World
Russia Pushes Ambitious Plan for Africa
By Kester Kenn Klomegah
Russia and African states have traditionally enjoyed friendly, time-tested relations, and a significant role was in the liberation of the continent, supporting the struggle of its peoples against colonialism, racism and apartheid.
Today, the development and strengthening of mutually beneficial ties with African countries and their integration associations is one of Russia’s foreign policy priorities, thus on October 23-24, Sochi hosted the first Russia-Africa Summit.
The idea to organise such an event emerged quite a long time ago; however, it has taken some time and considerable preparatory work to make this summit a starting point for building fair partnership relations based on equality and mutual practical interest.
Putin has outlined a comprehensive plan and taken note of key factors that includes:
* Russia, together with the international community, renders comprehensive assistance to Africa, inter alia, by way of reducing the debt burden of its states. With a number of countries, Russia is carrying out debt-for-development swap programmes.
* As for the potential level of investment in Africa in the next five years, the figure expected to be quite high, with a number of billion-dollar investment projects with Russia’s participation. Both Russia and Russian companies have substantial resources. African partners, in turn, will have create the necessary stable and predictable business environment and investment protection mechanisms and ensure favourable investment climate.
* Africa’s infrastructure needs are increasing, and African population is rapidly growing, as are its demands. All of this, in turn, calls for an expanded domestic market and greater consumption. Of course, where there are promising prospects for investment and profit, there is always competition, which, unfortunately, at times goes beyond the bounds of decency.
* Russia has certainly taken note of these factors and draw conclusions. Russia is not going to participate in a new “repartition” of the continent’s wealth; rather, ready to engage in competition for cooperation with Africa, provided this competition is civilized and develops in compliance with the law. Russia has a lot to offer to its African friends.
Under the headline “Russia-Africa Summit: Future-Oriented Agenda” for the Valdai Discussion Club, Deputy Director and Chief Researcher at the Institute for African Studies of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Professor Vladimir Shubin, noted that one should not be surprised that the first summit bringing together Russia and the leaders of African countries should take place after almost three decades. It id ude to multiple factors during the period after Soviet collapse.
Further, he mentioned that one serious obstacle to the development of comprehensive ties is the lack of objective information about Russia in Africa, and about Africa in Russia. The potential of bilateral relations can be realised only if both sides shed the stereotypes imposed from outside and develop mutually beneficial cooperation, grounded in reality.
Shubin added, regrettably that “the state of bilateral economic relations leaves much to be desired.” But, Moscow seeks to create favourable conditions by writing off the debt of African countries (US$20 billion), as well as introducing a system of preferences for traditional African export goods.
However, trade turnover remains limited, at less than 3% of Russia’s total foreign trade. According to the African Development Bank, Russian investment in Africa peaked at US$20 billion, although its flow is hardly stable. Unfortunately, in these areas Western sanctions have become an obstacle in recent years.
Russia’s presence in Africa has remained marginal, but this could soon change. Several delegations from African states have visited Moscow during the past few years and the Russian government appears determined to strengthen ties with Africa.
But, Russia’s intensified move to invite delegations has often been interpreted among academics and policy experts as a result of escalating competition and increasing economic influence by many foreign players in Africa.
Professor Georgy Toloraya, Chair of the Regional Projects Department, Russkiy Mir Foundation, and Executive Director, BRICS National Research Committee in Russia, explained that in the wake of increasing conflict with the West and European Union, Russia has to turn its attention (especially in economy) elsewhere and Africa is the obvious choice. The time has come to make meaningful efforts to implement agreements on bilateral basis.
Some experts acknowledge that it is never too late for Russia to enter the business game but what it requires here is to move beyond old stereotypes, prioritise corporate projects and have a new policy strategy for the continent – a market of some 350 million middle-class Africans.
Russia has to risk by investing and recognise the importance of cooperation on key potential investment issues, work closely with African leaders on the challenges and opportunities on the continent, Andy Kwawukume, an independent policy expert told me in an emailed discussion from London, noting that Russians have been trying to restage a comeback over the past few years, which was a commendable step forward.
Kwawukume, a Norwagian trained graduate, pointed out that “there is enough room and gaps in Africa for Russians to fill too, in a meaningful way, that can benefit all parties involved. The poor and low level of infrastructural development in Africa constitutes a huge business for Russian construction companies to step in. Energy is another sector Russians can help in developing. Russian officials should consider using its Russian trained African graduates as bridges to stimulate business cooperation.”
But, John Mashaka, a Tanzanian financial analyst at Wells Fargo Capital Markets in the U.S., argues that Russia is going to remain relevant in Africa if its leaders can design a policy or mechanism that will enable its people and corporations to secure credits – loans – with favourable terms including payment.
It must counter China’s increasing economic influence with much better packages such as concessional and low-interest loans. There are chances to turn the business tide and if Russians can come with a different mix of economic incentives, without doubt, they will be taking off from the track where the former USSR left after the collapse of the Soviet era.
Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov reiterated that it was to develop a trustworthy political dialogue and strengthen mutually beneficial bilateral cooperation in accordance with the declaration on strategic partnership and to forge cooperation in mutually beneficial economic spheres.
Lavrov further stressed the situation in different African regions, including to the north of the Sahara, in the region of the Horn of Africa, including the situation in Somalia, in the Republics of Sudan and South Sudan, the Central African Republic, in the Great Lakes Region, which is the key focus of attention in the foreign policy.
“We would like to contribute to the normalisation of all multifaceted ties, as well as the settlement of other problem issues in the African continent,” said Foreign Minister Lavrov. As far back as May 2014, while addressing African diplomatic representatives, Lavrov said: “We will continue to assist states of the continent in other areas both in bilateral and multilateral formats. As it is known, Russia has written off over US$20 billion debt of African states. We are undertaking steps to further ease the debt burden of Africans, including through conclusion of agreements based on the scheme debt in exchange for development.”
In an article headlined: “Russia and Sub-Saharan Africa: Time-proven Relations” published in the magazine Russian View in May, Sergey Lavrov gave additional information on gains made in policy implementation in Africa.
“Our country takes significant practical steps to assist sustainable development of African states. Russia provides African countries with extensive preferences in trade and contributes to alleviating their debt burden – the total amount of debt relief exceeds US$20 billion. Debt-for-development agreements for a total amount of US$552 million were concluded with certain States,’ Lavrov wrote in the article.
Obviously, Russia continues providing the necessary politico-diplomatic follow-up for the African activities of leading Russian companies such as Alrosa, Gazprom, Lukoil, Rusal, Renova, Gammakhim, Technopromexport, VEB and VTB banks, which are engaged in large-scale investment projects on the continent. Positive dynamics are evident in the development of Russian-African cooperation in the minerals and raw materials, infrastructure, energy and many other spheres.
Some experts have offered both criticism and expert advice, often comparing Russia’s economic investment and influence to other foreign players. As Dane Erickson, a lecturer at the Graduate School of Public Affairs at the University of Colorado and formerly a visiting scholar at the Africa Studies Center at Beijing University, argues that the reality is that China is among many international players that have increased their attention to Africa in recent years.
Largely due to Africa’s growing reputation as a region for commerce, over the past few years China, India, Japan, and the European Union all have hosted regional meetings similar to the U.S.-Africa Leaders Summit. Africa’s fractional share in global foreign direct investment (FDI) is on the rise, and trade between Africa and a multitude of nations is also increasing rapidly, according to Erickson.
China’s trade has increased rapidly. For example, China is the most conspicuous among these actors. China’s first Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC) occurred in 2000 and larger conferences have taken place every three years since. And while China’s official FDI is only 25 percent of that of countries like the U.S. and France, its trade dwarfs the figures of other nations. Up from just US$10 billion in 2000, Chinese-African trade came to over US$200 billion double that of the United States, the continent’s second largest trading partner.
Professor Gerrit Olivier at the Department of Political Sciences, University of Pretoria, and former South African Ambassador to the Russian Federation, wrote that “what seems to irk the Russians, in particular, is that very few initiatives go beyond the symbolism, pomp and circumstance of high level opening moves.
Professor Olivier added that Russian presence in Africa could be directed at promoting economic development and political stability in Africa by introducing more healthy competition, partnership, and greater responsibility on the continent.
Important though is the fact that the Soviet Union never tried to colonize Africa. Soviet influence in Africa disappeared almost like a mirage with the collapse of the Soviet system in 1991. In the current assessment of Russia’s influence in Africa, despite efforts towards resuscitation, has remained marginal. While, given its global status, it ought to be active in Africa as Western Europe, the European Union, America and China are, it is all but absent, playing a negligible role, according to the views of the retired diplomat.
Russia, of course, is not satisfied with this state of affairs. At present “paper diplomacy” dominates its approach, a plethora of agreements being entered into with various African countries, official visits from Moscow proliferate apace, but the outcomes has remained hardly discernible. Be that as it may, the Kremlin has revived its interest in the African continent and it will be realistic to expect that the spade work it is putting in now will at some stage show more tangible results, Professor Olivier wrote from Pretoria in South Africa.
Foreign Affairs Minister Sergey Lavrov has said that trade between Russia and Africa would grow further as more and more African partners continued to show interest in having Russians in the economic sectors in Africa.
“Our African partners are interested in Russian business working more actively there. This provides greater competition between the companies from Western countries, China, and Russia. With competition for developing mineral resources in Africa, it is easier and cheaper for our African colleagues to choose partners,” he told the staff and students at Moscow State Institute of International Affairs early September.
Soviet Union and Africa had very close and, in many respects, allied relations with most of the African countries during the decolonisation of Africa. For obvious reasons, the Soviet Union ceased to exist in 1991. As a result, Russia has to struggle through many internal and external difficulties. The past few years, it is still struggling to survive both the United States and European sanctions.
For decades, Russia has been looking for effective ways to promote multifaceted ties and new strategies for cooperation in economic areas in Africa. A number of foreign countries notably China, the United States, European Union, India, France, Turkey, Japan, and South Korea have held gatherings of this kind in that format. Now, Kremlin has held the first Russia-Africa Summit with high hopes of enhancing multifaceted ties, reshape the existing relationships and significantly roll out ways to increase effectiveness of cooperation between Russia and Africa.
Kester Kenn Klomegah is an independent researcher and policy consultant on African affairs and Brics. He is the author of the Geopolitical Handbook titled “Putin’s African Dream and The New Dawn: Challenges and Emerging Opportunities” devoted to the first Russia-Africa Summit 2019.
World
Ukraine Reveals Identities of Nigerians Killed Fighting for Russia
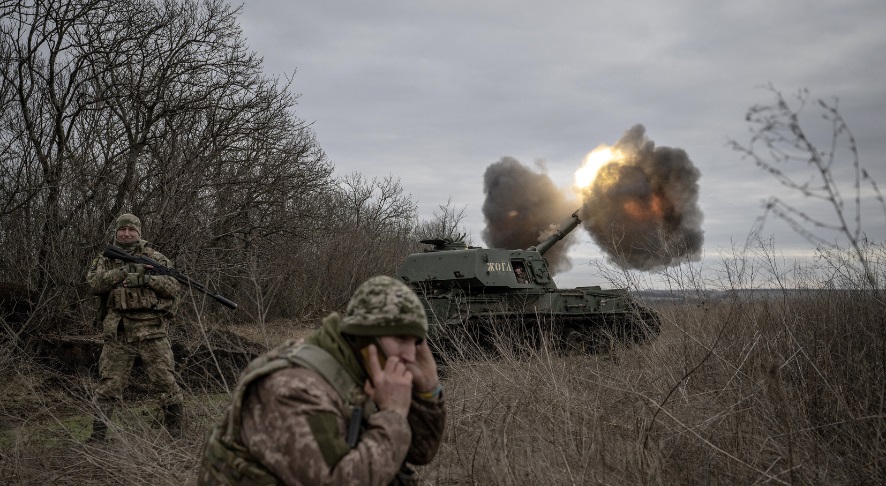

By Adedapo Adesanya
The Ukrainian Defence Intelligence (UDI) has identified two Nigerian men, Mr Hamzat Kazeem Kolawole and Mr Mbah Stephen Udoka, allegedly killed while fighting as Russian mercenaries in the war between the two countries ongoing since February 2022.
The development comes after Russia denied knowledge of Nigerians being recruited to fight on the frontlines.
Earlier this week, the Russian Ambassador to Nigeria, Mr Andrey Podyolyshev, said in Abuja that he was not aware of any government-backed programme to recruit Nigerians to fight in the war in Ukraine.
He said if at all such activity existed, it is not connected with the Russian state.
However, in a statement on Thursday, the Ukrainian Defence released photographs of Nigerians killed while defending Russia.
“In the Luhansk region, military intelligence operatives discovered the bodies of two citizens of the Federal Republic of Nigeria — Hamzat Kazeen Kolawole (03.04.1983) and Mbah Stephen Udoka (07.01.1988),” the statement read.
According to the statement, both men served in the 423rd Guards Motor Rifle Regiment (military unit 91701) of the 4th Guards Kantemirovskaya Tank Division of the armed forces of the Russian Federation.
UDI said that they signed contracts with the Russian Army in the second half of 2025 – the deceased Mr Kolawole on August 29 and Mr Udoka on September 28.
“Udoka received no training whatsoever — just five days later, on October 3, he was assigned to the unit and sent to the temporarily occupied territories of Ukraine,” the report read.
It added that no training records for Mr Kolawole have been preserved; however, it is highly likely that he also received no military training, but his wife and three children remain in Nigeria.
Both Nigerians, the report added, were killed in late November during an attempt to storm Ukrainian positions in the Luhansk region.
“They never engaged in a firefight — the mercenaries were eliminated by a drone strike,” UDI stated, warning foreign citizens against travelling to the Russian Federation or taking up any work on the territory of the “aggressor state”.
“A trip to Russia is a real risk of being forced into a suicide assault unit and, ultimately, rotting in Ukrainian soil,” the statement read.
In an investigation earlier this month, CNN reported that hundreds of African men have been enticed to fight for Russia in Ukraine with the promise of civilian jobs and high salaries. However, the media organisation uncovered that they are being deceived or sent to the front lines with little combat training.
CNN said it reviewed hundreds of chats on messaging apps, military contracts, visas, flights and hotel bookings, as well as gathering first-hand accounts from African fighters in Ukraine, to understand just how Russia entices African men to bolster its ranks.
World
Today’s Generation of Entrepreneurs Value Flexibility, Autonomy—McNeal-Weary

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
The Young African Leaders Initiative (YALI) is the United States’ signature step to invest in the next generation of African leaders. Since its establishment in 2010 by Obama administration, YALI has offered diverse opportunities, including academic training in leadership, governance skills, organizational development and entrepreneurship, and has connected with thousands of young leaders across Africa. This United States’ policy collaboration benefits both America and Africa by creating stronger partnerships, enhancing mutual prosperity, and ensuring a more stable environment.
In our conversation, Tonya McNeal-Weary, Managing Director at IBS Global Consulting, Inc., Global Headquarters in Detroit, Michigan, has endeavored to discuss, thoroughly, today’s generation of entrepreneurs and also building partnerships as a foundation for driving positive change and innovation in the global marketplace. Here are the excerpts of her conversation:
How would you describe today’s generation of entrepreneurs?
I would describe today’s generation of entrepreneurs as having a digital-first mindset and a fundamental belief that business success and social impact can coexist. Unlike the entrepreneurs before them, they’ve grown up with the internet as a given, enabling them to build global businesses from their laptops and think beyond geographic constraints from day one. They value flexibility and autonomy, often rejecting traditional corporate ladders in favor of building something meaningful on their own terms, even if it means embracing uncertainty and financial risk that previous generations might have avoided.
And those representing the Young African Leaders Initiative, who attended your webinar presentation late January 2026?
The entrepreneurs representing the Young African Leaders Initiative are redefining entrepreneurship on the continent by leveraging their unique perspectives, cultural heritage, and experiences. Their ability to innovate within local contexts while connecting to global opportunities exemplifies how the new wave of entrepreneurs is not confined by geography or conventional expectations.
What were the main issues that formed your ‘lecture’ with them, Young African Leaders Initiative?
The main issues that formed my lecture for the Young African Leaders Initiative were driven by understanding the importance of building successful partnerships when expanding into the United States or any foreign market. During my lecture, I emphasized that forming strategic alliances can help entrepreneurs navigate unfamiliar business environments, access new resources, and foster long-term growth. By understanding how to establish strong and effective partnerships, emerging leaders can position their businesses for sustainable success in global markets. I also discussed the critical factors that contribute to successful partnerships, such as establishing clear communication channels, aligning on shared goals, and cultivating trust between all parties involved. Entrepreneurs must be proactive in seeking out partners who complement their strengths and fill gaps in expertise or resources. It is equally important to conduct thorough due diligence to ensure that potential collaborators share similar values and ethical standards. Ultimately, the seminar aimed to empower YALI entrepreneurs with practical insights and actionable strategies for forging meaningful connections across borders. Building successful partnerships is not only a pathway to business growth but also a foundation for driving positive change and innovation in the global marketplace.
What makes a ‘leader’ today, particularly, in the context of the emerging global business architecture?
In my opinion, a leader in today’s emerging global business architecture must navigate complexity and ambiguity with a fundamentally different skill set than what was previously required. Where traditional leadership emphasized command-and-control and singular vision, contemporary leaders succeed through adaptive thinking and collaborative influence across decentralized networks. Furthermore, emotional intelligence has evolved from a soft skill to a strategic imperative. Today, the effective modern leader must possess deep cross-cultural intelligence, understanding that global business is no longer about exporting one model worldwide but about genuinely integrating diverse perspectives and adapting to local contexts while maintaining coherent values.
Does multinational culture play in its (leadership) formation?
I believe multinational culture plays a profound and arguably essential role in forming the kind of leadership required in today’s global business environment. Leaders who have lived, worked, or deeply engaged across multiple cultural contexts develop a cognitive flexibility that’s difficult to replicate through reading or training alone. More importantly, multinational exposure tends to dismantle the unconscious certainty that one’s own way of doing things is inherently “normal” or “best.” Leaders shaped in multicultural environments often develop a productive discomfort with absolutes; they become more adept at asking questions, seeking input, and recognizing blind spots. This humility and curiosity become strategic assets when building global teams, entering new markets, or navigating geopolitical complexity. However, it’s worth noting that multinational experience alone doesn’t automatically create great leaders. What matters is the depth and quality of cross-cultural engagement, not just the passport stamps. The formation of global leadership is less about where someone has been and more about whether they’ve developed the capacity to see beyond their own cultural lens and genuinely value differences as a source of insight rather than merely tolerating them as an obstacle to overcome.
In the context of heightening geopolitical situation, and with Africa, what would you say, in terms of, people-to-people interaction?
People-to-people interaction is critically important in the African business context, particularly as geopolitical competition intensifies on the continent. In this crowded and often transactional landscape, the depth and authenticity of human relationships can determine whether a business venture succeeds or fails. I spoke on this during my presentation. When business leaders take the time for face-to-face meetings, invest in understanding local priorities rather than imposing external agendas, and build relationships beyond the immediate transaction, they signal a different kind of partnership. The heightened geopolitical situation actually makes this human dimension more vital, not less. As competition increases and narratives clash about whose model of development is best, the businesses and nations that succeed in Africa will likely be those that invest in relationships characterized by reciprocity, respect, and long-term commitment rather than those pursuing quick wins.
How important is it for creating public perception and approach to today’s business?
Interaction between individuals is crucial for shaping public perception, as it influences views in ways that formal communications cannot. We live in a society where word-of-mouth, community networks, and social trust areincredibly important. As a result, a business leader’s behavior in personal interactions, their respect for local customs, their willingness to listen, and their follow-through on commitments have a far-reaching impact that extends well beyond the immediate meeting. The geopolitical dimension amplifies this importance because African nations now have choices. They’re no longer dependent on any single partner and can compare approaches to business.
From the above discussions, how would you describe global business in relation to Africa? Is it directed at creating diverse import dependency?
While it would be too simplistic to say global business is uniformly directed at creating import dependency, the structural patterns that have emerged often produce exactly that outcome, whether by design or as a consequence of how global capital seeks returns. Global financial institutions and trade agreements have historically encouraged African nations to focus on their “comparative advantages” in primary commodities rather than industrial development. The critical question is whether global business can engage with Africa in ways that build productive capacity, transfer technology, develop local talent, and enable countries to manufacture for themselves and for export—or whether the economic incentives and power irregularities make this structurally unlikely without deliberate policy intervention.
World
Russia Expands Military-Technical Cooperation With African Partners

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
Despite geopolitical complexities, tensions and pressure, Russia’s military arms and weaponry sales earned approximately $15 billion at the closure of 2025, according to Kremlin report. At the regular session, chaired by Russian President Vladimir Putin on Jan. 30, the Commission on Military and Technical Cooperation with Foreign Countries analyzed the results of its work for 2025, and defined plans for the future.
It was noted that the system of military-technical cooperation continued to operate in difficult conditions, and with increased pressure from the Western countries to block business relations with Russia. The meeting, however, admitted that export contracts have generally performed sustainably. Russian military products were exported to more than 30 countries last year, and the amount of foreign exchange exceeded $15 billion.
Such results provide an additional opportunity to direct funds to the modernization of OPC enterprises, to the expansion of their production capacities, and to advanced research. It is also important that at these enterprises a significant volume of products is civilian products.
The Russian system of military-technical cooperation has not only demonstrated effectiveness and high resilience, but has created fundamental structures, which allow to significantly expand the “geography” of supplies of products of military purpose and, thus strengthen the position of Russia’s leader and employer advanced weapons systems – proven, tested in real combat conditions.
Thanks to the employees of the Federal Service for Military Technical Cooperation and Rosoboronexport, the staff of OPC enterprises for their good faith. Within the framework of the new federal project “Development of military-technical cooperation of Russia with foreign countries” for the period 2026-2028, additional measures of support are introduced. Further effective use of existing financial and other support mechanisms and instruments is extremely important because the volumes of military exports in accordance with the 2026 plan.
Special attention would be paid to the expansion of military-technological cooperation and partnerships, with 14 states already implementing or in development more than 340 such projects.
Future plans will allow to improve the characteristics of existing weapons and equipment and to develop new promising models, including those in demand on global markets, among other issues – the development of strategic areas of military-technical cooperation, and above all, with partners on the CIS and the CSTO. This is one of the priority tasks to strengthen both bilateral and multilateral relations, ensuring stability and security in Eurasia.
From January 2026, Russia chairs the CSTO, and this requires working systematically with partners, including comprehensive approaches to expanding military-technical relations. New prospects open up for deepening military-technical cooperation and with countries in other regions, including with states on the African continent. Russia has been historically strong and trusting relationships with African countries. In different years even the USSR, and then Russia supplied African countries with a significant amount of weapons and military equipment, trained specialists on their production, operation, repair, as well as military personnel.
Today, despite pressure from the West, African partners express readiness to expand relations with Russia in the military and military-technical fields. It is not only about increasing supplies of Russian military exports, but also about the purchase of other weapons, other materials and products. Russia has undertaken comprehensive maintenance of previously delivered equipment, organization of licensed production of Russian military products and some other important issues. In general, African countries are sufficient for consideration today.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn











