Technology
The Growing Importance of Privacy Amongst Customers and How Businesses Should Cater to it

By Kehinde Ogundare and Veerakumar Natarajan
Privacy is a growing concern for technology consumers worldwide. While there was a time when that may not have been the case for countries like Nigeria and Kenya, that’s no longer the reality. As connectivity becomes more affordable and ubiquitous, Kenyans and Nigerians have become increasingly tech-savvy and conscious regarding how much data they share with technology companies and what the latter is doing with it.
In the face of these growing concerns, companies operating in Africa need to be mindful of the increasing privacy mindset of their customers. Aside from regulatory compliance, companies should actively demonstrate that they care about their customers’ privacy concerns to build and sustain trust and to show they’re taking a proactive approach to protect their personal information.
The importance of regulatory compliance
The first step any company should take to safeguard their customers’ privacy is ensuring they’re compliant with all of the relevant laws and regulations. In countries like Kenya and Nigeria, data protection regulations are relatively new.
The Data Protection Act of 2019, enforced by the Office of the Data Protection Commissioner (ODPC), regulates data protection in Kenya. The act expressly prohibits organisations from processing personal data if their consent has not been provided first. Each organisation must have a data controller and/or a data processor whose responsibility is to prove they’ve obtained consent before processing a person’s data.
Nigeria’s Data Protection Act, meanwhile, was signed into law in 2023. The act governs both manual and automatic data processing. The act also established the Nigeria Data Protection Commission (NDPC), which is an independent body that governs data protection and regulation in the country. In addition to defining sensitive personal data as including an individual’s genetic and biometric data as well as their race, ethnicity, and health status, among other things, the act also provides specific grounds for the processing of this sensitive personal data. According to the act, such data can be processed where consent is provided or where processing is necessary for social security or employment laws.
Both of these laws are in line with similar laws and regulations around the world, such as Europe’s GDPR. That means they’re not only a good place for Nigerian and Kenyan businesses to start for compliance, but they also help businesses gain a good footing when it comes to protecting customer data should they start operating internationally.
Beyond compliance
Companies should, however, view regulatory compliance as the bare minimum when it comes to meeting their customers’ privacy needs. Given the parlous state of privacy protection across many African countries, going above and beyond with customer privacy can be a positive differentiator for companies that get it right.
Among the initiatives they can undertake in this direction are investing in data centre security to minimise the collection of data, requesting permission from customers while collecting sensitive information, and ultimately reducing their reliance on selling user data for revenue gains. Another initiative that organisations can implement is implementing multi-factor authentication if they require customers to log in to an account to access their products and services.
Another aspect that businesses should pay close attention to is which technology vendor they work with to run their internal operations. Businesses should ensure the third-party tech tools they deploy within their IT infrastructure also come with strong data privacy and protection controls, and the corresponding vendors also practice transparent data collection practices. Should one of these vendors fall victim to a cybersecurity breach, the customer data of the organisations using it could easily fall into nefarious hands.
Businesses should, therefore, ensure they make use of software providers and vendors that are, themselves, compliant with all the relevant privacy laws and regulations, and offer a comprehensive set of security measures and procedures, including controlled user access, enterprise mobility management (EMM) integration, IP restrictions, and secure integrations.
Riding the positives of proactive protection
While there are many negatives associated with data protection failures, including reputational damage and legal punishments, it’s also important that organisations understand the positives associated with proactive data protection.
High up on the list of those positives is building trust. Customers who trust the companies they buy from are more likely to be loyal in the long term, make repeat purchases in the future, and act as evangelists to others. At a time when customers are increasingly concerned about data privacy, building that trust is more difficult, but also more rewarding than ever. It, in other words, is something worth investing in.
Kehinde Ogundare is the Country Manager for Zoho Nigeria and Veerakumar Natarajan is the Country Head for Kenya Zoho Corp.
Technology
TikTok Invests Fresh $200K in AI Media Literacy in Africa

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
An additional $200,000 will be invested in Artificial Intelligence (AI) media literacy initiatives across Sub-Saharan Africa, TikTok announced during its third annual Sub-Saharan Africa Safer Internet Summit in Nairobi, Kenya.
The platform hosted government officials, regulators, online safety partners and industry leaders for the event, reinforcing its commitment to collaborative approaches to online safety.
The funds will be provided in ad credits to help support local organisations in the region to expand AI media literacy.
This investment builds on the company’s initial $2 million AI Literacy Fund, launched in November 2025, which awarded 20 global non-profits to create content that boosts public understanding of AI.
In Sub-Saharan Africa, TikTok initially supported three organisations to advance digital literacy and combat misinformation.
“With the rapid advancement of AI, we are committed to educating our community online, so they feel empowered to have responsible experiences with AI, whether that’s as viewers or creators.
“We are partnering with trusted local organisations that communities already know and rely on, because their expertise and deep local connections are essential to making AI literacy programs truly impactful,” the Global Head of Partnerships, Elections and Market Integrity at TikTok, Mr Valiant Richey, stated.
Earlier, the Head of Government Relations and Public Policy for Sub-Saharan Africa at TikTok, Ms Tokunbo Ibrahim, said, “As we host the 3rd Annual Safer Internet Summit here in Kenya, our mission is clear: to share learnings, insights, tackle common challenges and collaboratively advance actionable solutions that protect citizens online.
“By bringing together a diverse coalition of policymakers, tech innovators, and creators, we are ensuring that the conversations we have at this Summit are all-inclusive and lead to a more resilient digital landscape.”
The summit featured expert panels and discussions on critical topics, including TikTok’s Trust and Safety efforts, protecting young people online, and policy frameworks for responsible AI governance.
A key highlight of the event was showcasing how TikTok uses AI to transform how people share their creativity and discover new passions, while ensuring the community remains safe through transparent and responsible AI practices.
The platform also shared more about how recent advancements in AI are helping the platform moderate content faster and more consistently at scale, by improving automated moderation and empowering human teams with better moderation tools.
With over 100 million pieces of content uploaded daily to TikTok, these advances, which work alongside human moderation teams, are helping get violative content down faster, reducing the likelihood of the community seeing it.
According to the latest Community Guidelines Enforcement Q3 2025, TikTok removed over 14 million videos across Sub-Saharan Africa, with 96.7 per cent detected and removed proactively using automated technology, underscoring TikTok’s commitment to proactive moderation and swift action.
Technology
Interswitch Technovation 4.0 Hackathon Winners Share N10m

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
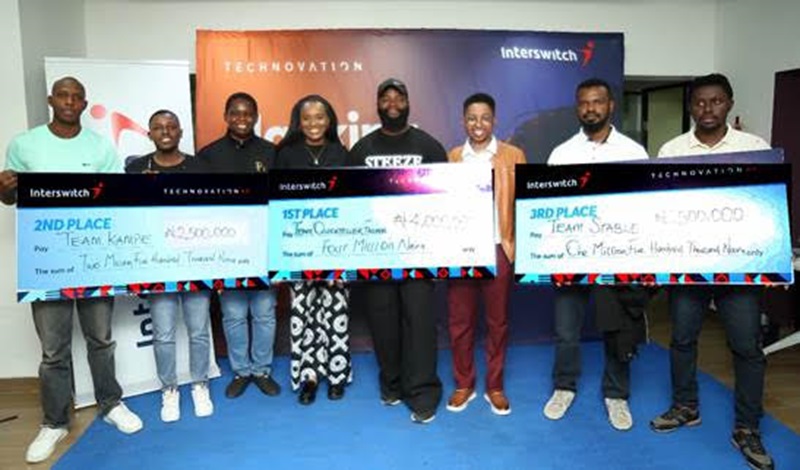
The winners of the Technovation 4.0 Hackathon, themed The Wicked Hackathon, organised by Interswitch, have been given N10 million in cash prizes for their efforts.
At the one-day finale event, which took place on Wednesday, March 4, 2026, at the Interswitch Innovation Lab and Co-Working Space, the money was shared among the top teams whose innovative solutions stood out during the rigorous multiple phases of the competition.
Team Quickteller Fashion emerged as the overall winner, securing the grand prize of N4 million for a solution that impressed judges with its originality, practicality, and strong strategic relevance. Team Kampe claimed second position with N2.5 million, while Team Stable placed third, receiving N1.5 million. Up to N300,000 worth of cash prizes were also awarded to the fourth, fifth and sixth qualifying teams.
For nine months, cross-functional teams from across the organisation collaborated to conceptualise, validate, develop, and refine solutions, moving from raw ideas to minimum viable products (MVPs) with ready-to-market potential and deployment across the business.
The atmosphere at the grand finale reflected that of preparation and anticipation as the top 9 teams presented their innovations through live demonstrations and detailed pitches, fielding questions from a distinguished panel of judges before the top three winners were selected. Each presentation highlighted rigorous validation processes, thoughtful market considerations, and a strong emphasis on measurable impact.
While many of the solutions remain confidential due to their strategic relevance, the diversity and depth of ideas showcased during the hackathon’s final underscored the organisation’s growing culture of intrapreneurship and structured innovation. The projects illustrated how technology-driven thinking can unlock efficiencies, strengthen operational capabilities, and open new pathways for growth across the digital payments and commerce ecosystem.
“Technovation continues to reflect who we are as an organisation, bold, forward-thinking, and deeply committed to building impactful solutions from within. Over the years, we have seen ideas conceived during this programme evolve into meaningful capabilities that strengthen our ecosystem.
“The passion, discipline, and ingenuity demonstrated by our teams this year reinforce our belief in the power of African innovation to solve complex challenges and shape the future of technology on the continent,” the Chief Innovation Officer for Interswitch, Ms Adaobi Okerekeocha, stated.
Technology
Google Introduces Yorùbá, Hausa Language Support for AI Search Features
By Modupe Gbadeyanka
The language support for its AI Search features has been expanded by Google, with the inclusion of Yoruba and Hausa in Nigeria.
This is part of a broader effort to make AI more inclusive across the continent, with support now extending to a total of 13 African languages.
Under the AI Overviews and AI Mode, speakers of both Nigerian languages can utilise AI-powered Search experiences in their mother tongue for quick summaries and conversational exploration.
This means existing AI features in Google Search are now accessible to people like the student in Kano asking a question in Hausa, and the trader in Ibadan seeking advice in Yorùbá.
By addressing language barriers, this update ensures that technology reflects the identity and culture of the people it serves. With this expansion, more people can now use AI Mode to ask complex questions in their preferred language, while exploring the web more deeply and naturally through text or voice.
The 13 languages now supported across Africa include Afrikaans, Akan, Amharic, Hausa, Kinyarwanda, Afaan Oromoo, Somali, Sesotho, Kiswahili, Setswana, Wolof, Yorùbá, and isiZulu.
These languages were chosen based on the vibrant search activity across the continent, ensuring that our AI experiences reach the communities that need them most.
Commenting on the development, the Communications and Public Affairs Manager for Google in West Africa, Taiwo Kola-Ogunlade, said, “Building a truly global Search goes far beyond translation — it requires a nuanced understanding of local information.
“With the advanced multimodal and reasoning capabilities of our custom version of Gemini in Search, we’ve made huge strides in language understanding, so our most advanced AI search capabilities are locally relevant and useful in each new language we support.
“This is about ensuring Nigerians can converse with Search in their mother tongues, making information more helpful for everyone.”
To use AI Overviews and AI Mode in the local language, users must open the Google app on an Android or iOS device, or via the Web. They are required to tap on AI Mode within the Search experience. Thereafter, they can type or speak the question in their preferred language, such as Hausa or Yorùbá, and let the AI guide the journey.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn