Economy
Putin, Sassou-Nguesso Discuss COVID-19, Libya, Investment
By Kester Kenn Klomegah
Russian President Vladimir Putin announced Russia’s readiness to provide COVID-19 aid to the Republic of the Congo during his phone call with the Republic’s President Denis Sassou-Nguesso July 6.
“Vladimir Putin noted Russia’s readiness to provide aid to the Republic of the Congo to counter the coronavirus infection spread,” the Kremlin announced.
During the first week of July, Russia itself was battling more than half a million coronavirus cases, the fourth global spot after the United States, Brazil and India.
Republic of the Congo recorded 1557 coronavirus cases since the epidemic began, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). In addition, it reported 44 deaths and 501 recoveries.
Russia is very vociferous in tackling the political conflict in Libya. It has been mapping out possibilities of South Africa (as the chair of the African Union), Egypt being a close neighbouring state that could be involved in finding solution to Libyan crisis. Now Congo is the chair of the African Union’s High Level Committee on Libya.
“Considering the Congo’s presidency in the African Union’s High Level Committee on Libya, the sides exchanged opinions on the situation in the country. The sides underscored the necessity of peaceful resolution of the conflict through political dialogue involving all Libyan sides.”
The president of the Republic of the Congo congratulated Vladimir Putin on the outcome of the nationwide vote on the amendments to the Russian Constitution.
“The sides discussed the pressing issues of bilateral cooperation in the context of implementation of agreements, achieved during the highest-level talks in Moscow in May 2019,” the Kremlin said, adding that the two leaders agreed to continue their contacts.
Last year May 23, the business talks between Putin and Sassou-Nguesso took place in the Kremlin. According to the Kremlin report, the package of documents signed following the talks included intergovernmental agreements on cooperation in the peaceful use of nuclear energy and mass communications.
The documents also concern the settlement of the Republic of the Congo’s debt to the Russian Federation under previously issued loans, cooperation between the Russian Interior Ministry and the Congolese Ministry of the Interior and Decentralization, cooperation in agriculture, and sending Russian military experts to the Republic of the Congo.
In addition, documents on the relations between LUKOIL and the State Oil Company of the Republic of the Congo as well as between TMK (Pipe Metallurgical Company) and the National Petroleum Company of the Congo were signed.
The Pipe Metallurgical Company (TMK) is Russia’s leading pipe manufacturer. The project is to build a major oil pipeline, running more than 1,300 km from the port city of Pointe-Noire in the Republic of the Congo to the border with Cameroon.
Congo, with an estimated 5.3 million population, is located in the central-western part of sub-Saharan Africa, along the Equator. It has become the fourth largest oil producer in the Gulf of Guinea, providing the country with a degree of prosperity despite economic instability in some areas and unequal distribution of oil revenue nationwide.
The country has a large untapped mineral wealth, large untapped metal, gold, iron and phosphate deposits. In 2018, the Republic of the Congo joined the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries.
Economy
Champion Breweries Concludes Bullet Brand Portfolio Acquisition

By Aduragbemi Omiyale
The acquisition of the Bullet brand portfolio from Sun Mark has been completed by Champion Breweries Plc, a statement from the company confirms.
This marks a transformative milestone in the organisation’s strategic expansion into a diversified, pan-African beverage platform.
With this development, Champion Breweries now owns the Bullet brand assets, trademarks, formulations, and commercial rights globally through an asset carve-out structure.
The assets are held in a newly incorporated entity in the Netherlands, in which Champion Breweries holds a majority interest, while Vinar N.V., the majority shareholder of Sun Mark, retains a minority stake.
Bullet products are currently distributed in 14 African markets, positioning Champion Breweries to scale beyond Nigeria in the high-growth ready-to-drink (RTD) alcoholic and energy drink segments.
This expansion significantly broadens the brewer’s addressable market and strengthens its revenue base with an established, profitable portfolio that already enjoys strong brand recognition and consumer loyalty across multiple markets.
“The successful completion of our public equity raises, together with the formal close of the Bullet acquisition, marks a defining moment for Champion Breweries.
“The support we received from both existing shareholders and new investors reflects strong confidence in our long-term strategy to build a diversified, high-growth beverage platform with pan-African scale.
“Our focus now is on disciplined execution, integration, and delivering sustained value across markets,” the chairman of Champion Breweries, Mr Imo-Abasi Jacob, stated.
Through this transaction, Champion Breweries is expected to achieve enhanced foreign exchange earnings, expanded distribution leverage across African markets, integrated supply chain efficiencies, portfolio diversification into high‑growth consumer beverage categories, and strengthened presence in the RTD and energy drink segments.
The acquisition accelerates Champion Breweries’ transition from a regional brewing business to a multi-category consumer platform with continental reach.
Bullet Black is Nigeria’s leading ready-to-drink alcoholic beverage, while Bullet Blue has built a strong presence in the energy drink category across several African markets.
Economy
M-KOPA Nigeria Plans Expansion to Edo, Others After N231bn Credit Milestone

By Adedapo Adesanya
Emerging market fintech firm, M-KOPA, has announced plans to deepen its reach in Nigeria to the South South and South East regions, starting with Edo this year, after providing N231 billion in credit to over 1 million customers in the country.
The firm released its first Nigeria-focused Impact Report, which showed that Nigeria is M-KOPA’s fastest-growing market and fastest to reach the milestone.
Since its foray into the Nigerian market in 2019, M-KOPA has been working to dismantle barriers to financial inclusion by providing flexible smartphone financing and digital financial tools that align with how people in the informal economy earn and manage their money.
It operates in six states in the country, including Lagos, Ogun, and Oyo, among others.
The report highlights the company’s contribution to income generation, digital inclusion and economic opportunity for Every Day Earners across the country.
The report showed that M-KOPA has enabled 290,000 first-time smartphone users, while 56 per cent of agents accessed their first income opportunity through the platform.
It showed high income and livelihood gains among its users, with about 77 per cent of customers leveraging smartphones or digital loans obtained through the platform to generate income, indicating that access to financed devices is directly supporting micro-entrepreneurial activity and informal sector productivity.
Furthermore, 75 per cent of users report higher earnings since gaining access to M-KOPA’s services, suggesting measurable improvements in personal revenue streams. On the distribution side, 99 per cent of agents disclose increased earnings, reflecting positive spillover effects across the company’s value chain.
In addition, 81 per cent of long-term customers state that their household expenses have improved, pointing to enhanced financial stability and better consumption smoothing over time.
Speaking on the report, Mr Babajide Duroshola, General Manager, M-KOPA Nigeria, said, “Nigeria represents extraordinary potential, and we’re proud that it has become M-KOPA’s fastest-growing market. Our Impact Report shows that when Every Day Earners gain access to the right digital and financial tools, they use them to create stability and long-term progress for their families. This is about access that unlocks opportunity and sustained prosperity.”
On its expansion plans Nigeria-wide, the M-KOPA helmsman said, “Many of the states we are considering are already similar to the ones we are currently in proximity… So, there is proximity and similarity between these states, and that’s what we are going to do, starting with Edo.”
He noted that as M-KOPA Nigeria continues to expand, the focus remains on ensuring more everyday earners gain access to the digital and financial tools they need to build resilient, prosperous futures in Nigeria’s rapidly digitising economy.
Economy
Tinubu Okays Extension of Ban on Raw Shea Nut Export by One Year

By Aduragbemi Omiyale
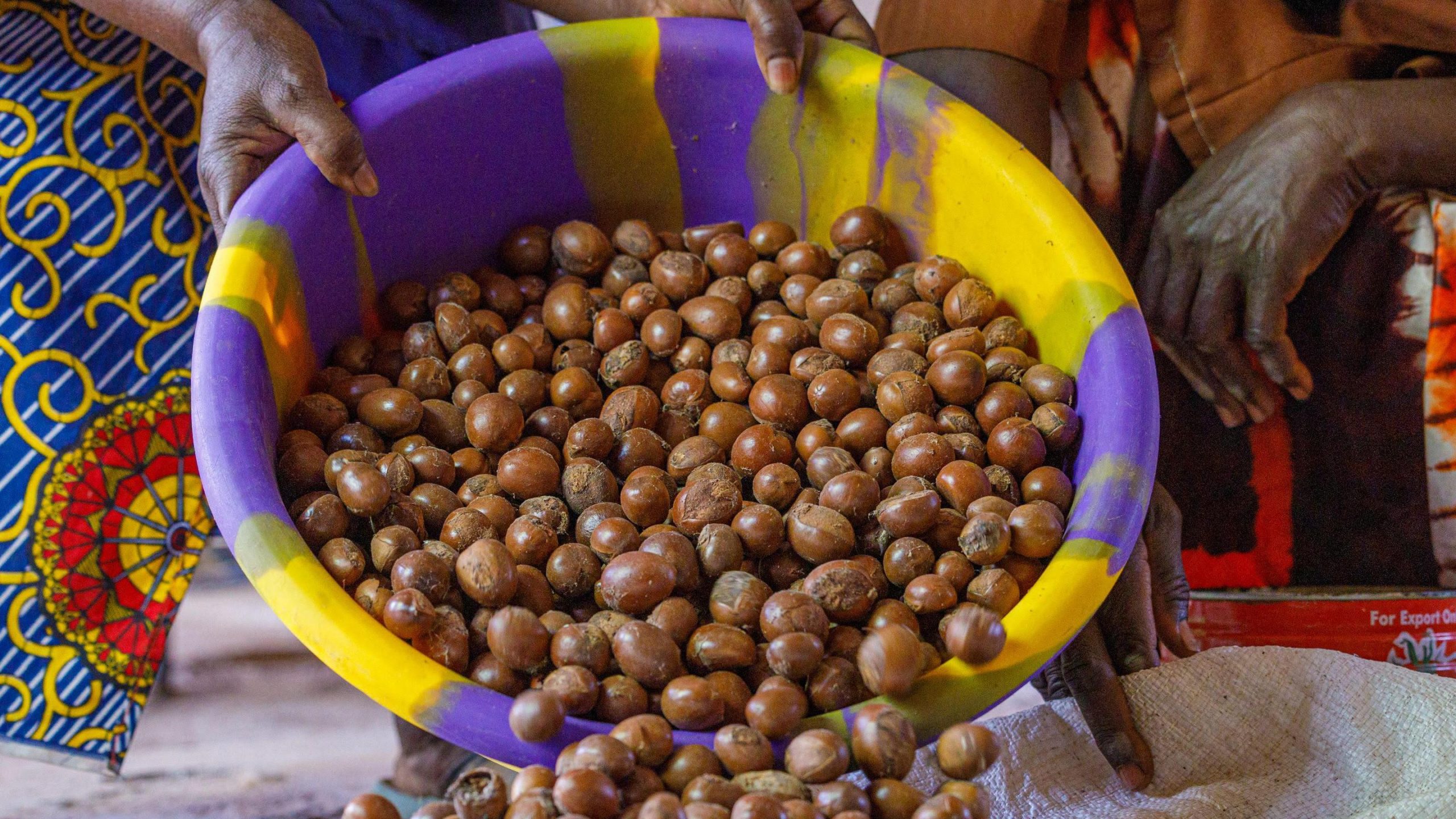
The ban on the export of raw shea nuts from Nigeria has been extended by one year by President Bola Tinubu.
A statement from the Special Adviser to the President on Information and Strategy, Mr Bayo Onanuga, on Wednesday disclosed that the ban is now till February 25, 2027.
It was emphasised that this decision underscores the administration’s commitment to advancing industrial development, strengthening domestic value addition, and supporting the objectives of the Renewed Hope Agenda.
The ban aims to deepen processing capacity within Nigeria, enhance livelihoods in shea-producing communities, and promote the growth of Nigerian exports anchored on value-added products, the statement noted.
To further these objectives, President Tinubu has authorised the two Ministers of the Federal Ministry of Industry, Trade and Investment, and the Presidential Food Security Coordination Unit (PFSCU), to coordinate the implementation of a unified, evidence-based national framework that aligns industrialisation, trade, and investment priorities across the shea nut value chain.
He also approved the adoption of an export framework established by the Nigerian Commodity Exchange (NCX) and the withdrawal of all waivers allowing the direct export of raw shea nuts.
The President directed that any excess supply of raw shea nuts should be exported exclusively through the NCX framework, in accordance with the approved guidelines.
Additionally, he directed the Federal Ministry of Finance to provide access to a dedicated NESS Support Window to enable the Federal Ministry of Industry, Trade and Investment to pilot a Livelihood Finance Mechanism to strengthen production and processing capacity.
Shea nuts, the oil-rich fruits from the shea tree common in the Savanna belt of Nigeria, are the raw material for shea butter, renowned for its moisturising, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. The extracted butter is a principal ingredient in cosmetics for skin and hair, as well as in edible cooking oil. The Federal Government encourages processing shea nuts into butter locally, as butter fetches between 10 and 20 times the price of the raw nuts.
The federal government said it remains committed to policies that promote inclusive growth, local manufacturing and position Nigeria as a competitive participant in global agricultural value chains.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn






















