Feature/OPED
Nigeria 2019 Governorship Election: Appraising the Verdict

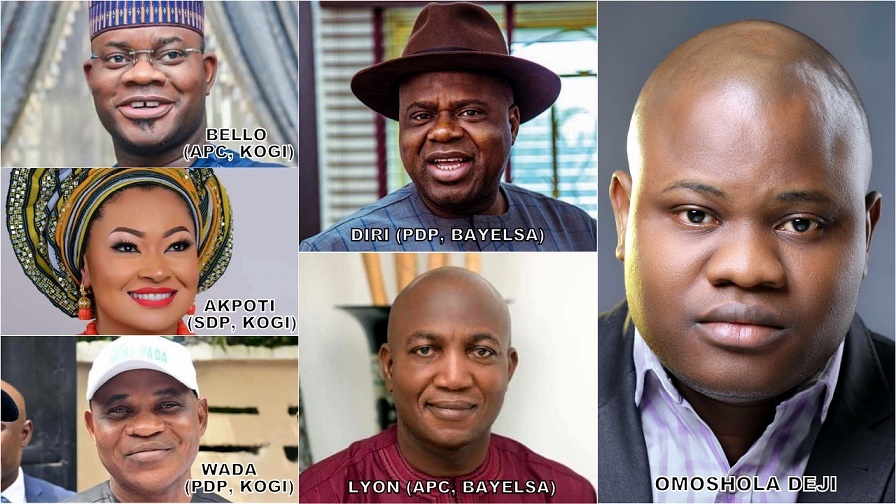
By Omoshola Deji
Election in Nigeria is a battle of fists rather than a game of wits. The nation has gotten almost nothing right since independence and still cannot conduct free, fair and credible elections. The insatiable thirst for power has made the leadership recruitment process a battle; turning properties to ashes and beings to corpse. Shame on the leaders and politicians. Shame on the Independent National Electoral Commission (INEC) and the security agencies. Shame on Nigeria.
The 2019 general election is the worst in Nigeria’s history. It is the most protracted and onerous, despite being the most expensive. The polls scheduled to wind-up in three weeks has dragged on for six and still counting. Do the arithmetic. The presidential election initially slated for February 16 was postponed to 23 for ‘logistics reasons’ and the governorship election conducted on March 9 is yet to be concluded.
The must-win approach of politicians and the incompetence of the security agencies and INEC rendered the governorship election inconclusive in Kano, Benue, Plateau, Bauchi, Sokoto, Adamawa and Rivers State. The electoral process in Kano, Benue, Plateau and Sokoto has been completed while that of Bauchi, Adamawa and Rivers are still on hold.
Nigeria is the den of negative politicking. The misconducts that rendered the governorship elections inconclusive also made the supplementary elections held on 23 March unfree and unfair and un-credible, especially in Kano State. Desperate candidates unleashed thugs to kill and destroy, while the police looked on. The prevailing either-me-or-nobody politics is endangering our hard-earned democracy and may return Nigeria into the hands of the men in uniform.
The 2019 general election has been an intriguing one. Politicians who were before now seen as undefeatable were defeated. The mighty fell and new ones emerged. Godfathers such as Bukola Saraki (Kwara State) Godswill Akpabio (Akwa-Ibom State), Aliyu Wammako (Sokoto State) and George Akume (Benue State) have been decimated. The death guzzling one’s mate is relaying a message that one’s turn is near. Bola Tinubu should start preparing. 2023 may be his turn.
Over 90 political parties participated in the governorship elections, but Nigerians mainly voted the ruling All Progressives Congress and the main opposition Peoples Democratic Party (PDP). In a piece titled “Nigeria 2019 Governorship Election: Foretelling the Outcome”, the writer, hereafter titled Pundit, foretold who’ll triumph in the 29 (out of 36) states where elections were conducted. Governorship election in the remaining 7 states is off-cycle.
Independently foretelling the outcome of governorship elections in a vast and plural nation like Nigerian is a difficult, almost impossible task. It entails a rigorous research into the election winning determinants in each state. Such research is usually sponsored and carried out by a team of leading Political Scientists.
Unaided, the pundit singly foretold the outcomes and did not perform poorly. He made accurate predictions, achieved his target of scoring high, but some predictions failed. The next section of this piece is an analysis of the election controversies, the landmarks, and what the future holds. The pundit’s prediction accuracy and shortcomings in the six geopolitical regions is also appraised.
North West
The region comprises of seven states, including Kano, Katsina, Kaduna, Kebbi, Sokoto, Jigawa, and Zamfara State. Elections were conducted in all.
Kano State: Governor Abdullahi Ganduje of the APC’s win was foretold and it came to pass, even though the Pundit never thought the election would be a keenly contested one. Ganduje garnered 1,033,695 votes to defeat PDP’s Abba Yusuf, who garnered 1,024,713 votes. Ganduje allegedly won via electoral fraud. The supplementary election was a farce and brazen murder of democracy. It was characterized by voter harassment, vote buying, underage voting and violence. Political thugs unleashed mayhem without being resisted by the police. The evidence of electoral infractions is so mammoth that it’ll be difficult for Ganduje to complete his tenure, if the result is challenged at the tribunal.
Observers of the ruling APC’s antecedent and political behaviour knows the party would never allow PDP take control of Kano. The state has the highest number of registered voters and needs to be kept in the bag for 2023. APC also went all out to retain Kano in order to bury arguments that the presidential election was rigged in the state for President Muhammadu Buhari.
Katsina State: Aminu Masari of the APC’s win was foretold and it came to pass. He scored 1,178,868 votes to defeat PDP’s Yakubu Lado who scored 488,705 votes.
Kaduna State: Nasir El-Rufai of the APC’s win was foretold and it came to pass. He garnered 1,044,710 votes to defeat PDP’s Isah Asiru who garnered 814,168 votes. Balancing religion equation is an unconstitutional rule politicians obey, except El-Rufai. He took the risk of running with a fellow Muslim and won. That it works for him doesn’t mean it’ll work for others. Nigeria’s prevailing ethno-religious sensitivity will deny others who copy him a win.
Kebbi State: Abubakar Bagudu of the APC’s win was foretold and it came to pass. He defeated PDP’s Isa Galaudu with 571,092 votes.
Sokoto State: the pundit wrongly predicted a win for APC’s Ahmad Aliyu. He was ticked to win by a small margin, but that happened the other way round. Aminu Tambuwal of the PDP defeated him with 341 votes.
Jigawa State: Mohammad Badaru of the APC’s win was foretold and it came to pass. He garnered 810,933 votes to defeat PDP’s Aminu Ibrahim who polled 288,356 votes.
Zamfara State: the Pundit wrongly predicted a narrow win for PDP’s Bello Mutawalle. His selection of Mutawalle was based on the lingering intra-party crisis in Zamfara APC before the election. Mukhtar Shehu of the APC defeated PDP’s Mutawalle with 345,089 votes.
Overall, the pundit made 4 right and 2 wrong predictions in the North West.
South South
The six states in the region are Edo, Bayelsa, Delta, Rivers, Cross River and Akwa Ibom State. Edo and Bayelsa State governorship election are off-cycle.
Delta State: Ifeanyi Okowa of the PDP’s win was foretold and it came to pass. He defeated APC’s Great Ogboru with 710,236 votes.
Rivers State: PDP’s Nyesom Wike was ticked to win, but the electoral process was suspended due to military interference and human rights abuses. The court restrained APC from appearing on the ballot. Wike’s main opponent, Biokpomabo Awara of the AAC rose to prominence after securing the backing of the APC bigwigs. The Pundit maintains that Wike will defeat Awara.
Cross River State: Ben Ayade’s win was foretold and it came to pass. The PDP candidate defeated APC’s John Owan-Enoh with 250,323 votes.
Akwa Ibom State: PDP’s Udom Emmanuel’s win was foretold and it came to pass. He scored 520,163 votes to defeat APC’s Nsima Nkere who scored 172,244 votes. APC overrated ex-Governor Godswill Akpabio’s political capacity when he joined the party. His senatorial reelection loss and inability to deliver Akwa Ibom for the party has sent him into political oblivion, but he is yet to realize that. The party will relegate him after those elected are sworn-in on May 29.
Overall, out of the four states were election held, the Pundit made 3 right predictions, while the result of Rivers State is being awaited.
North East
The region comprises of six states including Adamawa, Yobe, Borno, Bauchi, Taraba and Gombe State. Elections were conducted in all.
Adamawa State: Ahmadu Fintiri of the PDP’s win was foretold, although the election remains inconclusive. The electoral process was suspended based on court order. The already declared results indicate that PDP’s Ahmadu Fintiri has 367,611 votes, while Governor Jibrilla Bindo of the APC has 334,995 votes. With a winning margin of 32,616 votes and the low number of voters in areas where the supplementary election will hold, PDP’s Fintiri will most likely defeat APC’s Bindo as initially predicted.
Yobe State: Mai Mala Buni of the APC was predicted to win by a landslide and it came to pass. He polled 444,013 votes to defeat PDP’s Umar Damagun who polled 95,803 votes.
Borno State: Babagana Zullum of APC’s wide margin win was foretold and it came to pass. He polled a staggering 1,175,445 votes to defeat PDP’s Mohammed Imam who garnered a paltry 66,117 votes. The large number of votes recorded in Borno state is surprising. The state has been ravaged by Boko Haram insurgents and many of the voting population are displaced. How elections across the state were so organized that many people voted, but residents of a peaceful state like Kano were attacked and prevented from voting during the supplementary poll is bewildering. APC’s interest is the switch that determines the operational effectiveness of the security agencies. They protect the votes in APC strongholds and let thugs destroy the ballot in PDP’s own.
Bauchi State: election is inconclusive. The court restrained INEC from proceeding with the collation of results, but the order has been vacated. Governor Mohammed Abubakar of the APC’s win was foretold, but that may not happen. PDP’s Bala Mohammed is leading in the main and supplementary election results. PDP has a total of 469,512 votes, while APC has 465,456 votes. Bauchi is amiss for the pundit as victory is most certain for PDP’s Mohammed.
Taraba State: Darius Ishaku’s (PDP) win was foretold and it came to pass. He garnered 520,433 votes to defeat APC’s Sani Danladi who scored 362,735 votes.
Gombe State: Inuwa Yahaya’s (APC) win was foretold and it came to pass. He defeated PDP’s Usman Nafada with 141,311 votes.
Overall, out of the six states were election held, the Pundit made 4 right predictions, while the results of Adamawa and Bauchi State is being awaited.
South East
The five states in the region are Anambra, Abia, Enugu, Ebonyi and Imo state. Anambra’s governorship election is off-cycle.
Abia State: Okezie Ikpeazu’s win was foretold and it came to pass. The PDP candidate defeated APC’s Uche Ogah with 161,553 votes.
Enugu State: Ifeanyi Ugwuanyi’s win was foretold and it came to pass. The PDP candidate garnered 449,935 votes to defeat APC’s Ayogu Eze, who garnered 10,423 votes.
Ebonyi State: David Umahi win was foretold and it came to pass. He defeated APC’s Sonni Ogbuoji with 257,146 votes.
Imo State: is a big plus for the Pundit. Many doubted him, but PDP’s Emeka Ihedioha won as foretold. He scored 273,404 votes to defeat Uche Nwosu of AA who scored 190,364 votes. Ifeanyi Ararume of APGA came third, while APC’s Hope Uzodinma came fourth. The former scored 114,676 votes, while the latter scored 96,458 votes.
Overall, PDP’s win was foretold in all the four states where elections held and it came to pass.
North Central
The region, also called the Middle Belt, comprises of six states, including Kogi, Benue, Kwara, Niger, Nassarawa and Plateau State. The governorship election in Kogi State is off-cycle.
Benue State: Samuel Ortom of the PDP’s win was foretold and it came to pass. He defeated APC’s Emmanuel Jime with 89,318 votes.
Kwara State: AbdulRahman Abdulrasaq of the APC’s win was foretold and it came to pass. He defeated PDP’s Rasak Atunwa with 216,236 votes.
Niger State: Abubakar Bello of the APC’s win was foretold and it came to pass. He garnered 526,351 votes to defeat PDP’s Umar Nasko who garnered 298,056 votes.
Nassarawa State: Abdullahi Sule of the APC’s win was foretold and it came to pass. He defeated PDP’s David Ombugadu with 142,970 votes.
Plateau State: the Pundit wrongly predicted a win for PDP’s Jeremiah Useni, but APC’s Simon Lalung defeated him with a meagre 2,672 votes.
Overall, out of the five states were election held, the Pundit made 4 right predictions and 1 wrong.
South West
The governorship election was conducted in only three (Oyo, Ogun, Lagos) out of the six states in the region. Ondo, Osun and Ekiti State governorship elections are off-cycle.
Oyo State: the Pundit wrongly predicted a narrow win for APC’s Bayo Adelabu. Seyi Makinde of the PDP however defeated him with 157,639 votes.
Ogun State: the pundit predicted a win for APM’s Adekunle Akinlade, but he lost. APC’s Dapo Abiodun defeated him with 19,517 votes. The pundit’s prediction was wrong in Oyo and Ogun state because of the intense last minute political horse-trading and alignments that occurred before the election. This made the pundit declare during prediction that “a lot of last minute endorsement and permutation is going on in the state and it’s quite different to state where the pendulum would swing”.
Lagos State: Babajide Sanwoolu of the APC’s win was foretold and it came to pass. He garnered 739,445 votes to defeat PDP’s Jimi Agbaje who garnered 206,141 votes.
Overall, the Pundit made 1 right and 2 wrong predictions in the South West region.
Accuracy Rate
Out of the 29 states where governorship elections were conducted, a winner is yet to be declared in Rivers, Bauchi and Adamawa State. Out of the 26 states where winners have been declared, the pundit made:
4 right and 2 wrong predictions in the North West;
3 right (out of 4) predictions in the South South, (Rivers is pending);
4 right (out of 6) predictions in the North East (Bauchi and Adamawa are pending);
4 right predictions in the South East, no wrong;
4 right and 1 wrong prediction in the North Central;
1 right and 2 wrong predictions in the South West.
In total, the pundit made 20 right predictions and got it wrong in 6.
In the election outcome prediction piece, the Pundit stated that he hopes to get it right in over 20 states and he succeeded as his prediction is about to come to pass in two out of the three pending states. Even though it’s difficult and looks impossible, the Pundit aims to foretell the right outcome in all the states in 2023.
For the Records
Across the country, Babagana Zullum, the APC candidate in Borno State won the 2019 governorship election with the highest margin of 1,109,230 votes. PDP’s Aminu Tambuwal of Sokoto State won with the lowest margin of 341 votes. Mohammed Imam, the PDP governorship candidate in Borno State scored the lowest votes: 66,117. Aminu Masari, the APC governorship candidate in Katsina State (President Buahri’s home state) scored an overall highest vote of 1,178,868. APC did not win any state in the South East but PDP won in all the six regions of the country. Power changed hands in four states: Oyo and Imo that are currently being ruled by the APC were won by the PDP, while Gombe and Kwara State being ruled by the PDP were won by the APC.
End Note
The 2019 general election brought joy to the winners and pain to those who lose, especially those who spent their life savings or borrowed money to campaign. It is difficult for credible candidates to win election in our violence prone and money based political system.
The monetization of politics is denying the best an opportunity to lead the rest. If this is not contained, Nigeria will in a few years be governed by fraudsters and drug barons. They’re the only ones who can afford to fund our expensive campaigns and politicking.
None or only one in a billion men of honest earnings can. In no distant time, the intellectuals would be relegated or at best be political godsons to those who have acquired enormous wealth through dishonest means. Vice President Yemi Osibajo is a case in point.
Declaring elections inconclusive is a recipe for electoral fraud as the supplementary polls are often marred with voter harassment and violence. Politics should be made less rewarding to discourage politicians from making elections a do or die affair. President Buhari needs to liaise with the national assembly to re-pass the amended electoral law and assent it. As long as electoral offenders remain unpunished, people will not desist from perpetrating crime and fraud during elections. A strict penalty such as jail terms with no option of fine should be enacted.
Leadership is service. Politicians offering money for votes are thieves seeking the power to steal, not serve. Politics is the most profitable investment in Nigeria and politicians don’t play to lose. We must stop rewarding failure and incompetence with our votes, if we wish to live the Nigeria of our dreams. 2019 is gone and we have no choice than to endure the pains — or enjoy the gains — of our political choice till 2023. May God help us!
Omoshola Deji is a political and public affairs analyst. He wrote in via mo******@***oo.com
Feature/OPED
Daniel Koussou Highlights Self-Awareness as Key to Business Success

By Adedapo Adesanya
At a time when young entrepreneurs are reshaping global industries—including the traditionally capital-intensive oil and gas sector—Ambassador Daniel Koussou has emerged as a compelling example of how resilience, strategic foresight, and disciplined execution can transform modest beginnings into a thriving business conglomerate.
Koussou, who is the chairman of the Nigeria Chapter of the International Human Rights Observatory-Africa (IHRO-Africa), currently heads the Committee on Economic Diplomacy, Trade and Investment for the forum’s Nigeria chapter. He is one of the young entrepreneurs instilling a culture of nation-building and leadership dynamics that are key to the nation’s transformation in the new millennium.
The entrepreneurial landscape in Nigeria is rapidly evolving, with leaders like Koussou paving the way for innovation and growth, and changing the face of the global business climate. Being enthusiastic about entrepreneurship, Koussou notes that “the best thing that can happen to any entrepreneur is to start chasing their dreams as early as possible. One of the first things I realised in life is self-awareness. If you want to connect the dots, you must start early and know your purpose.”
Successful business people are passionate about their business and stubbornly driven to succeed. Koussou stresses the importance of persistence and resilience. He says he realised early that he had a ‘calling’ and pursued it with all his strength, “working long weekends and into the night, giving up all but necessary expenditures, and pressing on through severe setbacks.”
However, he clarifies that what accounted for an early success is not just tenacity but also the ability to adapt, to recognise and respond to rapidly changing markets and unexpected events.
Ambassador Koussou is the CEO of Dau-O GIK Oil and Gas Limited, an indigenous oil and natural gas company with a global outlook, delivering solutions that power industries, strengthen communities, and fuel progress. The firm’s operations span exploration, production, refining, and distribution.
Recognising the value of strategic alliances, Koussou partners with business like-minds, a move that significantly bolsters Dau-O GIK’s credibility and capacity in the oil industry. This partnership exemplifies the importance of building strong networks and collaborations.
The astute businessman, who was recently nominated by the African Union’s Agenda 2063 as AU Special Envoy on Oil and Gas (Continental), admonishes young entrepreneurs to be disciplined and firm in their decision-making, a quality he attributed to his success as a player in the oil and gas sector. By embracing opportunities, building strong partnerships, and maintaining a commitment to excellence, Koussou has not only achieved personal success but has also set a benchmark for future generations of African entrepreneurs.
His journey serves as a powerful reminder that with determination and vision, success is within reach.
Feature/OPED
Pension for Informal Workers Nigeria: Bridging the Pension Gap

***The Case for Informal Sector Pensions in Nigeria
***A Crucial National Conversation
By Timi Olubiyi, PhD
In Nigeria today, the phrase “pension” evokes many different mixed reactions. For many civil servants and people in the corporate world, it conjures a bit of hope, but for the majority in the informal sector, who are in the majority in Nigeria, it is bleak. Millions of Nigerians are facing old age without any financial security due to a lack of retirement plans and a stable pension plan. Particularly, the millions who operate in markets, corner shops, transportation, agriculture, and loads of the nano and micro scale enterprises operators are without pension plans or retirement hope.
From the observation of the author and available records, staggering around 90 per cent of Nigeria’s workforce operates in the informal economy. Yet current pension coverage for this group is virtually non-existent. As observed, the absence of meaningful pension participation by this class of worker reinforces the vulnerability, intensifies poverty among older people, and puts pressure on families who are ill-equipped to shoulder the burden.
The significance of having a pension plan for informal workers in Nigeria, given the large number of people in that sector and the high level of unemployment and underemployment, cannot be overstated. As it is deeply connected to sustenance and the level of poverty in the country. Pension for informal workers in Nigeria is not just a technical policy matter; it is a story about dignity, security, and whether a lifetime of hard work ends in rest or in desperation.
Nigeria’s pension system, primarily structured around the Contributory Pension Scheme (CPS) managed by the National Pension Commission (PenCom), has made significant progress for formal sector employees, yet the large portion of the informal workforce which are traders, artisans, okada riders, small-scale farmers, domestic workers, and gig economy participants who drive the real engine of the economy.
Though the Micro Pension Plan (MPP) was launched in 2019, which is intended to provide a voluntary contributory framework for informal workers, its uptake has been underwhelming; after several years, only a fraction of the millions targeted have enrolled, and far fewer contribute actively. One big reason for this is that, unlike formal workers who receive regular salaries and have employers who deduct and remit pension contributions, informal workers face irregular incomes, a lack of documentation, limited financial literacy, and deep mistrust of government institutions, making traditional pension models ill-suited for their realities.
Moreso the informal worker most times live on day-to-day income. For instance, a motorcycle rider in Lagos who earns ₦14,000 on a good day but must pay for fuel, bike maintenance, police “settlements,” and family expenses, how can he realistically commit to a monthly pension contribution when his income fluctuates wildly? So, the Micro Pension Plan for the informal sector participation will remain low due to poor awareness, complex processes, lack of tailored contribution flexibility, and limited trust.
To truly make pensions work for informal workers, Nigeria must rethink the system from the ground up, designing it around the lived realities of its people rather than forcing them into rigid formal-sector structures. First, the government should introduce a co-contributory model where the state matches a percentage of informal workers’ savings, similar to what is practised in some European countries, turning pension contributions into a powerful incentive rather than a burdensome obligation.
Second, digital technology must be leveraged aggressively—mobile-based pension platforms linked to BVN or NIN could allow daily, weekly, or micro-contributions as small as ₦100, integrating seamlessly with fintech apps like OPay, Paga, or bank USSD services so that saving becomes as easy as buying airtime.
Third, automatic enrollment through cooperatives, trade unions, market associations, and transport unions could significantly expand coverage, with opt-out rather than opt-in mechanisms to counter human inertia.
Fourth, financial literacy campaigns in local languages via radio, community leaders, and religious institutions are essential to rebuild trust and demonstrate that pensions are not a “government scam” but a personal safety net.
Fifth, Nigeria should consider a universal social pension for elderly citizens who never participated in formal or informal schemes, modelled after systems in countries like Denmark and the Netherlands, ensuring that no Nigerian dies in poverty simply because they worked outside formal structures.
Sixth, investment strategies for pension funds must prioritise both security and development—allocating a portion to infrastructure projects that create jobs, improve power supply, and stimulate economic growth while maintaining prudent risk management.
Seventh, inflation protection should be built into pension payouts so that retirees’ purchasing power is not eroded by Nigeria’s volatile economy.
Eighth, the system must be inclusive of women, who dominate the informal sector yet often lack property rights or formal identification, by simplifying documentation requirements and providing gender-sensitive outreach.
Ninth, limited emergency withdrawal options could be introduced—strictly regulated—to help contributors handle crises without abandoning the system entirely.
Finally, transparency and accountability are non-negotiable; regular public reporting, independent audits, and user-friendly dashboards would strengthen confidence that contributions are safe and growing. If Nigeria can blend its innovative spirit with lessons from global best practices—combining Denmark’s social security ethos, Singapore’s savings discipline, and Canada’s inclusivity—it could transform the lives of millions of informal workers who currently face retirement with fear rather than hope.
Imagine Aisha, years from now, closing her market stall not in exhaustion and anxiety but in calm assurance that her pension will cover her basic needs; imagine Tunde hanging up his helmet knowing he can afford healthcare and shelter; imagine Ngozi harvesting not just crops but the fruits of a lifetime of secure savings. The suspense that hangs over the future of Nigeria’s informal workers can be resolved, but only if policymakers act boldly, creatively, and compassionately—because a nation that allows its hardest workers to age in poverty is a nation that undermines its own prosperity, while a nation that secures their retirement builds not just pensions, but peace.
Hope comes from innovation. Fintech-powered pension models that allow small, frequent contributions similar to informal savings associations like esusu offer ways to integrate pensions into existing savings cultures. Making pension contributions compatible with mobile money and agent networks could drastically reduce barriers to entry. Hope comes from public education. Building financial literacy campaigns, partnering with community leaders, marketplaces, trade associations, and digital platforms can help shift perceptions. A pension should be understood not as a distant bureaucratic programme, but as future self-insurance and dignity
The significance of having a pension plan for informal workers in Nigeria, given its large informal sector and high level of unemployment and underemployment, cannot be overstated, as it is deeply connected to social stability, economic sustainability, poverty reduction, and national development.
First, from a social protection and human dignity perspective, a pension plan for informal workers is critical because it provides a safety net for old age. Nigeria’s informal sector includes traders, artisans, mechanics, tailors, hairdressers, okada riders, gig workers, domestic workers, small-scale farmers, and street vendors, many of whom work hard throughout their lives but have no formal retirement benefits. Without a pension, these individuals often become completely dependent on their children, relatives, or charity in old age, which can strain families and increase intergenerational poverty. A well-structured pension system ensures that ageing informal workers can maintain a basic standard of living, access healthcare, and avoid extreme deprivation, thereby preserving their dignity and reducing elderly vulnerability.
Second, from an economic stability and poverty reduction standpoint, pensions play a crucial role in reducing old-age poverty. Nigeria already struggles with high poverty levels, and a large proportion of elderly citizens without income support exacerbates this problem. When informal workers lack pension savings, they continue working well into old age, often in physically demanding jobs, which reduces productivity and increases health risks. A pension system allows for smoother retirement transitions, reduces reliance on welfare, and ensures that older citizens remain consumers rather than economic burdens, thereby sustaining economic activity.
Third, pensions for informal workers are significant for financial inclusion and savings culture. Many Nigerians in the informal sector operate primarily in cash and have limited engagement with formal financial institutions. A pension plan tailored to informal workers, especially one integrated with mobile money and digital platforms, can encourage regular saving, improve financial literacy, and bring millions of people into the formal financial system. This, in turn, strengthens Nigeria’s overall financial sector and increases the pool of domestic savings available for investment in infrastructure, businesses, and development projects.
Fourth, the significance is evident in reducing dependence on government emergency support. Currently, the Nigerian government often has to intervene with ad-hoc social assistance programs, especially during crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic, inflation shocks, or economic downturns. If informal workers had functional pension savings, they would be better able to absorb economic shocks in retirement without relying heavily on government aid, reducing fiscal pressure on the state.
Fifth, pensions for informal workers contribute to intergenerational equity and family stability. In Nigeria, many elderly parents depend on their working children for survival, which places financial strain on younger generations who may already be struggling with unemployment, housing costs, and education expenses. A pension system reduces this burden, allowing younger Nigerians to invest in their own futures rather than being trapped in a cycle of supporting ageing relatives without external assistance.
Sixth, from a national development perspective, including informal workers in the pension system strengthens Nigeria’s long-term economic planning. Pension funds represent large pools of capital that can be invested in critical sectors such as housing, energy, transportation, and manufacturing. If millions of informal workers contribute even in small amounts, this could significantly expand Nigeria’s pension fund assets, providing stable, long-term financing for development projects that create jobs and stimulate growth.
Seventh, pensions for informal workers are important for gender equity, because women dominate many informal occupations in Nigeria, such as petty trading, market vending, tailoring, and caregiving roles. These women often have lower lifetime earnings, limited access to formal employment, and fewer assets. A targeted informal sector pension scheme can protect elderly women from destitution and reduce gender-based economic inequality in old age.
Eighth, the significance is also linked to public trust and governance. A transparent, accessible, and reliable pension system for informal workers can strengthen citizens’ trust in government institutions. Many informal workers currently distrust government programs due to past corruption, failed schemes, or poor implementation. A well-functioning pension plan that delivers real benefits would demonstrate that the state values all citizens, not just formal sector employees.
Lastly, given Nigeria’s demographic reality of a large and growing population, failing to integrate informal workers into a pension framework poses serious long-term risks. As life expectancy increases, the number of elderly Nigerians will rise significantly in the coming decades. Without a structured pension system for informal workers, Nigeria could face a severe old-age crisis characterised by mass poverty, social unrest, and increased pressure on healthcare and social services.
In summary, having a pension plan for informal workers in Nigeria is significant because it promotes social security, reduces poverty, enhances financial inclusion, supports economic stability, eases intergenerational burdens, strengthens national development, promotes gender equity, builds public trust, and prepares the country for its ageing population. For a nation where the majority of workers are informal, excluding them from pension coverage is not just an oversight; it is a major structural weakness that must be urgently addressed for Nigeria’s long-term prosperity and social cohesion.
Feature/OPED
Revived Argungu International Fishing Festival Shines as Access Bank Backs Culture, Tourism Growth
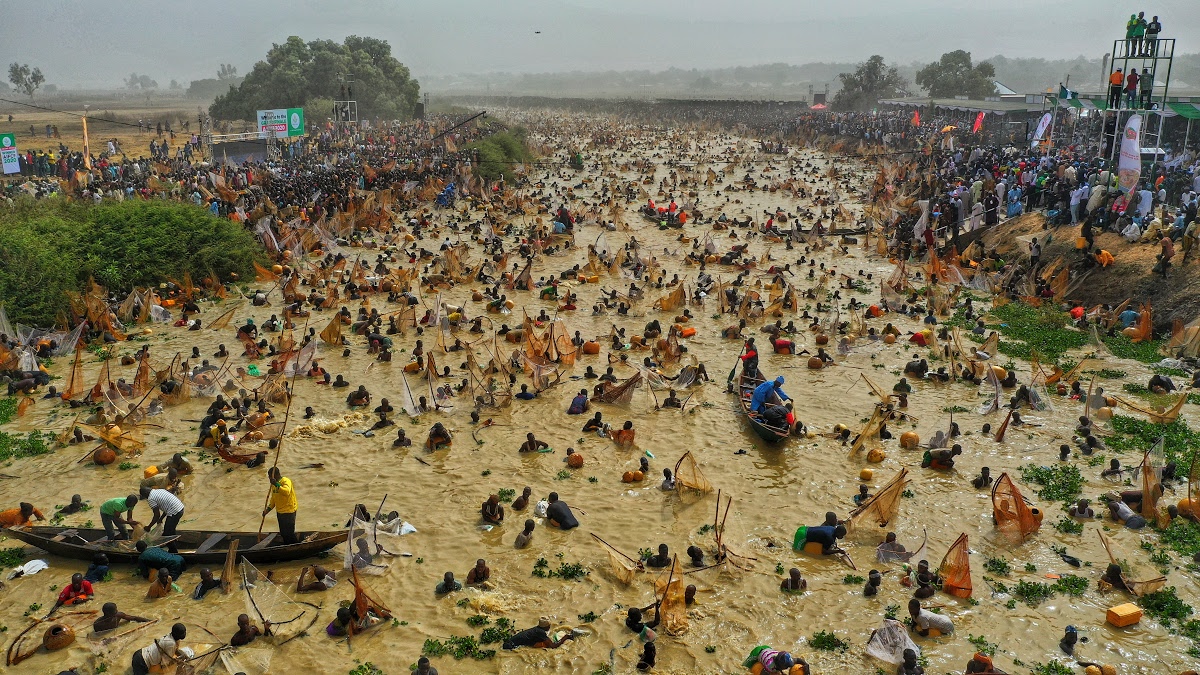

The successful hosting of the 2026 Argungu International Fishing Festival has spotlighted the growing impact of strategic public-private partnerships, with Access Bank and Kebbi State jointly reinforcing efforts to promote cultural heritage, tourism development, and local economic growth following the globally attended celebration in Argungu.
At the grand finale, Special Guest of Honour, Mr Bola Tinubu, praised the festival’s enduring national significance, describing it as a powerful expression of unity, resilience, and peaceful coexistence.
“This festival represents a remarkable history and remains a powerful symbol of unity, resilience, and peaceful coexistence among Nigerians. It reflects the richness of our culture, the strength of our traditions, and the opportunities that lie in harnessing our natural resources for national development. The organisation, security arrangements, and outlook demonstrate what is possible when leadership is purposeful and inclusive.”
State authorities noted that renewed institutional backing has strengthened the festival’s global appeal and positioned it once again as a major tourism and cultural platform capable of attracting international visitors and investors.
“Argungu has always been an iconic international event that drew visitors from across the world. With renewed partnerships and stronger institutional support, we are confident it will return to that global stage and expand opportunities for our people through tourism, culture, and enterprise.”
Speaking on behalf of Access Bank, Executive Director, Commercial Banking Division, Hadiza Ambursa, emphasised the institution’s long-standing commitment to supporting initiatives that preserve heritage and create economic opportunities.
“We actively support cultural development through initiatives like this festival and collaborations such as our partnership with the National Theatre to promote Nigerian arts and heritage. Across states, especially within the public sector space where we do quite a lot, we work with governments on priorities that matter to them. Tourism holds enormous potential, and while we have supported several hotels with expansion financing, we remain open to working with partners interested in developing the sector further.”
Reports from the News Agency of Nigeria indicated that more than 50,000 fishermen entered the historic Matan Fada River during the competition. The overall winner, Abubakar Usman from Maiyama Local Government Area, secured victory with a 59-kilogram catch, earning vehicles donated by Sokoto State and a cash prize. Other top contestants from Argungu and Jega also received vehicles, motorcycles and monetary rewards, including sponsorship support from WACOT Rice Limited.
Recognised by UNESCO as an Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity, the festival blends traditional fishing contests with boat regattas, durbar processions, performances, and international competitions, drawing visitors from across Nigeria and beyond.
With the 2026 edition concluded successfully, stakeholders say the strengthened collaboration between government and private-sector partners signals a renewed era for Argungu as a flagship cultural tourism destination capable of driving inclusive growth, preserving tradition, and projecting Nigeria’s heritage on the world stage.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn