Banking
40s Age Group Dominates Personal Loan Applications Despite Rising Rates

In 2025, personal loan application activity hit previously unheard-of heights, reflecting both changing financial habits and growing challenges from the expense of living among middle-aged Australians. Despite rising borrowing costs, research indicates that people in their 40s are significantly increasing the nation’s appetite for credit.
Australians took out $9.04 billion in fixed-term personal loans in the June quarter of 2025, according to the most recent data from the Australian Bureau of Statistics. The largest percentage of all personal loan applications (31%), of any age category, came from borrowers between the ages of 40 and 49.
This increase has continued even as average unsecured loan interest rates have increased to 13.87% annually, indicating that personal credit solutions are becoming more and more necessary as financial commitments like mortgages, school bills, and family spending continue to outstrip income growth.
Demographic Analysis: Understanding the 40s Borrowing Surge
Personal loan applications are most common among those in their 40s (31%), followed by those in their 30s (25%), and those in their 50s (22%), according to data from personal loan provider Plenti. Australians under 60 make up only 6% of applications, and younger Australians make up only 15% of loans.
The typical borrower profile shows important trends. Forty-five percent of people who apply for personal loans are homeowners with current mortgages, and 46 percent make between $50,000 and $100,000 a year.
Financial companies like CashLend have noticed this change in the population, as evidenced by the steady increase in applications from people in the 40–49 age range in 2025. This group consists of people who have reached their maximum earning potential but are nevertheless dealing with significant debt on several fronts.
The 40-year-old demographic is in a special economic position. In addition to managing their mortgage obligations, these borrowers frequently support dependent children and, more often, elderly parents financially. This financial responsibility across generations and ongoing cost-of-living hikes put household finances under previously unheard-of strain.
Changing the Way People Borrow: From Optional to Necessary
Analysing loan reasons reveals significant shifts in how people borrow money. Consolidation accounts for 51.92% of all personal loan applications, suggesting that borrowers are looking to manage their current debts rather than finance new purchases. The last two key categories, which are categorised as necessary rather than optional, are car purchases and home renovations.
This change from lifestyle and investment borrowing to applications driven by necessity represents a substantial divergence from past trends. According to the trend, customers are being forced to consolidate their existing loans due to economic stress, which may be a sign of increased financial fragility among Australian households.
Record Borrowing Amid Rising Costs
The $9.04 billion borrowed in June 2025 excludes an additional $1.66 billion in refinancing activity. This represents sustained growth since June 2020 following pandemic-related contraction.
Key Figures:
- Average loan amount: $22,643
- Typical loan term: 35.4 months
- Average weekly repayment: $178
Regional variations provide additional insight into borrowing habits. Australian Capital Territory borrowers request the largest amounts at $30,388 on average. South Australian residents follow at $26,266.
Northern Territory borrowers request the smallest amounts at $19,168. These differences reflect varying economic conditions and cost structures across jurisdictions. The sustained growth despite high interest rates raises concerns about household financial resilience.
Understanding Current Interest Rates
Personal loan interest rates remain elevated compared to other lending products. October 2025 data shows secured loans averaging 9.65% while unsecured loans average 10.65%. Credit scoring dramatically impacts available rates. Borrowers with excellent credit can access rates near 9.79%. Those with poor credit scores (0-459 range) face rates approaching 25.25%.
The Reserve Bank of Australia reduced the official cash rate three times during 2025. Cuts occurred in February, May and August, bringing the rate to 3.60%. However, personal loan rates have not declined proportionally. Several factors explain this disconnect.
Personal loans carry higher risk profiles than secured lending products with no collateral backing the debt. Lenders also employ risk-based pricing models that assess each applicant individually. CashLend and other industry participants utilise sophisticated credit assessment frameworks. These evaluate multiple risk factors beyond base rate considerations.
Strategic Approaches for BorrowersCredit Score Matters
Your credit score represents the primary determinant of available interest rates. Prospective borrowers should obtain credit reports before making any application. Improving your credit score can generate substantial interest savings.
Maintaining consistent bill payment histories helps. Reducing credit utilisation ratios makes a difference. Correcting reporting errors proves valuable. Even modest score improvements can shift applicants into lower rate categories. This potentially saves thousands in interest charges over loan terms.
Comparison Shopping Is Essential
Personal loan application processes require strategic thinking. Each lender offers different rates based on their specific assessment criteria and risk appetite. Financial experts recommend obtaining quotes from multiple providers.
Typically three to five comparisons provide adequate market insight. Most lenders offer preliminary rate assessments through soft credit inquiries. These do not impact credit scores. This allows applicants to compare actual offered rates rather than advertised rates.
Critical Assessment Factors:
- Total borrowing cost including all fees and interest charges
- Comparison rates reflecting true loan cost
- Fee structures (establishment, monthly and exit fees)
- Flexibility provisions for additional repayments
- Early repayment terms and potential penalties
Warning Signs to Watch
- Certain lending characteristics warrant caution. Establishment and ongoing fees exceeding 5% of loan principal represent above-average costs.
- Pressure to borrow larger amounts than requested should raise concerns. Unclear fee disclosures or “guaranteed approval” marketing indicate questionable lending practices.
- Affordability assessment must extend beyond basic serviceability calculations. Stress-test your budget against potential income disruptions or expense increases.
Alternative Financing Options
Before proceeding with a personal loan application, evaluate alternative approaches. Homeowners with mortgage redraw or offset facilities may access lower-cost finance through existing home loans.
Balance transfer credit cards offering promotional interest periods can provide cost-effective debt consolidation. This works best for disciplined borrowers who can repay within the promotional timeframe.
Direct negotiation with creditors may yield payment arrangements or hardship provisions. This avoids interest charges entirely in some cases.
Support Resources:
- National Debt Helpline: 1800 007 007 (free financial counseling)
- No-interest loan schemes for essential purchases
- Low-interest loan programs targeting low-income households
- Community organisation assistance programs
Looking Ahead
Market analysis projects continued growth in Australian personal lending. Forecasts indicate potential expansion to $13.16 billion by 2034. This represents a 23% compound annual growth rate. Digital lending platforms continue gaining market share. This may drive increased competition and improved rate offerings for consumers.
The current trend toward essential rather than discretionary borrowing appears likely to persist. Cost-of-living pressures show no signs of easing in the near term. As millennials transition into their 40s, demographic factors may further increase demand. This could intensify competition for creditworthy borrowers among lenders. Regulatory oversight of responsible lending practices continues strengthening. Increased focus on affordability assessments and suitability determinations aims to protect consumers.
Conclusions: Navigating Complex Lending Decisions
Not greater prosperity, but broader economic stresses are the reason behind record personal loan application volumes among Australians in their 40s. Despite RBA rate cuts, average rates are still high at 13.87%, meaning that borrowers must pay a high price for loans.
When applying for a personal loan, potential borrowers should take a calculated approach, comparing offers from several lenders, getting thorough credit evaluations, and carefully weighing their options. Free counseling programs and expert financial help are excellent resources for complicated borrowing decisions.
Economic challenges, high borrowing prices, and demographic considerations all combine to make life difficult for Australian households. To effectively manage debt while preserving long-term financial stability, careful comparison, realistic affordability assessment, and informed decision-making are still crucial.
Banking
CBN Orders Banks, OFIs to Deploy AI Tech to Flag Illicit Money Flows

By Adedapo Adesanya
The Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) has rolled out fresh technology-driven rules compelling banks and other financial institutions to deploy automated anti-money laundering systems capable of detecting suspicious transactions in real time.
The directive, contained in a circular issued on March 10, 2026, applies to deposit money banks, mobile money operators, international money transfer operators, payment service providers, and other institutions under the apex bank’s supervision.
According to the regulator, the new framework sets minimum standards for automated anti-money laundering solutions designed to strengthen the detection and reporting of financial crimes within Nigeria’s rapidly digitising financial ecosystem.
In the circular, the CBN explained that the guidelines establish a baseline structure for financial institutions to deploy advanced monitoring tools capable of flagging suspicious financial activities instantly.
“The baseline standards provide a framework for implementing automated solutions that strengthen the detection and reporting of suspicious transactions in real time and enhance compliance with applicable AML/CFT/CPF laws and regulations, while also supporting the use of emerging technologies to improve overall financial crime risk management,” it stated.
The circular was jointly signed by the Director of Banking Supervision, Mrs Akinwunmi A. Olubukola, and Mrs Olubunmi Ayodele-Oni, acting for the Director of the Compliance Department.
Under the new policy, financial institutions must deploy automated anti-money laundering platforms that combine customer identification systems, transaction monitoring, sanctions screening, and risk assessment tools into a single integrated framework.
The CBN said the guidelines apply to all institutions operating within the financial system under its regulatory authority, including banks, payment companies, and other licensed financial service providers.
While the new rules take effect immediately, institutions have been given specific timelines to fully implement the required technology infrastructure.
Deposit money banks are expected to achieve full compliance within 18 months, while other financial institutions have 24 months to meet the regulatory requirements.
In addition, all institutions are required to submit detailed implementation roadmaps within three months of the issuance of the circular.
“The implementation of these guidelines shall start from the date of issuance, while full compliance shall be 18 months (for Deposit Money Banks) and 24-months (for Other Financial Institutions) from the date of issuance,” the apex bank added.
A major highlight of the framework is the emphasis on advanced technology tools such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, predictive analytics, and behavioural monitoring to identify unusual financial patterns that may indicate criminal activity.
Under the guidelines, institutions must deploy systems capable of conducting risk-based customer due diligence, monitoring transactions across multiple financial channels, and screening customers against sanctions databases and lists of politically exposed persons.
The CBN also directed that these automated systems must integrate seamlessly with core banking infrastructure and customer identity databases, enabling continuous real-time analysis of transaction flows and behavioural patterns.
According to the apex bank, traditional manual monitoring processes are increasingly inadequate in a financial environment that is becoming more complex and heavily driven by digital payments, fintech platforms, and mobile banking.
The regulator said automated surveillance systems would enable institutions to identify potential financial crimes earlier and report suspicious transactions promptly to authorities such as the CBN and the Nigerian Financial Intelligence Unit (NFIU).
The guidelines further require financial institutions to establish governance structures to oversee the performance of automated systems, validate artificial intelligence models, and ensure that data protection safeguards comply with Nigeria’s privacy regulations.
Beyond technology deployment, institutions must maintain detailed audit trails and case management systems that document investigations into suspicious financial activity and track regulatory reporting obligations.
The central bank warned that institutions that fail to comply with the new standards or operate ineffective anti-money laundering frameworks could face regulatory penalties.
Compliance will be monitored through a combination of off-site regulatory surveillance, on-site examinations, and targeted thematic reviews conducted by the banking regulator.
The CBN emphasised that the newly issued standards represent only the minimum compliance benchmark, adding that institutions may be required to implement stronger controls depending on their operational scale, transaction volumes, and risk exposure.
Banking
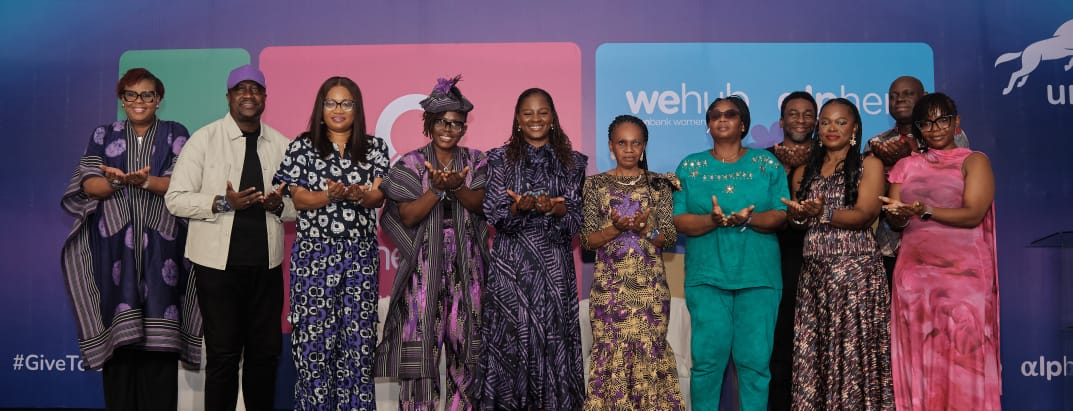
Union Bank Celebrates Women With Inclusion-First ‘Give to Gain’ Campaign

By Aduragbemi Omiyale
Union Bank of Nigeria is commemorating International Women’s Month 2026 with an initiative centred on women living with disabilities and women raising children with disabilities.
Throughout March, Union Bank will implement targeted initiatives to expand access, foster inclusion, and unlock sustainable opportunities.
Activities include a flagship event slated for The Stable, its multipurpose venue in Surulere, Lagos, on Saturday. The event convened women with disabilities, caregivers, supporting organisations, and advocates for dialogue, mentorship, and resource sharing.
Complementary efforts include outreach to disability support facilities and collaboration with educational institutions to distribute learning materials to female students with disabilities.
Tailored mentorship programmes will build confidence and capability in education, entrepreneurship, and careers.
Through its women’s banking proposition alpher and strategic partnerships, the bank will also deliver business sustainability training specifically designed for women living with disabilities and women raising children with disabilities.
Aligned with the global theme Give to Gain, the lender’s campaign Give to Gain: Creating Pathways for Inclusion and Endless Opportunities centres the lived experiences of women living with disabilities and underscores the need for intentional systems of support for social and economic advancement.
Internally, Union Bank will activate WeHub — its employee-led women’s network — to strengthen inclusive culture and support professional growth across the organisation.
“At Union Bank, inclusion is not an abstract ideal; it is a deliberate choice. While many conversations around women’s empowerment are important and necessary, women living with disabilities and women raising children with disabilities are too often left out entirely.
“This year’s theme, Give to Gain, reflects exactly what we believe: that when we intentionally open access, support, and opportunity to these women, the value created extends to families, communities, and society at large,” the Chief Brand and Marketing Officer for Union Bank, Ms Olufunmilola Aluko, stated.
Banking
Court Orders Final Forfeiture of N81m Stolen from Sterling Bank to FG

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
A Federal High Court sitting in Ikoyi, Lagos, has ordered the final forfeiture of N81.1 million to the Federal Government of Nigeria in favour of Sterling Bank.
The money was part of the N2.5 billion stolen by some customers of Sterling Bank and transferred to their own use as well as to the use of some third-party beneficiaries, owing to a system glitch experienced by the bank.
On October 2, 2025, the court granted an interim forfeiture order of the fund and also directed the publication of the same in a national newspaper for any interested party to show cause why the money should not be finally forfeited to the federal government.
When no one came forward to claim the money, Justice Yelim Bogoro on Monday, March 9, 2026, ordered the final forfeiture of the funds.
The matter was brought before the court by the Economic and Financial Crimes Commission (EFCC) after a petition from the financial institution on July 18, 2022.
The anti-graft agency, in its investigations, traced the stolen funds to various accounts, including that of a customer, Sulaiman Kehinde Ojora, who was one of the major beneficiaries of the monumental fraud.
Investigation further revealed that Sulaiman Kehinde Ojora fraudulently concealed the sum of N43.0 million in the account of his friend, Taiwo Oluwaseyi Alawode (Account No. 1233126860), domiciled in Access Bank, and the sum of N122.2 million in the account of his wife, Aminat Olatanwa Ojora (Account No. 0072889319), domiciled in Sterling Bank.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn