Feature/OPED
The Intersection of Religion and Human Rights: Balancing Freedom of Religion and Societal Interest in Nigeria

By Prince Charles Dickson PhD
Last week, I had the honor of a deep dive conversation with very respected men and women of the press, from the traditional to the digital space, citizen journalists, bloggers and more. It is an interesting cohort, and I am sure that at the end of this initiative, the impacts would be felt. Let me quickly appreciate the Search For Common Ground’s Katlong, Daniel, Temisan, Emmanuela, Fatima Madaki, the Country Director, and all the wonderful souls and the work we all do in this space.
My presentation was about the complex dynamics at the intersection of religion and human rights in Nigeria, with a focus on striking a balance between the fundamental right to freedom of religion and the broader societal interests. Using real-world examples, the session explored the challenges and opportunities inherent in navigating religious diversity while upholding human rights principles with fixation on media practitioners. From issues of religious minorities’ rights to the impact of religious beliefs on public policies, the presentation offered insights into the delicate equilibrium required for peaceful coexistence. By examining specific cases and their outcomes, I sought to give them a nuanced understanding of the intricate relationship between freedom of religion and the collective interests of Nigerian society.
I sincerely hope as takeaway they were able to understand a little of the legal framework surrounding freedom of religion in Nigeria, a comprehensive examination of the constitutional and statutory provisions, as well as their practical implications.
I danced graciously around Constitutional Provisions:
- Nigeria’s Constitution, particularly Chapter IV, guarantees the right to freedom of thought, conscience, and religion.
- Sections 38 and 39 specifically address freedom of religion, ensuring individuals the right to practice, change, and manifest their religion or belief.
I looked at the Limitations and Exceptions:
- We collectively agreed that despite constitutional guarantees, there are limitations to freedom of religion, especially when it comes to public order, safety, morality, and the rights of others.
I encouraged them to further look up Religious Freedom Laws:
- By examining specific legislation related to religious freedom, such as the Religious Discrimination (Prohibition, Prevention, etc.) Act.
- Exploring how these laws are enforced and their effectiveness in protecting religious minorities.
We touched a handful of Court Decisions:
- Analyzing landmark court decisions that have shaped the interpretation and application of freedom of religion.
- And also looking at cases involving conflicts between religious practices and other legal provisions or societal interests.
Conversations like these can’t be complete without Government Policies:
- Evaluating government policies that may impact freedom of religion, such as regulations on religious institutions, licensing, or recognition was important
- Assess the extent to which these policies promote or hinder religious freedom.
It was exciting listening to perspectives for Practical Implementation:
- Examining how freedom of religion is practically implemented at the grassroots level for media personnel.
- Encouraging journalists to investigate instances where there may be discrepancies between legal guarantees and actual experiences of individuals and communities.
And finally looking at Challenges and Opportunities:
- By identifying challenges faced by the media, the individuals or religious groups in exercising their freedom of religion.
- Explore opportunities for legal reforms or advocacy to strengthen religious freedom protections with the media personnel.
It was important that we x-rayed the Sharia Law Implementation:
- In some Northern states of Nigeria, the implementation of Sharia law has been a source of tension. Cases have arisen where individuals, often from minority religious groups, have faced legal consequences under Sharia law, leading to conflicts between religious freedom and the desire for a unified legal system.
Examine Religious Practices in Educational Institutions:
- Conflicts have emerged over the enforcement of religious practices in educational institutions. For instance, debates over the use of religious attire or the observance of specific religious rituals within schools have raised questions about the balance between religious freedom and the need for uniformity and inclusivity.
Discuss the Registration and Recognition of Religious Group and Interfaith Marriages:
- Issues related to the registration and recognition of religious groups have led to conflicts. Some groups may face challenges in obtaining official recognition, impacting their ability to practice and propagate their faith freely.
- Cases involving interfaith marriages sometimes face opposition or legal challenges, especially when societal norms or interpretations of religious laws conflict with the principles of freedom of choice in marriage.
My presentation looked at the Expression of Religious Beliefs in Public Spaces:
- Disputes have arisen regarding the expression of religious beliefs in public spaces. For example, debates over religious displays, public prayers, or proselytization activities may raise concerns about the potential impact on social harmony and the rights of individuals with different beliefs.
And the important issues surrounding Medical Practices and Religious Beliefs:
- Instances where medical practices conflict with religious beliefs, such as vaccination or blood transfusion, have sparked legal debates. Balancing individual religious rights with societal interests in public health and safety is a recurring challenge.
These examples demonstrate the complex nature of balancing religious freedom with societal interests in Nigeria. Legal cases and public debates surrounding these issues highlight the ongoing need for nuanced considerations and robust legal frameworks to address conflicts and protect individual rights.
Here are some key approaches that the journalists can navigate through:
- Legislative Clarity and Protection:
- Establish clear and comprehensive legislation that protects freedom of religion while also defining reasonable limitations to prevent abuse. Legislation should aim to strike a balance that respects individual rights and considers the broader welfare of the community.
- Interfaith Dialogue and Understanding:
- Promote interfaith dialogue and understanding to foster a sense of unity and respect among different religious communities. Increased understanding can reduce misconceptions and prejudices that may lead to conflicts.
- Education and Awareness:
- Implement educational programs to raise awareness about the diversity of religious beliefs and practices. This includes incorporating teachings on religious tolerance, pluralism, and respect for individual choices within school curricula.
- Mediation and Alternative Dispute Resolution:
- Establish mechanisms for mediation and alternative dispute resolution to address conflicts arising from religious differences. This allows for a more flexible and consensual approach to dispute resolution, minimizing the need for adversarial legal proceedings.
- Community Engagement and Participation:
- Encourage active participation of religious communities in decision-making processes that affect them. Inclusive governance structures can help ensure that policies and practices respect the diverse religious landscape of the community.
- Human Rights Education:
- Integrate human rights education that includes a focus on religious freedom into school curricula, professional training programs, and community outreach initiatives. This can empower individuals to understand their rights and responsibilities in a diverse society.
- Legal Aid and Advocacy:
- Provide legal aid services to individuals facing discrimination or restrictions on their religious freedom. Advocacy efforts can focus on challenging laws or practices that disproportionately impact specific religious groups.
- Collaboration with Religious Leaders:
- Engage religious leaders as advocates for religious freedom and tolerance. Religious leaders often play a significant role in shaping community attitudes, and their support can contribute to a more inclusive and harmonious society.
- National and Local Platforms for Dialogue:
- Create platforms at the national and local levels where representatives from different religious communities can engage in constructive dialogue. These platforms can address grievances, share perspectives, and find common ground.
- Regular Review of Legislation:
- Establish a mechanism for the regular review of legislation related to religious freedom to ensure its relevance and effectiveness. This process should involve input from diverse stakeholders, including legal experts, religious leaders, and civil society.
By adopting a multifaceted and collaborative approach, societies can work towards creating environments where individual rights and communal well-being are mutually respected and protected.
And in conclusion I opined that:
The role of media… in promoting understanding and tolerance in the context of religious freedom is crucial for fostering a harmonious and inclusive society. Here’s a discussion on their respective roles:
- Media:
- Promoting Diversity: Media outlets can contribute to understanding by accurately and respectfully representing the diverse religious landscape. Highlighting stories that showcase positive interfaith interactions and initiatives can challenge stereotypes and promote tolerance.
- Responsible Reporting: Journalists should adhere to ethical reporting standards, avoiding sensationalism or biased narratives that can contribute to misunderstanding and conflict. Responsible journalism includes providing context and avoiding the amplification of divisive rhetoric.
- Educational Campaigns: Media organizations can initiate educational campaigns that raise awareness about various religious beliefs, practices, and traditions. This can contribute to breaking down stereotypes and fostering a climate of acceptance.
I believe that FoRB is an important conversation that we must collectively engage in, so that, in the end—Nigeria will win!
Feature/OPED
The Hidden Workforce of the 2026 Access Bank Lagos City Marathon
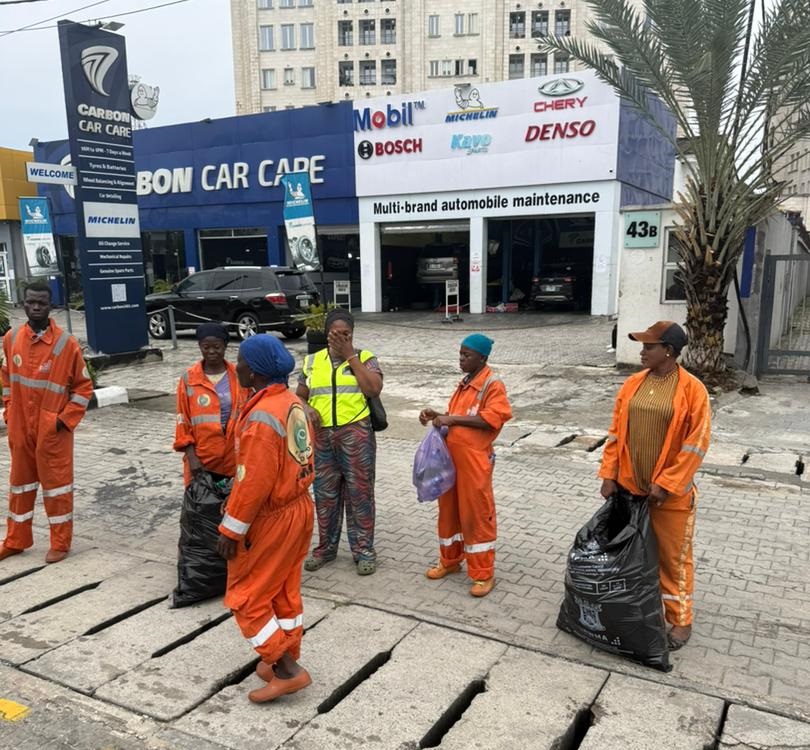

When the final runner crossed the finish line at the 11th edition of the Access Bank Lagos City Marathon (ABLCM), the applause began to fade. But for hundreds of workers across Lagos, the real work was just beginning.
Major highways had been closed to facilitate the event. Tens of thousands of runners moved through the city in a coordinated surge of athletic endurance. Thousands of bottles of water and energy drinks were distributed, alongside sachets containing essential medical supplies and medication. The race route itself was meticulously prepared, lined with banners, barricades, medical tents and precision timing systems that ensured safety, organisation and accurate performance tracking from start to finish.
What followed was the part that a few cameras lingered on, yet it remains one of the clearest indicators of institutional progress.
Within minutes of the race conclusion, coordinated sanitation teams fanned out across the marathon corridor. Their work went beyond sweeping. Waste was systematically sorted. Plastic bottles were separated from general refuse. Sachets were gathered in bulk. Collection trucks moved along predefined routes, ensuring rapid evacuation of waste. Temporary race infrastructure was dismantled with quiet precision.
In a megacity like Lagos, speed is a necessity. Urban momentum cannot pause for long. The ability to restore order quickly after an event of this magnitude reflects operational discipline across interconnected systems, municipal authorities, environmental agencies, private waste management partners and event coordinators.
Globally, large-scale sporting events are no longer evaluated solely by participation numbers or prize purses. Sustainability has emerged as a defining metric. Environmental responsiveness is now a core measure of credibility. Cities seeking tourism growth, foreign investment and international partnerships must demonstrate that scale does not compromise responsibility. The 2026 marathon provided a compelling case study in this evolution.
The clean-up operation itself generated meaningful economic activity. Temporary employment opportunities emerged for sanitation workers and logistics personnel. Recycling partners engaged in material recovery, reinforcing circular economy value chains. What was once viewed as routine waste disposal has evolved into a structured ecosystem of environmental services, a sector of increasing importance in modern urban economies.
This level of sustainability was the result of deliberate planning. Effective post-event recovery requires route mapping, waste volume projections, coordination between sponsors such as Access Bank Plc and municipal bodies, contingency planning for congestion points and clear communication protocols.
Each edition of the marathon has built on lessons from the last. International participation has expanded. Accreditation standards have strengthened. Media visibility has grown. Most importantly, environmental management has become embedded in the marathon’s operational framework rather than treated as an afterthought.
Progress rarely arrives in dramatic leaps, it advances through incremental improvements, refined systems and institutional learning. Just as elite runners close performance gaps through disciplined training, cities strengthen their global standing through consistent operational excellence.
The 2026 marathon, therefore, tells a story that extends far beyond athletic achievement. It is a story of coordination, sustainability as strategy rather than slogan, and the often unseen workforce, sanitation workers, planners, volunteers, security officials and environmental partners, whose discipline sustains the spectacle.
Because in the end, global cities are judged by how well they host and how responsibly they restore. On the marathon day in Lagos, it was the runners who demonstrated endurance and the systems, and the people behind them, who ensured that when the cheering stopped, the city kept moving.
Feature/OPED
N328.5bn Billing: How Political Patronage Built Lagos’ Agbero Shadow Tax Empire

By Blaise Udunze
Lagos prides itself as Africa’s commercial nerve centre. It markets innovation, fintech unicorns, rail lines, blue-water ferries, and billion-dollar real estate. Though with the glittering skyline and megacity ambition lies a parallel state, a shadow taxation regime run not from Alausa, but from motor parks, bus stops, and highway shoulders. They are called “agberos.” And for decades, they have functioned as Lagos’ unofficial tax masters.
What began as loosely organised transport unionism mutated into a pervasive and often violent system of extortion. Today, tens of thousands of commercial buses, over 75,000 danfos according to estimates by the Lagos Metropolitan Area Transport Authority, ply Lagos roads daily. Each bus is a moving ATM. Each stop is a tollgate. Each route is a revenue corridor.
Looking at the daily estimate from their operations, at N7,000 to N12,000 per bus per day, conservative calculations show that between N525 million and N900 million is extracted daily from drivers. Annually, that balloons toward N192 billion to N328.5 billion or more, money collected in cash, unreceipted, unaudited, unaccounted for. This illicit taxation on an industrial scale did not emerge in a vacuum.
The reality today is that to understand the scale of the problem, one must confront its political history. It was during the administration of Bola Ahmed Tinubu as Lagos State governor from 1999 to 2007, who is now the President, that the entrenchment of transport union dominance and motor park patronage deepened.
Under his political machine, transport unions became not just labour associations but mobilisation structures, formidable grassroots networks capable of crowd control, voter turnout engineering, and territorial enforcement. In exchange for political loyalty, street influence translated into operational latitude.
Motor parks became power bases. “Area boys” became enforcers. Union leadership became politically connected. What should have been regulated associations morphed into revenue-generating franchises with muscle.
The system outlived his tenure. It institutionalised itself. It professionalised. It is embedded in Lagos’ political economy.
And today, it thrives in broad daylight. Endeavour to visit Ajah under bridge, Ikeja under bridge, or Mile-2 along Ojo at 6:00 a.m. Watch drivers clutching crumpled naira notes. Observe men in green trousers and caps marked NURTW weaving between buses, collecting what drivers call òwò àrò, or evening as òwò iròlè money taken from passengers.
A korope driver shouts, “Berger straight!” His bus fills. The engines rumble. But before he moves, he must pay. If he refuses? The side mirror may disappear. The windscreen may crack. The conductor may be assaulted. The vehicle may be blocked with planks, and if they resist, the conductor or driver may be beaten. Movement becomes impossible. It is not optional.
This is common across Lagos, especially amongst drivers in Oshodi, Obalende, Ojodu Berger, Mile 2, Iyana Iba, and Badagry, and describes a three-layered structure ranging from street collectors, area coordinators, and union executives at each location. Daily targets flow upward. Commissions remain below.
One conductor disclosed he budgets at N8,500 daily for louts alone, excluding fuel, delivery to vehicle owners, and official tickets. Another driver says he parts with nearly N15,000 in total daily levies across routes.
Of N40,000 collected on trips, barely N22,000 survives before fuel. Sometimes, drivers go home with N3,500. Working like elephants. Eating like ants. The impact extends far beyond drivers.
Every naira extorted is transferred to commuters. An N700 fare becomes N1,500. A N400 corridor becomes N1,200 in traffic, and this is maintained even after fuel prices fall; fares rarely decline. The hidden levy remains.
Retail traders reduce stock purchases because transport eats profits. Civil servants watch salaries stagnate while commuting costs climb. Market women complain that surviving Lagos costs more than living in it.
This is not just a transport disorder. It is inflation engineered by coercion. Economists call it financial leakage, money extracted from the productive economy that never enters the fiscal system. Billions circulate annually without appearing in government ledgers. No roads are built from it. No hospitals funded. No schools renovated.
It is taxation without development. Small and Medium Enterprises form nearly half of Nigeria’s GDP and employ the majority of its workforce. In Lagos, they are under assault from informal levies layered on top of official taxes. Goods delivered by bus carry hidden transport premiums. Commuting staff face higher daily costs. Inflation ripples through supply chains.
The strike by commercial drivers in 2022 exposed the depth of resentment. Under the Joint Drivers’ Welfare Association of Nigeria (JDWAN), drivers protested “unfettered and violent extortion.” Lagos stood still. Commuters trekked. Appointments were missed. Businesses stalled.
Drivers alleged that half of their daily income vanished into motor park collections.
Some who protested were attacked. Yet the collections continued.
Drivers insist daily collections at single corridors can exceed N5 million. Park chairmen allegedly control enormous cash flows. Uniformed collectors operate with visible confidence.
Meanwhile, the Lagos State Government denies sanctioning any roadside extortion. Officials describe the tax system as institutionalised and structured. They promise reforms through Bus Rapid Transit, rail expansion and corridor standardisation. Yet the shadow toll persists.
Contrast this with Enugu State, where Governor Peter Mbah introduced a Unified e-Ticket Scheme mandating digital payments directly into the state treasury. Paper tickets were banned. Cash collections outlawed. Revenue flows are traceable. Harassment criminalised.
Drivers in Lagos say openly that they should be given a single N5,000 daily ticket paid directly to the government, and end the chaos. Instead, they face multiple actors, agberos, task forces, and traffic officials, each demanding settlement.
The difference is in governance philosophy. One digitises and centralises revenue to eliminate leakages.
The other tolerates fragmentation that breeds shadow collectors. The uncomfortable truth is that the agbero structure is politically sensitive. Transport unions are not just labour bodies; they are political instruments. They mobilise during elections. They maintain territorial presence. They command street loyalty. In return, they are allegedly tolerated, protected, or absorbed into broader political structures as they turn into war instruments and a battle axe in the hands of the government of the day. The underlying reality is that the agbero who are the street-level power structures and the government authorities benefit from each other; the line between unofficial influence and official governance becomes unclear, making reform politically sensitive.
The issue is not merely about street disorder; it is about economic governance. Illicit taxation distorts pricing mechanisms, reduces productivity, discourages the formalisation of businesses, and weakens public trust. If citizens are compelled to pay both official taxes and unofficial levies, compliance morale declines. Why comply with statutory taxation when parallel systems operate unchecked?
Dismantling them is not merely administrative; it is political. Perhaps unbeknownst to the people, the cost of inaction is immense. Lagos aspires to be a 21st-century smart megacity under such an atmosphere. But investors notice informal roadblocks. Businesses factor in unpredictability. Commuters absorb unofficial taxes daily. Across Lagos roads, the script repeats “òwò mi dà,” meaning, give me my money.
Passengers plead with collectors to reduce levies so they can proceed. Conductors argue over dues before departure. Citizens feel hostage to a system they neither elected nor authorised.
Taxation, constitutionally, belongs to the state. It must be legislated, receipted, audited and deployed for the public good.
Agbero taxation is none of these. It is coercive. It is not transparent. It is extractive. Lagos has launched rail lines and BRT corridors. The Lagos Metropolitan Area Transport Authority continues transport reforms. Officials promise that bus reform initiatives will eliminate unregistered operators. But reform cannot be selective. You cannot modernise rail while medieval tolling persists on roads. You cannot preach digital governance while cash collectors flourish at bus stops. You cannot aspire to global city status while informal muscle dictates movement.
The solution is not episodic arrests. It is a structural overhaul: mandatory digital ticketing across all parks; a single harmonised levy payable electronically; an independent audit of union revenue; protection for drivers who resist illegal collections; and political decoupling of unions from patronage networks.
The agbero empire is not merely about bus fares. It is about how patronage systems, once empowered, metastasise into parallel authorities. What may have begun as strategic alliance-building two decades ago has matured into a shadow fiscal regime embedded in daily life.
The challenge is that Lagosians are left with no choice as they now pay twice, once to the government, once to the streets. And unlike official taxes, shadow taxes leave no developmental footprint. No bridge bears their name. No hospital wing testifies to their billions. No classroom is built from their collections. Only inflated fares. Broken windscreens. Frustrated commuters. And drivers who sweat under the sun, calculating how much will remain after everyone has taken their cut.
The agbero question is ultimately a governance question. Is Lagos governed by law, or by tolerated coercion? Is taxation a constitutional function, or a roadside negotiation? Is political convenience worth permanent economic distortion? What is absolutely known is that the structure has a political backing and what politics created, politics can dismantle.
Unless meaningful reform takes place, Lagos will continue to remain a megacity with a shadow treasury, where movement begins not with ignition, but with payment to men who answer to no ledger without any tangible returns. This is to say that every danfo that moves carries not just passengers, but the weight of a system that taxes without law, collects without accountability and punishes the very people who keep the city alive.
Blaise, a journalist and PR professional, writes from Lagos and can be reached via: bl***********@***il.com
Feature/OPED
How to Nurture Your Faith During Ramadan

Many Muslims grow up learning how to balance life carefully. Faith, work, and responsibility all sit on the same scale, and during Ramadan, that balance becomes even more delicate. Days start earlier than usual, nights stretch longer, and energy is spent with intention.
Over time, this rhythm shapes more than schedules; it quietly shapes how Ramadan is experienced.
Between getting ready for work, navigating long days, preparing meals for iftar, observing prayers, and trying to rest, moments for reflection are often pushed to the side. When there’s finally time to pause, many people assume meaningful Islamic content requires complete silence, full attention, and emotional space, things that can feel scarce during the month.
They scroll past channels they believe may be too formal, or not suited to their everyday routine. They stick to what feels familiar, even if it doesn’t quite align with the spirit of the season and without realising it, they limit themselves.
What many don’t know is that content designed for moments like these already exists on GOtv. The Islam Channel offers programming that understands Ramadan as it is truly lived.
On the Islam Channel, viewers can find thoughtful discussions that explore faith in a way that feels relevant to modern life, educational programmes that break down Islamic teachings clearly and calmly, and inspiring shows that encourage reflection without feeling overwhelming. There are conversations that can play softly in the background while you’re cooking, reminders you can catch while getting dressed for work, and programmes that help you unwind gently after a long day of fasting.
What sets the channel apart is how it personalises Islamic themes, making them accessible not just during prayer time, but throughout the day. Its content is created to inform, reflect, and inspire, whether you’re actively watching or simply listening as life continues around you. And while it speaks directly to Muslim audiences, it also remains open and welcoming to non-Muslims interested in understanding Islamic values, culture, and everyday perspectives.
During Ramadan, television often becomes part of the atmosphere rather than the focus. And having access to content that aligns with the season can quietly enrich those in-between moments, the ones that often matter most.
This Ramadan, the Islam Channel is available on GOtv Ch 111, ready to meet you wherever you are in your day.
And here’s the exciting part: with GOtv’s We Got You offer, you can enjoy your current package and get access to the next package at no extra cost. There’s never been a better time to hop on and get more shows, more suspense, and more entertainment, all for the same price!
To upgrade, subscribe, or reconnect, download the MyGOtv App or dial *288#. For watching on the go, download the GOtv Stream App and enjoy your favourites anytime, anywhere.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn