Economy
NEPAD-IPPF Okays 8 Projects in Africa for $14.83m

By Dipo Olowookere
The New Partnership for Africa’s Development Infrastructure Project Preparation Facility (NEPAD-IPPF) has continued to support African countries to strengthen regional infrastructure connectivity by providing grants for project preparation and development for complex, cross-border regional infrastructure projects in energy, transport, ICT and trans-boundary water.
This directly supports Africa’s integration and industrialization efforts as well as trade in goods and services and helps to improve the quality of lives of Africans by improving access to infrastructure services – electricity, transport, communications and water.
NEPAD-IPPF provides grants to African countries through Regional Economic Communities (RECs) and specialized regional infrastructure institutions such as Power Pools to undertake feasibility, technical and engineering designs, environmental and social impact assessment studies, as well as preparation of tender documents and transaction advisory services to make projects bankable for financing and implementation in support of Africa’s socio-economic transformation.
Taking stock of achievements during 2016 at the Business Strategy Workshop for NEPAD-IPPF held at the headquarters of the African Development Bank (AfDB) in Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, on Friday, February 3, 2017, Shem Simuyemba, NEPAD-IPPF Fund Manager, informed the gathering that during 2016, NEPAD-IPPF had approved a total of $14.83 million for the preparation of eight regional projects covering energy, transport and water.
Five energy/power projects were approved, two in West Africa, two in Southern Africa and one in East Africa. In West Africa, these were, the Nigeria-Benin 330 kV Power Interconnector Reinforcement Project executed by the West African Power Pool (WAPP) and the Feasibility Study for Women in a Changing Energy Value Chain in West Africa under the ECOWAS Centre for Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency (ECREE) intended to unlock business opportunities for women entrepreneurs in the energy value chain. In East Africa, NEPAD-IPPF funded the Uganda-Tanzania Refined Oil Products Pipeline Project with oversight from the East African Community Secretariat.
In Southern Africa, approved projects were, the Zambia-Mozambique 400 kV Power Interconnector Project and the Kolwezi (DRC)-Solwezi (Zambia) 330 kV Power Interconnector Project linking the two copper-mining belts of Katanga in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and Northwestern Zambia.
The Executing Agency for the two projects is the Southern Africa Power Pool (SAPP). The Zambia-Mozambique Power Interconnector Project is co-financed with the US Trade and Development Agency (USTDA).
Project preparation and development work undertaken by NEPAD-IPPF has had a major impact in generating bankable projects, which have attracted financing for implementation.
An example is the Power Interconnector, 330 kV North Core Project involving Nigeria, Niger, Benin and Burkina Faso. NEPAD-IPPF provided $5.9 million for the preparation of this project (one of the largest grants for a single project).
The estimated financing cost of the project was $681.67 million.
However, at the North Core Financing Roundtable held on November 9, 2016, under the auspices of WAPP and the countries concerned, the project attracted $1.205 billion in financing pledges.
The two transport projects approved were the Route Multinationale, Kribi-Campo-Bata, the road/bridge over the Ntem River linking Cameroon to Equatorial Guinea, for a grant of $3.04 million under the Economic Community of Central African States, an important transport and trade corridor in Central Africa.
The other was in East Africa, the Lamu Port Development: Transaction Advisory Services and Technical Assistance – Phase 1 for a public-private partnership (PPP) to develop the new Port of Lamu in Kenya to serve the countries of Ethiopia, South Sudan and Kenya under the $20-billion LAPSEET mega infrastructure project.
One trans-boundary water project, the Multinational, Orange-Sengu River Basin Project, was also approved in 2016.
The purpose of the grant is to assist in the preparation of a Climate Resilient Water Resources Investment Strategy and Plan and Multipurpose Project for the Orange Senqu River Basin.
The project is co-funded by the Africa Water Facility and the Global Water Partnership (GWP) and is managed by the Orange River Basin Commission.
It will benefit the four countries of Lesotho, South Africa, Botswana and Namibia as it serves, among others, Africa’s most dense economic space, the Gauteng Province of South Africa with its mining, agricultural and industrial activities.
NEPAD-IPPF is a multi-donor Special Fund hosted by the African Development Bank (AfDB), established under the G8 as part of the support to the NEPAD African Action Plan and is managed in close partnerships with the African Union Commission (AUC) and the NEPAD Agency. Donors supporting NEPAD-IPPF include Canada, Denmark, Germany, Norway, Spain and the UK.
Since its establishment in 2005, NEPAD-IPPF has approved 72 grants for complex, cross-border regional infrastructure projects resulting in downstream financing of $7.88 billion, demonstrating the high leverage effect of well-prepared projects.
Under its current Strategic Business Plan (SBP) for the five-year period, 2016-2020, NEPAD-IPPF requires funding of about $250 million to prepare 80 to 100 regional infrastructure projects expected to generate $25 billion in infrastructure investments.
NEPAD-IPPF is also increasingly linking its project preparation work to financial closure and part of the thrust of its new business orientation is to engage early with project developers, financiers and investment houses to ensure that NEPAD-IPPF prepared projects respond better to investor needs.
“NEPAD-IPPF is a tested brand across Africa in supporting African countries to prepare complex, cross-border regional infrastructure projects and to bring them to bankability and therefore offers a total-project-development-solution,” said Simuyemba. He also observed that NEPAD-IPPF unlocks business opportunities across the “infrastructure value chain”, not just in advisory services, but also financing, construction, equipment supply, technology and skills as well as operations and maintenance.
Economy
Flour Mills Supports 2026 Paris International Agricultural Show

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
For the second time, Flour Mills of Nigeria Plc is sponsoring the Paris International Agricultural Show (PIAS) as part of its strategies to fortify its ties with France.
The 2026 PIAS kicked off on February 21 and will end on March 1, with about 607,503 visitors, nearly 4,000 animals, and over 1,000 exhibitors in attendance last year, and this year’s programme has already shown signs of being bigger and better.
The theme for this year’s event is Generations Solution. It is to foster knowledge transfer from younger generations and structure processes through which knowledge can be harnessed to drive technological advancement within the global agricultural sector.
In his address on the inaugural day of the Nigerian Pavilion on February 23, the Managing Director for FMN Agro and Director of Strategic Engagement/Stakeholder Relations, Mr Sadiq Usman, said, “At FMN, our mission is Feeding and Enriching Lives Every Day.
“This is a mandate we have fulfilled through decades of economic shifts, rooted in a culture of deep resilience and constant innovation. We support this pavilion because FMN recognises that the next frontier of global Agribusiness lies in high-level technical exchange.
“We thank the France-Nigeria Business Council (FNBC), the organisers of the PIAS, and our fellow members of the Nigerian Pavilion – Dangote, BUA, Zenith, Access, and our partners at Creativo El Matador and Soilless Farm Lab— we are exceedingly pleased to work to showcase the true face of Nigerian commerce.”
Speaking on the invaluable nature of the relationship between Nigeria and France, and the FMN’s commitment to process and product innovation, Mr John G. Coumantaros, stated, “The France – Nigeria relationship is a valuable partnership built on a shared value agenda that fosters remarkable Intercontinental trade growth.
“Also, as an organisation with over six decades of transformational footprint in Nigeria and progressively across the African Continent, FMN has been unwaveringly committed to product and process innovation.
“Therefore, our continuous partnership with France for the success of the Paris International Agricultural Show further buttresses the thriving relationship between both countries.”
PIAS is one of the most widely attended agricultural shows, with thousands of people from across the world in attendance.
Economy
NEITI Backs Tinubu’s Executive Order 9 on Oil Revenue Remittances

By Adedapo Adesanya
Despite reservations from some quarters, the Nigeria Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative (NEITI) has praised President Bola Tinubu’s Executive Order 9, which mandates direct remittances of all government revenues from tax oil, profit oil, profit gas, and royalty oil under Production Sharing Contracts, profit sharing, and risk service contracts straight to the Federation Account.
Issued on February 13, 2026, the order aims to safeguard oil and gas revenues, curb wasteful spending, and eliminate leakages by requiring operators to pay all entitlements directly into the federation account.
NEITI executive secretary, Musa Sarkin Adar, called it “a bold step in ongoing fiscal reforms to improve financial transparency, strengthen accountability, and mobilise resources for citizens’ development,” noting that the directive aligns with Section 162 of Nigeria’s Constitution.
He noted that for 20 years, NEITI has pushed for all government revenues to flow into the Federation Account transparently, calling the move a win.
For instance, in its 2017 report titled Unremitted Funds, Economic Recovery and Oil Sector Reform, NEITI revealed that over $20 billion in due remittances had not reached the government, fueling fiscal woes and prompting high-level reforms.
Mr Adar described the order as a key milestone in Nigeria’s EITI implementation and urged amendments to align it with these reforms.
He affirmed NEITI’s role in the Petroleum Industry Act (PIA) and pledged close collaboration with stakeholders, anti-corruption bodies, and partners to sustain transparent management of Nigeria’s mineral resources.
Meanwhile, others like the Petroleum and Natural Gas Senior Staff Association of Nigeria (PENGASSAN) have kicked against the order, saying it poses a serious threat to the stability of the oil and gas industry, calling it a “direct attack” on the PIA.
Speaking at the union’s National Executive Council (NEC) meeting in Abuja on Tuesday, PENGASSAN President, Mr Festus Osifo, said provisions of the order, particularly the directive to remit 30 per cent of profit oil from Production Sharing Contracts (PSCs) directly to the Federation Account, could destabilise operations at the Nigerian National Petroleum Company (NNPC) Limited.
Mr Osifo firmly dispelled rumours of imminent protests by the union, despite widespread claims that the controversial executive order threatens the livelihoods of 10,000 senior staff workers at NNPC.
He noted, however, that the union had begun engagements with government officials, including the Presidential Implementation Committee, and expressed optimism that common ground would be reached.
Mr Osifo, who also serves as President of the Trade Union Congress (TUC), expressed concerns that diverting the 30 per cent profit oil allocation to the Federation Account Allocation Committee (FAAC), without clearly defining how the statutory management fee would be refunded to NNPC, could affect the salaries of hundreds of PENGASSAN members.
Economy
Dangote Cement Deepens Dominance, Export Activities With $1bn Sinoma Deal

By Aduragbemi Omiyale
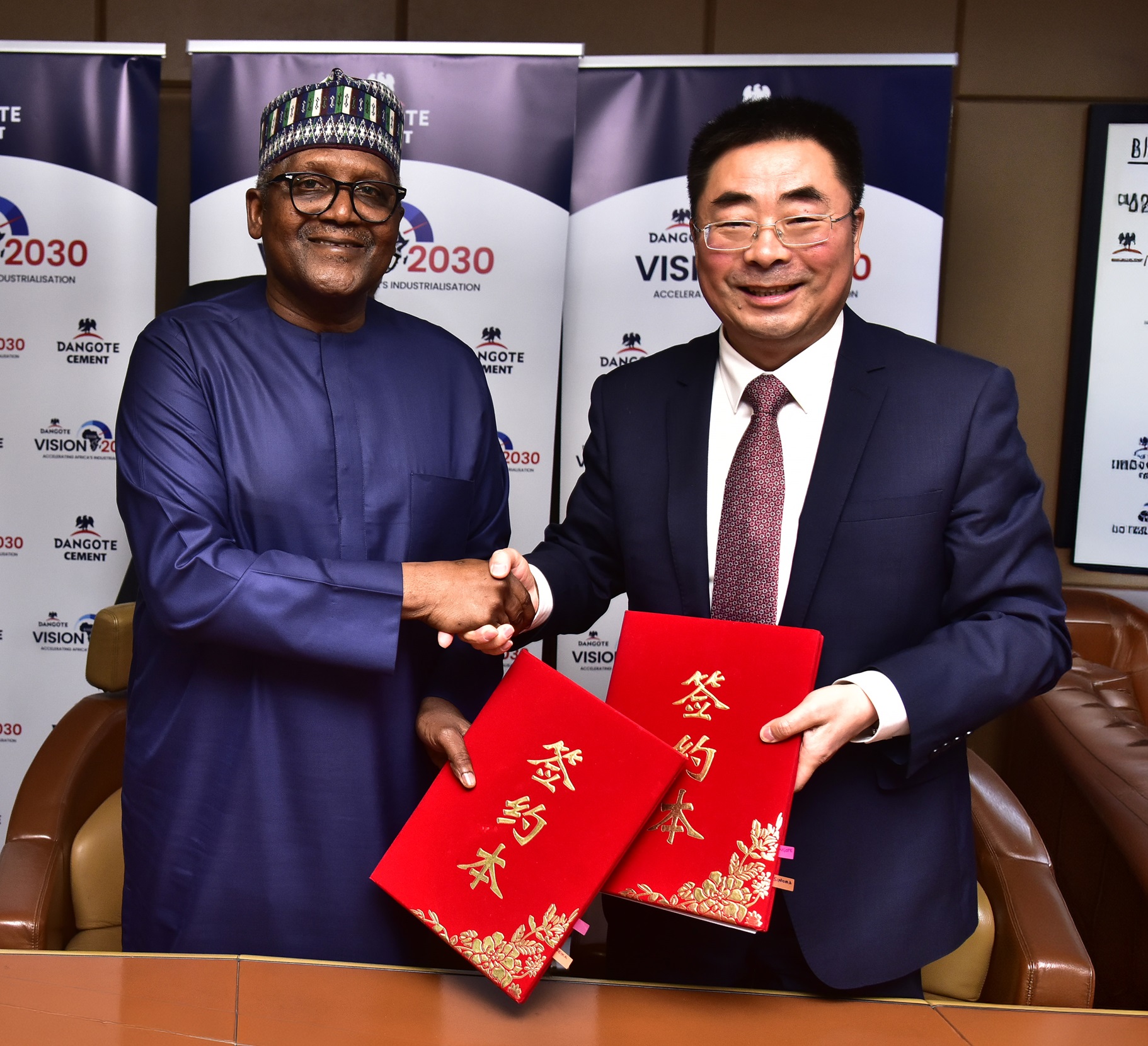
To strengthen its domestic market dominance, drive its export activities, optimise existing operational assets and enhance production efficiency and capacity expansion, Dangote Cement Plc has sealed $1 billion strategic agreements with Sinoma International Engineering for cement projects across Africa.
The president of Dangote Industries Limited, the parent firm of Dangote Cement, Mr Aliko Dangote, disclosed that the deal reinforces the company’s long-term growth strategy and aligns with the broader aspirations of the Dangote Group’s Vision 2030.
According to him, Sinoma will construct 12 new projects and expand others for the cement organisation across Africa, helping to achieve 80 million tonnes per annum (MTPA) production capacity by 2030, while supporting the group’s overarching target of generating $100 billion in revenue within the same period.
Under the Strategic Framework Agreement, Sinoma will collaborate with Dangote Cement on the delivery of new plants, brownfield expansions, and modernisation initiatives aimed at strengthening operational performance across key markets.
The new projects include a new integrated line in Northern Nigeria with a satellite grinding unit, a new line in Ethiopia and other projects in Zambia/Zimbabwe, Tanzania, Sierra Leone and Cameroon. In Nigeria, Sinoma will also handle different projects in Itori, Apapa, Lekki, Port Harcourt and Onne.
The projects signal Dangote Cement’s sustained commitment to consolidating its leadership position within the African cement industry, while enhancing its competitiveness on the global stage.
Chairman of the Dangote Cement board, Mr Emmanuel Ikazoboh, during the agreement signing event in Lagos, explained that the new projects would enable the company to play a critical role in actualising Dangote Group’s Vision 2030.
The new projects, when completed, will increase Dangote Cement’s capacity and dominant position in Africa’s cement industry.
On his part, the Managing Director of Dangote Cement, Mr Arvind Pathak, said the agreement reflects the company’s determination to grow its investments across African markets to close supply gaps and support the continent’s infrastructural ambitions.
According to him, Dangote Cement is committed to making Africa fully self‑sufficient in cement production, creating more value and linkages, leading to increased economic activities and a reduction in unemployment.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn












