Banking
Again, CBN Re-Introduces Charges on Cash Deposits, Withdrawals

By Daily Trust
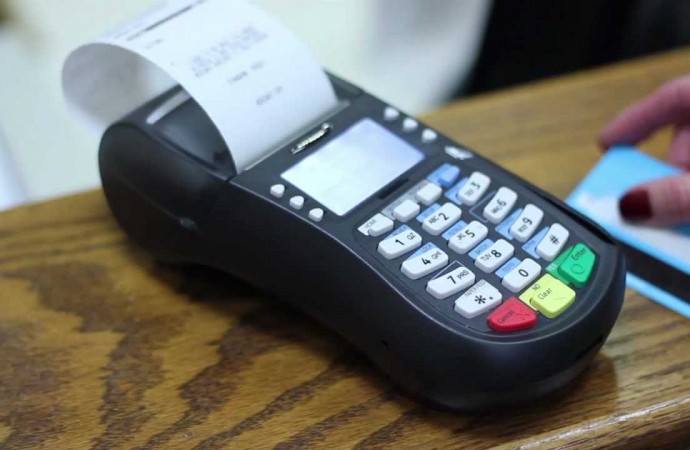
There are strong indications that the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) may have concluded arrangement to re-introduce cash handling fees for both deposits and withdrawals as its board of governors approve the full implementation of the cashless policy nationwide.
The CBN Deputy Governor, Operations, Mr Adebayo Adelabu, gave the hint while addressing the annual dinner of the Nigerian Electronic Fraud Forum (NeFF) in Lagos over the weekend.
Mr Adelabu said, “The committee of governors has approved the implementation of the full cashless policy yesterday and the CBN will release a circular which will detail out the process of re-adoption of the policy by next week (this week).”
It would be recalled that the apex bank had on April 22, 2017, suspended indefinitely, the nationwide implementation of the policy following massive outcry that greeted the reviewed cash handling fees.
In a circular signed by Mr Dipo Fatokun, Director, Banking and Payments System Department of CBN, the bank instructed banks to revert to old charges and refund customers who had been debited.
CBN had earlier announced new charges on deposits and withdrawals above a threshold of N500,000 for individuals and N3 million for corporate bodies.
The apex bank had directed banks to charge 1.5 percent and 2 percent for deposits and withdrawals ranging from N500,000 and N1 million in the individual category; 2 percent and 3 percent for amount above N1 million to N5 million; and 3 percent and 7.5 percent for amount above N5 million.
For corporate organisations, CBN fixed 2 percent and 5 percent for deposits and withdrawals between N3 million and N10 million respectively; 3 percent and 7.5 percent for above N10 million to N40 million; and 5 percent and 10 percent for amount above N40 million.
But the new circular said the existing policy before the announcement of the new policy shall remain in place in Lagos, Ogun, Kano, Abia, Anambra, Rivers and Abuja.
The circular further stated that the old charges to be reverted to are: 3 percent processing fee for withdrawals above N500,000 in the individual category and 5 percent for withdrawals above N3 million for corporate category, while no fees are charged for lodgements.
Cashless policy is a policy established in 2012 by the CBN to curb excesses in the handling of cash in Nigeria. It prescribed cash handling charges on daily withdrawals above N500,000 for individuals and N3,000,000 for corporate bodies. The policy was enforced not to eliminate the use of cash but to reduce the volume of cash in circulation.
The pilot run of the policy started on January 1, 2012 in Lagos State. The service charges were withheld till 30 March of the same year to allow for seamless migration from the manual to electronic devices.
The second stage of the pilot run started in Rivers, Anambra, Abia, Kano, Ogun and the Federal Capital Territory on July 1, 2013 while the programme nationwide started exactly a year after; on 31 July 2014.
Reacting to the announcement, Dr Uju Ogubunka, President, Bank Customers Association of Nigeria (BCAN) said, “The truth of the matter is that, there were reasons why the full implementation was suspended. The question therefore is, whether those reasons have been resolved.
“We all appreciate that we do not need to be carrying cash up and down, with its attendant cost of recycling.
“We also need to know if the policy will come under a new guideline or merely bringing back what they suspended before, we can then make informed decisions.”
Barrister Ken Ukaoha, President, National Association of Nigerian Traders (NANTS) commended the CBN for its laudable intervention in the economy but expressed worry that placing charges on deposits may encourage businesses keeping money outside the bank.
Mr Ukaoha said: “The CBN needs to do more on the domestic end. They need to reflect the views of the domestic trading environment.”
Ms Christine Lagarde, Managing Director of the International Monetary Fund (IMF), said Nigeria could save as much as $9 billion (N3.24 trillion) by shifting government payments from cash to digital systems.
Speaking in Ethiopia recently, Ms Lagarde said 1.7 percent of the country’s gross domestic product (GDP) could be saved via the digitisation of the country’s payment systems.
She said “the potential to help reduce corruption, increase revenues, and generate investments in health and education means digital tools could be a decisive factor in meeting the 2030 Sustainable Development Goals.”
Banking
All Set for Second HerFidelity Apprenticeship Programme

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
Registration for the second HerFidelity Apprenticeship Programme (HAP 2.0) organised by Fidelity Bank Plc has commenced.
The Divisional Head of Product Development at Fidelity Bank, Mr Osita Ede, informed newsmen that the initiative was designed to empower women with sustainable entrepreneurship skills.
The lender created the flagship women-empowerment initiative to equip women with practical, income‑generating skills and structured pathways to entrepreneurship.
“HerFidelity Apprenticeship Programme 2.0 reflects our commitment to continuous improvement. Having evaluated feedback from the first edition, we have returned with stronger partnerships and deeper mentorship programmes to ensure that women acquire not just skills, but sustainable economic opportunities,” he said.
“At the heart of the programme is guided, real‑world learning. Participants will undergo intensive apprenticeship training under reputable institutions and industry experts across select fields such as hair styling, shoe making, auto mechatronics, and interior decoration,” Mr Ede added.
He noted that HerFidelity Apprenticeship Programme 2.0 goes beyond skills acquisition by offering participants a wide range of business advisory services. These include business and financial literacy training, mentorship support throughout the apprenticeship journey, access to Fidelity Bank’s women‑focused and SME financial solutions, as well as guidance on business formalisation and growth strategies.
Further emphasising the bank’s vision, Mr Ede said, “By integrating structured mentorship with entrepreneurial development, Fidelity Bank is positioning women not just as trainees, but as future employers, innovators, and economic contributors within their communities. This aligns with our mandate to help individuals grow, businesses thrive, and economies prosper.”
Banking
The Alternative Bank Opens New Branch in Ondo

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
A new branch of The Alternative Bank (AltBank) has been opened in Ondo State as part of the expansion drive of the financial institution.
A statement from the company disclosed that the new branch would support export-oriented agribusinesses through Letters of Credit and commodity-backed trade finance, ensuring that local producers can scale beyond state borders.
For SMEs, the bank is introducing robust payment rails, asset financing for equipment and inventory, and supply chain-backed facilities that strengthen working capital without trapping businesses in interest-based debt cycles.
The Governor of Ondo State, Mr Lucky Aiyedatiwa, represented by his Chief of
Staff, Mr Olusegun Omojuwa, at the commissioning of the branch, underscored the importance of financial institutions in economic development.
“The pivotal role of financial institutions to economic growth and development of any economy cannot be overemphasised. It provides access to capital, supporting small and medium-scale enterprises and encouraging savings.
“Therefore, I have no doubt in my mind that the presence of The Alternative Bank in Ondo State will deepen financial services, create employment opportunities and stimulate economic activities across various sectors,” he said.
In her remarks, the Executive Director for Commercial and Institutional Banking (Lagos and South West) at The Alternative Bank, Mrs Korede Demola-Adeniyi, commended the state government’s leadership and outlined the lender’s long-term vision for Ondo State.
“As Ondo State steps into its next fifty years, and into the future anchored on the sustainable development championed during the recent anniversary celebrations, The Alternative Bank is here to be the financial engine for that vision. We didn’t come to Akure to hang banners. We came to fund work, farms, shops, and factories.”
With Ondo State’s economy anchored largely on agriculture, particularly cocoa production, poultry farming, and other cash crops, alongside a growing SME and trade ecosystem, AltBank is deploying sector-specific financing solutions tailored to these strengths.
For cocoa aggregators, processors and poultry operators, the bank will provide production financing, facility expansion support, machinery lease structures, and structured trade facilities under its joint venture and cost-plus financing models, with transaction cycles of up to 180 days for commodity trades and longer-term structured asset financing for equipment and infrastructure.
The organisation is a notable national non-interest bank with a physical network now surpassing 170 locations, deploying capital to solve real-world challenges through initiatives such as the Mata Zalla project, which saw to the training of hundreds of women as electric tricycle drivers and mechanics.
Banking
Recapitalisation: 20 Nigerian Banks Now Fully Compliant—Cardoso

By Adedapo Adesanya
The Governor of the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN), Mr Yemi Cardoso, announced on Tuesday that the country’s banking sector is making strong progress in the recapitalisation drive, with 20 banks now fully compliant.
Mr Cardoso disclosed this during a press conference at the first Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meeting of 2026, where he also highlighted positive developments in the nation’s foreign reserves.
On March 28, 2024, the apex bank announced an increase in the minimum capital requirements for commercial banks with international licences to N500 billion.
National and regional financial institutions’ capital bases were pegged at N200 billion and N50 billion, respectively.
Also, CBN raised the merchant bank minimum capital requirement to N50 billion for national licence holders.
The banking regulator said the new capital base for national and regional non-interest banks is N20 billion and N10 billion, respectively.
To meet the minimum capital requirements, CBN advised banks to consider the injection of “fresh equity capital through private placements, rights issue and/or offer for subscription”.
Following the development, several banks announced plans to raise funds through share and bond issuances.
In January, Zenith Bank said it had raised N350.46 billion through rights issue and public offer to meet the CBN minimum capital requirement.
Guaranty Trust Holding Company Plc (GTCO), on July 4, said it had successfully priced its fully marketed offering on the London Stock Exchange (LSE).
In September, the CBN governor said 14 banks fully met their recapitalisation requirements — up from eight banks in July.
With one month to the central bank’s March 31, 2026, recapitalisation deadline, 13 Nigerian lenders are yet to cross the finish line.
Additionally, the governor noted that 33 banks have raised funds as part of the ongoing recapitalisation exercise, signalling robust capital mobilisation across the sector.
He stated that gross foreign reserves have climbed to a 13-year high of $50.4 billion as of mid-February 2026.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn