Economy
Understanding Private Equity and Alternative Investments

By FBNQuest
Although there are a variety of options for raising capital and attracting investors, equity is one of the two most sought-after options.
It allows a company to give a share of ownership of its business to an investor in expectation of a return as the business grows. Unlike public equity (stock market) with ownership of shares in a public company, private equity (PE) simply means ownership of shares in a private company.
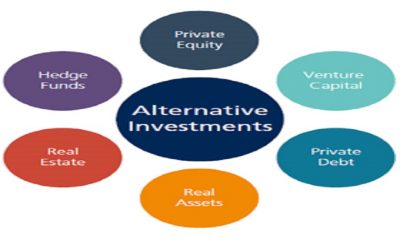
Private equity is a type of capital investment (asset or security) made to (target) companies that are not publicly traded on a stock exchange.
As an alternative form of private financing, private equity allows investors directly invest in companies through which such investors gain an ownership stake in the companies. Investors seek PE funds to earn returns that are considered to be better than those from the public equity markets.
To avoid debt, companies can sell their stocks to raise money that can be used to fund new technology, make acquisitions, expand working capital, and fund projects geared towards business growth.
Usually, the financial information on stocks of such a company is not disclosed to the public, rather, an investor can only speculate on the asset worth of the intending company.
Private equity involves three parties: the investors who supply the capital, the private equity firm that manages and invests the money on behalf of the investor via a private equity fund, and the company (known as Portfolio Company) that the private equity firm invests in.
A private equity firm’s ultimate goal is to sell or exit portfolio companies to deliver superior returns (above the benchmark return also referred to as Internal Rate of Return (IRR) to earn carried interests).
The most widely adopted investment strategies by PE investments are leveraged buyouts (LBOs) and venture capital (VC) investments.
In LBOs, a PE firm will raise debt from institutional investors on the back of a target company and assume control of the target company, while using the cash flows of the target company to pay the acquisition capital. Whereas, the VC makes investment in young and fast-growing companies in an industry that has the potential for exponential growth while adding value to the firm being taken up. In some cases, PE firms grow and improve a middle-market company with the aim to sell or exit to a mature company within a specified period.
Generally, private equity firms are active investors who are involved in the board level and monitor the financial and operating performance of portfolio companies.
However, some private equity firms are involved in the day-to-day operations of portfolio companies and may take C-level positions such as CEO, CFO, CIO and COO to ensure that value creation initiatives are implemented in the portfolio companies to ensure that increase in revenue, improvement of operational efficiency and corporate governance.
A private equity fund is typically opened to institutional and accredited (individual or business entity) investors who invest large sums of money for a long period.
Institutional investors are companies or organisations like endowment funds, commercial banks, hedge funds, mutual fund managers, and insurance companies that invest money on behalf of other people.
Accredited investors on the other hand are individuals or a business entity that invest based on their income, net worth, asset size, governance status, or professional experience. The reason is that private equity as an asset class is generally illiquid and has a long lock-up period and only ideal for investors with a large asset size (or AuM).
Other alternative investments include infrastructure assets, art, antique furniture, automobiles, real estate, commodities, exchange-traded funds, and hedge funds.
The market performance of traditional investments and alternative investments are independent of each other, hence, the inclusion of alternative investments in a portfolio can reduce its risk through diversification.
Before the coronavirus outbreak, PE investments in Nigeria have been flourishing and as a result, in 2019, Nigeria was described by the African Private Equity and Venture Capital Association (AVCA) as one of the most attractive destinations for PE investments. Between January and February 2019, PE in Nigeria recorded investments worth N277.64 billion ($767 million), an improvement of 345 per cent compared to N62.37 billion ($172 million) worth of deals closed during the corresponding period in 2018.
The deals within the first two months of 2019 included the 100 per cent acquisition of Chi Ltd by Coca-Cola Company for the sum of $500 million, which accounted for 65 per cent of the total private equity investments within that period.
Other notable deals included Access Bank Plc’s acquisition of Diamond Bank Plc, the Partech- led Series A funding of Kudi, a financial services provider, and the acquisition of Wakanow, a travel agency, by the Carlyle Group valued at $40 million, to mention a few.
Why invest in private equity?
Private equity firms have grown over the years to become attractive investment vehicles for wealthy individuals and institutions who manage large pools of capital.
PE often guarantees better returns compared to other investments, with some private equity managers outperforming the public markets.
To diversify holdings, investors turn to private equity for higher returns than do public market. Specifically, such investments are for investors who can afford to have capital locked up for long periods.
Investors in private equity funds are called limited partners. As a limited partner, you get a return on your investment when the private equity firm sells the company it purchases while the private equity firm (also called general partners) takes some percentage as profit.
In Nigeria, different PE firms like FBNQuest Funds have their specific deal sizes, investment horizons, sector focus, fundraising timelines, and exit strategies.
As one of the leading alternative investments managers in Nigeria, FBNQuest Funds has been in operations for over 17 years and has invested in over 70 private companies through direct investing and their expertise and exposure to PE and VC Funds. Domiciled in Nigeria, the firm has investments in companies in Nigeria and other countries within the Sub-Saharan Africa region.
Economy
NECA, CPPE Laud CBN’s 0.50% Interest Rate Cut

By Adedapo Adesanya
The Nigeria Employers’ Consultative Association (NECA) and the Centre for the Promotion of Private Enterprise (CPPE) have separately commended the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) for reducing the Monetary Policy Rate (MPR) from 27.0 per cent to 26.5 per cent at its 304th Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meeting.
In reaction, NECA Director-General, Mr Adewale-Smatt Oyerinde, praised the decision in a statement, noting that the 50 basis-point cut is “a cautious but noteworthy signal” that authorities were responding to sustained pressures on businesses.
He said the marginal reduction might not immediately lower lending rates, but reflected “a gradual shift toward supporting growth without undermining price stability”.
According to him, the overall stance remained tight, with the Cash Reserve Ratio retained at 45 per cent and the liquidity ratio at 30 per cent.
He added that the asymmetric corridor around the MPR was also maintained, reinforcing a cautious monetary approach.
“With a substantial portion of deposits still sterilised, banks’ capacity to expand credit to the real sector may remain constrained in the near term,” he said.
Mr Oyerinde described the move as “a careful balancing act” aimed at moderating inflation without worsening pressures on businesses.
He noted that firms continued to grapple with high operating costs, exchange rate volatility and weakened consumer demand.
“Inflation, particularly in food, energy and transportation, remains a significant challenge to employers and households,” he said.
He stressed that the modest easing must be supported by coordinated fiscal and structural reforms to address supply-side constraints.
Such reforms, he said, should improve infrastructure and enhance productivity across key sectors of the economy.
Mr Oyerinde urged financial institutions to ensure the MPR reduction was gradually reflected in lending conditions for manufacturers and SMEs.
He affirmed that although the MPC had not fully relaxed its tightening stance, the rate cut signalled cautious optimism.
“Sustained improvements in inflation, exchange rate stability and investor confidence will determine scope for further easing that supports growth and employment,” he said.
On its part, the CPPE said the decision reflected improving macroeconomic fundamentals and a cautious shift from aggressive tightening.
The organisation noted that sustained disinflation, stronger external reserves, an improved trade balance and relative exchange-rate stability had created room for monetary easing.
It said the rate cut could boost investor confidence and support private-sector growth, but cautioned that weak monetary transmission might limit its impact on lending rates.
The CPPE identified high cash reserve requirements, elevated lending rates, government borrowing and structural banking costs as major constraints to effective transmission.
The group also stressed the need for fiscal consolidation, citing high public debt, persistent deficits and rising debt-service obligations as risks to macroeconomic stability.
According to the chief executive of CPPE, Mr Muda Yusuf, effective policy coordination and stronger transmission mechanisms were critical to unlocking investment and sustaining growth, lauding the CBN for what he described as a measured and data-driven policy adjustment.
The CPPE boss noted that the easing reflected strengthening macroeconomic performance, declining inflation, growing reserves, improved trade balance and enhanced foreign exchange stability.
Mr Yusuf added that for the benefits of monetary easing to be fully realised, authorities must strengthen transmission to ensure lower lending rates for the real sector and advance credible fiscal consolidation to safeguard stability.
He said that if supported by structural reforms and disciplined fiscal management, the current policy direction could unlock a stronger investment cycle and more durable economic growth.
Economy
NASD Index Falls 0.28% as Investors Lose N6.64bn

By Adedapo Adesanya
The NASD Over-the-Counter (OTC) Securities Exchange extended the negative start to the week by 0.28 per cent on Tuesday, February 24, with the market capitalisation down by N6.64 billion to close at N2.378 trillion versus Monday’s N2.384 trillion, and the NASD Unlisted Security Index (NSI) falling by 11.1 points to 3,974.80 points from 3,985.90 points.
At the session, transaction value skyrocketed by 1,706.3 per cent to N1.2 billion from the previous day’s N61.8 million, as the transaction volume increased by 59.1 per cent to 11.6 million units from 7.3 million units, and the number of deals expanded by 23.1 per cent to 48 deals from the preceding session’s 39 deals.
Central Securities Clearing System (CSCS) Plc remained the most active stock by value on a year-to-date basis with 33.7 million units exchanged for N2.0 billion, Okitipupa Plc was next with 6.2 million units traded for N1.1 billion, and Geo-Fluids Plc occupied the third position with 121.0 million units valued at N474.9 million.
Resourcery Plc emerged as the most traded stock by volume on a year-to-date basis with 1.05 billion units worth N408.7 million, followed by Geo-Fluids Plc with the sale of 121.0 million units for N474.9 million, and CSCS Plc with 33.7 million units worth N2.0 billion.
Yesterday, the market breadth was flat after the bourse finished with three price gainers and three price losers led by MRS Oil Plc, which shed N14.50 to close at N200.00 per share versus the previous day’s N214.50 per share, CSCS Plc depleted by N1.39 to N65.82 per unit from N67.21 per unit, and Geo-Fluids Plc depreciated by 1 Kobo to close at N3.30 per share versus Monday’s N3.31 per share.
The price gainers were led by FrieslandCampina Wamco Nigeria Plc, which improved its value by N1.60 to close at N95.00 per unit compared with the preceding session’s N93.40 per unit, Afriland Property Plc gained 83 Kobo to sell at N18.00 per share versus N17.17 per share, and First Trust Mortgage Bank Plc advanced by 13 Kobo to N1.45 per unit from N1.32 per unit.
Economy
Nigerian Exchange Sheds 0.92%

By Dipo Olowookere
The Nigerian Exchange (NGX) Limited depreciated by 0.92 per cent on Tuesday after the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) slashed the benchmark interest rate by 0.5 per cent to 26.50 per cent at the end of its first Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meeting for 2026.
Sell-offs mainly occurred in the consumer goods and insurance sectors, shedding 4.74 per cent and 1.31 per cent, respectively.
However, bargain-hunting remained in the others, with the industrial goods index gaining 1.92 per cent, the banking counter grew by 1.23 per cent, and the energy sector soared by 0.15 per cent.
When the bourse ended for the session, the All-Share Index (ASI) gave up 1,779.03 points to close at 194,484.52 points compared with the previous day’s 196,263.55 points, and the market capitalisation declined by N1.142 trillion to N124.827 trillion from N125.969 trillion.
DAAR Communications depreciated by 10.00 per cent to N2.25, Tantalizers also declined by 10.00 per cent to N4.86, BUA Foods shrank by 9.99 per cent to N760.60, Ellah Lakes slumped 9.96 per cent to N10.40, and Japaul lost 9.95 per cent to trade at N3.80.
Conversely, Jaiz Bank appreciated by 10.00 per cent to N12.76, Infinity Trust Mortgage Bank went up by 9.83 per cent to N19.00, FCMB gained 9.72 per cent to close at N13.55, Fortis Global Insurance chalked up 9.09 per cent to finish at 72 Kobo, and Sterling Holdco grew by 7.50 per cent to N8.60.
A total of 27 stocks ended on the gainers’ chart and 40 stocks finished on the losers’ table, indicating a negative market breadth index and weak investor sentiment.
Yesterday, investors bought and sold 1.1 billion equities worth N53.4 billion in 72,218 deals compared with the 1.3 billion equities valued at N31.5 billion in 95,091 deals recorded a day earlier.
This showed that the value of transactions went up by 69.52 per cent, the volume of trades declined by 15.39 per cent, and a slip in the number of deals by 24.05 per cent.
During the session, Japaul was the most active stock with 102.4 million units worth N399.8 million, Access Holdings exchanged 97.9 million units valued at N2.6 billion, Fortis Global Insurance traded 75.2 million units for N54.1 million, Zenith Bank sold 67.6 million units valued at N6.2 billion, and FCMB transacted 46.4 million units worth N612.2 million.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn