World
Russia Shaping its Future Partnership with Africa
By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
The second Russia-Africa summit is planned to demonstrate Russia’s stance against Western hegemony and its capitalist domination across Africa, to show Russia’s “non-Western friends” and to further solicit enormous support for its war in Ukraine. On Africa’s side, leaders plan for their traditional deliberations on “no-cost delivery” of grains while the chosen special group of mediators continues to broker expected peace between Russia and Ukraine.
The St. Petersburg gathering is designed to determine the trajectory of Russia’s relations with African countries in the long term. The program includes more than 30-panel sessions and thematic events on the most important issues of interaction between Russia and African countries.
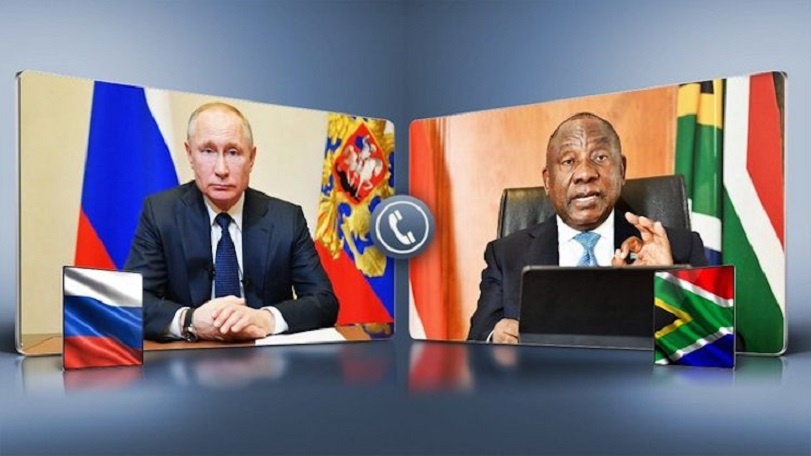
President Vladimir Putin and his South African counterpart Cyril Ramaphosa discussed during their phone conversation in mid-July about the African peace initiative on Ukraine. The African leaders on a Ukraine peace mission will again have an opportunity to talk with Russian President Vladimir Putin on the sidelines of the upcoming Russia-Africa summit in St. Petersburg, Kremlin Spokesman Dmitry Peskov told TASS News Agency.
Diplomatic sources earlier that the African leaders of the Ukraine peace mission from Egypt, Zambia, Comoros, Congo, Senegal, Uganda and South Africa expected to meet with the head of the Russian state before the opening of the Russia-Africa summit in St. Petersburg or during its work.
“The summit’s program is still being prepared. But there will surely be an opportunity to talk on the sidelines,” Peskov said, responding to a question about whether such a meeting was possible in St. Petersburg. As one of the sources told the news agency, the seven African leaders agreed to continue efforts and discuss proposals under the Ukraine peace mission.
A delegation of seven African countries that included the presidents of Zambia, Comoros, Senegal and South Africa, the Egyptian prime minister and representatives of the Republic of Congo and Uganda visited Kyiv on June 16, where it held talks with Ukrainian President Vladimir Zelensky.
Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov said in an interview with Lenta.ru daily that “the Russian Foreign Ministry is working on opening new embassies in a number of African countries.”
“Following the 1st Russia-Africa Summit in Sochi in 2019, the national leadership adopted decisions on expanding our diplomatic presence in Africa,” Lavrov said. “The Foreign Ministry is working to open new embassies in a number of African countries.”
On 12 July, Addis Ababa hosted a pre-summit roundtable; discussions focused on the prospects for the development of Russia-Africa economic and social partnership relations. “The Russia-Africa summit is an event that plays a key role in the development of relations between Russia and Africa. It is to achieve a whole new level of mutually beneficial partnership capable of meeting the challenges of the 21st century in the shortest possible time,” emphasized Evgeny Terekhin, Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary of Russia to Ethiopia.
The digitalization of Africa is attracting particular attention from Russians. We live in a digital world and undoubtedly, the future of civilization lies in the digital economy. For 20 years, digital transformation has been underway in all regions of Russia. Russia has the world’s best digital platforms for B2B, B2C, product labelling and educational services, and Moscow has become the best city in the world in terms of living comfort and digitalization of services offered, according to Igor Morozov, Chairman of the Coordinating Committee for Economic Cooperation with African Countries (AfroCom).
Senator Igor Morozov explained further that “the other cities in the top three are Toronto and Singapore. We certainly have a lot to share with our African partners, especially since they are already prepared for a new experience. The African Continental Free Trade Zone has started operating, and many African countries, including Ethiopia, are creating science and technology parks and IT clusters.”
As always, summit participants are arriving with foreign currency in their pockets or on their credit cards to St. Petersburg. It is a normal situation travelling African leaders with US dollars on their credit cards. Similarly, Russian officials exchange local rubles for foreign currency, for instance travelling to Miami leisure beach, Havana, Cuba or to their popular destination Dubai in the United Arab Emirates. Yet, Russians are the first partisan critics of de-dollarisation.
Everything now relates to colonialism, wraps up with neo-colonial clothes. Discourse on colonialism and neo-colonialism have become fashionable. Unsurprisingly, African migrants’ gruesome death at sea is also attributed to Europeans’ neo-colonialism. And no doubt, the movement of highly-skilled labour from Africa in search of employment opportunities on the global markets. In this case, African leaders primarily must share the blame for their utter failure to smoothly address development questions and to create better conditions at home.
Russia, like Africa, has also witnessed a ‘brain-drain’ these several years; most of its skilled specialists and professionals relocated to the United States, Canada and Europe. Understandably, more than three decades after the Soviet collapse, Russia has few well-trained multipolar-oriented specialists and professionals to work seriously on its diverse policy goals across Africa.
The Russian International Affairs Council, a non-government organisation and policy think-tank, published an opinion article authored by Kirill Babaev – Director of the Institute of Far Eastern Studies of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Professor at the Financial University. He made an excellent analysis of the relations between Russia and Africa.
The article highlighted future perspectives and successes in building political dialogues during the previous years. On the other hand, he was exposed for serious consideration by authorities to some existing obstacles and weaknesses.
Brain drain is seriously affecting Russia. Today the situation has changed radically, according to his assessment. Kirill Babaev pointed out the challenges Russia faces, one of them is “an immense lack of personnel for successful work in Africa” – and further suggested a necessity for putting together a distinctive group of experienced professionals and specialists to work on practical, consistent and effective policy challenges as well as geopolitical tasks with African countries.
In sharp contrast, during pre-summit roundtable discussions held this month, Oleg Ozerov, Head of the Secretariat of the Russia-Africa Partnership Forum, argued that Russia takes an interest in highly skilled specialists from Africa, but has no intention of encouraging any kind of “brain drain” like the West does by attracting and employing them in the United States.
“In other words, it is another form of neocolonialism, or the exploitation of Africa that has been carried out throughout centuries through the slave trade and the pumping of resources, and now it has evolved into ‘brain drain,'” Oleg Ozerov added. “In other words, those people who should boost Africa, transforming it into a new pole of growth. We are convinced that Africa has a vast future and potential, first and foremost, huge human potential in the continent.”
Reports from the World Bank indicated that the United States has the largest African diaspora, which has close-knitted business, educational and cultural links with African countries. This helps to support official efforts in promoting relations with Africa.
The US-Africa trade and commercial relations and engagement through the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) yields $78.01 billion per year, while, for instance, monetary remittances inflows to sub-Saharan Africa soared 14.1 per cent to $49 billion in 2021. Is that compared to Russia and China?
Beyond remittances, Africa benefits from the input of its diaspora considered very progressive. Ultimately, African leaders consistently engage with their diaspora, those excelling in sports, academia, business, science, technology, engineering and all those other significant sectors that the continent needs to optimise its potential and meet development priorities.
During the second week of July, St. Petersburg hosted Reversed Safari exhibit of contemporary African art, featuring works by 47 African and 14 Russian artists opened to the general public. There were over 300 pieces of art on display, including paintings, sculptures, photographs, and video footage, as well as three large-scale installations created specifically for the event. All exhibit items are devoted to the legacy of the colonial era, how different cultures interact, daily life and the search for identity.
According to Professor Gerrit Olivier, an emeritus professor at Pretoria University and former South African Ambassador to the Russian Federation and Kazakhstan, within the context of the current global changes of the 21st century, Russia is experiencing isolation, but African leaders would visit Moscow to meet Vladimir Putin. Today, Russia’s influence in Africa, despite efforts towards resuscitation, remains marginal. While, given its global status, Russia ought to be active with concrete development projects in Africa as Western Europe, the European Union, America, and China are, it is all but absent, playing a negligible role in Africa.
“These African leaders will realise that there will be no quid pro quo in Moscow, that a weakened Putin can offer nothing and his purpose with this meeting will mainly be to demonstrate support from Africa. This will probably be forthcoming in the form of a repeated ‘non-aligned’ posture (the African warped interpretation, that is), and those leaders presently under the protection of Wagner would no doubt insist on continuation. All this, no doubt, will be used as a propaganda piece against the West!”
Professor David Shinn, a former top U.S. diplomat and now an Adjunct Professor of International Affairs at George Washington University’s Elliot School of International Affairs, discusses a few significant points here relating to the forthcoming summit.
This is an interesting time for Russia to host the Africa summit. The emerging multipolar world, especially Russia’s partnership with China, briefly put Vladimir Putin in a stronger position in Africa vis-à-vis the West. Most African leaders seem to favour the multipolar order. Putin’s invasion of Ukraine significantly disrupted that positive trend for Russia. Just over half of Africa’s governments oppose or are skeptical of Moscow’s engagement in Ukraine while just under half were willing to express a neutral position and Eritrea to express support.
“The mutiny by the Wagner Group has further complicated Russia’s position in Africa and raises serious questions about the strength of its partnership with China. While a small number of autocratic African leaders beholden to the Wagner Group (and Eritrea) remain for the time being firm with Russia, I suspect the mutiny has raised second thoughts with other African leaders who were neutral and strengthened the concerns of those leaders who opposed or were sceptical of the invasion from the beginning,” Professor Shinn wrote further in his email.
According to the academic professor, Vladimir Putin would want to go forward with the Africa summit this month to “prove” to the world that the situation in Russia is back to normal. “But I wonder how enthusiastic most African leaders will be to participate at this time when the future of the Wagner Group in Africa is in doubt, Russia is doing poorly in Ukraine, and Moscow is less able to offer Africa much of tangible value. African attendance at the summit and the substance of the results will be most telling,” Professor Shinn concluded.
Dr Alex Vines, Africa Program Director at Chatham House, a policy think tank, told this author that “the Lavrov visits to Africa this year and Russian diplomacy has been focused at getting African leadership to attend the St Petersburg summit. The number of leaders attending is important for Moscow to show it’s not isolated and Africans still wish to engage with Russia diplomatically.”
Notwithstanding those several initiatives of engaging in the economic sectors and supporting Africa, Russia has its strengths and weaknesses based on history, but the balance is positive in this new world. Whatever African leaders wanted depended on their rational and calculated basis and on their ability to build up multifaceted development-oriented relations with Russia.
At the end of the summit, there would a joint declaration, pre-summit media reports indicated. Several other documents and agreements including those on cooperation in space, anti-terrorist activity and security, as well as economic and humanitarian cooperation. The second Russia-Africa summit and the Economic and Humanitarian Forum will be held in St. Petersburg at the ExpoForum Convention and Exhibition Centre on 27–28 July 2023.
World
Moscow: World-Renowned Fashionable City

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
Moscow is increasingly becoming popular among foreigners due to multiple reasons among them is its fashionable architecture and friendly people. Moscow’s architecture is world-renowned. In addition, Moscow’s status as the spiritual center of Russian orthodoxy and metropolitan buildings attract tourists from around the world. For much of its architectural history, Moscow is dominated by Orthodox churches.
Situated on the banks of the popular Moskva river, cultural parks and recreational centers offer an additional attraction especially during spring, summer and autumn seasons. The city has a population estimated at over 13 million. And public transport system is excellent for easy and fast connection to any part of the city. Today, the Moscow Metro comprises twelve lines, mostly underground with a total of 203 stations.
Moscow mayor Sergei Sobyanin shares in an interview with local Russian media that Moscow is becoming the world’s best megacity. But for South African Fashion entrepreneur, Stephen Manzini, Moscow’s contrasting features make it more fashionable to explore for fun and entertainment. Read Stephen Manzini’s impressions here:
Would you describe Moscow as a ‘fashionable’ city, if fashion is not limited to clothes and bags?
Moscow can be described as a fashionable city if it wasn’t for the weather. We would see beautiful display of runway pieces on the streets, however we do see this in indoor spaces it’s just overshadowed outdoors by the winter coats and jackets. Walking about Moscow does give you a European fashion appeal.
But Moscow as a fashionable city, do you think it is inaccessible from consumers, from tourists?
Moscow the fashionable city can be accessible to consumers. However when it comes to tourists, it’s a bit inaccessible as it takes on-site education to understand the dynamics. It cannot be understood from a distance due to the neo-propaganda that overshadows it.
Do you mean to conclude that cities such Venice, Miami, New York and London are more fashionable and attract more customers, tourists than Moscow?
Moscow’s tourism industry is barely in existence. To no fault of it’s own. Unfortunately, global online search engines are very unkind in referring to it as an undesirable tourist destination.
How then would you suggest rebranding Moscow?
The rebranding of Moscow would have to be intentional and would not happen overnight. It will have to start at a political level and then cascade it’s way to media and tourism.
World
Shockwaves Over Trump’s Tariffs Reverberate Across Africa

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
After taking office early 2025, U.S. President Donald Trump has embarked on rewriting American foreign policy and plans to create a new geopolitical history under the “America First” doctrine.
The first three months have seen efforts to implement tariffs, which finally was splashed early April world-wide, including on a grand scale across Africa.
Seemingly, a blanket of tariffs is one of the standout actions of the new administration. Trump’s changing approach to the world, using geoeconomic tools, including tariffs has now sparked extensive debates and discussions.
Our media chief, Kestér Kenn Klomegâh, took a quick chance and asked Vsevolod Sviridov, deputy director at the High School of Economics (HSE) University Center for African Studies, a few questions pertaining to the aspects and implications of the U.S. tariffs for Africa. Here are the interview excerpts:
How would you interpret trade war between China and the United States?
There has been a global trend towards overspending over the last two decades. We have seen commodity boom, rise of China with its global investments drive and infrastructure development projects like BRI, excessive budget spending by the OECD countries during COVID-19, etc. Now countries are trying to optimize their spending. Considering that there is a certain trend towards deglobalization, external trade and deficits are the first to fall victims to this policy. While China almost halved its lending, US are trying to cut their ODA (see South Africa’s case) and adjust their trade deficit, which is fuelling their vast debt.
What could be the reasons for Donald Trump to extend that kind of economic policy, trade tariffs, to Africa?
His latest actions indicated that was possible. Trump has imposed increased tariffs on 14 African countries, including South Africa (30%), Madagascar (47%), Tunisia (28%), Côte d’Ivoire (21%), and others. The primary selection criterion was the trade deficit with the U.S., though there are exceptions, such as Libya, which was left off the list despite a US$1 billion deficit. Additionally, seven more countries, including Egypt, Morocco, and Kenya, will face a base tariff of 10%, meaning that for Washington stable relations with them are more important.
The hardest-hit country will be Lesotho (50%), where the textile industry, heavily reliant on the U.S. market, will suffer. However, South Africa will bear the greatest overall impact, as it accounts for 70% of the U.S.-Africa trade deficit. In addition to the 30% base tariff, there will be an extra 25% duty on imported cars. This will affect factories operated by VW, Toyota, BMW, and other automakers, whose exports to the U.S. total US$2-3 billion annually. Angola, which had backed the Democratic Party, is also facing penalties (32%).
If these tariffs take effect as announced, they could lead to the collapse of African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA). However, the U.S. has not needed AGOA as much since the 2010s when it reduced dependence on African oil and gas. AGOA is set to expire in September 2025, and Trump’s actions make its renewal highly unlikely.
Trump has suggested that affected countries relocate production to the U.S., but this is difficult for African nations that mainly export raw materials. The new tariff preference system is expected to consider political and economic factors, making it less predictable and less favourable for African suppliers. On the other hand, this shift could encourage African countries to focus on regional markets and develop industries tailored to their domestic economies.
It could be excellent, from academic perspectives, to evaluate and assess the impact of AGOA in relation to Africa?
For Africa, the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) meant establishment of several mainly export-oriented industries, like textile or car manufacturing. For instance, almost 2/3 of cars manufactured in RSA are being exported to US and Europe, with only 1/3 being sold on the local market and tiny part exported to other African countries (20k out of 600k prod).
They created employment opportunities for locals but never contributed to local markets and industries development, technology and knowledge sharing. Collapse of AGOA would mean additional opportunities for African industries and producers to target local and regional markets and develop industrialization strategies considering their national interests first (like Trump does).
Assessing the reactions over the tariffs world-wide, and talking about the future U.S.-Africa trade, and the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), what next for Africa?
The African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) gives Africa a chance to embark on the hard and long journey of developing intraregional trade. Still this emerging market could be easily used by non-African suppliers as a tool to expand their presence, given that without protection nascent African industries are hardly able to compete in price and from time to time in quality. Especially now, when we are clearly seeing that the US are more interested in selling then buying. So any external aid and knowledge sharing assistance in this sphere should be received with caution.
World
Trump’s Tariffs Will Affect Global Trade—Okonjo-Iweala

By Adedapo Adesanya
The Director-General of the World Trade Organisation (WTO), Mrs Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala, has said the recent tariffs announced by the United States would have substantial implications for global trade and economic growth prospects.
Mrs Okonjo-Iweala said this in a statement in reaction to recent tariffs imposed on goods from other countries by US President Donald Trump.
The WTO DG added that the organisation was closely monitoring and analysing the measures announced by the United States on April 2, 2025.
She noted that many members have reached out to the WTO and the organization is actively engaging with them in response to their questions about the potential impact on their economies and the global trading system.
“While the situation is rapidly evolving, our initial estimates suggest that these measures, coupled with those introduced since the beginning of the year, could lead to an overall contraction of around 1 per cent in global merchandise trade volumes this year, representing a downward revision of nearly four percentage points from previous projections.
“I’m deeply concerned about this decline and the potential for escalation into a tariff war with a cycle of retaliatory measures that lead to further declines in trade,” the WTO DG stated.
She, however, noted that despite the emerging tariffs war, the vast majority of global trade is still being conducted under the WTO’s Most-Favored-Nation (MFN) terms.
“Our estimates now indicate that this share currently stands at 74 per cent, down from around 80% at the beginning of the year. WTO members must stand together to safeguard these gains,” the former Nigeria’s Finance Minister said.
Nevertheless, Mrs Okonja- Iweala urged caution while advising members to utilise the platform of WTO to prevent the tariff war from escalating.
“Trade measures of this magnitude have the potential to create significant trade diversion effects. I call on Members to manage the resulting pressures responsibly to prevent trade tensions from proliferating.
“The WTO was established to serve precisely in moments like this — as a platform for dialogue, to prevent trade conflicts from escalating, and to support an open and predictable trading environment. I encourage Members to utilize this forum to engage constructively and seek cooperative solutions,” she remarked.
-

 Feature/OPED5 years ago
Feature/OPED5 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism9 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz2 years ago
Showbiz2 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking7 years ago
Banking7 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy2 years ago
Economy2 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking2 years ago
Banking2 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports2 years ago
Sports2 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn
-

 Technology4 years ago
Technology4 years agoHow To Link Your MTN, Airtel, Glo, 9mobile Lines to NIN























