World
INTERPOL Arrests 11 Suspects Linked with Terrorism in Nigeria

By Adedapo Adesanya
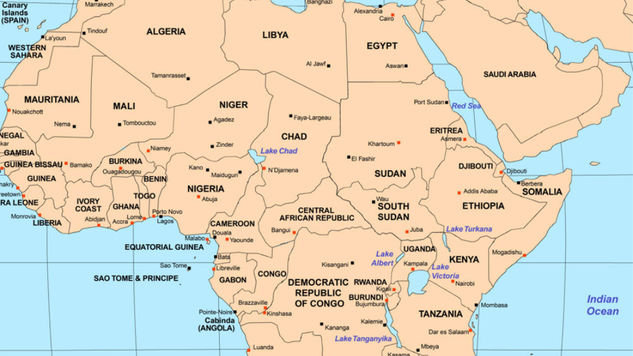
The International Criminal Police Organisation (INTERPOL) says 11 high-level members of terrorist groups have been arrested in Nigeria as part of a wider sting operation in Africa.
The arrests were part of Operation Catalyst, a landmark operation targeting terrorism financing and related criminal activities across six African countries.
According to INTERPOL, the three-month operation, conducted between July and September 2025, led to 83 arrests and identified 160 persons of interest.
Countries that participated in the operation include Nigeria, Angola, Cameroon, Kenya, Namibia, and South Sudan.
In Nigeria, INTERPOL confirmed that 11 suspected terrorists, including senior members of various terrorist groups, were apprehended.
The operation also uncovered several financial networks suspected of funding terrorism activities through illegal transactions and online fraud schemes.
INTERPOL said law enforcement screened over 15,000 persons and entities, revealing about $260 million in fiat and virtual currencies linked to terrorism financing.
Approximately $600,000 has already been seized, while further investigations are ongoing to trace and recover additional assets.
The operation also exposed financial fraud, cyber-enabled scams, money laundering, and illicit use of virtual assets as major sources of terrorist funding.
The operation was jointly coordinated by INTERPOL and the African Union Mechanism for Police Cooperation (AFRIPOL).
INTERPOL Secretary General Valdecy Urquiza said the collaboration was crucial to tackling the complex networks funding terrorism.
“Operation Catalyst is the first time financial crime, cybercrime and counter-terrorism units from multiple African countries have joined forces.
“By sharing intelligence, expertise and resources, we can more effectively disrupt the financial flows that support terrorist activities and keep our communities safe,” Mr Urquiza said.
AFRIPOL Executive Director Ambassador, Mr Jalel Chelba lauded the operation’s success, describing it as proof of Africa’s united front against terrorism.
“This joint endeavour, dedicated to disrupting the financing of terrorism, illustrates how coordinated action between Member States can address complex and evolving security threats,” Mr Chelba said.
Listing its operation in other African countries, the agency said in Angola, authorities detained 25 individuals and seized USD 588,000, 100 phones, and 40 computers in a related probe.
In Kenya, police dismantled a $430,000 virtual asset laundering network with suspected terrorism links. Two people were arrested.
Another Kenyan case saw two suspects arrested for using cryptocurrency to recruit youths into terrorist groups across East and North Africa.
A separate cryptocurrency-based Ponzi scheme affecting at least 17 countries, including Nigeria, was also uncovered. It defrauded victims of $562 million.
Meanwhile, the organisation said a Red Notice had been issued for a suspect behind a $5 million cryptocurrency scam used to fund terrorism.
The operation was conducted under the ISPA programme, funded by the German Federal Foreign Office, to strengthen AFRIPOL’s fight against transnational organised crime and terrorism.
It said investigators believe the funds were redirected through multiple exchanges to hide their origins and convert them into fiat currency.
INTERPOL said investigations into the financial networks and assets linked to terrorism financing are still ongoing.
World
Trump Picks Kevin Warsh to Succeed Jerome Powell as Federal Reserve Chair

By Adedapo Adesanya
President Donald Trump has named Mr Kevin Warsh as the successor to Mr Jerome Powell as the Federal Reserve chair, ending a prolonged odyssey that has seen unprecedented turmoil around the central bank.
The decision culminates a process that officially began last summer but started much earlier than that, with President Trump launching a criticism against the Powell-led US central bank almost since he took the job in 2018.
“I have known Kevin for a long period of time, and have no doubt that he will go down as one of the GREAT Fed Chairmen, maybe the best,” Mr Trump said in a Truth Social post announcing the selection.
US analysts noted that the 55-year old appear not to ripple market because of his previous experience at the apex bank as Governor, with others saying he wouldn’t always do the bidding of the American president.
If approved by the US Senate, Mr Warsh will take over the position in May, when Mr Powell’s term expires.
Despite having argued for reductions recently, “Warsh has a long hawkish history that markets have not forgotten,” one analyst told Bloomberg.
President Trump has castigated Mr Powell for not lowering interest rates more quickly. His administration also launched a criminal investigation of Powell and the Federal Reserve earlier this month, which led Mr Powell to issue an extraordinary rebuke of President Trump’s efforts to politicize the independent central bank.
World
BRICS Agenda, United States Global Dominance and Africa’s Development Priorities

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
Donald Trump has been leading the United States as its president since January 2025. Washington’s priority is to Make America Great Again (MAGA). Trump’s tariffs have rippled many economies from Latin America through Asian region to the continent of Africa. Trump’s Davos speech has explicitly revealed building a ‘new world order’ based on dominance rather than trust. He has also initiated whirlwind steps to annex Greenland, while further created the Board of Peace, aimed at helping end the two-year war between Israel and Hamas in Gaza and to oversee reconstruction. Trump is handling the three-year old Russia-Ukraine crisis, and other deep-seated religious and ethnic conflicts in Africa.
These emerging trends, at least in a considerable short term, are influencing BRICS which has increased its geopolitical importance, and focusing on uniting the countries in the Global East and Global South. From historical records, BRICS, described as non-western organization, and is loosing its coherence primarily due to differences in geopolitical interests and multinational alignments, and of course, a number of members face threats from the United States while there are variations of approach to the emerging worldwide perceptions.
In this conversation, deputy director of the Center for African Studies at Moscow’s National Research University High School of Economics (HSE), Vsevolod Sviridov, expresses his opinions focusing on BRICS agenda under India’s presidency, South Africa’s G20 chairmanship in 2024, and genegrally putting Africa’s development priorities within the context of emerging trends. Here are the interview excerpts:
What is the likely impact of Washington’s geopolitics and its foreign policy on BRICS?
From my perspective, the current Venezuela-U.S. confrontation, especially Washington’s tightened leverage over Venezuelan oil revenue flows and the knock-on effects for Chinese interests, will be read inside BRICS as a reminder that sovereign resources can still be constrained by financial chokepoints and sanctions politics. This does not automatically translate into BRICS taking Venezuela’s side, but it does strengthen the bloc’s long-running argument for more resilient South-South trade settlement, diversified energy chains, and financing instruments that reduce exposure to coercive measures, because many African and other developing economies face similar vulnerabilities around commodities, shipping, insurance, and correspondent banking. At the same time, BRICS’ expansion makes consensus harder: several members maintain significant ties with the U.S., so the most likely impact is a technocratic push rather than a loud political campaign.
And highlighting, specifically, the position of BRICS members (South Africa, Ethiopia and Egypt, as well as its partnering African States (Nigeria and Uganda)?
Venezuela crisis urges African members to demand that BRICS deliver usable financial and trade tools. For South Africa, Ethiopia, and Egypt, the Venezuela case is more about the precedent: how quickly external pressure can reshape a country’s fiscal room, debt dynamics, and even investor perceptions when energy revenues and sanctions compliance collide. South Africa will likely argue that BRICS should prioritize investment, industrialization, and trade facilitation. Ethiopia and Egypt, both debt-sensitive and searching for FDI, will be especially attentive to anything that helps de-risk financing, while avoiding steps that could trigger secondary-sanctions anxieties or scare off diversified investors.
Would the latest geopolitical developments ultimately shape the agenda for BRICS 2026 under India’s presidency?
India’s 2026 chairmanship is already framed around “Resilience, Innovation, Cooperation and Sustainability,” and Venezuela’s shock (paired with broader sanction/market-volatility lessons) will likely sharpen the resilience part. From an African perspective, that is an opportunity: South Africa, Ethiopia, and Egypt can press India to translate the theme into deliverables that matter on the ground: food and fertilizer stability, affordable energy access, infrastructure funding. India, in turn, has incentives to keep BRICS focused on economic problem-solving rather than becoming hostage to any single flashpoint. So the Venezuela episode may function as a cautionary case study that accelerates practical cooperation where African members have the most to gain. And I would add: the BRICS agenda will become increasingly Africa-centered simply because Africa’s weight globally is rising, and recent summit discussions have repeatedly highlighted African participation as a core Global South vector. South Africa’s G20 chairmanship last year explicitly framed around putting Africa’s development priorities high on the agenda, further proves this point.
World
Afreximbank Terminates Credit Relationship With Fitch Amid Rating Tension

By Adedapo Adesanya
African Export-Import Bank (Afreximbank) has has officially terminated its credit rating relationship with Fitch Ratings, indicating friction between both firms.
According to a statement on Friday, the Cairo-based African lender said the decision follows a review of the relationship, and its firm belief that the credit rating exercise no longer reflects a good understanding of the bank’s Establishment Agreement, its mission, and its mandate.
“Afreximbank’s business profile remains robust, underpinned by strong shareholder relationships and the legal protections embedded in its Establishment Agreement, signed and ratified by its member states,” the statement added.
Business Post reports that Fitch had cut Afreximbank’s credit rating to one notch above ‘junk’ Status last year and currently has it on a ‘negative outlook’, which is a rating agency’s terminology for another downgrade warning.
Lower rating means higher borrowing costs for Afreximbank, which could directly impact its ability to lend and the low rates at which it does so.
Recall that Fitch in its report published in June 2025, had estimated Afreximbank’s non-performing loans at 7.1 per cent by the end of 2024, exceeding Fitch’s 6 per cent “high risk” threshold.
The African Peer Review Mechanism (APRM) contested Fitch’s assessment and argued that Fitch confused loan restructuring requests from South Sudan, Zambia, and Ghana by considering them as defaults, claiming this was inconsistent with the 1993 treaty establishing Afreximbank.
African policymakers have raised worries about the ratings by foreign rating agencies like Fitch, Moody’s, and S&P among others. This has increased call for an African focused agency, which is expected to have commenced but continues to face delays.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism9 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn