Economy
Drought Pushing Food Prices up Sharply in East Africa

By Dipo Olowookere
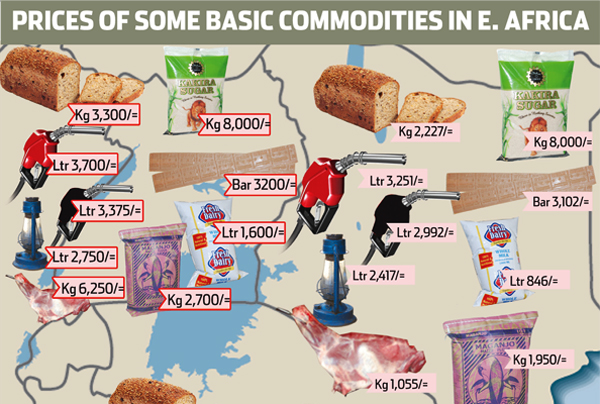
Drought throughout East Africa has sharply curbed harvests and pushed the prices of cereals and other staple foods to unusually high levels, posing a heavy burden to households and special risks for pastoralists in the region.
Local prices of maize, sorghum and other cereals are near or at record levels in swathes of Ethiopia, Kenya, Somalia, South Sudan, Uganda and the United Republic of Tanzania, according to the latest Food Price Monitoring and Analysis Bulletin (FPMA).
Inadequate rainfall in most areas of the sub-region has put enormous strain on livestock and their keepers. Poor livestock body conditions due to pasture and water shortages and forcible culls mean animals command lower prices, leaving pastoralists with even less income to purchase basic foodstuffs.
“Sharply increasing prices are severely constraining food access for large numbers of households with alarming consequences in terms of food insecurity,” said Mario Zappacosta, FAO senior economist and coordinator of the Global Information and Early Warning System.
The trends in East Africa, where prices of staple cereals have doubled in some town markets, stand in marked contrast to the stable trend of FAO’s Food Price Index, which measures the monthly change in international prices of a basket of traded food commodities.
The difference is due to the drought that is hammering the sub-region, where food stocks were already depleted by the strong El Niño weather event that ended only last year. Poor and erratic rainfall in recent months, crucial for local growing seasons, are denting farm output.
Somalia’s maize and sorghum harvests are estimated to be 75 percent down from their usual level, and some 6.2 million people, more than half of the country’s total population, now face acute food insecurity, with the majority of those most affected living in rural areas.
Soaring prices
The FPMA Bulletin tracks food price trends on a granular level and in local terms, with an eye to flagging instances where the prices of essential food commodities increase sharply or are abnormally high.
In Mogadishu, prices of maize increased by 23 percent in January, and. the increase was even sharper in the main maize producing region of Lower Shabelle. Overall, in key market towns of central and southern Somalia, coarse grain prices in January have doubled from a year earlier.With an earlier than usual depletion of household stocks during the coming lean season and preliminary weather forecasts raising concerns for the performance of the next rainy season, prices are likely to further escalate in the coming months.
Maize prices in Arusha, United Republic of Tanzania, have almost doubled since early 2016, while they are 25 percent higher than 12 months earlier in the country’s largest city, Dar Es Salaam.
In South Sudan, food prices are now two to four times above their levels of a year earlier, exacerbated by ongoing insecurity and the significant depreciation of the local currency.
In Kenya, where eastern and coastal lowlands as well as some western areas of the Rift Valley all suffered below-average rainfall, maize prices are up by around 30 percent, with the increase somewhat contained somewhat thanks to sustained imports from Uganda.
Cereal prices aren’t the only ones rising. Beans now cost 40 percent more in Kenya than a year earlier, while in Uganda – where maize prices are now up to 75 percent higher than a year earlier – and increasing around the key border trading hub of Busia, the prices of beans and cassava flour are both about 25 percent higher than a year ago in the capital city, Kampala.
Double jeopardy for pastoralists
Drought-affected pastoral areas in the region face even harsher conditions.
In Somalia, goat prices are up to 60 percent lower than a year ago, while in pastoralist areas of Kenya the prices of goats declined by up to 30 percent over the last twelve months.
Shortages of pasture and water caused livestock deaths and reduced body mass, prompting herders to sell animals while they can, as is also occurring in drought-wracked southern Ethiopia. This also pushes up the prices of milk, which is, for instance, up 40 percent on the year in Somalia’s Gedo region.
Lower income from livestock collides with higher prices for cereals and other staple foods in a wrenching shock to terms of trade for pastoralist households. A medium-sized goat in Somalia’s Buale market was worth 114 kilograms of maize in January 2016, but at today’s prices can be traded for only 30 kilograms of the grain.
FAO uses its proprietary FPMA Tool, accessible to the public online, to monitor local markets and gather data for more than 1350 domestic price series in 91 countries around the globe in order to produce its Indicator of Food Price Anomalies.
Economy
Again, OPEC Cuts 2024, 2025 Oil Demand Forecasts

By Adedapo Adesanya
The Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) has once again trimmed its 2024 and 2025 oil demand growth forecasts.
The bloc made this in its latest monthly oil market report for December 2024.
The 2024 world oil demand growth forecast is now put at 1.61 million barrels per day from the previous 1.82 million barrels per day.
For 2025, OPEC says the world oil demand growth forecast is now at 1.45 million barrels per day, which is 900,000 barrels per day lower than the 1.54 million barrels per day earlier quoted.
On the changes, the group said that the downgrade for this year owes to more bearish data received in the third quarter of 2024 while the projections for next year relate to the potential impact that will arise from US tariffs.
The oil cartel had kept the 2024 outlook unchanged until August, a view it had first taken in July 2023.
OPEC and its wider group of allies known as OPEC+ earlier this month delayed its plan to start raising output until April 2025 against a backdrop of falling prices.
Eight OPEC+ member countries – Saudi Arabia, Russia, Iraq, United Arab Emirates, Kuwait, Kazakhstan, Algeria, and Oman – decided to extend additional crude oil production cuts adopted in April 2023 and November 2023, due to weak demand and booming production outside the group.
In April 2023, these OPEC+ countries decided to reduce their oil production by over 1.65 million barrels per day as of May 2023 until the end of 2023. These production cuts were later extended to the end of 2024 and will now be extended until the end of December 2026.
In addition, in November 2023, these producers had agreed to voluntary output cuts totalling about 2.2 million barrels per day for the first quarter of 2024, in order to support prices and stabilise the market.
These additional production cuts were extended to the end of 2024 and will now be extended to the end of March 2025; they will then be gradually phased out on a monthly basis until the end of September 2026.
Members have made a series of deep output cuts since late 2022.
They are currently cutting output by a total of 5.86 million barrels per day, or about 5.7 per cent of global demand. Russia also announced plans to reduce its production by an extra 471,000 barrels per day in June 2024.
Economy
Aradel Holdings Acquires Equity Stake in Chappal Energies

By Aduragbemi Omiyale
A minority equity stake in Chappal Energies Mauritius Limited has been acquired by a Nigerian energy firm, Aradel Holdings Plc.
This deal came a few days after Chappal Energies purchased a 53.85 per cent equity stake in Equinor Nigeria Energy Company Limited (ENEC).
Chappal Energies went into the deal with Equinor to take part in the oil and gas lease OML 128, including the unitised 20.21 per cent stake in the Agbami oil field, operated by Chevron.
Since production started in 2008, the Agbami field has produced more than one billion barrels of oil, creating value for Nigerian society and various stakeholders.
As part of the deal, Chappal will assume the operatorship of OML 129, which includes several significant prospects and undeveloped discoveries (Nnwa, Bilah and Sehki).
The Nnwa discovery is part of the giant Nnwa-Doro field, a major gas resource with significant potential to deliver value for Nigeria.
In a separate transaction, on July 17, 2024, Chappal and Total Energies sealed an SPA for the acquisition by Chappal of 10 per cent of the SPDC JV.
The relevant parties to this transaction are working towards closing out this transaction and Ministerial Approval and NNPC consent to accede to the Joint Operating Agreement have been obtained.
“This acquisition is in line with diversifying our asset base, deepening our gas competencies and gaining access to offshore basins using low-risk approaches.
“We recognise the strategic role of gas in Nigeria’s energy future and are happy to expand our equity holding in this critical resource.
“We are committed to the cause of developing the significant value inherent in the assets, which will be extremely beneficial to the country.
“Aradel hopes to bring its proven execution competencies to bear in supporting Chappal’s development of these opportunities,” the chief executive of Aradel Holdings, Mr Adegbite Falade, stated.
Economy
Afriland Properties Lifts NASD OTC Securities Exchange by 0.04%

By Adedapo Adesanya
Afriland Properties Plc helped the NASD Over-the-Counter (OTC) Securities Exchange record a 0.04 per cent gain on Tuesday, December 10 as the share price of the property investment rose by 34 Kobo to N16.94 per unit from the preceding day’s N16.60 per unit.
As a result of this, the market capitalisation of the bourse went up by N380 million to remain relatively unchanged at N1.056 trillion like the previous trading day.
But the NASD Unlisted Security Index (NSI) closed higher at 3,014.36 points after it recorded an addition of 1.09 points to Monday’s closing value of 3,013.27 points.
The NASD OTC securities exchange recorded a price loser and it was Geo-Fluids Plc, which went down by 2 Kobo to close at N3.93 per share, in contrast to the preceding day’s N3.95 per share.
During the trading session, the volume of securities bought and sold by investors increased by 95.8 per cent to 2.4 million units from the 1.2 million securities traded in the preceding session.
However, the value of shares traded yesterday slumped by 3.7 per cent to N4.9 million from the N5.07 million recorded a day earlier, as the number of deals surged by 27.3 per cent to 14 deals from 11 deals.
Geo-Fluids Plc remained the most active stock by volume (year-to-date) with 1.7 billion units sold for N3.9 billion, trailed by Okitipupa Plc with 752.2 million units valued at N7.8 billion, and Afriland Properties Plc with 297.5 million units worth N5.3 million.
Also, Aradel Holdings Plc remained the most active stock by value (year-to-date) with 108.7 million units worth N89.2 billion, followed by Okitipupa Plc with 752.2 million units valued at N7.8 billion, and Afriland Properties Plc with 297.5 million units sold for N5.3 billion.
-

 Feature/OPED5 years ago
Feature/OPED5 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism8 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz2 years ago
Showbiz2 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking6 years ago
Banking6 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy2 years ago
Economy2 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking2 years ago
Banking2 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports2 years ago
Sports2 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn
-

 Technology4 years ago
Technology4 years agoHow To Link Your MTN, Airtel, Glo, 9mobile Lines to NIN























