Banking
GCR Affirms A-(NG) Rating on First Bank With Stable Outlook

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
Lagos Nigeria, 11 September 2017 — Global Credit Ratings has affirmed the national scale ratings assigned to First Bank of Nigeria Limited of A-(NG) and A1-(NG) in the long term and short term respectively; with the outlook accorded as Stable. The ratings are valid until August 2018.
RATING RATIONALE
Global Credit Ratings (“GCR”) has accorded the above credit ratings to First Bank of Nigeria Limited1 (“FirstBank” or “the Bank”) based on the following key criteria:
The ratings of FirstBank are supported by its established franchise and systemically important status, with likelihood of strong support from the Federal Government of Nigeria in the event that such support is required. Offsetting these key rating drivers is the Bank’s moderated profitability in recent years, primarily due to the level of loan impairment charges.
Asset quality remains a key rating concern, with the Bank’s gross non-performing loan (“NPL”) ratio escalating to 24.2% at FY16 (FY15: 17.8%). This was largely driven by rising delinquent loans, particularly within the troubled oil and gas sector, where the Bank remains highly exposed. While management efforts towards revamping the risk management framework and architecture are noted, additional impairment pressure is expected, as the exposure within the oil and gas sector remains substantial (constituting 38.6% of gross loans at 1H FY17), with the likelihood of offsetting the full impact of recovery efforts at FY17. Based on the unaudited results for 1H FY17, gross NPLs stood at 21.8% of total gross loans.
The Bank remains adequately capitalised reporting a risk weighted capital adequacy ratio of 17.8% at FY16 FY15: 17.1%), above the prudential threshold of 15%. The position is not expected to change imminently, given management’s muted loan growth prospects, with focus on organic growth through earnings accretion.
FirstBank has a robust funding structure, supported by its strong franchise, and diversified deposit book, though largely short-dated on contractual basis. Liquidity risk is considered low, with regulatory liquidity ratio of 52.7% at FY16 (for FirstBank Nigeria only), well above the prudential minimum of 30%.
The Bank’s exposure to foreign currency risk remains a concern. At FY16, about 51% of gross loans were denominated in foreign currency, the bulk of which remains within the troubled oil and gas sector. Additionally, exposure exists within borrowings and deposits. While FirstBank is taking necessary mitigating measures (including portfolio realignment), the volatility in the foreign exchange market remains a significant risk.
Although FirstBank’s net-interest income of N294.3bn stood above its peers, its bottom-line earnings were considerably weakened, due to high loan impairment charges. Thus, pre-tax profit remained low around N10.7bn (FY15: N9.7bn) in FY16, far below the peer average. According to management, the Bank will continue to enhance its risk management processes and operational efficiency in order to improve operating performance in the coming years.
While the challenging operating environment has heightened uncertainties across all forward looking scenarios, positive rating momentum is dependent on a rebound to strong asset quality and profitability, with markedly improved competitive positioning. Conversely, sustained negative trends in asset quality and profitability, coupled with a significant deterioration in the Bank’s liquidity and capital ratios could result in negative rating action.
1 First Bank of Nigeria Limited is the commercial banking group of FBN Holdings Plc. All figures are for the commercial banking group except where stated otherwise.
Banking
Public Offer: Sterling Holdco Allots 13.812 billion Shares to 18,276 Shareholders

By Aduragbemi Omiyale
Sterling Financial Holdings Company Plc has allotted shares from its public offer of 2025 to investors with valid applications.
The allotment follows the earlier receipt of final approval from the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) and the recent clearance by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
In September 2025, the financial institution offered for sale about 12,581,000,000 ordinary shares of 50 kobo each at N7.00 per share in public offer.
However, the exercise received wide participation from the investing public, with the company getting 18,280 applications for 16,839,524,401 ordinary shares valued at approximately N117.88 billion.
Following a thorough verification process, valid applications were received from 18,276 shareholders for a total of 13,812,239,000 ordinary shares, representing a subscription level of 109.79 per cent and reflecting sustained confidence in Sterling Holdco’s strategic direction, governance, and long-term growth prospects.
The firm approached the capital market for additional funds for the recapitalisation of its two flagship subsidiaries, Sterling Bank and The Alternative Bank.
The capital injection will support the commencement of full operations and contribute to the group’s revenue diversification objectives.
In line with the guidelines set out in the offer prospectus, Sterling Holdco confirmed that all valid applications will be allotted in full. Every investor who complied with the terms of the offer will receive all the shares for which they applied.
A very small number of applications were not processed or were partially rejected due to non-compliance with the offer terms, including duplicate payments and failure to meet the minimum subscription requirement of 1,000 units or its multiples, as stipulated in the offer documents.
The group ensures a seamless post-offer process, with refunds for excess or rejected applications, along with applicable interest, to be remitted via Real Time Gross Settlement or NIBSS Electronic Funds Transfer directly to the bank accounts detailed in the application forms.
Simultaneously, the electronic allotment of shares has be credited to successful shareholders’ accounts with the Central Securities Clearing System (CSCS) on February 17, and for applicants who do not currently have CSCS accounts, their allotted shares will be temporarily held in a registrar-managed pool account pending the submission of their completed account opening documentation to Pace Registrars Limited, after which the shares will be transferred to their personal CSCS accounts.
Banking
CBN Governor Seeks Coordinated Digital Payment Reforms
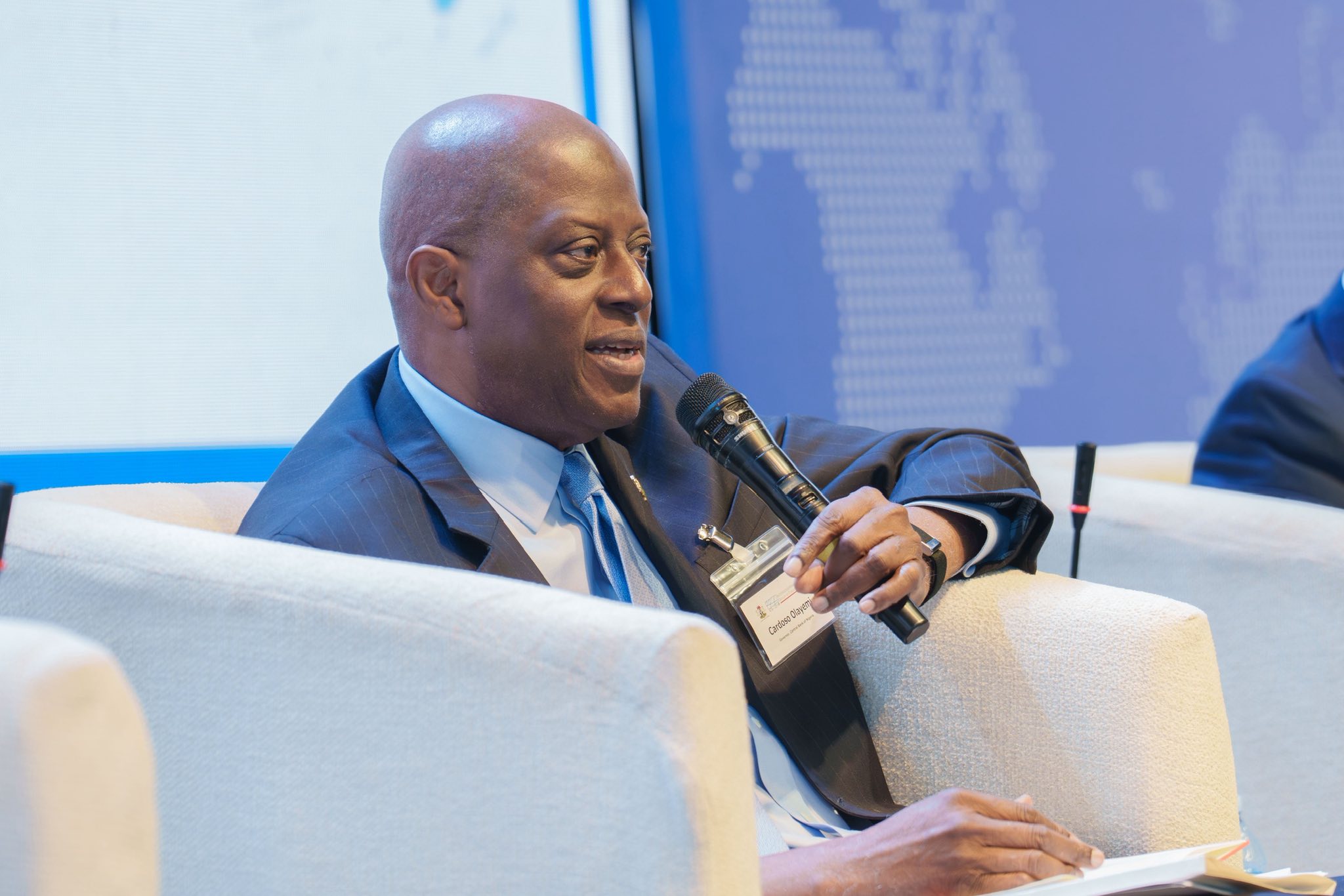

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
To drive inclusive growth, strengthen financial stability, and deepen global financial integration across developing economies, there must be coordinated reforms in digital cross-border payments.
This was the submission of the Governor of the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN), Mr Olayemi Cardoso, at the G‑24 Technical Group Meetings in Abuja on Thursday, February 19, 2026.
According to him, high remittance costs, settlement delays, fragmented systems, and heavy compliance burdens still limit the participation of households and Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in global trade.
The central banker emphasised that efficient payment systems are essential for economic inclusion, highlighting that global remittance corridors still incur average costs above 6 per cent, with settlement delays of several days, excluding millions from modern economic activity.
Mr Cardoso cautioned that while digital payments present significant opportunities, they also carry risks such as currency substitution, weakened monetary transmission, increased FX volatility, capital-flow pressures, and regulatory fragmentation.
The G-24 TGM 2026, themed Mobilising finance for sustainable, inclusive, and job-rich transformation, convened global financial stakeholders to advance the modernisation of finance in support of emerging and developing economies.
The CBN chief reaffirmed Nigeria’s commitment to working with G-24 members, the IMF, the World Bank Group, and other partners to build a more inclusive, resilient, and development-oriented global financial architecture.
“We have strengthened our AML/CFT frameworks in line with FATF guidelines, requiring strict dual-screening of cross-border transactions to mitigate risks.
“To deepen regional integration, the CBN introduced simplified KYC/AML requirements for low-value cross-border transactions to encourage broader participation in PAPSS, easing processes for Nigerian SMEs and enabling faster intra-African trade payments.
“We have also embraced fintech innovation through our Regulatory Sandbox, allowing payment-focused fintechs to test secure, instant cross-border solutions under close CBN supervision,” he disclosed.

Banking
Unity Bank, Providus Bank Merger Awaits Final Court Approval

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
The merger and business combination between Unity Bank Plc and Providus Bank Limited remains firmly on course, a statement from one of the parties disclosed.
According to Unity Bank, there is no iota of truth in reports in certain sections of the media suggesting that the merger process had stalled, as the transaction remains firmly on track.
It was disclosed that the necessary regulatory steps have been completed, but only a few other steps to finalise the transaction, especially the final court sanction.
There had been speculations that both lenders may not meet the new minimum capital requirement of the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) before the March 31, 2026, deadline.
However, it was noted that the combined capital base of Unity Bank and Providus Bank exceeds N200 billion, which is the minimum requirement to retain a national banking licence under the CBN’s recapitalisation framework.
When completed, the Unity-Providus merger is expected to deliver a stronger, more competitive, and customer-centric financial institution — one with the scale, innovation, and reach to redefine the retail and SME banking landscape in Nigeria.
“The merger with Providus Bank significantly enhances our capital base, operational capacity, and strategic positioning.
“We are confident that the combined institution will be better equipped to support economic growth and deliver innovative financial solutions across Nigeria,” the chief executive of Unity Bank, Mr Ebenezer Kolawole, stated.
Recall that a few months ago, shareholders authorised the merger between the two entities at Court-Ordered Meetings. They also adopted the scheme of merger at their respective Extraordinary General Meetings (EGMs) in September 2025,
The central bank also backed the merger, with a pivotal financial accommodation to support the transaction. The merger also received a further boost with a “no objection” nod from the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
The regulatory approvals form part of broader efforts to strengthen the resilience of Nigeria’s banking system, reinforce capital adequacy across the sector, and mitigate potential systemic risks.
The development positions the combined entity among the 21 banks that have satisfied the apex bank’s new capital threshold for national banking operations.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn