working missions in the Republic of Cameroon, planned for May 2026, and gave many practical tips on maintaining women’s health.
Social and Cultural Challenges – Warning About Dangers: An important block of questions concerning safety and conscious motherhood was highlighted by Mme Zima épouse Ndong Toung Celestine Charlotte, Cultural Advisor at the Embassy of Cameroon. She had a frank conversation, warning the girls about scammers and dishonest individuals offering attractive working conditions, behind which often lie indecent earnings and dangerous situations.
The Advisor reminded that for those who came to Russia to study, education should remain their main priority. She urged lady students to be vigilant, not to give in to dubious offers, and to postpone questions of pregnancy and starting a family to a later period, after completing their studies. She touched upon the legal and moral aspects of unwanted pregnancy, calling on the girls to engage in conscious life planning.
Economic Independence and Earning Opportunities: Luciana Tchami, a member of the executive bureau of Diaspocam, a non-profit social organisation, presented a report on “Women’s Capabilities: Professions and Part-Time Jobs for Young Women in Russia.” She gave examples of successful strategies for earning money and building a career within the conditions of the Russian labour market that are accessible to foreign students and young professionals.
The speaker detailed specific areas of work: young women can take short-term training courses and work in beauty salons (manicure, pedicure); many cafes and restaurants offer convenient part-time jobs. Luciana also mentioned specialised websites with attractive conditions for job seekers and opportunities for remote work: becoming a freelancer and helping with tasks online, for online stores, and in other areas.
Spiritual Support: A Reminder of a Woman’s Value. The conference concluded with Pastor Gustave Mbeng, responsible for charity at Diaspocam. His prayer-speech was dedicated to women’s rights and spiritual awakening. As a pastor, Mbeng reminded the participants that woman is the last and most ideal creation of God, perfect in all parameters of the universe. He emphasised that women are more beautiful and harmonious than men, and urged the girls to take care of themselves and not to distance themselves from God, so that there would be fewer difficulties and questions in life.
Pastor Gustave further paid special attention to the theme of preserving life. He took a stand against abortion, reminding that every child is a creation of God, and in the eyes of the Almighty, there is no such concept as abortion. If pregnancy does occur, it is important to preserve the child’s life and trust in God’s providence.
Technical organisation, moderation, translation and coordination of the conference were provided by Iness Zengue Abeng, President of the Association of International Students “Russia-Africa,” and Belle-Grâce Euphrasie, Dean, who acted as interpreter during the online event.
Conclusion and Future Plans: At the end, Louis Gouend extended gratitude to all participants, speakers, and presenters for the warm and trusting atmosphere.
The conference was held in an open dialogue format on the”Yandex Telemost” platform, which allowed women from different parts of Russia to ask questions live and receive moral support. Following the meeting, the organisers decided to hold such an online gathering, including organising a series of meetings not only for women but also for foreigners living in Russia.
The topics of future conferences will aim at education, open discussions, and debate on issues important for Africans in the Russian Federation: knowing one’s rights, being able to avoid unpleasant situations, behaving correctly in difficult life circumstances, and preserving cultural and spiritual identity.
Until now, prejudice and reactionary attitudes have denied full-fledged civic rights to millions of women, who are considered as workers, mothers, family partners, and citizens worldwide. Nevertheless, International Women’s Day, with its chequered history, is a public holiday in several countries. The United Nations observes the holiday in connection with a particular issue, campaign, or theme in women’s rights across the world.
World
Beijing Readies to Hand Over New ECOWAS Building Complex

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
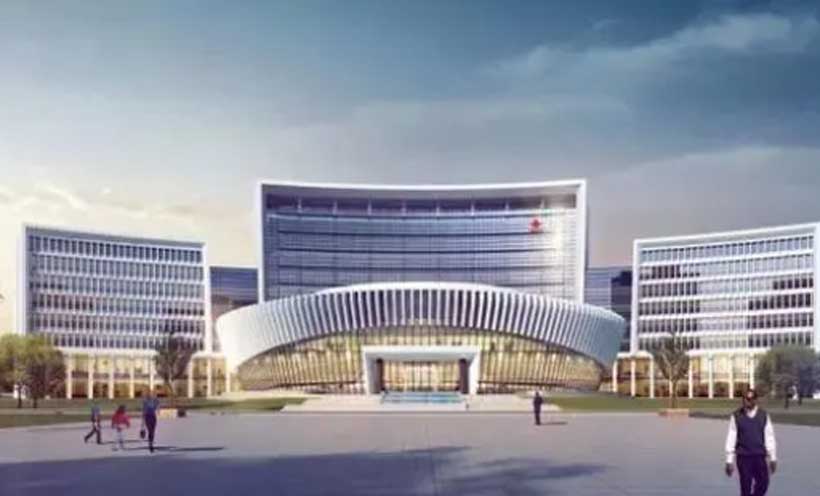
Beijing’s decades-long policy decision to expand Chinese presence in Africa has, largely, transcended into gifting buildings. The African Union and Africa’s CDC to Zimbabwe’s parliamentary village, Ghana’s Foreign Ministry headquarters, and Egypt’s sports stadium, among many others, are classic examples. Following all these, China will hand over the new headquarters of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) in mid-March 2026.
Since the turn of the 21st century, China has risen to become Africa’s geopolitical partner, addressing concrete infrastructural projects across the continent. As is well-known, Beijing does so, with the sole aim of spending thousands of dollars to gain strategic control of the continent’s critical resources.
In an official news release, the regional bloc’s president, Dr Omar Alieu Touray, said that the new headquarters complex in Abuja, Nigeria, which will house the Commission, Parliament, and Court of Justice of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), will be operational in March 2026.
Built on a 7-hectare site along the road to Abuja airport, the building is currently completed. Known as the ‘Eye of West Africa,’ the new ECOWAS headquarters complex is entirely funded and built by the People’s Republic of China through the China International Development Cooperation Agency (China Aid).
It is a modern and functional administrative building, designed to meet the needs of the West African organisation. It will provide services to create a favourable working environment for the community’s staff members. The new complex comprises a main administrative building with three restaurants/cafeterias, banking rooms, a crèche, a gym, and three blocks containing 899 workstations: block A (central) has 11 floors, and blocks B and C have eight floors each.
It also includes a multipurpose building with security facilities, shops, a water tank, and archive rooms, as well as car parks with a total capacity of 702 parking spaces, a 720-seat auditorium, two committee rooms, a conference room, an equipment room, guard posts, and a helipad.
The new ECOWAS headquarters complex is seen as a symbol of the strengthening cooperation between China and the regional organisation. It is part of a technical and institutional partnership aimed at further supporting ECOWAS’ operational capacities, as well as part of ongoing cooperation between the two parties.
Accordingly, the headquarters complex will enable greater operational efficiency, reduced costs, and increased staff productivity. ECOWAS has expressed deep gratitude and sincere appreciation to China for its commitment and support to the regional organisation through the construction, seen as a ‘symbol of Beijing’s steadfast commitment to West African integration.’
World
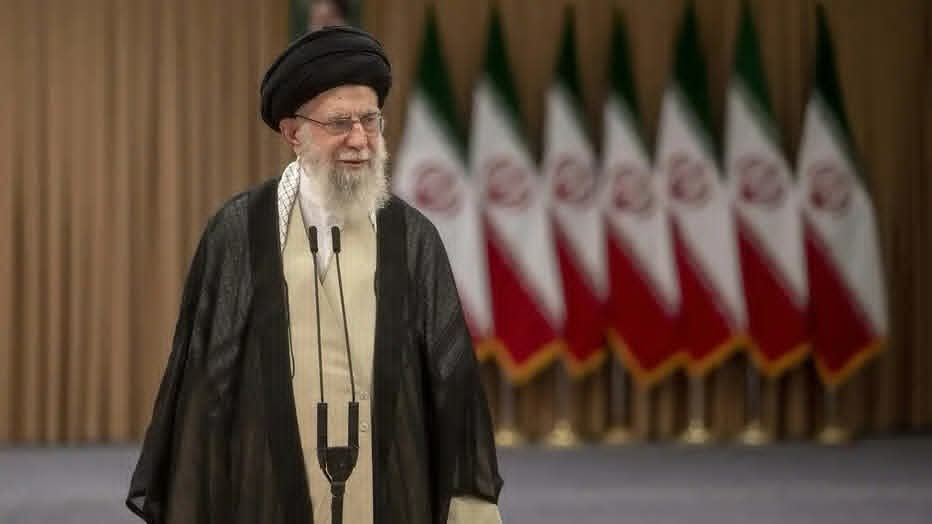
Iranian Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei Dies After Air Strikes

By Dipo Olowookere
Iranian Supreme Leader, Mr Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, has died after coordinated airstrikes carried out by the United States and Israel on Tehran on Saturday morning.
His death was confirmed on Sunday morning by Iranian state media, which also disclosed that his daughter and grandchild were among those killed in the bombardment, which destroyed his compound.
Mr Khamenei was killed during a meeting with top leaders of the Middle East country yesterday, including the Defence Minister Amir Nasirzadeh and Revolutionary Guard commander Mohammad Pakpour, who reportedly died too.
His elimination has sparked mixed reactions, with some Iranians on the streets celebrating his demise, and others condemning the joint air strikes.
The President of the United States, Mr Donald Trump, described the late Iranian leader as “one of the most evil people in history,” expressing satisfaction at the action, which he said was “successful,” as it represented justice for both Iranians and Americans.
Meanwhile, Tehran has vowed to further respond to the attacks after initially firing missiles at six neighbours, including Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, UAE, Bahrain, and Jordan.
Flight operations in the region have been disrupted because of the retaliatory action of Iran over the weekend, though most of the missiles were intercepted.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn