Economy
Fitch Fears Another Naira Devaluation, Downgrades 3 Banks

By Dipo Olowookere
The ratings of three banks in Nigeria have been downgraded Fitch Ratings amid fears that their operations would be negatively impacted by a further devaluation of the Naira.
A statement issued by the agency said the banks and others in the country will face material pressures from a weaker operating environment over the next few months given the price of crude oil and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on individuals and businesses.
The downgraded lenders are Zenith Bank, Guaranty Trust Bank (GTBank) and United Bank for Africa (UBA). Their ratings were lowered to Long-Term Issuer Default Rating (IDR) ‘B’ and Viability Rating (VR) ‘b’.
In the statement, Fitch said it has also placed the Long-Term IDRs, VRs and National Ratings of all 10 rated Nigerian banks (excluding Stanbic IBTC Holdings and Stanbic IBTC Bank, which are not assigned VRs and IDRs) on Rating Watch Negative (RWN).
According to the rating firm, before the current crisis, its outlook for the Nigerian banking sector was negative, which reflected tough operating conditions, including slow GDP growth, rising regulatory risks and potential performance pressures.
Fitch said it expects banks’ credit profiles to suffer from weaker asset quality and reduced profitability in the more severe downside scenario.
“Based on experiences from 2015/2016, we expect the current oil price shock to adversely impact the oil and gas sector.
“This sector accounts for around 30 percent of the banking sector’ gross loans, of which a large proportion was restructured during the previous crisis (some are still classified as Stage 2 under IFRS 9).
“Our stress tests show that asset-quality risks arising from deterioration of the banks’ oil and gas exposures are the biggest threat to their ratings.
“Additionally, we expect the non-oil segment to be impacted by the slower economy, but also due to the COVID-19 crisis, which could severely affect communities and industries. It would particularly test the quality of consumer and SME loans,” it said.
Fitch noted that lower oil revenues also raise the prospect of a material Naira devaluation, which would put pressure on the banks’ regulatory capital ratios.
However, it stated that given the banks’ net long foreign-currency positions, its stress tests show that in most cases the impact on Fitch Core Capital (FCC) ratios is tolerable under several scenarios.
“Nigerian banks have reasonable loss absorption buffers, underpinned by strengthened capitalisation since the last crisis.
“In the near-term, healthy earnings will continue to absorb larger credit losses but future profits will be under pressure from slowing loan growth, reduced client activity and higher levels of provisioning for expected credit losses under the IFRS 9 accounting framework,” it noted.
Fitch added that, “On balance, the near-term impact from the oil price shock and COVID-19 on funding and liquidity is likely to be tolerable.
“The primary risk is that lower oil revenues (and Nigeria’s falling FX reserves) could limit banks’ access to foreign currency (FC) liquidity.
“Furthermore, adverse global conditions could impede some banks in raising external financing. Local-currency liquidity remains strong with banks funded mainly by low-cost customer deposits.”
Fitch said it will resolve the RWN once it has assessed how this economic shock impacts the banking system and the credit profiles of each bank, as well as the banks’ ability to adapt.
The Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) recently announced relief measures, which should alleviate some near-term asset-quality pressures.
Some of these include requesting banks to restructure loan tenors and terms for consumers and business that are most affected, particularly borrowers in the oil and gas, agriculture and manufacturing sectors.
Economy
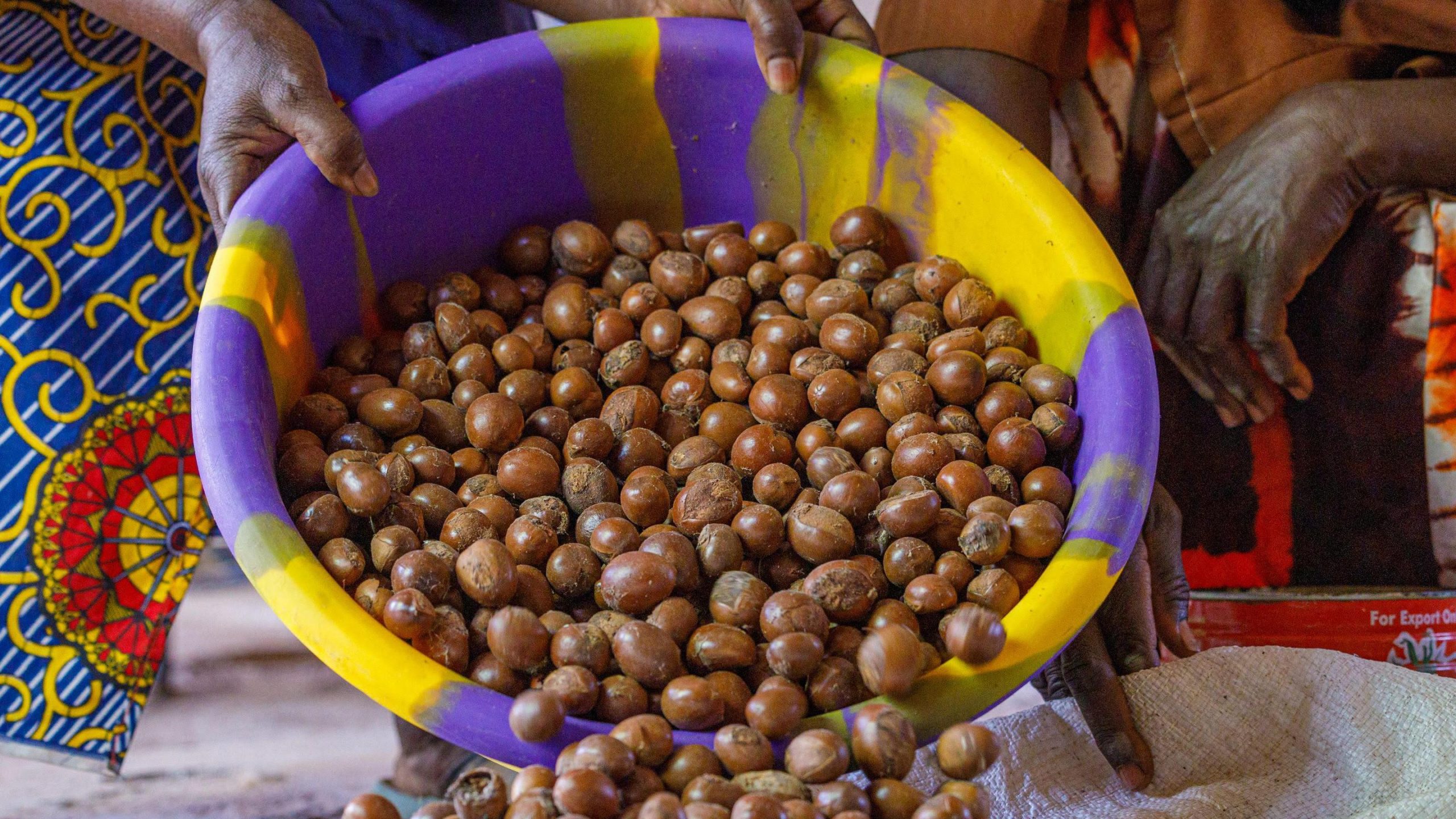
Tinubu Okays Extension of Ban on Raw Shea Nut Export by One Year

By Aduragbemi Omiyale
The ban on the export of raw shea nuts from Nigeria has been extended by one year by President Bola Tinubu.
A statement from the Special Adviser to the President on Information and Strategy, Mr Bayo Onanuga, on Wednesday disclosed that the ban is now till February 25, 2027.
It was emphasised that this decision underscores the administration’s commitment to advancing industrial development, strengthening domestic value addition, and supporting the objectives of the Renewed Hope Agenda.
The ban aims to deepen processing capacity within Nigeria, enhance livelihoods in shea-producing communities, and promote the growth of Nigerian exports anchored on value-added products, the statement noted.
To further these objectives, President Tinubu has authorised the two Ministers of the Federal Ministry of Industry, Trade and Investment, and the Presidential Food Security Coordination Unit (PFSCU), to coordinate the implementation of a unified, evidence-based national framework that aligns industrialisation, trade, and investment priorities across the shea nut value chain.
He also approved the adoption of an export framework established by the Nigerian Commodity Exchange (NCX) and the withdrawal of all waivers allowing the direct export of raw shea nuts.
The President directed that any excess supply of raw shea nuts should be exported exclusively through the NCX framework, in accordance with the approved guidelines.
Additionally, he directed the Federal Ministry of Finance to provide access to a dedicated NESS Support Window to enable the Federal Ministry of Industry, Trade and Investment to pilot a Livelihood Finance Mechanism to strengthen production and processing capacity.
Shea nuts, the oil-rich fruits from the shea tree common in the Savanna belt of Nigeria, are the raw material for shea butter, renowned for its moisturising, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. The extracted butter is a principal ingredient in cosmetics for skin and hair, as well as in edible cooking oil. The Federal Government encourages processing shea nuts into butter locally, as butter fetches between 10 and 20 times the price of the raw nuts.
The federal government said it remains committed to policies that promote inclusive growth, local manufacturing and position Nigeria as a competitive participant in global agricultural value chains.
Economy
NASD Bourse Rebounds as Unlisted Security Index Rises 1.27%

By Adedapo Adesanya
The NASD Over-the-Counter (OTC) Securities Exchange expanded for the first session this week by 1.27 per cent on Wednesday, February 25.
This lifted the NASD Unlisted Security Index (NSI) above 4,000 points, with a 50.45-point addition to close at 4,025.25 points compared with the previous day’s 3,974.80 points, as the market capitalisation added N30.19 billion to close at N2.408 trillion versus Tuesday’s N2.378 trillion.
At the trading session, FrieslandCampina Wamco Nigeria Plc grew by N5.00 to trade at N100.00 per share compared with the previous day’s N95.00 per share, Central Securities Clearing System (CSCS) Plc improved by N4.18 to sell at N70.00 per unit versus N65.82 per unit, and First Trust Mortgage Bank Plc increased by 14 Kobo to trade at N1.59 per share compared with the previous day’s N1.45 per share.
However, the share price of Geo-Fluids Plc depreciated by 27 Kobo at midweek to close at N3.27 per unit, in contrast to the N3.30 per unit it was transacted a day earlier.
At the midweek session, the volume of securities went down by 25.3 per cent to 8.7 million units from 11.6 million units, the value of securities decreased by 92.5 per cent to N80.7 million from N1.2 billion, and the number of deals slipped by 33.3 per cent to 32 deals from the preceding session’s 48 deals.
At the close of business, CSCS Plc remained the most traded stock by value on a year-to-date basis with 34.1 million units exchanged for N2.0 billion, trailed by Okitipupa Plc with 6.3 million units traded for N1.1 billion, and Geo-Fluids Plc with 122.0 million units valued at N478.0 million.
Resourcery Plc ended the trading session as the most traded stock by volume on a year-to-date basis with 1.05 billion units valued at N408.7 million, followed by Geo-Fluids Plc with 122.0 million units sold for N478.0 million, and CSCS Plc with 34.1 million units worth N2.0 billion.
Economy
Investors Lose N73bn as Bears Tighten Grip on Stock Exchange

By Dipo Olowookere
The bears consolidated their dominance on the Nigerian Exchange (NGX) Limited on Wednesday, inflicting an additional 0.09 per cent cut on the market.
At midweek, the market capitalisation of the domestic stock exchange went down by N73 billion to N124.754 trillion from the preceding day’s N124.827 trillion, and the All-Share Index (ASI) slipped by 114.32 points to 194,370.20 points from 194,484.52 points.
A look at the sectoral performance showed that only the consumer goods index closed in green, gaining 1.19 per cent due to buying pressure.
However, sustained profit-taking weakened the insurance space by 3.79 per cent, the banking index slumped by 2.07 per cent, the energy counter went down by 0.24 per cent, and the industrial goods sector shrank by 0.22 per cent.
Business Post reports that 25 equities ended on the gainers’ chart, and 54 equities finished on the losers’ table, representing a negative market breadth index and weak investor sentiment.
RT Briscoe lost 10.00 per cent to sell for N10.35, ABC Transport crashed by 10.00 per cent to N6.75, SAHCO depreciated by 9.98 per cent to N139.35, Haldane McCall gave up 9.93 per cent to trade at N3.99, and Vitafoam Nigeria decreased by 9.93 per cent to N112.50.
Conversely, Jaiz Bank gained 9.95 per cent to settle at N14.03, Okomu Oil appreciated by 9.93 per cent to N1,765.00, Trans-nationwide Express chalked up 9.77 per cent to close at N2.36, Fortis Global Insurance moved up by 9.72 per cent to 79 Kobo, and Champion Breweries rose by 5.39 per cent to N17.60.
Yesterday, 1.4 billion shares worth N46.2 billion were transacted in 70,222 deals compared with the 1.1 billion shares valued at N53.4 billion traded in 72,218 deals a day earlier, implying a rise in the trading volume by 27.27 per cent, and a decline in the trading value and number of deals by 13.48 per cent and 2.76 per cent, respectively.
Fortis Global Insurance ended the session as the busiest stock after trading 193.7 million units for N152.7 million, Zenith Bank transacted 120.7 million units worth N11.1 billion, Japaul exchanged 114.8 million units valued at N407.0 million, Ellah Lakes sold 98.4 million units worth N999.2 million, and Access Holdings traded 63.1 million units valued at N1.7 billion.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn