Technology
Best Practices for Keeping Your CMS Updated and Secure
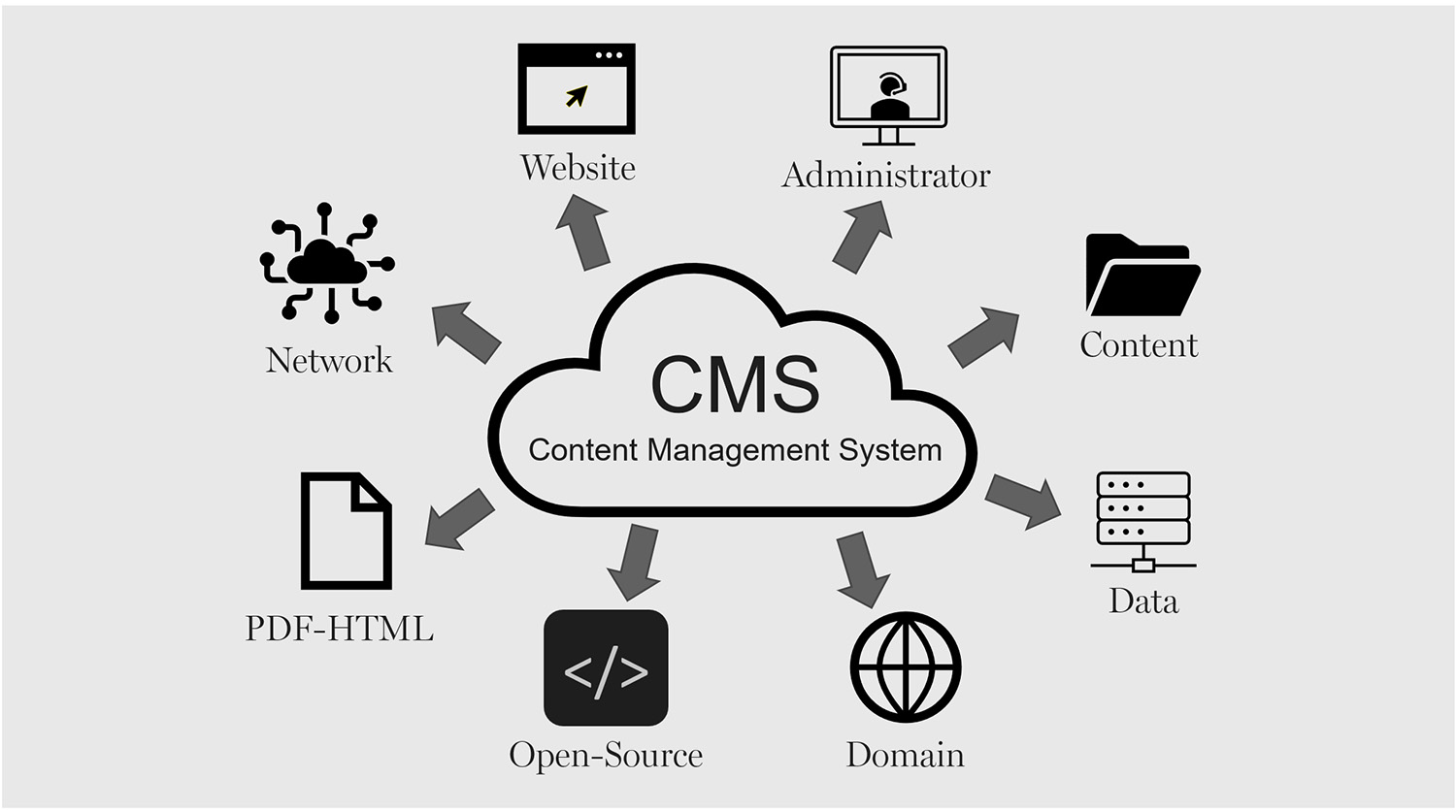
A Content Management System (CMS) drives many websites as it offers the best creation, maintenance, and deployment of digital content for an expanding enterprise. However, CMS can be an issue if not regularly updated or if security patches are bypassed. When hackers realize a CMS version is vulnerable, they attempt to breach it, gaining entry into a system to steal information or shut down a website.
A secure and reliable headless CMS requires constant updating, specific log-in and access, and continuous monitoring. Thus, a business that requires a secure CMS will ensure that client information is kept private, the experience is overall more seamless, and compliance is easier. This article outlines all the necessary updates and security patches to keep a secure and reliable CMS.
Regularly Updating CMS Core, Plugins, and Themes
One of the quickest ways to eliminate security vulnerabilities is by keeping the headless CMS core software and plugins/themes up to date. Developers are always updating for security vulnerabilities, enhancements of functionality, and added features. Failing to keep current opens a portal of exploitation for sites that developers have already fixed, making these sites low-hanging fruit for hackers. For example, if a retail business has a WordPress CMS for its website, and the WordPress CMS is outdated, it opens the site to being hacked.
There are WordPress fail issues that have not yet been addressed, which give hackers the chance to enter the system and add in malware. If a site has a lot of pending updates, many security vulnerabilities can be prevented. By checking often or setting up automatic updates, any business will have the most secure system possible. In addition, plugins or themes that are no longer supported by developers are ones to avoid as well. An unsupported plugin—with or without updates is a vulnerability, and it should be changed for something that gets consistent updates.
Strengthening Authentication and Access Control
A headless CMS such as the one that Storyblok provides usually has multiple users with different access levels. From administrators and editors to simple content creators, everyone can be a guest on the CMS. However, without access controls, a standard user can be granted administrative privileges either accidentally or on purpose and delete information or leave the CMS open for attack or intentional editing. Access control authorization relies on authentication. The ultimate protection for a CMS is multi-factor authentication. Multi-factor authentication reduces the likelihood of an account being compromised because it requires another form of validation aside from a username and password.
These can include one-time passwords or biometric fingerprints. Furthermore, implement super admin access to only what is necessary. If many team members need access to a project, role-based access (RBAC) gives everyone access only to what their job requires. The fewer the super admin accounts, the fewer the chances of insider threats and accidental security misconfiguration. Furthermore, the company should have password policies in place to require complicated passwords capitalization, numbers, special characters and employees should be educated on changing their passwords regularly. The chances of credential compromise are minimized with password managers.
Using Secure Hosting and Encrypted Connections
A headless CMS is only as good as its hosting. Should a company choose a reliable hosting service that includes security (firewalls, DDoS protection, malware scanning along with proper backup solutions), the company can maintain a secure level from the very beginning. On the other hand, unreliable hosts are vulnerable and subject to server-level attacks, which leave a site vulnerable to hacks and shutdowns. Another major component of security is a Secure Socket Layer (SSL) certificate, which protects all information sent from users to the site from prying third-party eyes.
With SSL encryption, this allows a company to avoid handing over to hackers any passwords, compromised personal information, or credit card numbers during those vulnerable transactions. Companies that deal with sensitive customer information needing additional security may opt for a managed hosting service with built-in, automated security management. Managed hosting services are more likely to secure vulnerabilities, watch for nefarious activity, and perform security hardening so these companies don’t have to delegate duty.
Conducting Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments
Regular security audits and vulnerability scans uncover vulnerabilities in a headless CMS before a hacker gets the chance to exploit them. Security audits ensure correct user permissions, potential database corruption, and server configurations so that no unintended levels of access exist. For example, a content-managed eCommerce site should assess how often rogue administrators can access the CMS via security audits to avoid malicious penetration that could lead to poor choices. Thus, a content-managed eCommerce site wants to ensure that accidental charge transactions do not happen on the checkout function, so a vulnerability scan is regularly required.
Security plugins within the headless CMS and external vulnerability scanning websites provide assessments of malware injections, brute force login attempts, and unnecessary file permissions. Furthermore, simply keeping an eye on the CMS logs to check for oddities, surprising login attempts, changes in core files, individuals visiting the admin panel when they should not be granted visibility would keep a company apprised of its security. An apprised awareness of security would avoid a lot of exploits from escalating into a massive cybersecurity event.
Implementing a Reliable Backup Strategy
Fail-safe backup solution. Even with the most secure CMS, there’s always a chance that a hack or malfunctioning headless CMS occurs or even a wipe happens accidentally. A backup solution that is fail-safe ensures that no matter what type of catastrophic security issue occurs on the site, it can be restored with ease and no major downtime. Backup should be automatic and regular, off-site or an encrypted cloud solution. This ensures that even if the primary server is hacked, nothing is lost. A backup solution should encompass full database, full file, and full configuration backups for the CMS to guarantee that everything is restorable when needed.
For example, a headless CMS-centric, news-driven site and a digital asset manager are hacked and all posts are erased. They’ll be restored in a flash unless the backup from last night is still there. These types of restorations need to be regularly tested to confirm they are there and up to date.
Securing API Integrations and Third-Party Extensions
Many CMS have third-party applications, payment processors, and other services via API integrations for extended functionality. However, these integrations are potential weaknesses that hackers can infiltrate without proper security protocols. All API integrations should require secure authentication encrypted API keys and OAuth tokens and unauthenticated services should never have unrestricted access to sensitive data. Furthermore, only externally developed plug-ins and extensions should be used and those created by trusted developers and extensively vetted; antiquated, unpoliced third-party applications can open disastrous loopholes.
Of course, being a financial center, a headless CMS for investment and sourcing and getting reputable user information should have all third-party APIs and financial integrations assessed for security compliance to prevent data leaks or accidental purchases. By assessing and strengthening these external integrations, companies reduce the risk that additional vulnerabilities will penetrate the CMS ecosystem from the outside.
Monitoring and Responding to Cyber Threats
Yet regardless of how bulletproof a site may be, the ideal method of learning about and addressing cybersecurity weaknesses will always be preemptive and responsive awareness. Thus, companies need to adopt further real-time security monitoring to be notified of nefarious actions, unauthorized logins, and breaches. For example, a retail website’s enterprise content management system should include intrusion detection systems (IDS) and web application firewalls (WAF) to prevent accidental access from those who don’t belong or to prevent interactions with bots.
In addition, a cyber incident response plan ensures that there are trained protocols for rapid response if a breach were to happen. For instance, an incident response plan dictates that one must quarantine affected machines, roll back to backups, notify stakeholders, and determine how to prevent this from happening again. This level of understanding empowers organizations to be ahead of the game and mitigate as much destruction to their content management systems that cyber intrusions would create.
Conclusion
A maintained, safe CMS is not static. There are security updates, there is testing and debugging, and vulnerabilities are always there. Thus, for these enterprises that fail to secure their CMS systems, the chance for attacks is great resulting in breaches and costly downtime, which creates not only chaos in brand identity but in the company’s balance sheet. These measures minimize exposure and build a resilient, secure environment when organizations change default CMS files, update passwords, enhance server security, and engage in security audits.
Secure API integrations, knowledge of cybersecurity developments, and the ability to restore backups reliably, create a CMS more resistant to ever-increasing threats. A secure Content Management System essentially protects vital proprietary and customer data and keeps sites up and running with appropriate user confidence. Firms with a comprehensive Content Management System security strategy render their businesses transferable to the digital arena with more growth potential and less concern for cyber attacks.
Technology
Google Introduces Yorùbá, Hausa Language Support for AI Search Features
By Modupe Gbadeyanka
The language support for its AI Search features has been expanded by Google, with the inclusion of Yoruba and Hausa in Nigeria.
This is part of a broader effort to make AI more inclusive across the continent, with support now extending to a total of 13 African languages.
Under the AI Overviews and AI Mode, speakers of both Nigerian languages can utilise AI-powered Search experiences in their mother tongue for quick summaries and conversational exploration.
This means existing AI features in Google Search are now accessible to people like the student in Kano asking a question in Hausa, and the trader in Ibadan seeking advice in Yorùbá.
By addressing language barriers, this update ensures that technology reflects the identity and culture of the people it serves. With this expansion, more people can now use AI Mode to ask complex questions in their preferred language, while exploring the web more deeply and naturally through text or voice.
The 13 languages now supported across Africa include Afrikaans, Akan, Amharic, Hausa, Kinyarwanda, Afaan Oromoo, Somali, Sesotho, Kiswahili, Setswana, Wolof, Yorùbá, and isiZulu.
These languages were chosen based on the vibrant search activity across the continent, ensuring that our AI experiences reach the communities that need them most.
Commenting on the development, the Communications and Public Affairs Manager for Google in West Africa, Taiwo Kola-Ogunlade, said, “Building a truly global Search goes far beyond translation — it requires a nuanced understanding of local information.
“With the advanced multimodal and reasoning capabilities of our custom version of Gemini in Search, we’ve made huge strides in language understanding, so our most advanced AI search capabilities are locally relevant and useful in each new language we support.
“This is about ensuring Nigerians can converse with Search in their mother tongues, making information more helpful for everyone.”
To use AI Overviews and AI Mode in the local language, users must open the Google app on an Android or iOS device, or via the Web. They are required to tap on AI Mode within the Search experience. Thereafter, they can type or speak the question in their preferred language, such as Hausa or Yorùbá, and let the AI guide the journey.
Technology
Telecom Operators to Issue 14-Day Notice Before SIM Disconnection

By Adedapo Adesanya
Telecommunications operators in Nigeria will now be required to give subscribers a minimum of 14 days’ notice before deactivating their SIM cards over inactivity or post-paid churn, following a fresh proposal by the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC).
The proposal is contained in a consultation paper, signed by the Executive Vice Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of the NCC, Mr Aminu Maida, and titled Stakeholders Consultation Process for the Telecoms Identity Risks Management Platform, dated February 26, 2026, and published on the Commission’s website.
Under the proposed amendments to the Quality-of-Service (QoS) Business Rules, the Commission said operators must notify affected subscribers ahead of any planned churn.
“Prior to churning of a post-paid line, the Operator shall send a notification to the affected subscriber through an alternative line or an email on the pending churning of his line,” the document stated.
It added that “this notification shall be sent at least 14 days before the final date for the churn of the number.”
A similar provision was proposed for prepaid subscribers. According to the Commission, operators must equally notify prepaid customers via an alternative line or email at least 14 days before the final churn date.
Currently, under Section 2.3.1 of the QoS Business Rules, a subscriber’s line may be deactivated if it has not been used for six months for a revenue-generating event. If the inactivity persists for another six months, the subscriber risks losing the number entirely, except in cases of proven network-related faults.
The new proposal is part of a broader regulatory review tied to the rollout of the Telecoms Identity Risk Management System (TIRMS), a cross-sector platform designed to curb fraud linked to recycled, swapped and barred mobile numbers.
The NCC explained in the background section of the paper that TIRMS is a secure, regulatory-backed platform that helps prevent fraud stemming from churned, swapped, barred Mobile Station International Subscriber Directory Numbers in Nigeria.
It said this platform will provide a uniform approach for all sectors in relation to the integrity and utilisation of registered MSISDNs on the Nigerian Communications network.
In addition to the 14-day notice requirement, the Commission also proposed that operators must submit details of all churned numbers to TIRMS within seven days of completing the churn process, strengthening oversight and accountability in the system.
The consultation process, which the Commission said is in line with Section 58 of the Nigerian Communications Act 2003, will remain open for 21 days from the date of publication. Stakeholders are expected to submit their comments on or before March 20, 2026.
Technology
Silverbird Honours Interswitch’s Elegbe for Nigeria’s Digital Payments Revolution

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
The founder of Interswitch, Mr Mitchell Elegbe, has been honoured for pioneering Nigeria’s digital payments revolution.
At a ceremony in Lagos on Sunday, March 1, 2026, he was bestowed with the 2025 Silverbird Special Achievement Award for shaping Africa’s financial ecosystem.
The Silverbird Special Achievement Award recognises individuals whose innovation, vision, and sustained impact have left an indelible mark on society.
Mr Elegbe described the award as both humbling and symbolic of a broader journey, saying, “This honour represents far more than a personal milestone. It reflects the courage of a team that believed, long before it was fashionable, that Nigeria and Africa could build world-class financial infrastructure.”
“When we started Interswitch, we were driven by a simple but powerful idea that technology could democratise access, unlock opportunity, and enable commerce at scale.
“This recognition by Silverbird strengthens our resolve to continue building systems that empower businesses, support governments, and expand inclusion across the continent,” he said when he received the accolade at the Silverbird Man of the Year Awards ceremony attended by several other dignitaries, whose leadership and contributions continue to shape national development and industry transformation.
In 2002, Mr Elegbe established Interswitch after he was inspired by a bold conviction that technology could fundamentally redefine how value moves within and across economies.
Under his leadership, the company has evolved into one of Africa’s foremost integrated payments and digital commerce companies, powering financial transactions for governments, banks, businesses, and millions of consumers.
Today, much of Nigeria’s electronic payments ecosystem traces its foundational architecture to the systems and rails established under his leadership.
“Mitchell’s journey is inseparable from Nigeria’s digital payments evolution. His foresight and resilience helped establish foundational infrastructure at a time when the ecosystem was still nascent.
“This recognition affirms not only his personal legacy, but the broader impact of Interswitch in enabling commerce and strengthening financial systems across Africa,” the Executive Vice President and Group Marketing and Communications for Interswitch, Ms Cherry Eromosele, commented.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn











