World
Russia’s Vaccine Matters to the World
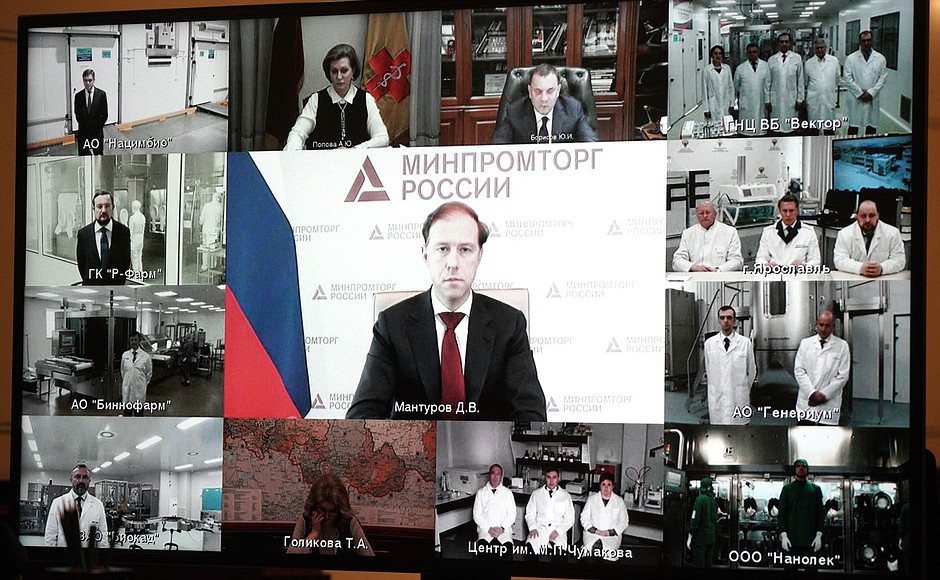
By Kester Kenn Klomegah
President Vladimir Putin has praised the entire healthcare system and particularly the hard-working team of scientists and specialists from different institutions for their efforts at research and creating a series of coronavirus vaccines for use against the coronavirus both at home and abroad.
Three vaccines already registered in Russia, two of them – Sputnik V and EpiVacCorona – are produced in large quantities by Russian pharmaceutical companies and are currently used for vaccination. It is additionally planned to roll out another one – CoviVac.
Despite the pandemic-related challenges, the domestic pharmaceutical companies, in conjunction with research institutes, have managed to accomplish a multitude of objectives in order to deploy new vaccine production sites in a short amount of time, Putin said during a videoconference meeting focused on increasing the manufacturing capacity of COVID-19 vaccines and the progress of vaccination in Russia.
Unreservedly made reference to staff qualities such as consistent and effective hard-work, truly selfless work and responsible attitude, and further urged them to continue making relentless efforts in stabilising the spread of the coronavirus infections and in protecting the life and health of millions of people in the country.
Putin further noted that the implementation of a wide range of preventive measures, including widespread vaccination, has played a significant role in normalising the epidemic situation.
Overall, 6.3 million Russians have taken the first part of the vaccine, of these 4.3 million have been vaccinated in full, that is, they have received both vaccine components.
“We can safely say, and the practical results indisputably corroborate, the fact that the Russian vaccines are absolutely safe and dependable. Our success is recognised abroad as well. The number of countries using the Sputnik V vaccine is expanding fast, more countries around the world are showing interest in our vaccine with 55 countries having authorised its use,” he told the meeting.
In addition, Russia now has a number of contracts with foreign manufacturers, – these are foreign manufacturers who will be producing our vaccine on their territory – have been signed for the number of doses needed to vaccinate 700 million people per year.
The latest, it has signed a contract with an Indian company for doses to vaccinate 100 million people. Indisputably, working with 55 countries means a total population of 1.4 billion. There are plans to expand the number of partner countries and that will reach an estimated 2.5 billion people.
While Russia and its pharmaceutical companies are considering the dynamics of the global market and the demand for Russian-made vaccines, and expanding their production capacities, it equally places emphasis on domestic needs, supplying and vaccinating Russian citizens with vaccines, is an absolute priority.
It is estimated that at least 60 per cent of all adults in the country must be vaccinated for complete stabilisation. This requires 69.8 million sets of vaccine doses. At any rate, there are more than 20 million Sputnik V doses, according to the Russian president, quoting his Prime Minister Mikhail Mishustin.
In his contribution at the meeting, Minister of Industry Denis Manturov informed that under the plan, 12.5 million sets of the vaccine must be produced in March. The planned figure for April is 17 million. It is planned to continue building up production so as to have over 80 million two-component doses by the first six months.
According to him, all these amounts will be primarily used to vaccinate Russian citizens. In order to meet the global demand for Russian vaccines, his ministry is working on scaling up the production of vaccines and on transferring technology abroad. It already has comprehensive agreements on this with manufacturers in 10 countries.
Healthcare Minister Mikhail Murashko informed the meeting about organisations that keep monitoring the virus’s mutations, including those in Russia. “We are analysing the efficiency of medicines for preventing the disease caused by various strains. This work is ongoing continuously and involves several agencies,” he said, and further mentioned the need to increase the speed of vaccination.
By the end of March, our healthcare facilities will receive over 6.5 million doses of Sputnik V. We expect that a total of some 30 million doses will be delivered in April and May. As of now, there are 4,500 stationary vaccination stations across Russia and plans to increase this figure, as well as over 1,000 mobile stations.
Participating in the meeting, Pharmstandard Chairman of the Board Viktor Kharitonin also discussed the production capability of the vaccine and pointed to the successful completion of the transfer of laboratory technology, scaled and fine-tuned the manufacturing technology abroad.
“It should be specifically pointed out that, thanks to our cooperation with the Russian Direct Investment Fund, we have started supplying the vaccine to foreign markets. We have already transferred the production technology to Kazakhstan and Belarus and continue working with other countries, including India and Italy. In Italy, Sputnik V was highly praised by both scientists and our colleagues from pharmaceutical companies,” added Kharitonin.
Taking his turn, Chairman of the Board of the R-Pharm Group Alexei Repik talked about efforts that are currently focused on the creation and manufacturing of new forms of the vaccine that will be easier to use and also to transport. He noted that it will increase the attractiveness of the vaccines on foreign markets, including countries with a hot climate: the Middle East, Africa and Latin America.
“Our factory is now producing the first registration batches of a promising lyophilic form of the vaccine created by our experts. It has proved stable at temperatures between +2 and +8 C. We are now studying its stability at room temperature. There are grounds to believe that we will succeed. This form will allow us to make the vaccine available in hard-to-reach regions of the country, which is especially important ahead of the spring and summer period,” informed Alexei Repik.
Director of the Gamaleya National Research Centre for Epidemiology and Microbiology Alexander Gintsburg also highlighted a few aspects of the vaccine production and about documents for registration. According to him, the Gamaleya Research Centre also addresses the problem of expanding the production of the Sputnik Light vaccine.
In addition, as the holder of the registration certificate, the Centre assumes all responsibility for quality control of this vaccine at all enterprises where it is manufactured in this country and abroad.
Moreover, the Centre is directly involved in launching contractual production that is mostly organised by the Russian Direct Investment Fund. The Centre has prepared the entire package of documents for registering the Sputnik Light vaccine in 55 countries. Considering that each country has its own regulatory system, this is not a fixed package of documents that will apply everywhere, therefore it has to adapt it to every country’s regulatory system.
He further spoke about The Lancet, a highly prestigious and popular medical journal, that published two articles on the results of scientific data and clinical trials. This provides important scientific evidence proving the vaccine’s efficacy, this has completely eliminated the Western academic community’ scepticism regarding the vaccines’ quality and efficacy.
Alexander Gintsburg explained a little about children’s vaccination. According to him, children must be divided into several age groups. Russian experts and specialists in paediatric immunology are working in this direction. He said that a vaccine has been developed, patented, and are currently launching clinical trials of Sputnik V’s intranasal form. This is a very gentle and patient-friendly form of vaccination for children, especially little children, who can be traumatised when they see a syringe or when possible side effects arise. The first experiments show that the intranasal form is completely free from any side effects.
CEO of the Russian Direct Investment Fund (RDIF) Kirill Dmitriev stressed patent protection and protecting intellectual rights for Russian made vaccines and other medical products. “Our patent protection is very strong. We submitted applications early on, much earlier than other countries, and thus got a headstart. Accordingly, the Gamaleya Institute owns the innovations that are available even at these foreign sites, which include over 20 partner companies in 10 countries,” he told the meeting.
On foreign cooperation, “Mr President, I would like to thank you, because it was your idea to build production partnerships with various countries, and 20 manufacturers from over 10 countries responded. For them, it’s about vaccine safety and independence, and Russia was the only country to have come up with this offer. Thank you very much. They are very grateful to you for this,” Kirill Dmitriev said in appreciation.
Director-General of the Vektor State Research Centre of Virology and Biotechnology Rinat Maksyutov discussed various research operations. Vektor is the only WHO COVID-19 reference laboratory in Russia. It not only conducts the entire range of viral studies of the novel coronavirus but is also monitoring its genetic mutations across the country on a regular basis.
“By now, we have found over 5,300 genetic variations across the genome. In the overwhelming number of cases, the replacement does not change the epidemiological characteristics of the virus. At the same time, we have also found over 50 variations of the British strain, three cases of the South African strain and over 20 unique variations of the virus that must be thoroughly studied,” he said.
According to Rinat Maksyutov, the Research Centre Vektor is studying these variations of the virus in accordance with a special algorithm. “We are studying the virus’s stability on various surfaces; we are also using unique equipment, which has no analogues throughout the world, to study the ability of the virus to be transmitted between living organisms. We have found that the British strain of the novel coronavirus can be effectively neutralised by serum taken from those who had COVID and those vaccinated with Sputnik V or EpiVacCorona,” he told the meeting.
Director-General of the Chumakov Federal Scientific Centre for the Research and Development of Immune and Biological Products (Russian Academy of Sciences) Aidar Ishmukhametov spoke about their engagement and involvement in research and production of medical products, tracing its roots to the Soviet Union.
The Chumakov Centre is one of the oldest facilities in the Russian Federation and the oldest vaccine developer in Russia. That in the 1960s, this centre’s achievements helped the country deal with polio. The centre back then developed a unique vaccine that supplied to the entire world, including the United States, Europe, Japan and many other countries. In fact, now this facility, the Institute of Poliomyelitis, is well-known around the world.
It is continuing this tradition. As of today, it has developed and produced five vaccines, including for tick-borne encephalitis, rabies and the yellow fever vaccine that is supplied to almost 50 countries, which is perhaps Russia’s biggest export in the pharmaceutical industry.
This type of organisation that has a research and development facility at its core that can outline the task and release a certain number of batches of the vaccine consisting of tens of millions [of doses], on one hand, and well-coordinated work with research institutes and the search for partners, on the other hand, is a very efficient model.
“We did not intend to work exclusively on the coronavirus vaccine. It was important to us to maintain the same production volume and supply vaccines according to the national vaccination calendar as well as deliver on the exports. So we needed to fit this new objective into our existing model. We inherited this research and development facility from the Soviet Union where it was a leader in this industry, and we are developing it,” he underlined the importance of his institution at the meeting.
CEO of the National Immunobiological Company, Rostec State Corporation, Andrei Zagorsky, however, noted that vaccine production is growing steadily. He highlighted the question of warehousing (storage), freezer facility and shipping to the regions. This is carried out in close cooperation with the manufacturing sites, as well as cargo recipients in the regions. These tasks are fulfilled on schedule, he said.
“We monitor the entire production process, especially the temperature, all the way from production, transport, acceptance to a warehouse, storage at the warehouse, to shipment to a recipient region. All products are transported in thermal containers, which can keep temperatures at 18 degrees below zero Celsius for about five days,” he added, speaking at the meeting.
Deputy Prime Minister Tatyana Golikova concluded with high appreciation. The meeting ended with a clear understanding of what direction should be moving to overcome the coronavirus pandemic and at the same time, extend assistance to foreign countries that are in need.
She, however, reiterated that, in a fairly short time, despite the difficulties and amid the challenging pandemic of 2020, all her colleagues have indeed accomplished something that seemed almost impossible, worked 24/7 and made Russia the leader in the production and use of vaccines, primarily, for the public in Russia.
Kester Kenn Klomegah is a versatile researcher and a passionate contributor. Most of his well-resourced articles are reprinted elsewhere in a number of reputable foreign media.
World
AfDB Attracts $2.2bn for Nigeria’s Special Agro-industrial Processing Zones

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
Investors are interested in investing about $2.2 billion in the Special Agro-Industrial Processing Zones Nigeria Phase II project.
This was recently facilitated by the African Development Bank Group (AfDB) at the Africa Investment Forum.
The initiative is expected to revolutionize Nigeria’s agricultural sector, as it will create agro-industrial hubs that drive productivity, enhance food security, raise living standards and create jobs.
Those interested in the project include Arise IIP, Arab Bank for Economic Development in Africa, Africa Export-Import Bank, Sahara Farms, BPI France, Africa50, and the US Development Finance Corporation.
They engaged the Nigerian government at a meeting on Wednesday, December 4, 2024.
The SAPZ Nigeria Program is a country-wide government-enabled and private-sector-led investment program that will, (i) provide infrastructure for the establishment of agro-industrial zones, (ii) strengthen institutional capacity and business environment for agro-industrial development and (iii) support agricultural productivity, skills, and private investment across value chains.
SAPZs are established in areas with high agricultural production potential. They are provided with infrastructure, common services, and supported by policy incentives to integrate agricultural and industrial businesses. Through value-added manufacturing, they have the potential to trigger the long-delayed structural transformation that revitalizes rural areas, enhance food security, improve employment, and boost regional and international trade.
Phase I Nigerian States benefiting from the program are Cross River, Imo, Ogun, Oyo, Kaduna, Kwara and Kano, and the Federal Capital Territory. SAPZ Nigeria Phase II is underway to expand to an additional 24 States in Nigeria in the next 3 years and will link Nigeria’s agriculture to agro-industrialization to drive economic growth.
The president of AfDB, Mr Akinwumi Adesina, said, “This is a defining moment for Nigeria’s agricultural transformation.”
“The Nigeria SAPZ II project will create millions of jobs, empower smallholder farmers, and position Nigeria as a leader in agro-industrialization. These investments exemplify the power of collaboration to achieve sustainable development in Africa,” he added.
The bank’s Director General for Nigeria, Mr Abdul Kamara, said, “I am pleased to see this whopping investment interest and commitments by our financing partners for Nigeria, at a time when the country is ramping up efforts to attract investments into the agriculture sector to address food security, create job opportunities and boost economic growth.”
World
Russia, Africa Establish Cultural Telebridge

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
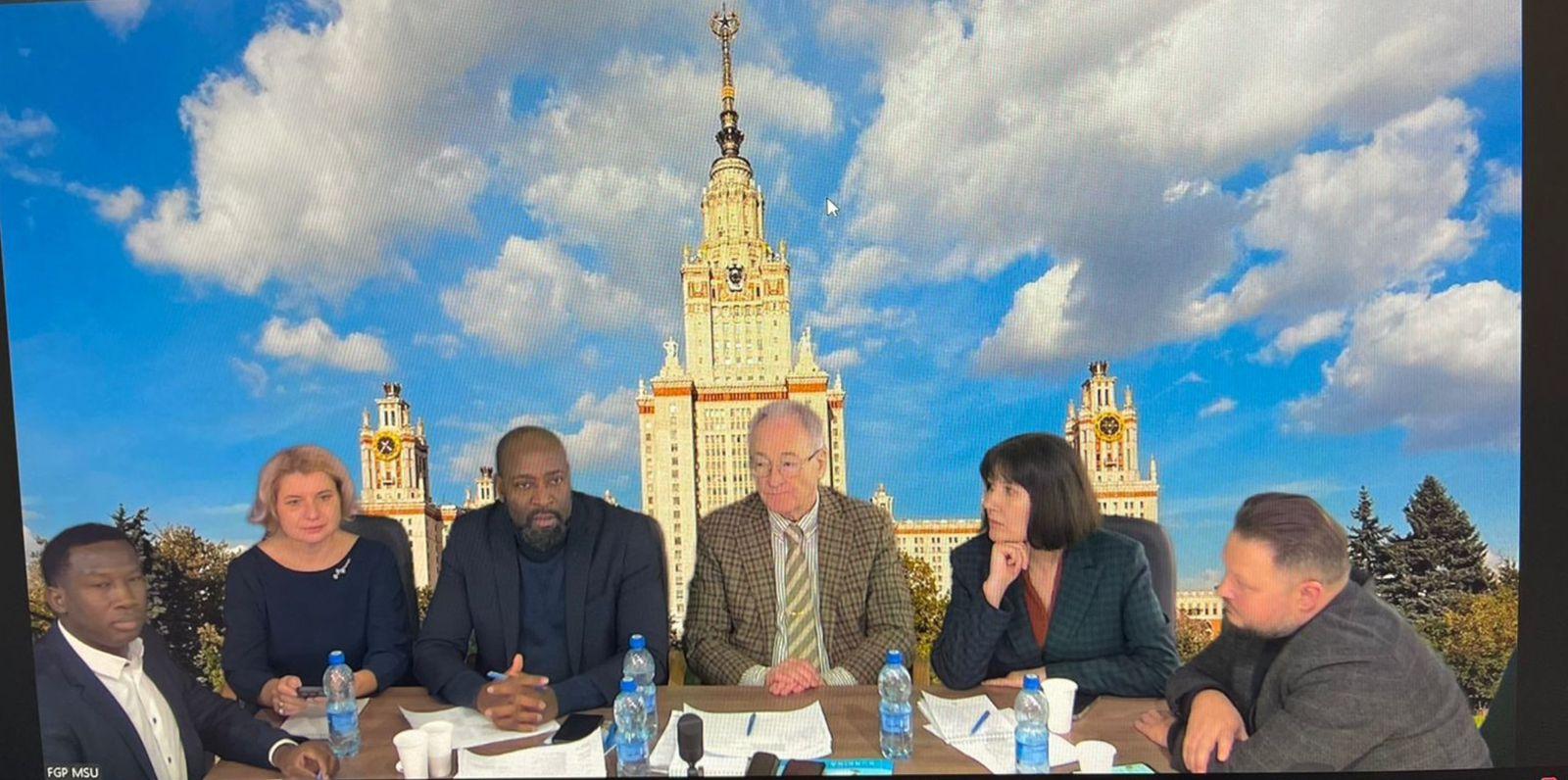
Russia and Africa have moved one more step forward in their bilateral relations by establishing a cultural telebridge dedicated to the formation and development of the Museum of African Cultures in Moscow. The cultural telebridge between Russia and Africa was organized by the Russian-African Club of Lomonosov Moscow State University (MSU) with the support of the Secretariat of the “Russia-Africa Partnership Forum” under the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Russian Federation.
The telebridge was held on three main platforms – in Moscow (Russia), Ouagadougou (Burkina Faso), and Yaoundé (Cameroon), and included participants from Morocco, Guinea, Benin, Côte d’Ivoire, Zambia, Burkina Faso, South Africa, and Egypt.
The main speakers of the telebridge included representatives of the ministries and cultural authorities of Russia and African countries, diplomats, museum specialists from Russia and Africa, private collectors, universities, NGOs, journalists, and members of the African diaspora.
The event was opened by Ilya Ilyin, Dean of the Faculty of Global Processes and First Vice-President of the Russian-African Club at MSU. He highlighted the topic of the telebridge on the development of the Museum of African Cultures which was deliberately chosen for discussion. The need to expand humanitarian cooperation with African countries was specifically emphasized at the second summit of the “Russia-Africa Partnership Forum” as well as at the Russia-Africa Ministerial Conference held in Sochi in November 2024. Work in this direction is being carried out in accordance with the priorities outlined by Russian President Vladimir Putin on March 30, 2020, under the “Priority Steps in Africa” decree. Among the key initiatives in the humanitarian field is the idea of creating the Museum of African Cultures, which will be the only museum outside of the African continent officially dedicated to African themes. The museum will be established at the renowned State Museum of Oriental Art.
Ilya Ilyin noted as a significant achievement the agreement to establish a branch of the Russian-African Club in Burkina Faso, and work on this initiative is ongoing. He expressed gratitude to Daniel Sawadogo, former cultural attaché of Burkina Faso’s Embassy in Russia, who participated in the telebridge, for his efforts in strengthening cooperation between Burkina Faso and Russia.
Ilyin reminded the audience that the year 2025 will mark the 270th anniversary of Moscow State University and the 220th anniversary of the Moscow Society of Naturalists, chaired by MSU Rector V.A. Sadovnichy. Additionally, in 2025, the Faculty of Global Processes of MSU will celebrate its 20th anniversary. The most significant event of 2025 will be the 80th anniversary of the Great Victory. In this regard, the Dean proposed continuing the tradition of holding a memorial event involving Russian-African youth at Poklonnaya Gora, as was done in 2023 and 2024.
Tatiana Dovgalenko, Ambassador-at-Large of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Russian Federation and head of the Secretariat of the Russia-Africa Partnership Forum spoke about the active work being carried out in conjunction with the Ministry of Culture of Russia, Rossotrudnichestvo, cultural institutions, and civil society circles in hosting thematic exhibitions, theatre festivals, cultural days, concerts, film screenings, and lectures in Africa. Significant projects are being implemented by the Russian Institute of Theatre Arts (GITIS), the Inopraktika Foundation, and the Moscow Conservatory. These and other initiatives demonstrate the explosive interest of Africans in Russian culture. The demand among African students for creative education in Russia continues to grow. Today, citizens from 20 African countries are studying in Russian cultural universities.
The Museum of African Cultures will immerse the Russian audience in the richness of African culture and peoples. It will display the collected artefacts housed in Russia, primarily African art pieces from the State Museum of Oriental Art. This collection comprises more than 1,100 items and is continuously replenished through scientific research expeditions, temporary exhibitions, and private collections donated by prominent Russian Africanists. T.E. Dovgalenko expressed confidence in the museum’s role as a profound cultural bridge.
The museum will become a significant platform in Russia for hosting educational, cultural, and business events, implementing educational programs, and conducting scientific research in the field of African studies, as well as simply a space of creative power.
The lead moderator of the telebridge, Alexander Berdnikov, Executive Secretary of the Russia-Africa Club of Lomonosov Moscow State University, introduced the co-moderators from the Russian side – Louis Gouend, Ilya Shershnev, and Inga Koryagina. He emphasized that the opening of the Museum of African Cultures is a highly important issue for both Russian and African societies.
In his opinion, it is also critical during the telebridge to address the prospects of communication with African countries in the field of humanities, particularly related to museums. The speaker reminded attendees about the “Russia Calling!” forum held on 4th December in Moscow, during which Russian President Vladimir Putin stated that Russia will develop new tools for advancing comprehensive cooperation with African countries. The Museum of African Cultures is one such new tool for collaboration in the humanitarian sphere.
The museum is being established as a multifunctional institution, also tasked with educational and expert goals, African studies training, and other functions.
Research Associate of the State Museum of Oriental Art and Africanist, Darya Vanyukova, emphasized at the beginning of her speech that no museum collection, no matter how large, can encompass the immense richness and diversity of the artistic culture of African countries. Therefore, as the expert noted, the idea of creating an exploratory museum must be approached honestly and openly. The speaker stressed the importance of developing long-term projects within the museum, which can serve as a foundation for a cultural program, allowing visitors to gain a deeper understanding of the African continent.
A key aspect of preparing for the museum’s opening involves creating a concept and designing the permanent exhibition. The expert shared plans for projects scheduled for 2025, including exhibitions dedicated to the Republic of Cameroon and the Republic of Mali. Vanyukova also mentioned that the Museum of Oriental Art’s team is counting on support from colleagues in African countries. She explained the museum’s plans to request artefacts from Russian and African museums for long-term storage, with a view to returning these valuable art pieces to their home countries once the established agreements expire.
Yuri Zaitsev, Head of Rossotrudnichestvo’s representative office in Tunisia, emphasized the importance of maintaining close ties with the African community and museum experts from the continent when establishing the museum. He expressed his hope that North Africa would be broadly represented in the museum. Additionally, Zaitsev offered comprehensive assistance and support from North African countries. He noted that the Russian House in Tunisia also supervises several countries without Rossotrudnichestvo representation, including Algeria, Libya, and Niger. This allows for facilitating communication with museum communities in those nations.
The expert proposed creating branches of the museum or exhibition complexes at VDNH or in other districts. He highlighted Tunisia’s rich historical heritage, including aspects that connect Tunisia and Russia, such as the history of the Russian Squadron and the work of artist Rubtsov, which, according to Zaitsev, should also be represented in the Museum of African Cultures.
Alla Stremovskaya, Associate Professor at the Department of Eastern Political Studies of the Faculty of Global Processes at Moscow State University, spoke about the role of museum diplomacy in international relations. She presented a report on online projects by key Russian museums. According to Stremovskaya, museum diplomacy is a form of cultural diplomacy that historically served as a strategic tool used by national governments to advance their foreign policy goals. Various countries have supported museum initiatives to disseminate their national values and ideas abroad.
Today, these functions are also fulfilled by museum online projects. Stremovskaya highlighted international online projects by the Russian Museum, the Hermitage, the Tretyakov Gallery, and the State Museum of Fine Arts. These projects combine a range of multimedia centre functions, including virtual tours, online lectures, and visits to exhibition compositions. She also mentioned major international museum online projects such as “European” and “Latino.” The expert stated that knowledge of these projects will help in creating a similar initiative for the new Museum of African Cultures.
Louis Gouend, Telebridge Moderator and Head of the Commission on Diaspora and Media Relations at the Russian-African Club of Moscow State University, expressed gratitude on behalf of the entire African community for the idea of establishing a Museum of African Cultures in Moscow, calling it a “cherished topic” for all Africans.
Gouend introduced the participating experts from the telebridge studios in Cameroon and Burkina Faso. The moderators for the telebridge in Cameroon were historian Professor Njock Nyobe Pascal, former Director of the Douala Maritime Museum, and Professor Jean-Baptiste Nzoge. The first speaker from Cameroon, Madame Rachel Mariembe, an expert in historical and cultural heritage, spoke about the work of the Douala Museum, whose collection is constantly being expanded, thanks to well-established connections with other museums, not only in Cameroon but also in other countries, as well as through collaboration with private museums.
Cameroonian museologist, Professor Michel Ndoh, expressed the opinion that the Museum of African Cultures in Moscow should represent a unique opportunity for Africans to establish strong ties with Russia. The success of the future museum in Moscow, according to the expert, depends on its programmatic policy.
The speaker highlighted that the primary mission of the museum should be showcasing Africa as a whole, while taking into account the uniqueness of each country on the continent. Africa itself must take the initiative and present its proposals, concluded Michel Ndoh.
His Majesty Mbombog Malet Ma Ndjami, Director General of the Palace of Culture and African Art, noted that a museum is a guardian of memory. According to the speaker, collaboration with Russia will provide the African continent with new opportunities to preserve its memory. Cameroonian museums were established following a model created in the 19th century, and it is from that period that the perspectives through which Africans view their memory — namely, Eurocentric perspectives — originate, noted the expert. He believes that cooperation with Russia will allow Africans to view their historical reality from a different perspective, through masterpieces of national African art. Africa shares a common memory with Russia, and together, we can embody this memory through museum partnerships.
Ndo, a museologist from Cameroon, considers the museum to be a lever for diplomacy. Diplomacy, he stated, is the interaction of all participants in the process. Therefore, the expert emphasized the importance of hearing from Russian colleagues about the specific types of support they expect from African specialists in the museum field. He proposed that mutual exchanges of conceptual ideas are crucial.
The telebridge was then passed to Burkina Faso, where the moderators were Moktar Sanfo, Director General of Culture and Arts (DGCA), and Sabari Christian Dao, Director General of the National Museum of Burkina Faso.
Christian Dao welcomed the participants of the telebridge and introduced his colleagues, gathered at the web studio in the National Museum of Burkina Faso, with a total of 20 people present. The speaker expressed collective excitement at the opening of the Museum of African Cultures in Moscow.
The first expert from Burkina Faso to speak was Juliette Congo, Director of the Women’s Museum in Kolgwendiese, founded in 2008. The Women’s Museum is a unique project as it not only showcases collections but also conducts educational programs. These initiatives highlight the role of women in African society and their contributions to national and cultural wealth. The museum houses collections dating back to the era of the Moro Kingdom, where women served as a ruling force.
Alassane Samura, Director of the Water Resources Museum, presented the concept of his museum, which is built on the idea that water permeates all of human history across all aspects of life; without water, there is no life. In Africa, where tremendous effort is often required to access water, people hold this natural resource in high regard. This is why the Water Museum was established. It features collections of ancient water storage containers and vessels, as well as tools for retrieving water.
Assane Romba, curator of the Georges Ouedraogo Museum of Music, described his museum as a “living place” where exhibits come to life. He spoke about the constant interaction with visitors through the universal language of music. The museum’s collection includes objects that serve sacred functions and are emblematic of Africa’s cultural heritage.
Sinali Djibo, Director of Exhibitions and Mediation at the National Museum of Burkina Faso, outlined the training of specialists in various areas of museum activities. The expert also shared his vision for organizing temporary exhibitions at the future Museum of African Cultures in Moscow. According to Djibo, such exhibitions must be accompanied by explanations for visitors, and he suggested using film as a tool for this purpose. He pointed out that this approach has already been implemented in Europe and parts of Africa.
Dr. Hoda Al-Saati, a representative of the Journalists’ Union of Alexandria (Egypt) and an active participant in cultural and historical events between Russia and Egypt, praised Russia’s efforts in preserving and developing the cultural heritage of African countries. She contrasted this with Western countries, which often regard Africa merely as a source of profit. The speaker supported the idea proposed by Russian and African colleagues that the museum should also function as an educational institution.
Swinni Driss, a representative of the National Museum of Morocco, spoke about the museum’s activities, and educational and cultural projects, in particular, the exhibition of postage stamps, which has become an interesting and popular event in the country.
Ernest Kpan, an expert from Côte d’Ivoire and head of the local branch of the International Council of Museums, believes that establishing a successful project requires defining the shared and fundamental foundations of the museum initiative. It is essential to know the budget allocated for the project and understand its base—both material and scientific. Another critical issue, according to the speaker, is the potential involvement of African specialists in the museum’s operations.
Tatyana Tudvaseva, President of the “Gatingo” Association and chief curator of the international art project “Africa’s World Today, Tomorrow, Yesterday,” stressed the need to include items of contemporary African art among the museum’s exhibits. The paintings of African artist-philosophers—singers of their culture and traditions—are filled with symbolism, meaningful ideas, and interest in human individuality and the surrounding nature. The speaker expressed confidence that these works of art would deeply move the Russian audience.
Moktar Sanfo, Director General for Culture and Arts and moderator in the webinar studio in Burkina Faso requested representatives of the Russian-African club to inform African colleagues about opportunities for advanced training at Moscow-based universities and the areas covered within this framework.
Suleiman Sedogo, President of the Association of Museum Professionals of Burkina Faso, stated that the primary goals of their organization are to improve the quality of museum practices in the country, develop new directions, and support collaboration between private museums and the state.
Daniel Sawadogo, former cultural and scientific advisor to the Embassy of Burkina Faso in the Russian Federation, emphasized the undeniable importance of this telebridge, which has become a significant platform for exchanging expert opinions and practical proposals between museum specialists in Russia and Africa.
Ali Degee, an expert from Burkina Faso and a graduate of a Soviet university, highlighted the exceptional importance of professional staff training in the museum field. The speaker expressed hope that such training would become accessible to the current young generation from African countries. For instance, graduates of museum studies courses organized in Burkina Faso could be sent to Russia for further education.
In conclusion, A.F. Berdnikov, the lead moderator, thanked all participants of the telebridge and noted that the event was productive and constructive. He supported the idea of making this telebridge format regular, as it would provide an excellent opportunity for the mutual exchange of proposals and concrete recommendations, not only for developing the Museum of African Cultures but also for fostering museum-sector cooperation between Russia and Africa as a whole.
World
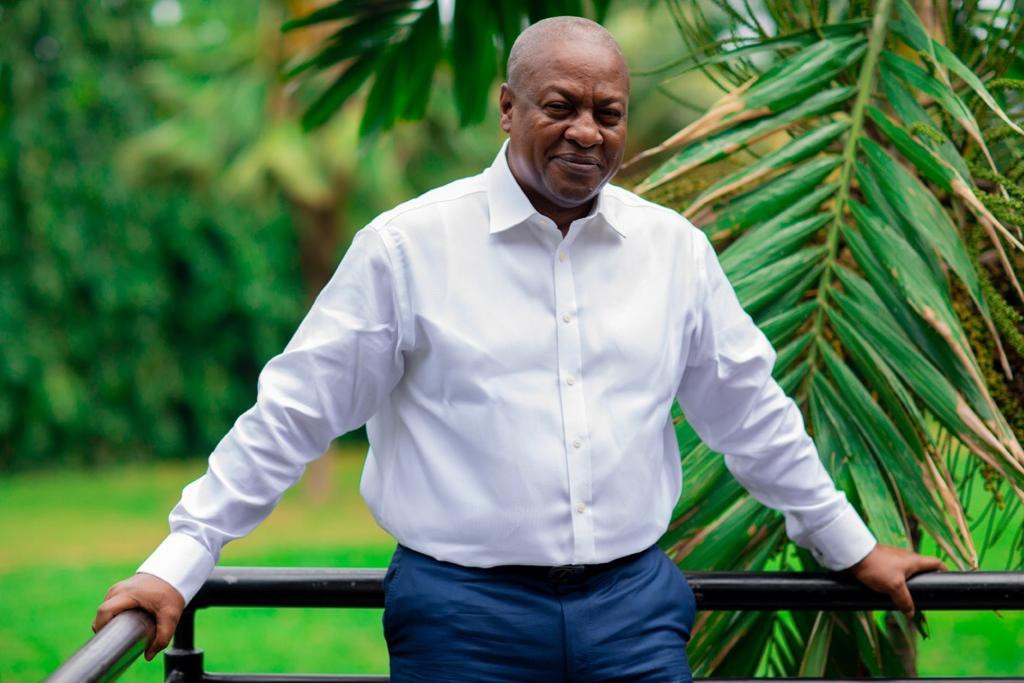
John Mahama Wins Presidential Poll to Return as Ghana’s President

By Adedapo Adesanya
Former President of Ghana, Mr John Dramani Mahama of the National Democratic Congress (NDC), has won a historic comeback election victory on Sunday as voters pushed out the ruling New Patriotic Party (NPP) over its management of economic crisis in the West African country.
NPP candidate and current Vice President Mahamudu Bawumia to incumbent President Nana Akufo-Addo today conceded defeat in the weekend presidential election after failing to shake off widespread frustration over high costs of living.
Results showed that Mr Mahama won 56.3 per cent of the vote against 41.3 per cent for Bawumia.
Mr Mahama, who ruled as president from 2012-2017, will return to lead the country on his third attempt to reclaim the nation’s top post after falling short in 2016 and 2020 elections.
Ghana’s two main parties, the NPP and NDC, have alternated in power equally since the return to multi-party politics in 1992.
The country’s economic woes dominated the election after the continent’s top gold producer and the world’s second-largest cocoa exporter went through a crisis of default and currency devaluation, ending with a $3 billion bailout from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
Meanwhile, President Bola Tinubu has congratulated Mr Mahama on his victory in the December 7 general election.
In a telephone call to Mr Mahama, President Tinubu hoped that Mahama’s ascension to power for the second time would further bring stability to the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS).
According to a statement by presidential spokesman, Mr Bayo Onanuga, the Nigerian President commended the people of Ghana for their commitment to democracy, which was demonstrated through the peaceful and successful conduct of both the presidential and parliamentary elections.
-

 Feature/OPED5 years ago
Feature/OPED5 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism8 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz2 years ago
Showbiz2 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking6 years ago
Banking6 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy2 years ago
Economy2 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking2 years ago
Banking2 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports2 years ago
Sports2 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn
-

 Technology4 years ago
Technology4 years agoHow To Link Your MTN, Airtel, Glo, 9mobile Lines to NIN










