Feature/OPED
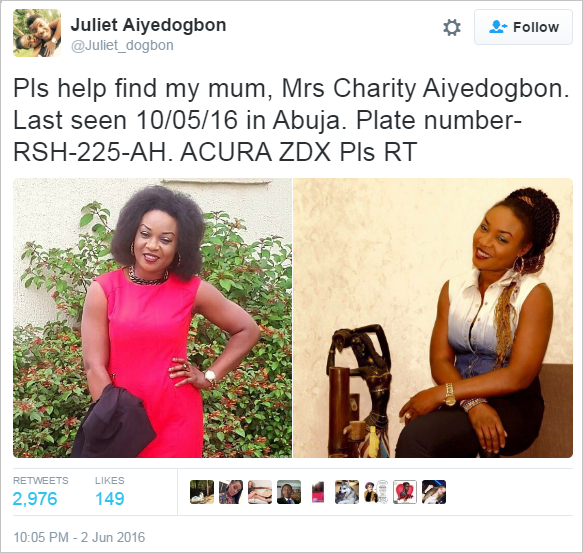
Missing Charity Aiyedogbon: One Year After
Destiny Ugorji
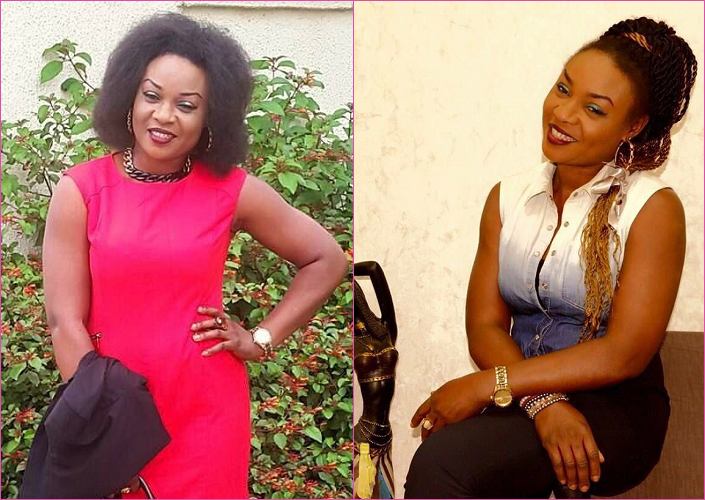
It is exactly one year that an Abuja-based business woman, Charity Aiyedgbon was declared missing by her Facebook friends. Charity, popularly known as ‘Chacha’, is said to have gone missing since the 9th of May, 2016 and family, friends and Security Agencies said to be working to unravel the mystery behind her sudden disappearance.
Speculations on the possible whereabouts of the 44-year-old mother of four, also known as Deepdeal Chacha Dehammer were rife.
First, a Lagos-based lawyer, Emeka Ugwuonye said he had overwhelming evidence that the missing Charity was dead, accusing her erstwhile husband, David Aiyedogbon of having a hand in her disappearance; an allegation he posted on his Facebook group, The Due Process Advocates.
Reacting to Ugwuonye’s allegation, former husband of the missing woman, Mr. David Aiyedogbon washed his hands over the disappearance of the lady and wrote his accuser, through his lawyers, demanding an apology, failure which he would seek legal redress.
The letter titled: “Defamation of the character of David Aiyedogbon; demand for apology,” signed by his lawyer, Obiora Illo esq (Ogbulafor Chambers) and made available to newsmen, expressly states: “It is our instruction to demand an unqualified apology from you to our client through our chambers for the defamatory publications you have made of and concerning our client.”
Also, addressing newsmen in Abuja, Mr. Aiyedogbon urged the Inspector General of Police, Ibrahim Idris to investigate the allegation against him, describing it as “cruel, criminal and untrue”, stressing that his estranged wife Charity left their matrimonial home on the 28th of May, 2014, noting that since then, he had neither heard from her, nor had any dealings with her.
While the controversy lasted, a Civil Society Organisation, Coalition against Crime (CAC) called on Nigeria’s Inspector General of Police, Ibrahim Idris to arrest Lagos-based lawyer, Ugwuonye to explain his role in the disappearance of Charity Aiyedogbon.
National Coordinator of the group, Harrison Pepple, made the call while addressing newsmen in Abuja, arguing that Mr. Ugwuonye had some questions to answer.
In a Petition to the Inspector General of Police, the group quoted Mr. Ugwuonye as saying: “…Charity Aiyedogbon is said to have been missing since the 11th of May, 2016 and one Emeka Ugwuonye claims he has evidence that the woman is dead and was murdered. He also posted a photograph of a dead person, part of whose body was dismembered. How can Police be looking for a missing person and someone says he has a clue and he has not been invited or arrested.”?
Following the intervention by the Civil Society Organisation, the Police eventually arrested Mr. Ugwuonye and later released him on bail, after questioning, while investigations continued.
Several developments aided Police investigations. First, those believed to be close to Chacha are quoted as saying that she went missing on the 9th of May, 2016, but her lawyer, Barrister Nsikak Udoh, handling a suit filed at the Federal High Court, Lokoja on 29th April, 2016 against 29 respondents, including her biological children and former husband, claimed she (Chacha) came to his house on the 18th of May, 2016 (eight days after her purported disappearance) and one of his staff accompanied her to Federal High Court, to sign and depose to an affidavit in support of the ex-parte motion filed along with the case. How could someone who was declared missing on the 9th of May reappear on the 18th and then disappear again?
Today, it has been established that Chacha’s signature was forged; as the lawyer, Barrister Nsikak Udo has recanted. He says he did not see Chacha, as earlier claimed. He confessed to the Police that he forged Charity’s signature in an affidavit he filed in court. Apparently, Charity was not behind the filing of the suit, but her lawyer, Barrister Nsikak Udoh. He therefore lied on oath. Both himself and the Commissioner for oaths in the Federal High Court Abuja jurisdiction risk being prosecuted by the Police for forgery and perjury.
Another puzzle is that a corpse, said to have been dismembered beyond identification was allegedly seen in Abuja on the 12th of May and Mr. Ugwuonye claimed it was Chacha’s body. Till date, who has identified the corpse as that of Chacha? Impeccable sources say a DNA test conducted on the body revealed otherwise. Children of the missing woman have also chorused on several platforms that their mother was NOT dead. They have also stated that the displayed corpse is not that of their mother. The missing woman also has siblings and parents who have been going about their normal businesses and have neither said their sister was missing, dead, nor joined in the search for her.
The missing Chacha has a case of forgery that is yet to be concluded. A suit instituted in a High Court of the Federal Capital Territory (FCT High Court 8) on the 14th of March, 2016, with suit number CV/1231/16, between Messrs Chibuzor Ogugua and Chigozie Eme (plaintiffs) and Mrs. Charity Aiyedogbon (defendant), made eight prayers to the Court. The last prayer reads: “an order of the Honourable Court directing the defendant to pay the plaintiffs the sum of 200,000,000.00 (Two Hundred Million Naira) as damages for the losses suffered on the ground of the unauthorized and fabricated Valuation Report by the defendant.”Could she have disappeared to frustrate the Suit or evade justice?
In the last one year, a lot has happened. The law enforcement agencies and private investigators have worked very hard to unravel the mystery behind the disappearance of Mrs. Charity Aiyedogbon, aka Chacha Dehammer. Cases have been instituted and some already decided.
Some friends of Chacha, believed to have earlier raised the alarm recanted. They are said to be at war with Emeka Ugwuonye, who said he was briefed by same Chacha’s friends on the matter. They engaged in war of words on Facebook. One of them, Pamela Nwansoh allegedly confronted Mr. Ugwuonye in a Police premises in Abuja over an obvious sense of disenchantment with his activities, alleging extortion of members of the public (in the name of looking for Chacha) using his Facebook Group, the Due Process Advocates (DPA). Ugwuonye had, via a post on the group, solicited financial contributions for his trip to Abuja to respond to Police invitation to explain himself over the case of the missing Chacha.
One of the ladies said to be involved in the search for Chacha, Viola Ifeyinwa Okolie, on the 14th of July, 2016, also made a worrisome post on her Facebook wall, expressing disenchantment with Mr. Ugwuonye’s antics.
Also in a post on The Due Process Advocates on the 17th of July, 2016, Ugwuonye attacked Viola Okolie, making spurious allegations. The post was titled: “How the search for Chacha took strange turns and her friends turn out not to be friends after all.” The drama continued.
But, how did Emeka Ugwuonye get involved in this matter? Was he really in America when the incident happened, as he claimed? Available records suggest otherwise.
Barrister Ugwuonye claimed to have been in the United States of America as at the time of Chacha’s disappearance and only came into Nigeria in June, 2016, after being briefed to handle the matter, but his call log betrayed him, showing that he was in Abuja on the 10th, 11th and 12th of May, 2016; same time Chacha is said to have got missing. Information from private investigators and telecommunication service providers revealed that he made calls around Jabi area of Abuja, up till midnight same 10th and 11th and departed Abuja on the 12th of May, 2016. When confronted by the Police in Abuja with evidence of his movement, he owned up.
Three key suspects earlier arrested by the Police in connection with Chacha’s disappearance were said to have been released at his instance. He claimed at the FCT Police Hqrs that they were his clients; but when brought face to face with Mr. Ugwuonye, they denied all his claims, saying they neither briefed him nor identified any corpse to him as that of Chacha.
As at today, Police sources reveal that Mr. Ugwuonye has not provided any evidence to substantiate his claims. The only person he claims showed and identified the corpse as that of missing Chacha (Jo) denied him.
Today, Chacha’s car has been recovered. Two of her handsets have also been recovered. Is it a coincidence that he (Ugwuonye) has been questioned more than thrice by the Police in Chacha’s case?
The first puzzle is solved, with the admission by one of Chacha’s lawyers, Barrister Nsikak Udo that Chacha’s signature was forged. He admitted that he lied on oath and his fate shall be determined by the laws of the land soon.
Second, Chacha’s last Facebook post before she ‘went missing’ shows that she sat on the passenger’s seat of her car. That was the last she posted on Facebook, using that particular User ID- Deepdealdehammer. The question of who drove the car may have also been addressed.
Her car has been recovered, following a tip-off by one of the suspects that were in Police custody, IK Ezeugo. IK never opened up until Police arrested one of Jekwu’s friends, who now gave the lead, indicating that he (IK) personally drove the vehicle to the place where it was parked. His (Ik’s) younger brother, identified as Paul Chukwujekwu Ezeugo (still at large) is believed to have been in custody of the vehicle. He (Chukwujekwu) is also believed to have driven the missing woman on that last trip. The car was found in Enugu State by the Police, in the residence of one Uche, with its Plate Number and particulars already changed.
Again, Chacha’s two handsets have been recovered. One of them, a Nokia handset, is said to have been found with Chukwujekwu’s biological mother, Mrs. Ezeugo. The second handset (a Samsung phone) was recovered from one Augustine, who claimed that one Odinaka, Chukwujekwu’s friend and phone repairer sold it to him for Twenty Five Thousand Naira. The proceeds, according to Odinaka, were handed over to Chukwujekwu. Just like the vehicle, the both handsets were found in Enugu. Chukwujekwu is still at large.
Why is it that almost all the persons arrested/suspected so far in connection with Chacha’s case are from Enugu State? Precisely, six suspects so far arrested in the case are from Enugu State. Emeka Ugwuonye is from Enugu and Chacha’s car and handsets were found in Enugu. Chacha’s maternal home is Enugu. In fact, Paul Chukwujekwu Ezeugo and the missing Chacha’s mother are both from Oba-Nsukka, in Enugu State.
Mr Ugwuonye’s relationship with one of the prime suspects, Chukwujekwu Ezeugo is suspicious and his call log points in the same direction. He is also suspected to have aided his escape, as, according to Police sources, the day he (Jekwu) was to be arrested, Ugwuonye personally called the Police, promising to produce him, only to revert 24hours later, telling the Police that he had escaped.
Understanding how bad the matter was getting, Ugwuonye at a point, announced his withdrawal from Chacha’s case, a move Police sources described as diversionary, since he is already a suspect in the case.
David Aiyedogbon fights back
Following his refusal to apologize, ex-husband of the missing woman, Mr. David Aiyedogbon dragged Lagos- based Lawyer, Emeka Ugwuonye to the Nigerian Bar Association (NBA) over what he described as unprofessional publications against his person.
A letter dated 22nd August, 2016, captioned: “Petition against Emeka Ugwuonye for Unprofessional Publications and False Allegations”, addressed to the General Secretary of the Nigerian Bar Association (NBA), urged the professional body to investigate the matter and invoke appropriate disciplinary actions against the lawyer. Till date, Mr. Ugwuonye has not responded to a query issued him by the NBA, following Aiyedogbon’s petition.
Also, for falsely accusing him of, having a hand in the sudden disappearance of his estranged wife, Charity Aiyedogbon, Mr. Aiyedogbon instituted a defamation of character suit of Ten Billion Naira (N10b) against Lagos Lawyer, Emeka Ephraim Ugwuonye.
The Suit, with number CV/2750/16, between David Aiyedogbon (Plaintiff) and Emeka Ugwuonye (Defendant) on defamation of character, before Justice Peter Kekemeke of Federal Capital Territory (FCT) High Court 14, Apo Abuja; also prays that the defendant be ordered to pay the cost of the suit.
The Plaintiff is also seeking an order of perpetual injunction “restraining the Defendant, his Agents, Privies, Associates or whosoever called” from making further defamatory publications against him and his family members. The matter is adjourned to Thursday, 18th May, 2017.
Sources also reveal that Mr. Aiyedogbon’s lawyer, Tony Ogbulafor may have also filed a personal suit against Mr. Ugwuonye for wrongly accusing him of giving a bribe (in an envelope) to a Police man to detain him.
Police sources also reveal that, while some persons have already been charged to Court (awaiting trial) for their roles in the disappearance of Charity Aiyedogbon, others that have questions to answer will also be charged soon, to explain their roles in the controversy.
Meanwhile, the suit purportedly filed by Chacha at the Federal High Court, Lokoja, wherein Barrister Nsikak Udoh represented her has been decided in favour of David Aiyedogbon.
One year after, Chacha’s case is getting more interesting. We await the explanation of those in possession of Chacha’s car and handsets on their roles, accomplices and her whereabouts.
While we wait patiently for the unfolding drama, the Police must realise that Nigerians and indeed the world are watching. They must address Nigerians now on the extent of their investigation.
Again, Police must expedite actions in charging suspects to court. Waiting endlessly on the matter does not help the course of justice.
One is still at a loss as to why the prime suspect in the matter, Jekwu is yet to be declared wanted; and why Charity Aiyedogbon has not been declared missing. The Police must clear the air now.
As the whereabouts of Charity Aiyedogbon remain unknown, I join millions of Nigerians to demand that Emeka Ugwuonye provides his “overwhelming evidence” regarding what happened to Chacha or get prosecuted for false information and criminal conspiracy.
Feature/OPED
PETROAN, ‘Abiku Refineries’ and the Comfort of Collapse

A sector that keeps reviving what has repeatedly failed, while resisting what works, is not trapped by fate but comforted by collapse. PETROAN’s latest outburst exposes just how invested some interests remain in Nigeria’s ritualised dysfunction.
By Abiodun Alade
Nigeria’s oil and gas sector has endured many seasons of noise masquerading as advocacy. From time to time, pressure is applied not in pursuit of reform, but in defence of habits that have outlived their usefulness. The latest episode is revealing not because it is novel, but because it exposes, with unusual clarity, the discomfort of rent-seeking intermediaries when genuine change threatens familiar margins.
That discomfort has recently found expression in the agitation by the Petroleum Products Retail Outlets Owners Association of Nigeria over comments made by Bayo Ojulari, Group Chief Executive Officer of the Nigerian National Petroleum Company Limited. In demanding his resignation, PETROAN has inadvertently illuminated a deeper problem in Nigeria’s petroleum political economy: the resistance of entrenched intermediaries to reform that narrows the space for easy rent.
Ojulari’s offence was not misconduct. It was candour. He observed, correctly, that the Dangote Petroleum Refinery has provided breathing space at a time when government-owned refineries are shut, and that the NNPC should not rush back into the familiar ritual of pouring millions of dollars into turnaround maintenance for facilities that have become monuments to waste. This is not heresy; it is prudence.
For a quarter of a century, Nigeria has chased the mirage of refinery rehabilitation. Public records suggest that between $18 billion and $25 billion has been spent on turnaround maintenance and rehabilitation of the four state-owned refineries, with little to show for it. Like the abiku of Yoruba lore, these refineries are revived with ceremony, only to relapse almost immediately. Working today, dying tomorrow. To insist that this cycle must continue, regardless of evidence, is not patriotism. It is sabotage dressed as concern.
PETROAN’s reaction is therefore instructive. In a recent statement, its spokesman, Joseph Obele, described it as “most worrisome” that there was no urgency to restart the Port Harcourt Refinery because Dangote is meeting current fuel needs. The association went further, threatening to lobby civil society groups and pursue legal options to force the removal of the NNPC GCEO should the refinery not resume operations by March 1. This is not policy engagement. It is pressure politics.
Why would a body of retailers, whose business model depends largely on buying and reselling products refined elsewhere, be so hostile to domestic refining capacity? The answer lies in incentives. Domestic refineries compress margins. They reduce arbitrage. They expose inefficiencies that thrive in scarcity. For decades, fuel importation and the dysfunction it encouraged created space for unearned profits across the value chain. Local refining threatens that arrangement.
History offers a useful parallel. In Mancur Olson’s classic work The Logic of Collective Action, he explains how small, organised interest groups often prevail over the broader public interest because they are better motivated to defend narrow gains. PETROAN’s conduct fits this pattern. It speaks loudly, often, and with confidence, but for whom does it really speak?
It is also worth recalling PETROAN’s posture during earlier periods of distress in the sector. At moments when the national oil company was accumulating unsustainable obligations, remitting little or nothing to the Federation Account and absorbing enormous costs, commendations flowed freely. Laurels were dished out even as the system bled. That era ended with the Federal Government writing off substantial debts, including about $1.42 billion and N5.57 trillion after reconciliation. Nigerians paid the price for that indulgence.
During the years when Nigeria’s petroleum sector was driven to the brink, PETROAN looked the other way. The record is clear. The national oil company captured the entire value chain, seizing crude exports, monopolising refined product imports, and then forcing the Federal Government to borrow an estimated N500 billion monthly to sustain opaque subsidy claims. By controlling nearly 90 per cent of the roughly $3 billion in monthly crude proceeds routed through the Central Bank, and combining this with subsidy payments and other shocks, fiscal space collapsed, driving the government into massive Ways and Means financing.
At the same time, refinery rehabilitation became an industry without output. About $10 billion was spent over a decade on maintenance with nothing to show for it, not even a litre of petrol. A further $3 billion was later securitised against future crude sales for yet another failed repair cycle, a sum that could have delivered dozens of modular refineries. Even after the Petroleum Industry Act prioritised Domestic Crude Obligation, compliance remained elusive, while Nigeria continued to burn scarce foreign exchange importing substandard fuel into a system with no functional midstream. These were not marginal errors but a business model that plunged the country into crisis. Throughout it all, PETROAN’s voice was conspicuously muted, generous with praise where scrutiny was required.
This is why the current agitation rings hollow. Reform always unsettles those who prospered under disorder. President Bola Tinubu’s administration has signalled, through words and decisions, that it intends to break with the old script. Ojulari’s mandate at NNPC is clear: commercial discipline, efficiency and profitability. That mandate cannot be reconciled with endless rehabilitation theatre.
There is another uncomfortable question PETROAN has not answered. What value does its leadership bring to the petroleum sector beyond television appearances and press statements? Serious business leadership is measured in assets built, jobs created and value added. Publicly available information suggests that some of the companies associated with PETROAN’s leadership are modest in scale, with limited project footprints. Allegations and controversies reported in the public domain around some of these entities, whether in the power metering space or elsewhere, only reinforce the need for caution in elevating moral authority. Perhaps PETROAN’s members would do well to examine the records of those who speak in their name before an association meant to represent many is reduced to the private estate of a few and recast as an adversary of the public interest.
This is not to say that retailers have no role in policy debate. They do. But influence must be earned through insight, integrity and alignment with the national interest. Threats and ultimatums betray a lack of confidence in argument.
Nigeria stands at a fork in the road. One path leads back to ritualised waste, institutional failure and the comfort of familiar inefficiencies. The other leads to local capacity, competition and a petroleum industry that finally works for Nigerians. The Dangote Refinery is not a silver bullet, but it is a signal that the old excuses are losing credibility.
PETROAN’s nuisance value thrives only when reformers flinch. President Tinubu has shown little appetite for cheap blackmail. Ojulari enjoys his confidence for a reason. The task before NNPC is too important to be derailed by those nostalgic for a broken system. If PETROAN wishes to be relevant in this new era, it must evolve from noise to nuance. Otherwise, history will remember it not as a defender of consumers, but as a footnote in Nigeria’s long struggle to escape the tyranny of waste.
Abiodun, a communications specialist, writes from Lagos
Feature/OPED
What If the Problem Isn’t Just the Government?

By Blaise Udunze
Recent reports in the media space highlighting threats of “naked protests” by market women across several states if the federal government fails to address the issue of hardship underscore the depth of hunger and poverty gripping the nation. No doubt, there is hardship in the country, of which Nigeria’s poverty crisis is often framed as the government’s failure, poor policies, weak institutions, corruption, and economic mismanagement.
From a balanced viewpoint, while these factors are undeniable, they do not tell the full story in its totality. The reality is that the majority of Nigerians, being the larger populace experiencing this challenge, will definitely oppose the ideology that poverty in Nigeria is not merely a policy problem; it is also a societal one. The underlying truth is that this is shaped by citizens’ behaviours, choices, cultural norms, and civic attitudes. This will remain a lived experience of the people until this dimension is confronted honestly; reforms will continue to yield limited results.
Nigeria’s economy has witnessed growth as inflation has decelerated, with headline inflation easing to 15.15percent and food inflation retreating to 10.84 per cent. The exchange rate was stabilising, and foreign reserves ($46.7 billion) had climbed to a seven-year peak. Despite the growth figures and ambitious government targets, millions of Nigerians remain trapped in poverty. More alarming is the recent estimates suggesting that an additional two million people could fall below the poverty line this year alone.
The intrigue is that the geographic distribution of these figures tells a deeper story, and this is more revealing than the numbers; however, there is an uneven geographical spread. Of concern here, which is troubling, is why states such as Yobe, Jigawa, Katsina, Kano, and Zamfara tend to experience or be deep in poverty when compared to other states like Lagos, Port Harcourt, Aba, Enugu, and Onitsha, which are projected to experience less poverty. This disparity raises a critical question, which calls for an urgent answer to why poverty outcomes differ so starkly within the same country, because no doubt, much of the explanation lies beyond government failures.
While governance challenges exist nationwide, the explanation extends beyond Abuja. Perhaps this is from deliberate ignorance of the people; the reality is that it lies in education, cultural practices, social norms, and individual responsibility play decisive roles in shaping economic outcomes.
One key alarming fact that has deeply entrenched poverty in many northern states, unlike other regions, is limited access to education, especially for girls, early marriage, polygamy, and large family sizes. There have been several factors that reinforce cycles of poverty by stretching limited household resources, reducing educational attainment, and limiting economic mobility, and this will continue to be a long-standing challenge or lived experience for the people if not addressed.
It is clearer that practical comparison illustrates this reality. Taking into consideration that a low-income worker in Yobe who marries four wives and raises over twenty children will inevitably struggle to provide adequate education, healthcare, and opportunities for his family, while in contrast, a similar worker in Aba is more likely to marry later, have fewer children, and invest in their education. Without much ado, over time, the children in the latter household acquire skills, productivity, and economic relevance because their parents chose to prioritise education for them, while the former remain trapped in subsistence and dependency. These differences are not subjective; they are structural and measurable.
Religion and culture further complicate the picture as record has it that Nigeria is one of the most religious countries in the world, yet religiosity often serves personal aspirations, prosperity, miracles, or divine favour rather than reinforcing civic responsibility and social ethics. Today in Nigeria, political leaders frequently reinforce this distortion and moral narrative. Only recently, it was announced that public officials in Abuja celebrate marrying off multiple children at once, some governors borrow billions to spend public funds on religious pilgrimages, while underfunding education, healthcare, and infrastructure, they send a clear message about priorities. In contrast, states that invest deliberately in education, such as Enugu with its smart school initiatives, demonstrate how leadership choices influence societal outcomes.
Still, the crisis of responsibility is not confined to any region. It is national, as proved during the discussions at Lagos State’s 12th Summit of the Association of Retired Heads of Service and Permanent Secretaries (ALARHOSPS), it was emphasised that societal progress depends not only on leadership but on citizenship behaviour. According to Professor Wusu Onipede, citizenship is defined by commitment to collective welfare, not mere residence.
The truth is not far-fetched, going by the saying that actions, positive or negative, directly impact society. What would have informed the common actions, such as stealing public assets, vandalising infrastructure, ignoring traffic laws, or tolerating corruption, all accumulate into widespread societal harm as seen in our everyday lives. Conversely, volunteering, mentorship, and community engagement generate resilience, opportunity, and shared prosperity. With close reading, one will notice that this dynamic was captured succinctly in Professor Oluwatomi Alade’s “Triangle for Change,” which pointed to the home, the school, and the community. Parents must brace up to understand that the primary responsibility is upon them to start prioritising education, teachers who impart both knowledge and character, and communities that uphold civic values create the foundation for sustainable development because the truth is that the change does not only rest on the government. In the same manner, it will be said that neglect in any of these spheres, whether through early marriage, disregard for schooling, or normalisation of polygamy, undermines national progress.
Religious institutions, as Professor Oguntola-Laguda argues, must also evolve, which means that beyond spiritual teachings, they should emphasise practical social ethics in the areas of responsibility, productivity, gender inclusion, and civic duty. In regions where harmful norms persist, faith leaders, traditional authorities, and elders possess the influence necessary to drive change, if they choose not to use it, otherwise the society will remain impoverished.
Globally, the link between social norms and poverty is well established, and norms that condone child marriage, gender exclusion, or unchecked family sizes perpetuate intergenerational deprivation. Over the period, in other countries, it is clear that economic interventions alone cannot dismantle these patterns because countries like India show that combining education incentives, political inclusion, and social protection can reduce poverty among marginalised groups. Initiatives such as Uganda’s SASA, which is a program that demonstrates that shifting attitudes toward gender and empowerment lead to improved economic outcomes. Nigeria’s poverty strategy must similarly integrate social transformation with economic reform.
None of this absolves government responsibility. Poorly sequenced reforms, rising taxes, insecurity, weak infrastructure, and inadequate social protection continue to deepen hardship. Senator David Mark of the African Democratic Congress has criticised what he terms “vicious policies” that worsen citizens’ vulnerability. Nigerians are acutely aware of these failures. What they demand is not statistics or political rhetoric, but practical policies that reduce hardship, enable productivity, and promote inclusion.
Even at this, Nigerians must take into cognisance that government action alone is insufficient. Poverty cannot be eradicated where large families are unsustainable, education is undervalued, and corruption is tolerated at the household and community levels. Individual responsibility remains the missing link. Citizens must be discreet in their timing for marriage until they can provide adequately, manage family sizes responsibly, educate all children, especially girls and reject the glorification of excess and impunity.
Insecurity further illustrates this shared responsibility. Though one will argue that the state bears the constitutional duty to protect lives and property, law and order, what about the dwellers? Communities must actively support security efforts through vigilance, information sharing, and conflict resolution. Silence in the face of crime and corruption enables disorder because independence loses meaning when citizens disengage from safeguarding their own communities.
Another critical aspect that is akin to insecurity is that economic development also falters when citizens undermine progress through dishonesty, rent-seeking, and apathy. What people fail to understand is that entrepreneurship, accountability, and cooperation are as vital as government-led job creation. The same thing can be said of cooperatives, vocational training, and local enterprise, which can deliver immediate relief and long-term sustainability. Wealthier Nigerians must focus on genuine social investment, creating opportunities, supporting education, and building institutions that outlast personal interest or individual generosity, rather than charity or wasteful spending or fueling crimes. Social responsibility must become a social norm.
One laughable misconception people harbour about independence, which must be clarified, is that it is not simply freedom from colonial rule; it is the presence of civic responsibility. It must be understood that poverty persists not only because of policy gaps but because of harmful norms, cultural practices, and neglected duties. Anyone can argue this, but the truth is that there will always be a replay of this menace kicked against because every child denied education, every early marriage, every act of corruption, reinforces the cycle.
Breaking this repeating problem, known as poverty, takes several coordinated strategies working together, not just one solution. There must be an understanding that the issues are complex and interconnected; they must be addressed from different angles at the same time. For these reasons, the government must provide stable policies, infrastructure, and social protection and the citizens, in like manner, must reform behaviours that perpetuate poverty. The same must be said of the families that must prioritise education, and also, the communities must reward civic engagement and innovation. Religious and cultural leaders must promote responsibility alongside faith because these are critical platforms that have the attention of the greater number of people. The policymakers at this juncture must ensure that policies not only deliver relief but also incentivise behaviours that support sustainable development.
Without too much argument, it is glaring that Nigeria’s potential is evident in states and communities that have embraced education, civic virtue, and social reform. Judging by the developments in different states, one will conclude that Lagos demonstrates how engagement and accountability improve outcomes, while Enugu shows that investing in children yields long-term dividends. Conversely, regions where harmful norms persist remain trapped, regardless of federal spending.
Without much ado, all Nigerian stakeholders must come to the terms that Nigeria’s poverty challenge cannot be reduced to government failure alone. It is a collective problem rooted in culture, norms, and personal choices because sustainable development demands both accountable leadership and responsible citizenship. The fact remains that poverty will remain an enduring shadow, irrespective of the repeated threats of “naked protests,” but until Nigerians fully embrace their role as architects, not just beneficiaries of national progress. True independence begins when citizens accept that the future of the nation rests as much in their daily choices as in public policy.
Blaise, a journalist and PR professional, writes from Lagos and can be reached via: [email protected]
Feature/OPED
AU Must Reform into an Institution Africa Needs

By Mike Omuodo
From an online post, a commentator asked an intriguing question: “If the African Union (AU) cannot create a single currency, a unified military, or a common passport, then what exactly is this union about?”.
The comment section went wild, with some commentators saying that AU no longer serves the interest of the African people, but rather the interests of the West and individual nations with greedy interests in Africa’s resources. Some even said jokingly that it should be renamed “Western Union”.
But seriously, how has a country like France managed to maintain an economic leverage over 14 African states through its CFA Franc system, yet the continent is unable to create its own single currency regime? Why does the continent seem to be comfortable with global powers establishing their military bases throughout its territories yet doesn’t seem interested in establishing its own unified military? Why does the idea of an open borders freak out our leaders, driving them to hide under sovereignty?
These questions interrogate AU’s relevance in the ensuing geopolitics. No doubt, the AU is still relevant as it still speaks on behalf of Africa on global platforms as a symbol of the continent’s unity. But the unease surrounding it is justified because symbolism is no longer enough.
In a continent grappling with persistent conflict, economic fragmentation, and democratic reversals, institutions are judged not by their presence, but by their impact.
From the chat, and several other discussion groups on social media, most Africans are unhappy with the performance of the African Union so far. To many, the organization is out of touch with reality and they are now calling for an immediate reset.
To them, AU is a club of cabals, whose main achievements have been safeguarding fellow felons.
One commentator said, “AU’s main job is to congratulate dictators who kill their citizens to retain power through rigged elections.” Another said, “AU is a bunch of atrophied rulers dancing on the graves of their citizens, looting resources from their people to stash in foreign countries.”
These views may sound harsh, but are a good measure of how people perceive the organization across the continent.
Blurring vision
The African Union, which was established in July 2002 to succeed the OAU, was born out of an ambitious vision of uniting the continent toward self-reliance by driving economic Integration, enhancing peace and security, prompting good governance and, representing the continent on the global stage – following the end of colonialism.
Over time, however, the gap between this vision and the reality on the ground has widened. AU appears helpless to address the growing conflicts across the continent – from unrelenting coups to shambolic elections to external aggression.
This chronic weakness has slowly eroded public confidence in the organization and as such, AU is being seen as a forum for speeches rather than solutions – just as one commentator puts it, “AU has turned into a farce talk shop that cannot back or bite.”
Call for a new body
The general feeling on the ground is that AU is stagnant and has nothing much to show for the 60+ years of its existence (from the times of OAU). It’s also viewed as toothless and subservient to the whims of its ‘masters’. Some commentators even called for its dissolution and the formation of a new body that would serve the interests of the continent and its people.
This sounds like a no-confidence vote. To regain favour and remain a force for continental good, AU must undertake critical reforms, enhance accountability, and show political courage as a matter of urgency. Without these, it may endure in form while fading in substance.
The question is not whether Africa needs the AU, but whether the AU is willing and ready to become the institution Africa needs – one that is bold enough to initiate a daring move towards a common market, a single currency, a unified military, and a common passport regime. It is possible!
Mr Omuodo is a pan-African Public Relations and Communications expert based in Nairobi, Kenya. He can be reached on [email protected]
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism9 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn













