Education
AC vs DC Power: All the Pros and Cons for Your Business Needs
Thanks to the marvels of our constantly advancing and eternally impressive technological advancements, flicking on a light switch or plugging in a laptop is even simpler than primitive tasks like combing your hair or putting on clothes.
But when you’re in business, power is even more useful than keeping the lights on. A stable, reliable supply of electricity keeps your operations safe and productive, keeps you in touch with your customers, streamlines your operations, and keeps those profits flowing as consistently as the power to your computers, machines and premises.
Digging a little deeper, though, reveals the true marvel of power. Because while the power to your power-points is AC, the power delivered to your computers, phones and other electronic devices and equipment is much more likely to be DC. Why’s that? What’s the difference? And why does it matter for your business?
Let’s dive in:
AC versus DC
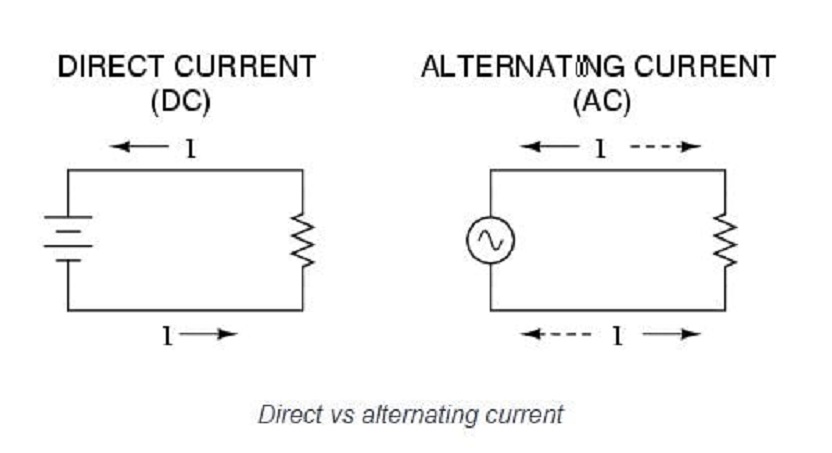
If your knowledge of AC/DC extends a little further than the rock’n’roll band, let’s start right from the beginning: the difference between the acronyms.
AC stands for alternating current, which can both change direction and magnitude, while DC is direct current – an electrical charge that is one-directional.
Thomas Edison famously pioneered DC, but it ultimately proved difficult to convert into either the lower voltages required for the end-user.
Luckily, Nikola Tesla was busily experimenting with AC, which ‘alternates’ multiple times with each blink of the eye – and the rest is history.
In fact, the power supplied to every home and business across the world runs on the Tesla principle, which is generally understood to be an easier and more reliable way to transmit power across long distances.
DC, though, is easier to manage and store locally, especially with the delicate workings and ultra-thin wiring of most applications and devices familiar with the DC power connectors you use both at home and work.
AC: The pros and cons
As well as being better for transmitting electricity from its source to the user, AC power is easily ‘stepped up’ or ‘stepped down’ from lower or higher voltages, including the more stable and precise DC requirements of most of the devices we use power for. AC generators and motors are also quite significantly simpler and cheaper than their DC counterparts.
However, despite the simplicity and the other benefits, AC tends to interfere with other communication lines, including harmonics problems that electrical operations that are erratic and difficult to diagnose and remedy.
DC: The pros and cons
Transmitting DC power requires only one or two smaller conductors, and there are also fewer issues in terms of capacitance, phase displacement, inductance and even power surging. That means less insulation is needed for the same voltage as AC, while interference with other systems is also lower.
However, DC voltage is unable to be ‘stepped up’, unlike the much more versatile AC. In practice, that means a 240-volt device requires DC power delivered at precisely 240 volts, with any additional resistors or instruments to reduce the voltage only complicating the arrangement and wasting energy in the process.
Why it matters for your business
In a nutshell, that’s essentially why your business may be in the market for a DC power connector, which enables your small to medium devices to receive the precise power requirements via the AC source.
As a result, there are countless DC power connectors out there to enable safe, secure, efficient and reliable energy for your business needs, so talk to an expert today to match the right choice to your precise requirements.
Education
Entries for InterswitchSPAK 8.0 Begin, Over N40m up for Grabs

By Aduragbemi Omiyale
Senior secondary school students across Nigeria have been invited to apply and demonstrate their academic excellence on a national stage in the eighth edition of the prestigious national science competition known as InterswitchSPAK.
The contest is organised by Interswitch, Africa’s leading technology company focused on creating solutions that enable individuals and communities prosper.
Registration for InterswitchSPAK 8.0 via www.interswitchspak.com has opened and will close on Friday, May 24, 2026. For the first time, in addition to group registrations through schools, parents can also register their individual children for the competition.
This year’s edition features a scholarship pool exceeding N40 million, with Interswitch expanding the prize structure to ensure broader impact.
The overall winner will receive a N15 million tertiary scholarship, including monthly stipends. The first runner-up will be awarded a N10 million scholarship, including monthly stipends; while the second runner-up will receive a N5 million scholarship, also including monthly stipends. All scholarships are payable over 5 years. Also, the top 9 finalists will all receive brand new laptops and other exciting prizes.
In addition to the top prizes, Season 8 introduces enhanced rewards for student finalists ranked 4th to 9th, as well as increased recognition for teachers supporting qualifying students from 1st to 9th place. This expanded structure reinforces Interswitch’s commitment to rewarding academic excellence and recognising the critical role educators play in shaping student success.
“At Interswitch, we strongly believe that Nigeria’s future will be shaped by how well we nurture today’s young minds. InterswitchSPAK goes beyond competition; it is a long-term commitment to empowering students and supporting teachers who are laying the foundation for innovation, problem-solving, and national development.
“As we launch Season 8, we remain focused on creating opportunity, rewarding merit, and inspiring excellence across Nigeria,” the Executive Vice President for Group Marketing and Communications at Interswitch, Ms Cherry Eromosele, said.
Designed to empower young minds in the Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) areas, InterswitchSPAK identifies, nurtures, and rewards students while equipping them with the skills and knowledge required to excel in STEM fields and drive innovation.
Over the past seven seasons, InterswitchSPAK has positively impacted thousands of students across the country, offering full university scholarships, mentorship opportunities, and national recognition for outstanding academic performance.
Beyond these rewards, the programme has consistently reinforced the importance of STEM education as a critical driver of innovation, problem-solving, and sustainable national development.
Through a transparent, technology-enabled selection process, InterswitchSPAK has also promoted educational equity by providing students from diverse socio-economic backgrounds with equal access to opportunity, ensuring that performance and merit remain central to success.
Education
Appeal Court Orders CBN, ABU Zaria to Pay N2.5bn to 110 Illegally Sacked Workers

By Adedapo Adesanya
The Court of Appeal in Abuja has dismissed the fresh bids by the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) and the Ahmadu Bello University (ABU) Zaria to stop the implementation of N2.5 billion judgment debt against the school and in favour of the 110 workers of the University unlawfully sacked in 1996.
In two separate unanimous judgements by a three-member panel of justices, the appellate court ordered the CBN to immediately release N2.5 billion to the former workers of the higher institution of learning without further delay.
In the lead judgments delivered by Justice Okon Abang, the appellate court threatened to impose heavy sanctions on the prime movers of CBN should the apex bank further refuse to release the money kept in its custody since 2018 by ABU, for onward payment to the aggrieved workers.
Justice Abang dismissed the CBN’s claim that the 110 workers unlawfully sacked by ABU in 1996 but ordered reinstated by the National Industrial Court in Abuja, cannot use garnishee proceedings against it to collect the money.
The claims of the apex bank that consent of the Attorney General of the Federation and Minister of Justice (AGF) must first be obtained by the workers before payments can be effected were also dismissed by the Court of Appeal.
The CBN and ABU had, in separate appeals, challenged the implementation of the judgment of the Industrial Court, which ordered ABU to pay the entitlement of the 110 workers, having found that they were unlawfully laid off by the Sole Administrator of the University, General Mamman Kontagora, in 1996.
The two appellants also faulted the use of garnishee proceedings against them by the workers to effect payments.
The two appeals were dismissed for being unmeritorious.
Justice Rakiya Haastrup of the Industrial Court had on January 27, 2022, issued a “garnishee order absolute,” directing the CBN to pay the judgment sum to the workers from ABU’s funds.
Justice Abang held that the workers were right in filing garnishee proceedings against CBN to enforce payments of their entitlement as required by law.
The Court of Appeal admonished the apex bank for wasting public funds to engage lawyers to file a suit to frustrate the payments of the entitlement to the aggrieved workers.
According to the appellate court, the conduct of the CBN in opposing payments of the money was reckless and reprehensible to the workers since the ABU had deposited the money with it for the settlement of the judgment debt.
“In this matter, it is not the duty of the CBN to play the role of the advocate but to implement the court judgment that awarded the money to the workers in the absence of any contrary court order.
“It is also unethical for the lawyer to the CBN to have supported the bank in frustrating the judgment of the Industrial Court. The unfortunate action of the CBN had prolonged the sufferings and hardships of the workers.
“The lawyer ought to have advised the CBN not to play the role of the advocate, no matter how juicy the CBN brief. The action of CBN is cowardice. It took the matter personal against the workers who have been suffering since 2013.
“There is no lawful reason for the CBN to have filed this appeal against the judgment of the Industrial Court since the workers made no claims against the bank.
“The lawyer owes a duty to the court, to the country, and to the 110 workers to see that they are not unjustly punished or denied the fruits of their court victory. He ought to have withdrawn his services if CBN went against his advice. They ended up wasting the valuable judicial time of this Court.
“How can CBN be asking that the order of the court not made against it be vacated when it has been holding the workers’ money since 2018? The situation must not continue. There must be an end to it. The workers deserve the fruit of their labour,” he said.
The Court of Appeal awarded N5 million against CBN and another N5 million against ABU to be paid to the workers as costs of litigation in addition to the N2.5 billion.
Education
British High Commission Lauds 99 Chevening, Commonwealth Scholarship Beneficiaries

By Adedapo Adesanya
The British High Commission has celebrated 99 Nigerians who have recently completed their studies in the United Kingdom through the prestigious Chevening and Commonwealth scholarships, pursuing a wide range of master’s degree, PhD, and fellowship programmes.
In Abuja and Lagos, the commission held Welcome Home ceremonies for the 30 Chevening scholars who have completed their studies, as well as the 69 beneficiaries who make up the Commonwealth scholars and fellows.
Chevening Scholarships are the UK Government’s global scholarship programme, funded by the Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office (FCDO), partner organisations, and partner universities, while Commonwealth Scholarships are managed by the Commonwealth Scholarship Commission (CSC) in the UK.
At both events, the scholars and fellows shared their academic journeys and experiences, and their preparedness to use the skills and knowledge developed during their studies to contribute to Nigeria’s development. Additionally, they were celebrated for their exceptional academic achievements, received their completion certificates, and were officially inducted into the Chevening and Commonwealth alumni community in Nigeria.
Speaking at the reception, the British Deputy High Commissioner, Mrs Gill Lever (OBE), said, “We take great pride in welcoming back our Commonwealth and Chevening Scholars. Congratulations to every one of them for completing their studies, many with distinctions. I’m so happy that talented Nigerians have had the opportunity to study in the UK, returning with additional knowledge and skills to make a positive difference in their home country. I encourage them to aim for excellence in their future endeavours. I know they will be great ambassadors for the UK in Nigeria and make the most of the networking and knowledge sharing that being a Commonwealth or Chevening scholar presents. Keep in touch, everyone!”
British Council was represented at the welcome event by Mr Chikodi Onyemerela, Director of Programmes, British Council Nigeria. During his remarks, Chikodi congratulated the scholars for completing their master’s and PhD programmes in the UK.
He urged the scholars to be good Ambassadors of their institutions in Nigeria and urged them to apply the knowledge, skills and network that they have acquired in the UK to address challenges facing Nigeria in various sectors while maintaining ties with their UK institutions.
A Chevening Scholar, Nankur Pontip Ramdur, who studied Terrorism, International Crime and Global Security at Coventry University, UK, said, “I understand that peace and security are at the heart of every nation’s development and success; hence, I look forward to contributing to a safer Nigeria. I plan to continue outreach to schools and communities with my team, teaching responses and safe practices regarding sexual and gender-based violence. I am also currently writing a book to broaden the impact of this initiative in Nigeria and subsequently across the globe. I have so much more to meaningfully contribute to my country, and I am glad Chevening has propelled me towards achieving my dreams!”
A Commonwealth Scholar, Chimdi Ekwueme, who studied Health Policy, Planning and Finance at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, UK, said, “Studying in the UK has deepened my Nigerian perspective by allowing me to situate my local experience within wider international conversations and gaining practical insights I can apply at home.”
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn












