World
Russia Recruiting African Specialists
By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
With thousands conscripted into the army to fight in neighbouring Ukraine, several more thousands escaping military mobilization and migrating abroad, Russia currently lacks highly skilled labor for offices and unskilled labour for its industries, agriculture and construction. Reports indicated Russian employment agencies are seriously recruiting all kinds of employees, both skilled and unskilled, from Africa.
HeadHunters, a recruitment agency’s report announced in mid-July that a boom in attracting workers from Africa against the backdrop of a shortage of personnel across Russia. According to the report, in the first half of 2024, Russian companies significantly increased their activity in searching for employees in Africa.
In particular, countries such as Kenya, Zimbabwe, and Cameroon became the leaders in terms of the growth rate of vacancies in annual terms, while the number of advertisements in a number of European countries and the United States, on the contrary, decreased. Together with experts, RBC looked into the reasons for the growing popularity of employees from Africa and the main difficulties in hiring workers from abroad.
African hiring boom
According to HeadHunters’ data for the first half of 2024, seven out of ten foreign countries with the largest increase in vacancies from Russian organizations are African countries. If in the first half of 2023 in each of them one could find no more than 500 vacancies from Russian employers, then in the first six months of this year the number of job offers has increased multiple times, in some cases tens of times, analysts noted in the report.
Thus, the number of vacancies increased the most in Kenya – 39 times (from 161 vacancies in the first half of 2023 to 6.4 thousand vacancies in the first half of 2024). A number of other African countries have also seen a significant increase in the number of places offered, although more modest in absolute terms. Thus, in Zimbabwe the number of vacancies increased 15 times (to 165), in Cameroon – nine times (to 130), in Zambia – eight times (to 224). In addition, a sharp increase in the number of vacancies was recorded in Algeria (seven times, up to 1.7 thousand).
Among non-African countries, the leaders in terms of growth in the number of vacancies were Albania, Pakistan and Belgium. In addition, in 2024, Russian companies posted vacancies for the first time in countries such as Nepal, the Bahamas, Barbados, Malawi, Iceland, Sierra Leone, Gabon and the Central African Republic (CAR). The total number of vacancies in the listed countries in the first half of the year reached almost 300, analysts indicated.
The fact that the geography of migration to Russia could expand at the expense of African states was previously predicted in an interview with RBC by the director of the Institute of Demographic Research of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Marina Khramova. She also admitted that in future, migrants from Southeast Asian countries, such as Thailand or the Philippines, could be attracted to the domestic labor market.
Categories of workers for recruitment abroad
The composition of the most in-demand categories of employees when hiring from foreign countries among Russian employers has not changed over the year – these are customer service managers, IT specialists and marketers, as follows from the data on invitations to vacancies. The top ten also included specialists in the field of art and mass media, administrative personnel, workers and builders.
At the same time, the greatest increase in demand was shown by vacancies for workers in science and education – in the first half of the year, the number of invitations for employees in this field from abroad doubled. The number of invitations for foreign workers increased by 68%, agricultural specialists – by 63%, employees in the field of raw materials extraction and construction – by 53 and 51%, respectively.
It is necessary to understand that the search and invitations to employees for vacancies do not fully reflect the typical portrait of a migrant, since their hiring in general varies quite a lot depending on the specialty and region, noted Danina. “We can say with confidence that attracting migrants to positions as workers and construction workers (in general, low-skilled positions) is traditionally typical for Central Asian countries and this year for a number of African countries,” she explained.
At the same time, highly qualified specialists with knowledge of the specifics of local markets and business for the positions of marketers and account managers are sought all over the world, and the search for top managers this year was concentrated in the UAE, Serbia, Turkey, Thailand.
The number of African specialists who enter Russia is growing every year, noted Vsevolod Sviridov, an expert at the Center for African Studies at the Faculty of World Economy and International Politics at the National Research University Higher School of Economics. “African labor migrants occupy completely different niches in the labor market: some are actually employed in fairly low-skilled professions, for example in construction, work in warehouses, in agriculture, while others occupy high management positions in large Russian companies, the expert on Africa pointed out to local Russian media.
A recent example is Timothy Musa Kabba, a graduate of the Mining University in St. Petersburg, who worked as a geologist for Russian oil and gas companies for almost ten years, and he is now the Minister of Foreign Affairs of Sierra Leone, recalled Sviridov.
Difficulties in hiring foreigners
Employment of foreigners is associated with a number of complicating issues, notes Danina. For example, if we are talking about hiring workers or construction workers with relocation to Russia, then the main burden lies in organizing logistics (due to the lack of direct or regular flights with Russia), obtaining quotas, and the presence of language and cultural barriers in work teams. When working with highly qualified specialists from non-CIS countries, who are often hired without relocation, there may be problems with organizing financial payments, added Danina.
Migration regulation in Russia also has its own specifics, notes Sofia Luneva, a lawyer in the labor law practice at BGP Litigation. Thus, for foreigners who enter on visas, the registration procedure is the most complex, as it requires obtaining a permit to attract foreign labor for the company, an invitation from the employer to enter and a work permit for the foreigner (in a number of areas, their number may be limited by quotas).
An alternative could be the status of a highly qualified specialist – if it is available, the employee is not subject to quotas. The downside of this simplified procedure is increased costs for the employee. Registration of visa-free foreign citizens is much simpler in terms of documents.
At the same time, all migrants are required to have documents confirming that they have undergone fingerprinting, photography and medical examination. And in any case, regardless of the status of a foreign worker, the employer is obliged to notify the Russian Ministry of Internal Affairs about the conclusion/termination of an employment contract within no more than three working days. In conclusion, workers and employees are required in the Russian Federation. (Report made with addition materials from Russian media).
World
Today’s Generation of Entrepreneurs Value Flexibility, Autonomy—McNeal-Weary

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
The Young African Leaders Initiative (YALI) is the United States’ signature step to invest in the next generation of African leaders. Since its establishment in 2010 by Obama administration, YALI has offered diverse opportunities, including academic training in leadership, governance skills, organizational development and entrepreneurship, and has connected with thousands of young leaders across Africa. This United States’ policy collaboration benefits both America and Africa by creating stronger partnerships, enhancing mutual prosperity, and ensuring a more stable environment.
In our conversation, Tonya McNeal-Weary, Managing Director at IBS Global Consulting, Inc., Global Headquarters in Detroit, Michigan, has endeavored to discuss, thoroughly, today’s generation of entrepreneurs and also building partnerships as a foundation for driving positive change and innovation in the global marketplace. Here are the excerpts of her conversation:
How would you describe today’s generation of entrepreneurs?
I would describe today’s generation of entrepreneurs as having a digital-first mindset and a fundamental belief that business success and social impact can coexist. Unlike the entrepreneurs before them, they’ve grown up with the internet as a given, enabling them to build global businesses from their laptops and think beyond geographic constraints from day one. They value flexibility and autonomy, often rejecting traditional corporate ladders in favor of building something meaningful on their own terms, even if it means embracing uncertainty and financial risk that previous generations might have avoided.
And those representing the Young African Leaders Initiative, who attended your webinar presentation late January 2026?
The entrepreneurs representing the Young African Leaders Initiative are redefining entrepreneurship on the continent by leveraging their unique perspectives, cultural heritage, and experiences. Their ability to innovate within local contexts while connecting to global opportunities exemplifies how the new wave of entrepreneurs is not confined by geography or conventional expectations.
What were the main issues that formed your ‘lecture’ with them, Young African Leaders Initiative?
The main issues that formed my lecture for the Young African Leaders Initiative were driven by understanding the importance of building successful partnerships when expanding into the United States or any foreign market. During my lecture, I emphasized that forming strategic alliances can help entrepreneurs navigate unfamiliar business environments, access new resources, and foster long-term growth. By understanding how to establish strong and effective partnerships, emerging leaders can position their businesses for sustainable success in global markets. I also discussed the critical factors that contribute to successful partnerships, such as establishing clear communication channels, aligning on shared goals, and cultivating trust between all parties involved. Entrepreneurs must be proactive in seeking out partners who complement their strengths and fill gaps in expertise or resources. It is equally important to conduct thorough due diligence to ensure that potential collaborators share similar values and ethical standards. Ultimately, the seminar aimed to empower YALI entrepreneurs with practical insights and actionable strategies for forging meaningful connections across borders. Building successful partnerships is not only a pathway to business growth but also a foundation for driving positive change and innovation in the global marketplace.
What makes a ‘leader’ today, particularly, in the context of the emerging global business architecture?
In my opinion, a leader in today’s emerging global business architecture must navigate complexity and ambiguity with a fundamentally different skill set than what was previously required. Where traditional leadership emphasized command-and-control and singular vision, contemporary leaders succeed through adaptive thinking and collaborative influence across decentralized networks. Furthermore, emotional intelligence has evolved from a soft skill to a strategic imperative. Today, the effective modern leader must possess deep cross-cultural intelligence, understanding that global business is no longer about exporting one model worldwide but about genuinely integrating diverse perspectives and adapting to local contexts while maintaining coherent values.
Does multinational culture play in its (leadership) formation?
I believe multinational culture plays a profound and arguably essential role in forming the kind of leadership required in today’s global business environment. Leaders who have lived, worked, or deeply engaged across multiple cultural contexts develop a cognitive flexibility that’s difficult to replicate through reading or training alone. More importantly, multinational exposure tends to dismantle the unconscious certainty that one’s own way of doing things is inherently “normal” or “best.” Leaders shaped in multicultural environments often develop a productive discomfort with absolutes; they become more adept at asking questions, seeking input, and recognizing blind spots. This humility and curiosity become strategic assets when building global teams, entering new markets, or navigating geopolitical complexity. However, it’s worth noting that multinational experience alone doesn’t automatically create great leaders. What matters is the depth and quality of cross-cultural engagement, not just the passport stamps. The formation of global leadership is less about where someone has been and more about whether they’ve developed the capacity to see beyond their own cultural lens and genuinely value differences as a source of insight rather than merely tolerating them as an obstacle to overcome.
In the context of heightening geopolitical situation, and with Africa, what would you say, in terms of, people-to-people interaction?
People-to-people interaction is critically important in the African business context, particularly as geopolitical competition intensifies on the continent. In this crowded and often transactional landscape, the depth and authenticity of human relationships can determine whether a business venture succeeds or fails. I spoke on this during my presentation. When business leaders take the time for face-to-face meetings, invest in understanding local priorities rather than imposing external agendas, and build relationships beyond the immediate transaction, they signal a different kind of partnership. The heightened geopolitical situation actually makes this human dimension more vital, not less. As competition increases and narratives clash about whose model of development is best, the businesses and nations that succeed in Africa will likely be those that invest in relationships characterized by reciprocity, respect, and long-term commitment rather than those pursuing quick wins.
How important is it for creating public perception and approach to today’s business?
Interaction between individuals is crucial for shaping public perception, as it influences views in ways that formal communications cannot. We live in a society where word-of-mouth, community networks, and social trust areincredibly important. As a result, a business leader’s behavior in personal interactions, their respect for local customs, their willingness to listen, and their follow-through on commitments have a far-reaching impact that extends well beyond the immediate meeting. The geopolitical dimension amplifies this importance because African nations now have choices. They’re no longer dependent on any single partner and can compare approaches to business.
From the above discussions, how would you describe global business in relation to Africa? Is it directed at creating diverse import dependency?
While it would be too simplistic to say global business is uniformly directed at creating import dependency, the structural patterns that have emerged often produce exactly that outcome, whether by design or as a consequence of how global capital seeks returns. Global financial institutions and trade agreements have historically encouraged African nations to focus on their “comparative advantages” in primary commodities rather than industrial development. The critical question is whether global business can engage with Africa in ways that build productive capacity, transfer technology, develop local talent, and enable countries to manufacture for themselves and for export—or whether the economic incentives and power irregularities make this structurally unlikely without deliberate policy intervention.
World
Russia Expands Military-Technical Cooperation With African Partners

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
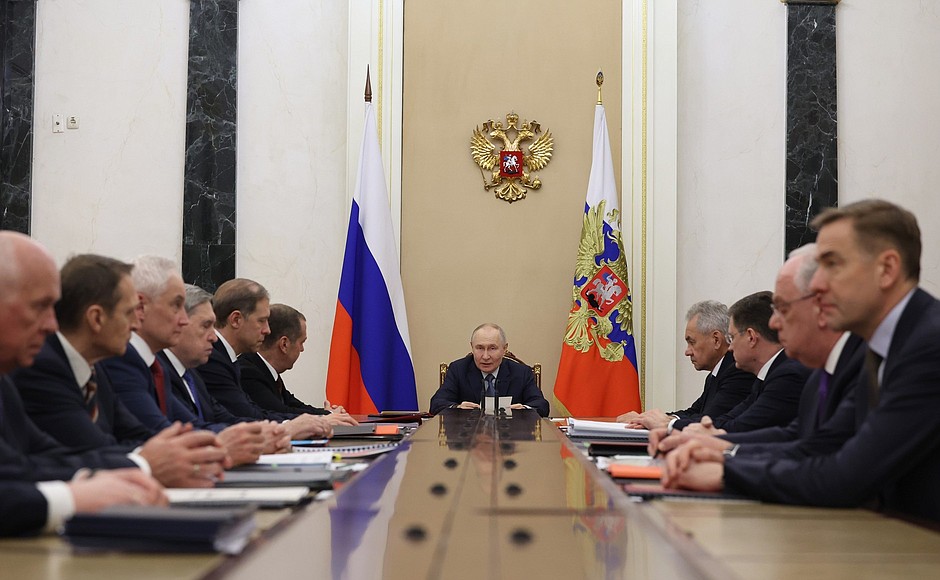
Despite geopolitical complexities, tensions and pressure, Russia’s military arms and weaponry sales earned approximately $15 billion at the closure of 2025, according to Kremlin report. At the regular session, chaired by Russian President Vladimir Putin on Jan. 30, the Commission on Military and Technical Cooperation with Foreign Countries analyzed the results of its work for 2025, and defined plans for the future.
It was noted that the system of military-technical cooperation continued to operate in difficult conditions, and with increased pressure from the Western countries to block business relations with Russia. The meeting, however, admitted that export contracts have generally performed sustainably. Russian military products were exported to more than 30 countries last year, and the amount of foreign exchange exceeded $15 billion.
Such results provide an additional opportunity to direct funds to the modernization of OPC enterprises, to the expansion of their production capacities, and to advanced research. It is also important that at these enterprises a significant volume of products is civilian products.
The Russian system of military-technical cooperation has not only demonstrated effectiveness and high resilience, but has created fundamental structures, which allow to significantly expand the “geography” of supplies of products of military purpose and, thus strengthen the position of Russia’s leader and employer advanced weapons systems – proven, tested in real combat conditions.
Thanks to the employees of the Federal Service for Military Technical Cooperation and Rosoboronexport, the staff of OPC enterprises for their good faith. Within the framework of the new federal project “Development of military-technical cooperation of Russia with foreign countries” for the period 2026-2028, additional measures of support are introduced. Further effective use of existing financial and other support mechanisms and instruments is extremely important because the volumes of military exports in accordance with the 2026 plan.
Special attention would be paid to the expansion of military-technological cooperation and partnerships, with 14 states already implementing or in development more than 340 such projects.
Future plans will allow to improve the characteristics of existing weapons and equipment and to develop new promising models, including those in demand on global markets, among other issues – the development of strategic areas of military-technical cooperation, and above all, with partners on the CIS and the CSTO. This is one of the priority tasks to strengthen both bilateral and multilateral relations, ensuring stability and security in Eurasia.
From January 2026, Russia chairs the CSTO, and this requires working systematically with partners, including comprehensive approaches to expanding military-technical relations. New prospects open up for deepening military-technical cooperation and with countries in other regions, including with states on the African continent. Russia has been historically strong and trusting relationships with African countries. In different years even the USSR, and then Russia supplied African countries with a significant amount of weapons and military equipment, trained specialists on their production, operation, repair, as well as military personnel.
Today, despite pressure from the West, African partners express readiness to expand relations with Russia in the military and military-technical fields. It is not only about increasing supplies of Russian military exports, but also about the purchase of other weapons, other materials and products. Russia has undertaken comprehensive maintenance of previously delivered equipment, organization of licensed production of Russian military products and some other important issues. In general, African countries are sufficient for consideration today.
World
Trump Picks Kevin Warsh to Succeed Jerome Powell as Federal Reserve Chair

By Adedapo Adesanya
President Donald Trump has named Mr Kevin Warsh as the successor to Mr Jerome Powell as the Federal Reserve chair, ending a prolonged odyssey that has seen unprecedented turmoil around the central bank.
The decision culminates a process that officially began last summer but started much earlier than that, with President Trump launching a criticism against the Powell-led US central bank almost since he took the job in 2018.
“I have known Kevin for a long period of time, and have no doubt that he will go down as one of the GREAT Fed Chairmen, maybe the best,” Mr Trump said in a Truth Social post announcing the selection.
US analysts noted that the 55-year old appear not to ripple market because of his previous experience at the apex bank as Governor, with others saying he wouldn’t always do the bidding of the American president.
If approved by the US Senate, Mr Warsh will take over the position in May, when Mr Powell’s term expires.
Despite having argued for reductions recently, “Warsh has a long hawkish history that markets have not forgotten,” one analyst told Bloomberg.
President Trump has castigated Mr Powell for not lowering interest rates more quickly. His administration also launched a criminal investigation of Powell and the Federal Reserve earlier this month, which led Mr Powell to issue an extraordinary rebuke of President Trump’s efforts to politicize the independent central bank.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn












