Feature/OPED
Tax, Inflation, and Still Broke: The Economic Divide

By Chiamaka Happiness Madueke
What’s worse than being taxed? Being taxed invisibly and twice.
When the government tightens monetary policy; hikes taxes, and removes subsidies, all in one breath, you would expect the economy to breathe easier. But in Nigeria, the air seems to feel thinner.
Over the past few years, Nigeria has embraced a series of bold economic reforms; floating the Naira, removing fuel subsidies, and pushing revenue generation targets. These actions can generally signal fiscal discipline and long-term growth.
For example, the Nigerian government reportedly saved N3.6 trillion from subsidy removal in just the second half of 2023, but beneath the policy headlines lies a quieter story: one where debt servicing, inflation, taxation, and informal charges collide to create an invisible burden on everyday transactions.
Yes, between visible taxes, invisible inflation, and unofficial levies collected by everyone and no one, low-income Nigerians allegedly seem trapped in a system that squeezes them from every direction.
Let me digress for a second, but I’ll bring it back in a bit, I promise.
At first glance, taxation and inflation may seem like two separate forces: one a fiscal tool, the other a macroeconomic consequence. But in Nigeria’s current climate, they’re colliding in real time, shaping the daily experience of citizens and businesses alike.
The Taxation Puzzle
Nigeria’s tax-to-GDP ratio remains among the lowest globally; just 10.86 per cent as of 2022, according to the Federal Inland Revenue Service (FIRS). That’s well below the 15–25 per cent global average, and even lower than the African average. Yet, the informal economy, which contributes nearly 58 per cent to GDP, bears much of the untracked tax burden through local levies and fees.
This mismatch reveals a chronic revenue problem and this challenge becomes even more critical when you consider the growing cost of debt. But borrowing isn’t inherently bad; in fact, strategic debt can stimulate growth if channelled into things like power, roads, manufacturing, or digital infrastructure, projects that have a way of boosting the economy.
In an interview with Arise News, the CEO of Sterling Bank, Mr Abubakar Suleiman, said, “If you are not collecting enough revenue to service a debt, that is a problem”. But it is even worse when you’re not using that debt for productive, economic reasons; that’s a structural problem.
Then I ran the numbers, in 2022, Nigeria reportedly spent a large per cent of its revenue on debt servicing. That means most of what we earn do not go to schools, hospitals, or industrial development, they go to paying back interest. That’s like living on a credit card and using it to buy lunch, not build a business that would make profit.
In 2023, 64.5 per cent of the federal government’s total revenue was used for debt servicing, according to a BusinessDay analysis of data from the Budget Office.
Although this was higher than the 48.5 per cent in 2022, it was still less than the 71.8 per cent in 2021. In 2023, actual revenue was N11.88 trillion, slightly above the predicted N11.05 trillion, while actual debt service costs were N7.66 trillion, 16.9 per cent higher than the projected N6.56 trillion.
In comparison, Nigeria’s revenue for the fiscal year 2022 was N7.76 trillion, falling short of the N9.97 trillion projection. The fact that debt servicing increased to N3.76 trillion from an anticipated N3.69 trillion in spite of this shortfall shows that debt obligations are an unavoidable burden even in cases where revenues are below budget.
This pattern emphasizes how little financial flexibility the government has, particularly when it comes to financing infrastructure or social projects.
By September 30, 2024, Nigeria’s total public debt had climbed to N142.3 trillion, reflecting a N8.02 trillion increase from N134.3 trillion in June 2024. This 5.97 per cent rise was attributed not only to additional borrowing but also to the depreciation of the Naira, which significantly inflated the naira value of external debt.
The surge in debt has not been matched by a proportional increase in productive investment, raising questions about the sustainability and strategic intent of government borrowing.
Adding to the concern, the total debt service cost reached an estimated N3.57 trillion in just the third quarter of 2024 alone.
With limited income from formal taxation, the government allegedly struggles to adequately fund infrastructure, education, healthcare, and essential services.
In response, efforts are underway to:
- Widen the tax base by formalizing more of the informal sector,
- Improve compliance through digital platforms and data integration,
- Rationalize outdated and inefficient tax incentives.
However, increasing tax pressure and its enforcement especially now can be politically unpopular and economically dangerous. Why? Because inflation is already eating through household budgets.
The Inflation Squeeze
Nigeria’s inflation rate has remained stubbornly high, largely driven by the rising cost of food prices, currency depreciation, removal of fuel subsidy and Monetary policies like floating the Naira.
As of early 2024, inflation was between 28–30 per cent, with core inflation also climbing. This diminishes buying power, worsens poverty, and increases the expenses of conducting business.
Essentially, inflation operates as an unnoticed tax, one that hits the vulnerable the hardest, especially low and middle-income earners whose wages aren’t keeping pace.
One key statement caught my attention in recent times, “We must choose between Taxation or Inflation.”
At first, that sounded a bit extreme. But the more I thought about it, the more it made sense.
Taxation is visible, structured, and can be progressive. Inflation, on the other hand, is unpredictable and regressive, a silent thief that spares no one, but affects the poor more because they have less to spend.
For low-income Nigerians, a controlled tax system paired with targeted public investment, might be more manageable than the current wave of inflation that raises the price of garri, beans, and palm oil every other week for Aunty Onyeka and thousands like her.
The “Other” Taxes We Don’t Talk About
But this brings me to a creeping question. What about the unofficial taxes? The ones no one talks about?
How are the indirect taxes collected from public transporters by local levy collectors accounted for? The levies collected from Mama Basirat who hawks around Oshodi market selling cooked food has watched the price of palm oil jump three times in six months while still paying a N500 “market ticket” every morning before selling a single plate of rice. Who tracks that revenue?
Yes, the most shocking revelation for me has been realizing that even hawkers – hawkers, who sell sachet water or fruit walking down roads and the street corners are being taxed in some areas.
Or rather, charged daily levies by local agents. And no, I am not condemning that, just that this issue raises some serious questions in my head:
- Where does this money go?
- Is it remitted to any official government account?
- What public service is being provided in return?
If we zoom out, the irony becomes obvious. We keep saying Nigeria’s tax-to-GDP ratio is too low. Yet, many of the poorest Nigerians are already being taxed, just not in ways that show up in FIRS data.
They’re taxed by local councils, market unions, transport associations, and sometimes even self-appointed local revenue agents. Is this form of taxation? It’s neither progressive nor transparent, nor accountable.
So, What Are We Really Talking About?
When we push for increasing tax revenue, we often picture corporate profits or high-net-worth individuals. But the reality? Many of the levies, fees, and informal charges disproportionately hit those in the informal sector; drivers, traders, hawkers, the same people inflation is already punishing the most. It’s a vicious cycle.
Drivers hike transport fares to meet the levies. Hawkers bump up prices to stay afloat and somewhere in the middle, people start paying more for food, transport, and basic needs. So, yes, taxation may be more beneficial than inflation but only if it’s fair, formal, and genuinely
used to improve lives. Until then, we seem to remain stuck in a system where the poorest pay the most, twice over: Once through rising prices that their income can barely meet, and again through levies that don’t even show up in the books. The informal sector is already contributing indirectly through taxes and levies. But where that money goes, that’s the real mystery.
The discussion about taxation in Nigeria must expand beyond the official tax system to consider these informal levies. And that, more than anything, is what really got my thinking juices flowing.
Maybe the conversation shouldn’t just be about taxing more, but taxing better, and ensuring value for those already overburdened.
Feature/OPED
Revived Argungu International Fishing Festival Shines as Access Bank Backs Culture, Tourism Growth
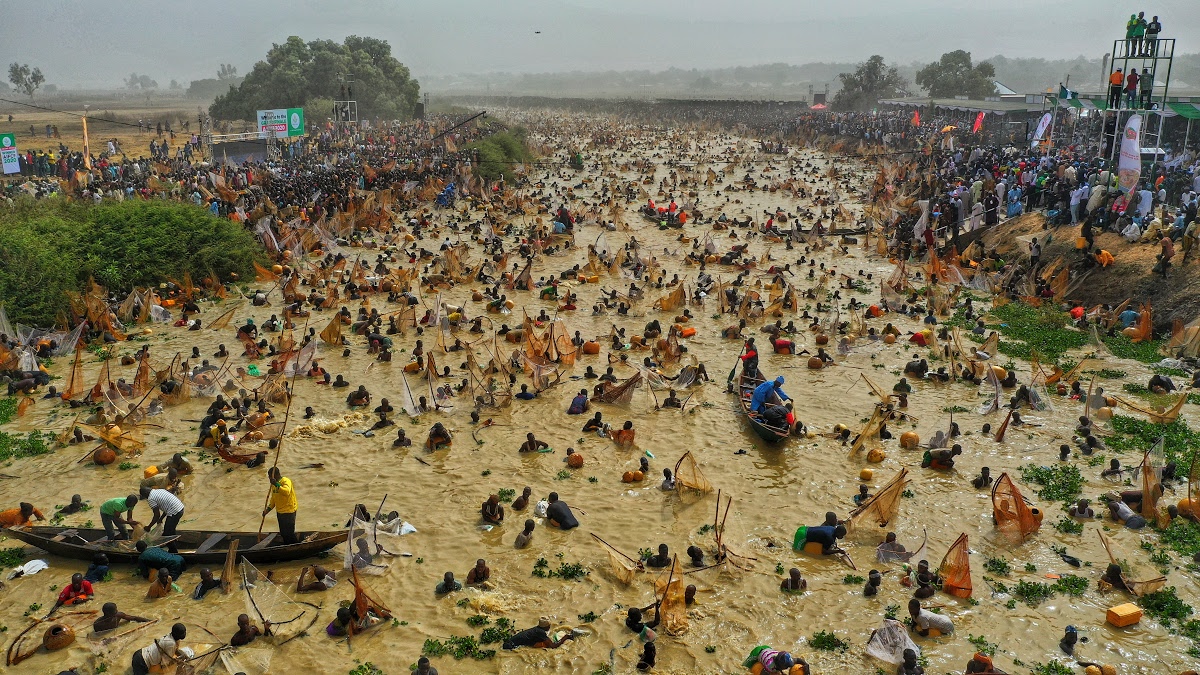

The successful hosting of the 2026 Argungu International Fishing Festival has spotlighted the growing impact of strategic public-private partnerships, with Access Bank and Kebbi State jointly reinforcing efforts to promote cultural heritage, tourism development, and local economic growth following the globally attended celebration in Argungu.
At the grand finale, Special Guest of Honour, Mr Bola Tinubu, praised the festival’s enduring national significance, describing it as a powerful expression of unity, resilience, and peaceful coexistence.
“This festival represents a remarkable history and remains a powerful symbol of unity, resilience, and peaceful coexistence among Nigerians. It reflects the richness of our culture, the strength of our traditions, and the opportunities that lie in harnessing our natural resources for national development. The organisation, security arrangements, and outlook demonstrate what is possible when leadership is purposeful and inclusive.”
State authorities noted that renewed institutional backing has strengthened the festival’s global appeal and positioned it once again as a major tourism and cultural platform capable of attracting international visitors and investors.
“Argungu has always been an iconic international event that drew visitors from across the world. With renewed partnerships and stronger institutional support, we are confident it will return to that global stage and expand opportunities for our people through tourism, culture, and enterprise.”
Speaking on behalf of Access Bank, Executive Director, Commercial Banking Division, Hadiza Ambursa, emphasised the institution’s long-standing commitment to supporting initiatives that preserve heritage and create economic opportunities.
“We actively support cultural development through initiatives like this festival and collaborations such as our partnership with the National Theatre to promote Nigerian arts and heritage. Across states, especially within the public sector space where we do quite a lot, we work with governments on priorities that matter to them. Tourism holds enormous potential, and while we have supported several hotels with expansion financing, we remain open to working with partners interested in developing the sector further.”
Reports from the News Agency of Nigeria indicated that more than 50,000 fishermen entered the historic Matan Fada River during the competition. The overall winner, Abubakar Usman from Maiyama Local Government Area, secured victory with a 59-kilogram catch, earning vehicles donated by Sokoto State and a cash prize. Other top contestants from Argungu and Jega also received vehicles, motorcycles and monetary rewards, including sponsorship support from WACOT Rice Limited.
Recognised by UNESCO as an Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity, the festival blends traditional fishing contests with boat regattas, durbar processions, performances, and international competitions, drawing visitors from across Nigeria and beyond.
With the 2026 edition concluded successfully, stakeholders say the strengthened collaboration between government and private-sector partners signals a renewed era for Argungu as a flagship cultural tourism destination capable of driving inclusive growth, preserving tradition, and projecting Nigeria’s heritage on the world stage.
Feature/OPED
$214Bn Missing, Institutions Silent: Is Accountability Dead in Nigeria?

By Blaise Udunze
Between 2010 and 2026, a staggering $214 billion, approximately N300 trillion in public funds, has been reported as missing, unaccounted for, diverted, unrecovered, irregularly spent, or trapped in non-transparent fiscal structures across Nigeria’s public institutions.
That figure is not speculative but a conservative estimate of unaccounted funds. It is drawn from audit reports, legislative probes, civil society litigation, executive directives, and investigative findings spanning more than a decade. If it is to go by the accurate figure, the true national loss is likely higher but difficult to quantify precisely due to data gaps, overlapping figures, and incomplete audits.
The challenge is that in many of the most prominent cases, prosecutions have stalled, hearings have dragged without resolution, investigations have gone cold, and no defining jail terms have etched accountability into Nigeria’s institutional memory. The irony is that the number is historic, the silence is louder. And the economic damage is cumulative.
The pattern stretches from the oil sector to social investment programmes, from the Nigeria Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) interventions to ministry-level expenditures. In 2014, between $10.8 billion and $20 billion in unremitted oil revenues linked to the Nigerian National Petroleum Corporation triggered national outrage. Under the then CBN governor, Lamido Sanusi, who warned that persistent oil revenue leakages were making exchange rate stability “extremely difficult.” He cautioned that without full remittances, the alternative would be currency devaluation and financial instability. This concern spans the 2010 to 2013 oil revenue period. That warning proved prophetic.
This is because, years later, the lack of transparency in the oil industry did not disappear, but rather it festered like cancer. It further led to the elongated audit queries, which have continued to trail the Nigerian National Petroleum Company Limited, including unremitted revenues, questioned deductions, and management fee structures under the Petroleum Industry Act. With an extraordinary move aimed at blocking revenue leakages at source, President Bola Ahmed Tinubu has recently issued an Executive Order suspending certain deductions and directing direct remittance of taxes, royalties, and profit oil into the Federation Account, which involves the reassessment of NNPC’s 30 per cent management fee and 30 per cent frontier exploration deduction under the Petroleum Industry Act.
Such presidential intervention underscores the scale of concern, which means that Nigeria cannot afford a structural lack of transparency in its most strategic revenue sector. But oil is only one chapter.
The Central Bank of Nigeria has faced some of the most far-reaching audit alarms in recent years. In suit number FHC/ABJ/CS/250/2026, the Socio-Economic Rights and Accountability Project (SERAP) is asking the Federal High Court to compel the CBN to account for N3 trillion in allegedly missing or diverted public funds. The Auditor-General’s 2025 report cited failures to remit over N1.44 trillion in operating surplus to the Consolidated Revenue Fund, over N629 billion paid to “unknown beneficiaries” under the Anchor Borrowers’ Programme, and more than N784 billion in overdue, unrecovered intervention loans.
There were also N125 billion in questioned intervention expenditures, irregular contract variations exceeding N9 billion, and procurement gaps running into hundreds of billions. The Auditor-General repeatedly recommended recovery and remittance. No date has been fixed for the hearing. Meanwhile, Nigeria continues to borrow.
Elsewhere, the House of Representatives has launched a probe into over N30 billion recovered during investigations into the National Social Investment Programme Agency (NSIPA). The funds, reportedly frozen during investigation, have not been remitted back into the Treasury Single Account, stalling poverty-alleviation schemes like TraderMoni and FarmerMoni. Millions of vulnerable Nigerians remain exposed while lawmakers search for money already “recovered.” The irony is staggering as funds are found, but programmes remain frozen.
A top discovery recently that put the nation on red alert was made by the Senate committee, which claimed to have found N210 trillion in financial irregularities in NNPC accounts between 2017 and 2023, including unaccounted receivables and accrued expenses. A critical concern is that, as of early 2026, this has sparked commentary but no clear prosecutions.
Only recently, in the power sector, SERAP has urged the President to probe alleged missing or unaccounted N128 billion at the Federal Ministry of Power and the Nigerian Bulk Electricity Trading Plc. Of concern is that despite the enormous funds channelled in this sector, Nigeria’s chronic electricity instability persists, even as billions meant to stabilise the grid face audit scrutiny.
Across MDAs, audit reports between 2017 and 2022 flagged trillions in unsupported expenditures, unremitted taxes, unauthorised payments, and statutory liabilities never recovered. These sums are dizzying and are also alarming; N300 billion here, N149 billion there, N3.403 trillion across agencies, N30 trillion-plus Treasury discrepancies raised at the Senate level.
Individually, they shock. Collectively, they define a structural pattern. And patterns shape economies.
Nigeria operates with structural fiscal deficits and also lives with them routinely and comfortably. Expenditure persistently exceeds revenue. When public funds disappear, fail to be remitted, or are trapped outside constitutional channels, the deficit widens. The government must borrow to fill gaps created not only by low revenue, but by revenue leakage.
Debt servicing now consumes a disproportionate share of federal revenue. Borrowing meant for capital projects increasingly finances recurrent obligations. The country shifts from borrowing to build to borrowing to survive. Every missing naira compounds tomorrow’s liability.
The Treasury Single Account (TSA) was designed to plug such leakages. It consolidated government revenues under Section 80 of the Constitution into a unified framework. International financial institutions commended it as a landmark reform. Yet even today, the Minister of Finance, Wale Edun, has admitted that substantial government funds remain outside the TSA and outside the CBN’s consolidated visibility. Until August 1, 2024, he revealed, the federal government could not fully see its own balance sheet at the apex bank. That admission should alarm any serious economy.
Fiscal lack of transparency constrains planning. It undermines monetary coordination. It weakens debt sustainability projections. It distorts policy responses. And when systems are in flux, money vanishes more easily.
Changing or weakening the TSA in such an environment would be catastrophic. Transitions create windows of vulnerability. Old accounts close. New accounts open. Reconciliation’s lag. Ghost contractors reappear. Double payments slip through.
Albeit, the government must learn to tread with caution as Nigeria’s institutional bandwidth is already strained by simultaneous tax reforms, exchange-rate adjustments, subsidy removal, and fiscal restructuring. One truth that cannot be argued is that layering additional structural upheaval onto fragile systems risks revenue loss that the country cannot afford. Investors are watching.
Credit markets evaluate not just numbers but institutional consistency. A nation that abandons or weakens its most credible fiscal reform sends a destabilising signal. Stability lowers borrowing costs. Institutional drift raises them. But beyond markets lies the human cost.
N300 trillion represents roads not built, power plants not completed, irrigation systems not funded, schools not modernised, and hospitals not equipped. It represents jobs not created and industries not catalysed. It represents stalled productivity and deferred growth.
When intervention loans remain unrecovered, agricultural output suffers. When power sector funds are unaccounted for, electricity remains unstable. When social investment funds are frozen, poverty deepens.
Inflation then compounds the pain. Revenue gaps push borrowing. Borrowing pressures, interest rates and by extension, liquidity misalignment fuel price instability. Citizens pay through higher food costs, transport fares, and rent. The poor pay first. The middle class erodes quietly.
Perhaps most corrosive is the trust deficit. When audit queries fade without visible accountability, tax morale weakens. Compliance declines. Cynicism hardens. A nation cannot modernise where trust in fiscal integrity is fragile.
Section 15(5) of the Constitution requires the abolition of corrupt practices. Financial Regulations mandate a surcharge and referral to anti-corruption agencies where public officers fail to account for funds. The Fiscal Responsibility Act empowers citizens to enforce compliance to ensure that government officials follow fiscal rules. But enforcement defines seriousness.
Nigeria’s problem is not a lack of audit findings. It is the distance between findings and finality.
Nations do not collapse overnight due to a lack of funds. They drift. Infrastructure decays incrementally. Debt rises gradually. Growth slows subtly. Confidence erodes quietly. Then one day, stagnation feels permanent. $214 billion (N300 trillion), sixteen years of recurring audit alarms. Few conclusive accountability outcomes are proportionate to the scale. Truly, the consequences have been less strong. For the same reason, the country witnessed President Tinubu nominating ex-NIA boss Ayodele Oke as ambassador despite a $43 million loot in an Ikoyi apartment.
See the research breakdown of some of the audit figures that reveal staggering sums as enumerated above:
– $10.8 billion and separately $20 billion in unaccounted oil revenues at the NNPC in 2014
– $1.1 billion controversial Malabu Oil and Gas oil deal in 2015
– $2.2 billion arms procurement irregularities in 2015
– N3.4 billion from IMF COVID-19 financing flagged in a 2020 audit.
– N149.36 billion, N37.2 billion, and multiple irregular MDA expenditures in 2020 alone.
– N300 billion cited in public audit concerns in 2017.
– N210 trillion in financial irregularities uncovered, N103 trillion in ‘accrued expenses’, and another N107 trillion in unaccounted ‘receivables’ (2017 -2023).
– N57 billion Ministry of Humanitarian Affairs – (2021)
– N3 trillion and N1.44 trillion flagged in 2022 audit issues involving the Central Bank of Nigeria.
– Nearly N630 billion under the Anchor Borrowers Programme is reportedly unrecovered.
– N784 billion in overdue intervention loans flagged.
– Over N3.403 trillion unaccounted for across federal MDAs between 2019 and 2021.
– Roughly 30 trillion+ in Treasury Single Account and Consolidated Revenue Fund discrepancies raised at the Senate level.
– N500 billion in unremitted oil revenues between 2019 and 2024.
– N80 billion tied to alleged fictitious contracts in the Accountant-General’s office.
– N69.9 billion in uncollected statutory tax liabilities.
– Billions more in unauthorised or undocumented expenditures across ministries.
The institutions differ. The years differ. The audit language differs. The pattern does not.
Nigeria’s economic future will not be determined solely by how much oil it produces, how many reforms it announces, or how many executive orders it signs. It will be determined by whether every naira earned enters the Federation Account transparently, whether every intervention loan is tracked and recovered, whether every surplus is remitted constitutionally, and whether every diversion carries consequences. Revenue generation matters. Revenue protection is destiny. Because when government funds go missing, nations do not stand still. They move backwards.
Blaise, a journalist and PR professional, writes from Lagos and can be reached via: bl***********@***il.com
Feature/OPED
The Hidden Workforce of the 2026 Access Bank Lagos City Marathon
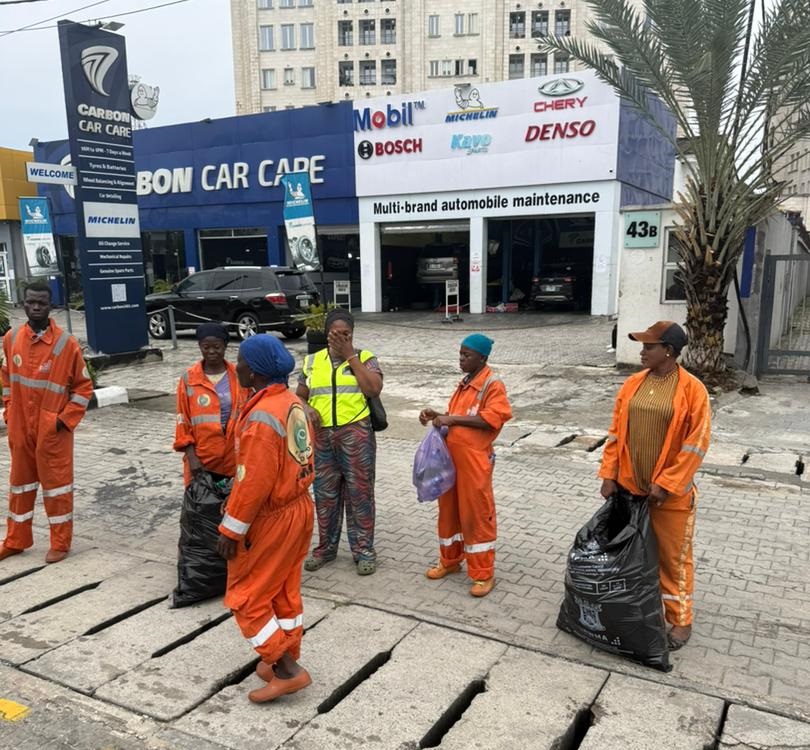

When the final runner crossed the finish line at the 11th edition of the Access Bank Lagos City Marathon (ABLCM), the applause began to fade. But for hundreds of workers across Lagos, the real work was just beginning.
Major highways had been closed to facilitate the event. Tens of thousands of runners moved through the city in a coordinated surge of athletic endurance. Thousands of bottles of water and energy drinks were distributed, alongside sachets containing essential medical supplies and medication. The race route itself was meticulously prepared, lined with banners, barricades, medical tents and precision timing systems that ensured safety, organisation and accurate performance tracking from start to finish.
What followed was the part that a few cameras lingered on, yet it remains one of the clearest indicators of institutional progress.
Within minutes of the race conclusion, coordinated sanitation teams fanned out across the marathon corridor. Their work went beyond sweeping. Waste was systematically sorted. Plastic bottles were separated from general refuse. Sachets were gathered in bulk. Collection trucks moved along predefined routes, ensuring rapid evacuation of waste. Temporary race infrastructure was dismantled with quiet precision.
In a megacity like Lagos, speed is a necessity. Urban momentum cannot pause for long. The ability to restore order quickly after an event of this magnitude reflects operational discipline across interconnected systems, municipal authorities, environmental agencies, private waste management partners and event coordinators.
Globally, large-scale sporting events are no longer evaluated solely by participation numbers or prize purses. Sustainability has emerged as a defining metric. Environmental responsiveness is now a core measure of credibility. Cities seeking tourism growth, foreign investment and international partnerships must demonstrate that scale does not compromise responsibility. The 2026 marathon provided a compelling case study in this evolution.
The clean-up operation itself generated meaningful economic activity. Temporary employment opportunities emerged for sanitation workers and logistics personnel. Recycling partners engaged in material recovery, reinforcing circular economy value chains. What was once viewed as routine waste disposal has evolved into a structured ecosystem of environmental services, a sector of increasing importance in modern urban economies.
This level of sustainability was the result of deliberate planning. Effective post-event recovery requires route mapping, waste volume projections, coordination between sponsors such as Access Bank Plc and municipal bodies, contingency planning for congestion points and clear communication protocols.
Each edition of the marathon has built on lessons from the last. International participation has expanded. Accreditation standards have strengthened. Media visibility has grown. Most importantly, environmental management has become embedded in the marathon’s operational framework rather than treated as an afterthought.
Progress rarely arrives in dramatic leaps, it advances through incremental improvements, refined systems and institutional learning. Just as elite runners close performance gaps through disciplined training, cities strengthen their global standing through consistent operational excellence.
The 2026 marathon, therefore, tells a story that extends far beyond athletic achievement. It is a story of coordination, sustainability as strategy rather than slogan, and the often unseen workforce, sanitation workers, planners, volunteers, security officials and environmental partners, whose discipline sustains the spectacle.
Because in the end, global cities are judged by how well they host and how responsibly they restore. On the marathon day in Lagos, it was the runners who demonstrated endurance and the systems, and the people behind them, who ensured that when the cheering stopped, the city kept moving.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn