Economy
West African Economies’ Risk-Reward Score Improve
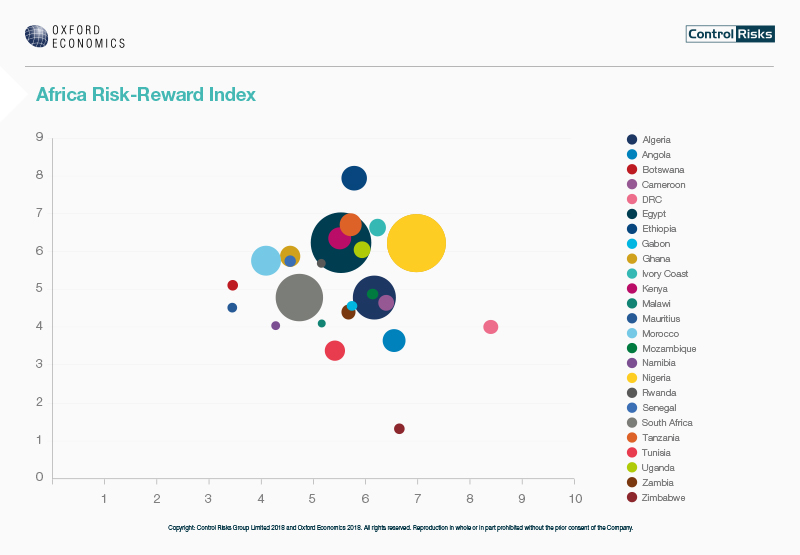
By Dipo Olowookere
Increased political stability, improved commodity prices and effective public economic reforms led to an improvement of the risk-reward score in several West African economies, according to the 2018 Africa Risk-Reward Index from Control Risks and Oxford Economics.
Ghana leads these positive developments for West Africa, recording the strongest improvement in its risk-reward score in Africa, after Zimbabwe and Egypt. Both Nigeria and Senegal benefit from a greatly improved risk score.
Tom Griffin, Senior Partner for West Africa at Control Risks, comments that, “In 2017 many West African governments have embarked on an impressive journey to implement the right reforms for economic growth and improvement of investors’ confidence.
“Since coming to power in January 2017, Ghana’s government has continued to undertake a programme of macroeconomic reforms which have focused on reducing the deficit and external debt. In the last year, this had a particularly positive impact on issues such as credit and exchange risk.
“At the same time, Ghana has attempted to improve the business environment for investors by reducing the bureaucratic and taxation burden, as well as laying out plans for further investment activity in the oil and gas and manufacturing sectors.
“In Nigeria, the recently initiated Economic Recovery and Growth Plan has begun to tackle some of the economy’s challenges, including corruption and an infrastructure deficit.
“The plan has also sought to remove bottlenecks to improve the ease of doing business, which in turn boosts investors’ confidence.
“In the last three years, Senegal’s Emerging Senegal Plan has already led to steady growth, reaching close to 6.4% in 2017.
“The reduction in its risk score is one of the most positive changes in the 2018 Africa Risk-Reward Index and can be explained by structural reforms to improve the business environment, strengthened macro-economic fundamentals and a controlled debt management policy.”
Further findings of the report showed that Angola’s leadership change has not yet improved its reward score, but its risk score has gone down: Angola’s new president, João Lourenço, has acted with remarkable speed and decisiveness to consolidate his authority. Efforts to dismantle his predecessor’s networks have provided new opportunities for foreign investment in sectors previously dominated by companies linked to the former president and his family. Combined with an improved regulatory environment, investors can seek opportunities predominantly in the oil and gas, diamond, and telecommunications sectors. Reward score: 3.65 / risk score: 6.55.
South Africa – slightly increased reward score and reduced risk score as political uncertainty eases: Investor confidence has increased since Cyril Ramaphosa assumed the presidency in February 2018. The implementation of policies – intended to consolidate fiscal expenditure and tackle corruption in public institutions and state-owned enterprises – increases opportunities for doing business in South Africa. But deeply entrenched patronage networks and electoral pressure ahead of the 2019 general elections will contribute to a slow recovery of South Africa. Reward score: 4.78 / risk score: 4.74
Kenya’s reward score remains one of the highest in sub-Saharan Africa, but the government’s external debt burden raises concerns: Winning the election in 2017, Kenya’s leading Jubilee Party of Kenya continues its pro-business policies. However, concerns arise over the government’s external debt burden, with a new USD 2bn Eurobond issued in February even as the proceeds of a previous issue have yet to be fully accounted for. Furthermore, improving relations between the government and the opposition will be instrumental in ensuring that political tensions do not undermine economic growth, and more prudent fiscal and macroeconomic policies are needed to maintain positive economic prospects. Reward score: 6.36 / risk score: 5.51
Côte d’Ivoire, with a forecasted real GDP growth rate of 7% in 2018, continues its impressive economic recovery, but great challenges remain: With reforms to the business environment and efforts to bring foreign investors back after the 2010-2011 crisis, Côte d’Ivoire has achieved amongst the highest growth rates in the world in recent years, and sectors such as construction, telecommunications, banking and retail have seen considerable growth. However, severe obstacles to a full recovery persist, including political interference and corruption, socioeconomic discontent, shortcomings in security-sector reform, and growing competition ahead of the potentially volatile 2020 presidential poll. Reward score: 6.51 / risk score: 6.24.
Senegal – growing investment and a reduced risk score presage continuous growth: Under the Emerging Senegal Plan, growth has increased steadily over the last three years, reaching close to 6.4% in 2017. Growing exports, a more diversified economy and increased interest from large international investors as a result of the promising offshore oil and gas discoveries make Senegal one of the poster children in sub-Saharan Africa. The reduction in its risk score is one of the most positive changes in the 2018 Africa Risk-Reward Index. Reward score: 5.76 / risk score: 4.56
Morocco – economic reforms improve the country’s resilience and make its exports more competitive, but social discontent remains a challenge: With one of the lowest risk scores on the 2018 Africa Risk-Reward Index and a relatively stable reward score, Morocco’s economic reforms prove to be a success. Medium-term growth will be enhanced by continued reforms to facilitate foreign investment, access to finance, quality of education and the business environment, as these represent the primary constraints to competitiveness and doing business. However, social-economic unrest over poor living conditions persists particularly in interior regions. Reward score: 5.77 / risk score: 4.10.
Economy
Naira Trades N1,390/$1 at Parallel Market, N1,335/$1 at Official Market

By Adedapo Adesanya
It was another wonderful day for the Nigerian Naira in the different segments of the foreign market (FX) market on Tuesday, February 17, as it appreciated against the United States Dollar at the close of business.
In the parallel market, it improved its value on the greenback by N30 to sell for N1,390/$1 compared with the previous day’s rate of N1,420/$1, and at the GTBank forex desk, it gained N4 to trade at N1,363/$1 versus the preceding session’s N1,367/$1.
As for the official market, which is known as the Nigerian Autonomous Foreign Exchange Market (NAFEX), the local currency gained N11.82 or 0.88 per cent to close at N1,335.96/$1 versus Monday’s price of N1,347.78/$1.
In the same segment of the market, the domestic currency chalked up N32.43 against the Pound Sterling to finish at N1,806.75/£1 compared with the previous day’s N1,839.18/£1, and gained N18.82 on the Euro to close at N1,579.24/€1 compared with the N1,598.06/€1 it was traded a day earlier.
Improved foreign exchange supply levels following recent high demand pressures helped to sustain the currency’s advance. A portion of the delayed demand was eliminated with licensed Bureau De Change (BDC) businesses fully helping to alleviate any development.
While other supply sources, including exporters, non-bank corporations, and other market actors, pause stoked pressures on the exchange rate, their presence is anticipated to increase liquidity and flow.
Foreign reserves were last reported at $47.80 billion after appreciating by $135.75 million. The build-up in reserves has been supported by favourable external conditions, including stronger oil-related inflows and improved FX market stability.
The market is looking forward to a rate cut when the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meets next week after inflation decelerated further to 15.10 per cent.
Meanwhile, the cryptocurrency market was down as software stocks continued to plunge, creating a ripple effect on the digital assets.
Market analysts noted that consolidation is expected as crypto searches for a new narrative strong enough to pull capital back from AI stocks and commodities.
Litecoin (LTC) declined by 1.8 per cent to $53.99, Bitcoin decreased by 1.7 per cent to $67,446.46, Cardano (ADA) dropped 1.5 per cent to trade at $0.2810, Binance Coin (BNB) slumped 1.4 per cent to $617.60, Solana (SOL) depreciated by 0.9 per cent to $84.97, Ripple (XRP) shrank by 0.7 per cent to $1.47, and Dogecoin (DOGE) went down by 0.04 per cent to $0.1005.
On the flip side, Ethereum (ETH) appreciated by 0.2 per cent to $1,992.22, while the US Dollar Tether (USDT) and the US Dollar Coin (USDC) remained unchanged at $1.00 apiece.
Economy
Oil Dips 2% Amid Progress in US-Iran Nuclear Talks

By Adedapo Adesanya
Oil was down by about 2 per cent on Tuesday on hopes tensions between the United States and Iran were easing after Iran’s foreign minister said the countries had reached an understanding regarding nuclear talks.
Brent futures fell $1.23 or 1.8 per cent to $67.42 a barrel, and the US West Texas Intermediate (WTI) futures slipped 56 cents or 0.9 per cent to $62.33 per barrel.
According to Iranian Foreign Minister, Mr Abbas Araqchi, his country and the United States reached an understanding on the main “guiding principles” in a second round of indirect talks in Geneva, Switzerland, over their nuclear dispute on Tuesday.
However, this does not mean a deal is imminent.
Iran’s supreme leader said on Tuesday that any US attempt to depose his government would fail as the US continued a military buildup exercise in the Middle East.
Iran will close parts of the critical oil shipping lane in the Middle East, the Strait of Hormuz, for a few hours on Tuesday as it is conducting military drills in the area. The government said the partial closure is due to security precautions.
The Strait of Hormuz, the narrow lane between Iran and Oman, is the world’s most critical oil transit chokepoint, and the oil market has time and again feared Iran could attempt to close the lane. In 2024, oil flow through the strait averaged 20 million barrels per day, or the equivalent of about 20 per cent of global petroleum liquids consumption.
Iran and fellow Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) members Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Kuwait and Iraq export most of their crude via the Strait, mainly to Asia.
Negotiators from Ukraine and Russia concluded the first of two days of US-mediated peace talks in Geneva on Tuesday, with US President Donald Trump pressing Ukraine to act fast to reach a deal to end the four-year conflict.
Meanwhile, Ukraine continued its attacks on Russian energy infrastructure. Its military said on Tuesday it struck the Ilsky refinery, while a drone attack was also reported at the port of Taman.
A peace resolution could see a lifting of sanctions on Russia, bringing Russian oil back to the mainstream market. In 2025, Russia was the third-biggest crude producer in the world behind the United States and Saudi Arabia.
Economy
MTN Reaches $6.2bn Deal to Fully Own IHS Towers

By Adedapo Adesanya
MTN Group has agreed to take full control of IHS Holding, buying the roughly 75 per cent stake it does not already own in a deal that values the tower operator at about $6.2 billion.
According to a statement, MTN, which is Africa’s biggest mobile operator, will pay $8.50 per share in cash.
The deal will be funded through the rollover of MTN’s existing stake of around 24% in IHS, as well as about $1.1 billion in cash from MTN, roughly $1.1 billion from IHS’s balance sheet, and the rollover of no more than existing IHS debt.
The offer represents a 239 per cent premium to the company’s share price when it announced a strategic review on March 12, 2024, a 36 per cent premium to its 52-week volume-weighted average price as of February 4, 2026, and a three per cent premium to its unaffected closing price of $8.23 on that same date.
The transaction will see MTN transition from being a minority shareholder in IHS to a full owner. Upon completion, IHS will delist from the New York Stock Exchange and become a wholly owned subsidiary of MTN.
For MTN, the deal represents a decisive shift as data demand surges and digital infrastructure becomes increasingly strategic with a booming digitally-oriented youth population on the continent.
Over the past decade, many African telecom operators sold tower assets to independent infrastructure firms to unlock capital and reduce balance sheet pressure. This marks a reversal of the trend.
MTN itself had reduced its direct exposure to tower ownership, retaining a roughly 24 per cent fully diluted stake in IHS before the agreement.
Speaking on this, Mr Ralph Mupita, group president and CEO, MTN Group, described the proposed acquisition as a pivotal step in strengthening MTN’s strategic and financial position in a future where digital infrastructure will be central to Africa’s development.
He said the deal would enhance MTN’s ability to partner with governments and support long-term connectivity growth across its markets.
“This proposed transaction is a pivotal step in further strengthening MTN Group’s strategic and financial position for a future where digital infrastructure will become ever more essential to Africa’s growth and development,” he said.
The board of IHS unanimously approved the agreement and recommended that shareholders vote in favor.
MTN has committed to vote all its shares in support of the deal, while long-term shareholder Wendel has also issued a letter backing the transaction. Together, they account for more than 40 per cent of shareholder support already secured.
On his part, Mr Sam Darwish, chairman and CEO of IHS, said the agreement offers shareholders certainty and immediate value realisation following a strategic review launched during a period of macroeconomic and geopolitical volatility across key markets.
Founded 25 years ago with a single tower in one market, IHS grew into one of the world’s largest independent tower companies by count, operating in 11 countries and managing approximately 40,000 towers at its peak.
If completed, the acquisition will create the largest standalone and integrated tower company in Africa under MTN’s control, tightening the alignment between network operations and physical infrastructure in a region where connectivity remains both a commercial battleground and a development imperative.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn












