Economy
Nigeria: Moody’s Predicts 2.5% GDP Growth in 2017, 4% in 2018

**Affirms Country’s B1 Rating With Stable Outlook
By Modupe Gbadeyanka
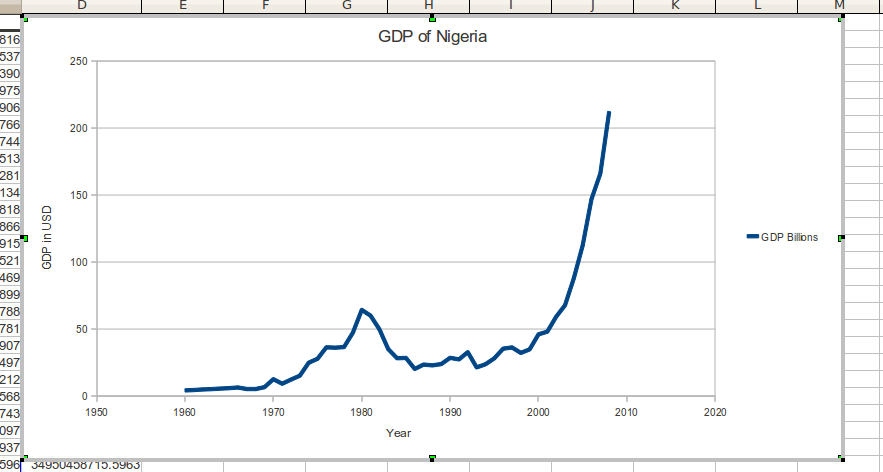
Moody’s Investors Service on Friday affirmed the B1 long-term issuer rating of the government of Nigeria with a stable outlook just as it forecasts that real GDP growth will rise to 2.5 percent in 2017 and accelerate further in 2018 to 4 percent.
The global rating firm disclosed that the key drivers for these were the medium term growth prospects remain robust despite the current challenging environment, with the rebound in oil production helping to rebalance the economy over the next two years; and the government’s balance sheet, which it said remains strong relative to its peers, resilient to the contractionary environment and temporarily elevated interest payments while the authorities pursue their efforts to grow non-oil taxes.
The long-term local-currency bond and deposit ceilings remain unchanged at Ba1. The long-term foreign-currency bond and deposit ceilings remain unchanged at Ba3 and B2, respectively.
Moody’s said it expects Nigeria’s medium term growth to remain robust, driven by the recovery in oil output and also over the near term, it expects Nigeria’s economic growth and US dollar earnings to improve in 2017, supported by a recovery in oil production.
According to Moody’s, after an estimated -1.5 percent real GDP growth in 2016, it forecasts real GDP growth to rise to 2.5% in 2017 and accelerate further in 2018 to 4%. A rebound in oil production to two million barrels per day (mbpd) will, if sustained, enhance economic growth and support the US dollar supply in the economy.
It noted that Nigeria has made significant gains in terms of governance and transparency in the oil sector. Improved availability of data, progress in restructuring the Nigerian National Petroleum Company (NNPC), rising effectiveness of operations at the refineries and a readiness to tackle difficult issues with partners (such as funding issues at the Joint Ventures) speak to a material improvement in the operating environment. The Petroleum Investment Bill (PIB bill), which had been blocked for 8 years in parliament, has been reactivated with a portion of the law drafted and passed by the Senate. Moreover, militant activity in the Niger Delta is set to wane following the resumption of payments from the government, though it will remain a threat to the recovery of the economy.
Moody’s further said the economy is also likely to benefit from the more timely implementation of the 2017 budget than its predecessor and in particular from the increase in capital spending on infrastructure which that will allow.
It also said the scarcity of Dollars, worsened by the soft capital controls imposed by the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN), is likely to continue to negatively affect important sectors of the economy especially in services and manufacturing sectors.
“We do not expect the current policy mix to significantly change over the short term but a gradual easing of restrictions is possible as foreign currency receipts improve with rising oil production,” the firm said on Friday in a statement obtained by Business Post.
In 2017 and 2018, we expect Nigeria’s balance of payments to move back into surplus, supported by government external borrowings and a falling current account deficit. The latter is quickly reducing, supported by falling imports and increased oil production.
Depreciation of the naira, soft capital controls and current dollar scarcity have been relatively effective at constraining imports. We expect foreign exchange reserves to grow modestly in 2017. While improved foreign investor sentiment should support the rebalancing of the economy over the medium term, with the return of portfolio investors improving dollar liquidity in the country, the continued existence of a parallel, unofficial foreign exchange market is likely to act as a strong deterrent over the near term.
RESILIENT GOVERNMENT BALANCE SHEET STRONGER THAN PEERS’ DESPITE TURBULENCE
Moody’s says it expects the medium-term impact of the oil price shock on Nigeria’s government balance sheet to be contained, and recent erosion of debt affordability to be reversed.
The effect of the recent downturn on the government’s budget sheet has been contained as the authorities have been able to offset the shortfall in revenue with large cuts in capital expenditure. As a result, Moody’s forecasts a budget deficit of 3 percent of GDP in 2016, comprised of a 2 percent of GDP federal government budget deficit and around 1% of arrears split between federal, state and municipality levels of government, it explained.
Moody’s forecasts the federal government deficit to remain around 2% of GDP in 2017 and 2018, with large capital expenditure outlays resuming as the government’s cash flow situation improves. Based on these underlying projections, Nigeria’s balance sheet will continue to compare favourably with peers’, with government debt remaining well below 20% of GDP over the coming years against 55% median for B1-rated peers.
By end-2016, Moody’s estimates the government debt stock will be comprised of 85% domestic borrowing and 15% external debt, resulting in a manageable external debt profile. Government external debt amounts to just 2.9% of GDP, with interest payments set to remain low, at around $330 million dollars per annum. Domestic debt has increased significantly in recent years, reaching its current level of NGN10 trillion. Around 30% of this debt is comprised of costly T-bills, which have increased refinancing risk and interest rate exposure. However, Moody’s expects the ratio of interest payments to government revenues to peak at 20% for general government, and close to 40% of revenues for federal government in 2017.
Although debt service costs are high, Nigeria’s domestic capital market is sufficiently developed to accommodate the yearly public sector borrowing requirements of around NGN5.5 trillion. This is another positive credit feature that distinguishes Nigeria from many similarly rated peers. The country’s banking sector is well-capitalised and liquid and the national pension fund still has additional capacity. Should banking sector liquidity decline, the Central Bank of Nigeria has tools at its disposal to support appetite for government securities, including lowering the cash reserve requirement ratio from its presently high level of 22.5%. However, appetite for government securities remains strong, with all instruments remain oversubscribed.
Moody’s expects the recent increase in debt service costs to prove temporary, as a result of i) the government’ initiatives to expand the non-oil revenue base, and ii) efforts to improve the structure of government debt.
Measures by the Federal Revenue Inland Service are expected to increase non-oil revenue to around NGN4 trillion in 2016 from NGN2.5 trillion in 2015. These include a tax amnesty on penalties and interest on tax liabilities due in 2013, 2014 and 2015. However, not all the initiatives have proven successful: the independent re-appropriation of revenues from the ministries departments and agencies (MDAs) has yielded disappointing results so far. Such outcomes highlight the considerable execution risks inherent in the transition to a less oil-dependent federal budget, and the implications for the government balance sheet should it not meet its objectives.
The government’s medium-term debt strategy should also help to lower the interest burden. The debt strategy is geared towards exchanging costly short-term debt with long-term concessional borrowing. Although a portion of future external borrowings are expected to be raised through the Eurobond markets, this is likely to be complemented with ongoing support from other multilateral institutions including the African Development Bank and the World Bank. The combined effect of these measures should help to bring interest payments/general government revenues down to 16.8% by 2018, from an estimated 19.8% in 2016.
RATIONALE FOR THE OUTLOOK AT STABLE
The stable outlook is driven by Moody’s view that the downside risks posed by the weakening of the country’s fiscal strength, and the external and economic pressures anticipated this year and next, are balanced by Nigeria’s strengths, which exceed those of sovereigns rated below B1. In 2016, Nigeria’s external vulnerability indicator of 31% will remain far below the expected B1 median of 51%, while its debt-to-GDP of 16.6% will remain far below the expected B1 median of 55%. Set against that, its expected debt servicing burden in terms of interest payments to revenue of 19% is more than double the B1 median of 9%. To a large extent, Moody’s believes that this reflects Nigeria’s underdeveloped public sector revenue base, a credit weakness that the administration is attempting to address.
WHAT COULD CHANGE THE RATING UP
Positive pressure on Nigeria’s issuer rating will be exerted upon: 1) successful implementation of structural reforms by the Buhari administration, in particular with respect to public resource management and the broadening of the revenue base; 2) strong improvement in institutional strength with respect to corruption, government effectiveness, and the rule of law; 3) the rebuilding of large financial buffers sufficient to shelter the economy against a prolonged period of oil price and production volatility.
WHAT COULD CHANGE THE RATING DOWN
Nigeria’s B1 issuer rating could be downgraded in the event of 1) a greater-than-anticipated deterioration in the government’s balance sheet or continued erosion of debt affordability, for example resulting from the failure to implement revenue reform; and 2) lower than expected medium term growth, for example as a result of delays in implementing key structural reforms, especially in the oil sector, or continued militancy in the Niger Delta, which undermine the level of oil production over the medium-term.
GDP per capita (PPP basis, US$): 6,184 (2015 Actual) (also known as Per Capita Income)
Real GDP growth (% change): -1.5% (2016 Estimate) (also known as GDP Growth)
Inflation Rate (CPI, % change Dec/Dec): 19% (2016 Estimate)
Gen. Gov. Financial Balance/GDP: -2.9% (2016 Estimate) (also known as Fiscal Balance)
Current Account Balance/GDP: -0.6% (2016 Estimate) (also known as External Balance)
External debt/GDP: 4.2% (2016 Estimate)
Level of economic development: Low level of economic resilience
Default history: No default events (on bonds or loans) have been recorded since 1983.
On 7 December 2016, a rating committee was called to discuss the ratings of the Government of Nigeria. The main points raised during the discussion were: The issuer’s economic fundamentals, including its economic strength, have not materially changed. The issuer’s fiscal or financial strength, including its debt profile, has not materially changed. The issuer’s susceptibility to event risks has not materially changed. Other views raised included: the issuer’s institutional strength/framework, have not materially changed. The issuer’s governance and/or management, have not materially changed.
The principal methodology used in these ratings was Sovereign Bond Ratings published in December 2015. Please see the Rating Methodologies page on www.moodys.com for a copy of this methodology.
The weighting of all rating factors is described in the methodology used in this credit rating action, if applicable.
Economy
Seplat to Boost Nigeria’s Oil Production With Mobil Assets Acquisition

By Adedapo Adesanya
Seplat Energy Plc will revive hundreds of Nigerian oil wells laying fallow after completing the acquisition of Mobil Producing Nigeria Unlimited (MPNU) from ExxonMobil.
The company said it aims to lift oil output to about 200,000 barrels a day, a move that will help boost Nigeria’s oil production levels, as it aims to reach 2 million barrels per day next year.
The transaction, according to Seplat, “is transformative for Seplat Energy, more than doubling production and positioning the company to drive growth and profitability, whilst contributing significantly to Nigeria’s future prosperity.”
The completion of the Seplat-ExxonMobil deal has created Nigeria’s leading independent energy company, with the enlarged company having equity in 11 blocks (onshore and shallow water Nigeria); 48 producing oil and gas fields; 5 gas processing facilities; and 3 export terminals.
Recall that the Nigerian Upstream Petroleum Regulatory Commission (NUPRC) in October approved the deal as part of a series of approvals, while it blocked Shell’s asset sale of up to $2.4 billion to the Renaissance consortium.
The acquisition of the entire issued share capital of MPNU adds the following assets to the Seplat Group: 40 per cent operated interest in OML 67, 68, 70 and 104; 40 per cent operated interest in the Qua Iboe export terminal and the Yoho FSO; 51 per cent operated interest in the Bonny River Terminal (‘BRT’) NGL recovery plant; 9.6 per cent participating interest in the Aneman-Kpono field; and approximately 1,000 staff and 500 contractors will transition to the Seplat Group.
MPNU adds substantial reserves and production to Seplat Energy; 409 million barrels of oil equivalent (MMboe) 2P reserves and 670 MMboe 2P + 2C reserves and resources as at 30 June 2024 and 6M 2024 average daily production of 71.4 kboepd (thousand barrels of oil equivalent).
Business Post reports that Seplat will be part of the payment this year, and will defer some to next year,
Speaking on the transaction, the Chairman of Seplat Energy, Mr Udoma Udo Udoma commended President Bola Tinubu for supporting this transaction and appreciated the support and diligence of the various ministries and regulators for all the work to reach a successful conclusion.
“We are delighted to welcome the MPNU employees to Seplat Energy. We are excited to begin our journey in a new region of the country, and we look forward to replicating the positive impacts we have achieved within our communities in our current areas of operations.
“Seplat’s mission is to deliver value to all our stakeholders, and we treasure the good relationships we have developed with the government, regulators, communities and our staff.”
On his part, the chief executive of Seplat Energy, Mr Roger Brown, described the acquisition as a major milestone, adding, “I extend my thanks to the entire Seplat team for their hard work and perseverance to complete this transaction.
“MPNU’s employees and contractors have a strong reputation for safety and operational excellence, and I welcome them to the Seplat Energy Group.
“We have acquired a company with one of the best portfolios of assets and related infrastructure in a world-class basin, providing enormous potential for the Seplat Group. Our commitment is to invest to increase oil and gas production while reducing costs and emissions, maximising value for all our stakeholders.
“MPNU is a perfect fit with our strategy to build a sustainable business that can deliver affordable, accessible and reliable energy for Nigeria alongside attractive returns to our shareholders”.
Economy
PenCom Projects N22trn Pension Assets for 2024

By Adedapo Adesanya
The National Pension Commission (PenCom) is projected to close the year with over N22 trillion in pension assets impacted by challenges like inflation and monetary policies.
This is according to PenCom Director-General, Mrs Omolola Oloworaran, at a press conference in Abuja on Thursday.
She said as of October 2024, the Contributory Pension Scheme (CPS) had 10.53 million registered contributors and pension fund assets worth N21.92 trillion.
Speaking at the conference-themed Tech-driven Transformation Shaping the Pension Landscape, which showcased PenCom’s strategic commitment to innovation, she said that the numbers reflected the agency’s unwavering commitment to fund safety, prudent management, and sustainable growth.
She explained that the pension environment was impacted by the wider economic challenges facing the country, noting that the sector battled multi-year high inflation, Naira devaluation, and the lingering effects of unorthodox monetary policies by the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN).
Business Post reports that the apex bank hiked interest rates by 875 basis points this year alone to tackle persistent inflation which peaked at 33.8 per cent as of October.
She said that these challenges eroded the real value of pension funds and impacted contributors’ purchasing power.
“To address these issues, the commission has initiated a comprehensive review of its investment regulations.
“It is focusing on diversifying pension fund investments into inflation-protected instruments, alternative assets, and foreign currency-denominated investments.
“The goal is to safeguard contributor savings and ensure resilience against future economic volatility,” she said.
She restated the commission’s commitment to expanding pension coverage, particularly through the advanced micro-pension plan designed to encourage participation from the informal sector using technology.
“This initiative will make it easier for everyday Nigerians to save for retirement, aligning with our vision of inclusive growth and financial stability for all.
“The backlog in retirement benefits for retirees of the Federal Government’s Ministries, Departments, and Agencies (MDAs) will soon be settled.
“The federal government recently disbursed N44 billion under the 2024 budget to settle approved pension rights.
“We are collaborating with the Federal Government to institutionalise a sustainable solution to ensure retirees receive their benefits promptly, eliminating delays,” Mrs Oloworaran said.
She said that PenCom’s technology-driven transformation aimed to make the CPS more accessible, reliable, and sustainable.
“From data management to seamless contributions and regulatory supervision, we are paving the way for a future where the pension industry serves all Nigerians effectively,” she said,
Mrs Oloworaran also said that the e-application portal for pension clearance certificates has replaced the manual processes and enhanced the ease of doing business in the sector.
“Since its deployment, 38,528 pension clearance certificates have been issued. This initiative ensures compliance and secures the future of Nigerians working in organisations that interact with the government,” she said.
Economy
NASD OTC Securities Exchange Closes Flat

By Adedapo Adesanya
The NASD Over-the-Counter (OTC) Securities Exchange closed flat on Thursday, December 12 after it ended the trading session with no single price gainer or loser.
As a result, the market capitalisation remained unchanged at N1.055 trillion as the NASD Unlisted Security Index (NSI) followed the same route, remaining at 3,012.50 points like the previous trading session.
However, the activity chart witnessed changes as the volume of securities traded at the bourse went down by 92.5 per cent to 447,905 units from the 5.9 million units transacted a day earlier.
In the same vein, the value of securities bought and sold by investors declined by 86.6 per cent to N3.02 million from the N22.5 million recorded in the preceding trading day.
But the number of deals carried out during the session remained unchanged at 21 deals, according to data obtained by Business Post.
When trading activities ended for the day, Geo-Fluids Plc remained the most active stock by volume (year-to-date) with 1.7 billion units sold for N3.9 billion, Okitipupa Plc came next with 752.2 million units valued at N7.8 billion, and Afriland Properties Plc was in third place with 297.5 million units worth N5.3 million.
Also, Aradel Holdings Plc remained the most active stock by value (year-to-date) with 108.7 million units worth N89.2 billion, followed by Okitipupa Plc with 752.2 million units valued at N7.8 billion, and Afriland Properties Plc with 297.5 million units sold for N5.3 billion.
-

 Feature/OPED5 years ago
Feature/OPED5 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism8 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz2 years ago
Showbiz2 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking6 years ago
Banking6 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy2 years ago
Economy2 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking2 years ago
Banking2 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports2 years ago
Sports2 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn
-

 Technology4 years ago
Technology4 years agoHow To Link Your MTN, Airtel, Glo, 9mobile Lines to NIN






















