Health
Nigeria Records Six More Cases of UK COVID-19 Strain
By Ahmed Rahma
The Director-General of the Nigeria Centre for Disease Control (NCDC), Dr Chikwe Ihekweazu, has disclosed that his agency and the African Centre for Genomics of Infectious Diseases (ACEGID) at the Redeemers University, Ede, Osun State, have detected an additional six UK’s COVID-19 strain known as B.1.1.7 variants in the country.
At the Presidential Task Force on COVID-19 national briefing on Monday, the DG explained that the additional cases were found on January 30.
He said five of the six new cases were from Osun State, while the remaining one was from Kwara State, which is very close to Osun State.
He stated that the five in Osun is most likely related to the fact that this is where ACEGID is and where they get a lot of samples from.
In total, Nigeria has now detected the B.1.1.7 variant in seven persons, noting that this could imply community transmission of this variant of concern.
He said efforts are being made to scale up on genomic surveillance, working very closely with ACEGID, adding that they have begun sequencing positive samples among travellers from the UK and South Africa, who test positive on the seventh day of testing.
“We are developing a protocol to sequence more samples from across states at ACEGID and our sister-agency, NIMR. This is in addition to our capacity at the NCDC National Reference Laboratory,” he explained.
The NCDC boss said that finally, there was really no magic bullet with the variants of concern. Currently, the message was still the same.
“Please, avoid large gatherings, wash your hands regularly, wear a face mask properly and ensure physical distancing,” he advised.
Mr Ihekweazu noted that the agency has continued to review the global and national situation with regards to the variants of concern, and how it affects the nation’s response.
“We are all aware that with the increasing transmission, the virus is adapting to the human population leading to what is known as variants of concern.
“In most countries, it is still not clear if the variants of concern are leading to increased transmission, or if the increase in cases is as a result of poor adherence to public health and social measures.
“An additional layer of response required to really understand the variants of concern is with genetic sequencing and genomic surveillance.
“We have begun this at the NCDC National Reference Laboratory with our partners at ACEGID at Redeemers University, Ede,” he explained.
Health
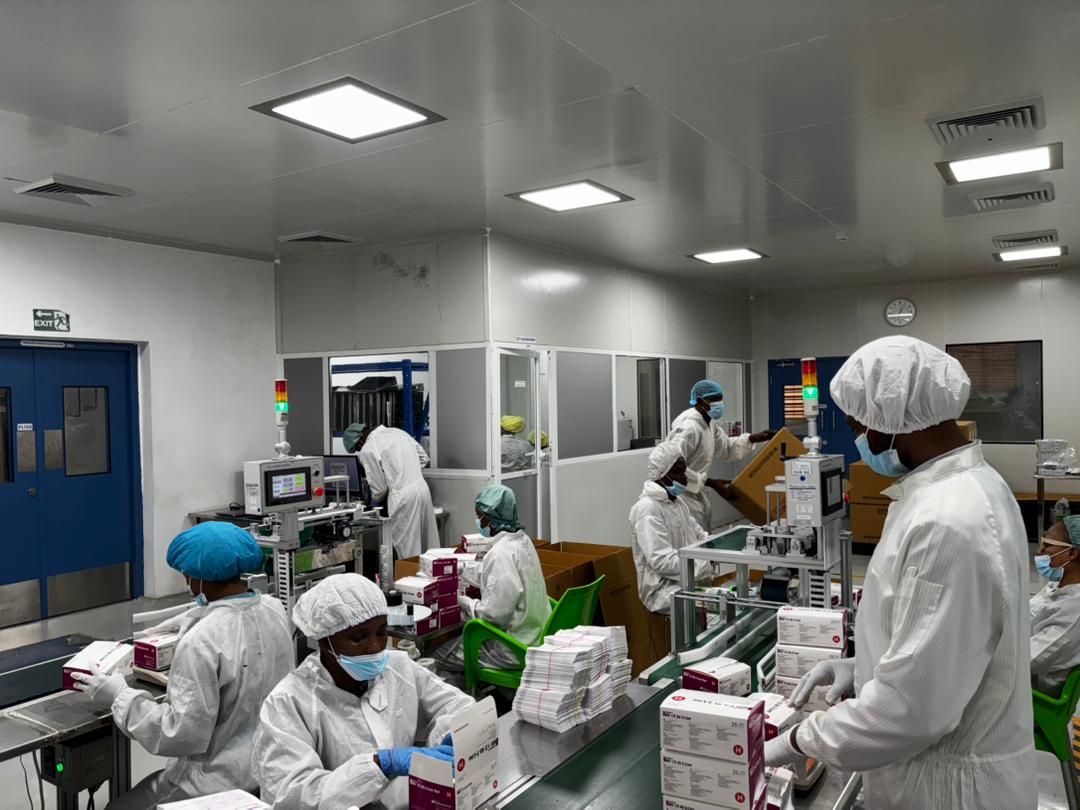
Local Packaging of WHO-Approved HIV Tests, a Shift in Africa’s Diagnostic Capacity

By Chidinma Onwumere
Nigeria’s public health system has taken a further step toward strengthening diagnostic self-reliance with the local packaging of a WHO pre-qualified HIV Rapid Diagnostic Test (RDT) at a facility in Lagos. The development highlights a broader shift in how essential health commodities are produced, supplied, and regulated across the continent.
The HIV test in question, the Standard Q HIV 1 & 2 RDT was previously manufactured and distributed as a fully imported finished product. Through regulatory approval granted under the WHO Pre-Qualification Change Notification, local packaging is now authorised at Colexa Biosensor, a Nigerian facility, making it the only site in Africa currently approved to package a WHO-prequalified HIV RDT.
While the technical designation may appear procedural, its implications are significant. WHO pre-qualification is a globally recognised quality benchmark used by national governments and international donors to guide procurement decisions for public health programs. Any change to a pre-qualified product, including where it is packaged, requires rigorous assessment to ensure that quality, safety, and performance remain unchanged.
For Nigeria, the approval represents more than a regulatory milestone. It addresses a longstanding vulnerability in health systems across Africa: dependence on imported diagnostics and the fragility of global supply chains. During recent global disruptions, including the COVID-19 pandemic, many countries experienced delays in access to essential medical commodities, exposing the risks of over-reliance on distant manufacturing hubs.
By enabling local packaging of a WHO-approved HIV test, Nigeria improves its ability to respond more quickly to demand fluctuations, reduce lead times, and maintain continuity of supply for national HIV programs. The test has been evaluated and approved by the Federal Ministry of Health and the National AIDS and STI Control Programme and is listed on the National HIV Testing Algorithm, making it eligible for procurement by government agencies and international partners supporting HIV services in the country.
From a programme perspective, inclusion on the national algorithm is critical. It ensures that test kits used in public health settings meet required performance standards and align with national testing strategies. It also allows donor-funded programs, such as those supported by multilateral agencies and global health initiatives, to procure the product locally while maintaining compliance with international quality requirements.
The shift toward local packaging also brings economic and institutional benefits. Shorter supply chains can lower logistics costs, improve predictability, and create opportunities for skills transfer in quality management, regulatory compliance, and manufacturing operations. Importantly, local involvement does not replace global standards; rather, it requires demonstrable adherence to them. WHO-approved local packaging is contingent on standardised processes, full traceability, and the ability to consistently prove compliance through documentation and audits.
Health policy experts note that such approvals challenge persistent assumptions that high-quality diagnostic manufacturing must occur outside Africa. Instead, they suggest a growing recognition that African facilities, when supported by strong regulatory oversight and technical partnerships, can meet the same benchmarks applied globally.
Beyond HIV diagnostics, the Lagos facility also produces blood glucose meters and test strips, reflecting a parallel focus on non-communicable diseases such as diabetes, which are rising rapidly across Nigeria and the continent. This dual focus on communicable and non-communicable diseases aligns with evolving health priorities, as African countries face a growing burden of chronic illness alongside infectious diseases.
The broader significance of this development lies in its potential scalability. While the immediate impact is national, the regulatory pathway demonstrated in Nigeria could inform similar initiatives elsewhere in Africa. Regional health bodies and policymakers have long advocated for greater local production of essential medical products as part of health security and economic development strategies. However, progress has often been constrained by regulatory complexity, quality assurance requirements, and limited technical capacity.
By meeting WHO pre-qualification standards for local packaging, Nigeria offers a practical example of how these barriers can be addressed. It also underscores the importance of collaboration between global manufacturers, local operators, regulators, and international agencies in building sustainable diagnostic capacity.
As demand for HIV testing remains high, particularly among key populations and in underserved areas, reliable access to quality-assured diagnostics remains central to prevention, treatment, and surveillance efforts. Local packaging does not eliminate the need for global supply chains, but it can make them more resilient, responsive, and context-appropriate.
More broadly, the development contributes to an ongoing debate about how African countries can move beyond consumption toward greater participation in the value chain of global health products. In this sense, the local packaging of a WHO-approved HIV test is less about a single facility or product and more about what it represents: a gradual but meaningful shift toward health system self-reliance grounded in global standards
As African governments and development partners continue to prioritise pandemic preparedness, universal health coverage, and supply chain resilience, such models may play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of healthcare delivery on the continent.
Health
Interswitch Takes eClinic Electronic Medical Records to Abia

By Aduragbemi Omiyale
To boost public healthcare delivery, the health-tech subsidiary of Interswitch, Interswitch eClat, has deployed its eClinic Electronic Medical Records (EMR) platform across public health facilities in Abia State.
This would be done in phases, with the kick-off phase to span six public health facilities, including three primary healthcare centres, two secondary facilities, and one tertiary hospital, creating an end-to-end digital care pathway that strengthens patient referrals, supports continuity of care, and enables data-driven decision-making across all levels of service delivery.
The EMR solution is built to reduce patient waiting times, strengthen referral processes, and ensure the secure handling of both clinical and administrative data, supported by a hybrid infrastructure that enables local hosting with cloud-based backup.
Officials of the leading African technology company held talks with the state government, especially from the Abia State Ministry of Health in Umuahia.
They discussed the implementation framework, and expected outcomes of the proposed eClinic deployment.
Discussions focused on deploying Interswitch’s eClinic solution in alignment with Abia State’s broader healthcare reform agenda under the current government’s administration, particularly the transition from fragmented, paper-based systems to secure, interoperable digital platforms across public health facilities.
“The Ministry of Health in Abia State is excited about the digitisation of health facilities, starting with Interswitch’s eClinic pilot phase involving three primary, two secondary, and one tertiary health centre.
“This initiative will enhance efficiency, accountability, and patient care by linking records across different levels of care.
“Global evidence shows that digital health improves access, reduces the cost of care, and maximises human resources while personalising services for our people.
“This partnership with Interswitch represents a key deliverable for this administration and aligns with the Governor’s vision for a modern, technology-driven health system,” the Commissioner for Health for Abia State, Mr Enoch Ogbonnaya Uche, said.
“Abia State has demonstrated a strong commitment to innovation and system reform. The alignment of the state’s healthcare priorities with national health digitisation objectives creates a solid foundation for meaningful progress.
“Interswitch’s eClinic platform is designed to improve hospital operations by automating workflows, securing patient data, and providing healthcare managers with reliable insights to guide decisions.
“Beyond improving patient experience, it supports stronger revenue tracking, operational efficiency, and accountability. Our focus is to ensure the success of this pilot phase and deliver tangible improvements across productivity, service delivery, and patient satisfaction,” the Vice President for Health Ecosystem (Public Sector) at Interswitch, Mr Babatunde Fadeyi, stated.
Health
Polaris Bank Sponsors Free Breast, Prostate Cancer Screenings

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
To commemorate World Cancer Day observed on Wednesday, February 4, 2026, Polaris Bank Limited is bankrolling free screenings for breast and prostate cancers across the country.
The financial institution partnered with a non-governmental organization (NGO) known as Care Organization and Public Enlightenment (COPE) for this initiative.
At least 100 women would be screened during the exercise, scheduled for Saturday, February 21, 2026, at the C.O.P.E Centre on 39B, Adeniyi Jones Avenue, Ikeja, Lagos, from 10:00 am to 2:00 pm.
The exercise will be conducted by trained health professionals and volunteers, ensuring participants receive both screening services and educational guidance on cancer prevention, self-examination, and follow-up care.
To participate in the free breast cancer screening programme, the applicants must be women, must be Polaris Bank account holders, and must have registered ahead of the day via bit.ly/BCS2026, with selection based on early and confirmed submissions.
Polaris Bank said the initiative was designed to promote awareness, screening, early detection, and preventive care, reinforcing its belief that access to health services is a critical foundation for individual and economic well-being.
The organization is already supporting an on-going free prostate cancer screening programme for 250 men aged 40 years and above across Nigeria.
The prostate cancer screening is being conducted at the Men’s Clinic, situated at 18, Commercial Avenue, Sabo, Yaba, Lagos, providing accessible, professional medical support for male participants seeking early detection and preventive care for prostate cancer.
Both initiatives (free breast and prostate cancer screenings) directly aligns with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, particularly SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being) through improved access to preventive healthcare and early detection services, SDG 5 (Gender Equality) by prioritizing women’s health and empowerment, and SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals) through strategic collaboration with civil society organizations such as C.O.P.E to deliver community-centered impact.
Educational materials, community engagement sessions, and digital awareness campaigns will be deployed to reinforce key messages around early detection, lifestyle choices, and the importance of regular medical check-ups.
The Head of Brand Management and Corporate Communications for Polaris Bank, Mr Rasheed Bolarinwa, emphasised that early detection remains one of the most effective tools in the fight against cancer.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn











