Economy
Russia-Ukraine Conflict Changing African Business with Europe
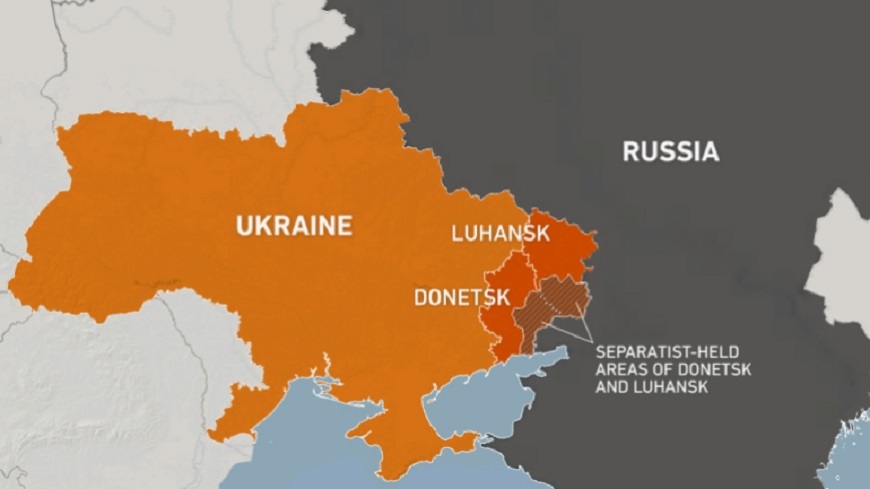
By Kester Kenn Klomegah
Russia has evaded neighbouring Ukraine located in Eastern Europe. As one of the former Soviet republics looking to climb onto the global stage and steadfastly develop the future, it, therefore, sets ambition to join the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) and the European Union (EU).
On the other hand, these two directions of its ambitions have angered Russia. As already known, Ukraine is in Eastern Europe and shares a border with Russia. It used to be part of the Soviet Union but became an independent country in 1991.
Under the directorship of Russian President Vladimir Putin, and approved by the both Federal Council and the State Duma, the Russian collective made the decision to hold a special military operation in response to the address of leaders of Donbass and Luhansk republics, both in eastern Ukraine.
Putin launched the “special military operation” repeating a number of unfounded claims, alleging that Ukraine’s democratically elected government had been responsible for eight years of genocide.
Putin feverishly seeks to demilitarize and denazify Ukraine. As a result of the waging war on Ukraine, Russia has to suffer from a raft of sanctions imposed by various foreign countries including the United States, Canada, Britain, the European Union and down to Australia. The results of the waging war on Ukraine.
The longer-term economic consequences for the rest of the world will be far less severe than they are for Russia, but they will still be a persistent challenge for policymakers, noted Jason Furman, a former chair of U.S. President Barack Obama’s Council of Economic Advisers.
He wrote in his opinion article published by Project Syndicate: “The medium- and long-term consequences for the global economy of Russia’s military operation in Ukraine will depend on choices. By launching the operation, Russia has already made one terrible choice.”
While the sanctions take their bites and associated snow-balling effects, it has opened huge significant potential opportunities for a number of African countries. In the first place, researchers at Oxford Economics Africa believe that Russia’s invasion of Ukraine could increase wheat prices in Angola and Mozambique, but the rise in oil and gas prices benefits the finances of these two African countries.
“Both Angola and Mozambique have a very limited level of trade with Russia and Ukraine; Angola imports wheat and yeast from Russia, while Mozambique imports a significant amount of wheat and a small amount of refined oil from Russia,” Oxford Economics Africa analyst who follows these two African economies told Mozambique News Agency.
“It appears that, at least for now, Angola is generally benefiting from higher oil and gas prices, which are partially driven by the conflict,” Gerrit van Rooyen said in remarks from Paarl, South Africa. Higher oil prices are positive for government revenues,” the analyst added. If the rise is sustained, “this could increase investment in Angola and lower debt levels faster than previously anticipated.”
“If gas prices remain high due to the conflict, this will be positive for investments in Mozambique’s liquefied natural gas [LNG],” his analysis continues, since “the profits from the natural gas in the Rovuma basin could be greater than the risk of armed extremist insurgency in the region.”
Despite the benefits for the public accounts of the two Portuguese-speaking states, van Rooyen points out that, for the average citizen, the disadvantages outweigh the advantages. Higher oil and wheat prices could be bad news for consumers, as inflation, which is already high in these countries, particularly in Angola and it is, however, expected to increase more than initially expected.
Monitoring media reports have indicated that a few oil and gas producing African countries have the possibility, if well-exploited, to supply Europe. For example, Algeria’s state energy firm is ready to supply Europe with more gas in view of a possible decline due to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
Sonatrach CEO Toufik Hakkar said the firm was ready to pump additional gas to the EU from its surplus via the Transmed pipeline linking Algeria to Italy. Sonatrach is “a reliable gas supplier for the European market and is willing to support its long-term partners in the event of difficult situations,” Hakkar said and was reported by the daily Liberte.
Hakkar nonetheless said this would be contingent on the availability of a surplus of gas or liquified natural gas [LNG], but have to fix its “contractual engagements” with the importing partner for the supplies to the European market.
Nonetheless, Algeria could only compensate for the decline in Russian gas supply by offering a maximum of two or three million additional cubic meters. Algeria plans to develop new reserves of shale gas. In January, Sonatrach said it would invest US$40 billion into oil exploration, production and refinement, as well as gas prospecting and extraction, between 2022 and 2026.
Arguments whether Africans can take advantage to increase their business, especially in oil and gas, are still varied. “For Africa, it’s again, it’s an opportunity, it presents that window of opportunity for African countries to see how they can increase their production capacity and meet the need of global demands of crude oil,” says Isaac Botti, a public finance expert told Voice of America.
However, Africa’s production combined accounts for less than a tenth of total global output. Nigeria is Africa’s largest producer of oil followed by Libya. Other notable producers are Algeria and Angola.
Algerian state-owned oil and gas giant said it would supply Europe if Russian exports dwindled as a result of the crisis, Botti noted and added that it’s a good example for other African nations. “We need to develop our capacity to produce locally, we need to look at various trade agreements that are existing,” he said.
For years African oil producers including Nigeria have been struggling to meet required daily output levels. Many experts, including Botti, worry strongly that African producers may struggle to fit into the big market with increasing global demands for crude oil.
Instead of African business to the United States and Europe, some researchers and experts have shown concern about the level of impact of the Russia-Ukraine conflict on Africa. Admittedly, they noted in their separate discussions that the war in Ukraine could further push oil prices up and increase inflation in Africa.
From an African agriculture perspective, the impact of the war will be felt in the near term through the global agriculture commodity prices channel. A rise in prices will be beneficial for farmers, especially for grain and oilseed farmers, the surge in prices presents an opportunity for financial gains.
In his research analysis, Wandile Sihlobo, Senior Fellow at the Department of Agricultural Economics, Stellenbosch University, wrote that some countries on the continent, such as South Africa, benefit from exporting fruit to Russia. In 2020 Russia accounted for 7% of South Africa’s citrus exports in value terms. And it accounted for 12% of South Africa’s apples and pears exports in the same year – the countries’ second-largest market.
But from Africa’s perspective, Russia and Ukraine’s agricultural imports from the continent are marginal – averaging only US$1,6 billion – in the past three years. The dominant products are fruits, tobacco, coffee, and beverages in both countries. Every agricultural role-player is keeping an eye on the developments in the Black Sea region. The impact will be felt in other regions, such as the Middle East and Asia, which also import a substantial volume of grains and oilseeds from Ukraine and Russia. They too will be directly affected by the disruption in trade, according to Sihlobo.
There is still a lot that’s not known about the geopolitical challenges that lie ahead. But for African countries, there are reasons to be worried given their dependency on grains imports. In the near term, countries are likely to see the impact through a surge in prices, rather than an actual shortage of the commodities. Other wheat exporting countries such as Canada, Australia and the US stand to benefit from any potential near term surge in demand.
“The last time we had a windfall from oil prices related to war was in 1991, during the Gulf War. We know it will directly impact the price of crude oil. The revenue may increase, but since we have shifted oil investment to multinational companies, they are more likely to reap greater revenues than the country itself.” Professor Abdul-Ganiyu Garba of the Department of Economics Ahmadu Bello University Zaria said.
“If there is an increase in crude oil prices, it means inflation will grow globally, the cost of most of our imports will also rise, which will transfer to the domestic crisis,” the Nigerian economist added. Commodity prices have skyrocketed in many African countries, making life more challenging for millions of people.
“People start starving once these countries fight because they [global powers] presented themselves to African countries as mother countries,” Dox Deezol, a South African entrepreneur and artist in Johannesburg, told DW.
As a member of BRICS [Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa] — the world’s five emerging economies — South Africa was relatively silent when Russia annexed Crimea in 2014. However, the South African government has urged restraint this time.
“South Africa is integrated into the global economy. So the war’s impact on the global economy, as we have seen in the soaring prices of oil and energy generally, will affect South Africa because when the world sneezes, South Africa catches a cold,” Professor Siphamandla Zondi, an international relations expert and head of BRICS studies at the University of Johannesburg, told DW.
It’s not just the oil prices that could impact Africa. For example, there is significant agricultural trade between African countries and Russia and Ukraine. Some say Africa’s trade with Russia and Ukraine could also be at stake. In 2020, African countries imported agricultural products worth US$4 billion from Russia. Wheat accounted for approximately 90% of these imports. Egypt was the largest importer, followed by Sudan, Nigeria, Tanzania, Algeria, Kenya, and South Africa.
Similarly, Ukraine exported agricultural products worth US$2.9 billion to Africa in 2020. Wheat accounted for roughly 48% of this, maize 31%, and sunflower oil, barley, and soybeans accounted for the remainder. The ongoing war could affect supply chains and raise the cost of imports. It is also unclear what effect the sanctions imposed by the US and its allies on Russia will have on Africa-Russia trade relations.
The repercussions of the conflict are readily felt in other economic sectors. Media reports indicated tourism and aviation business are also negatively affected. In terms of education and training, many African governments, ministries and departments struggle to evacuate their students and nationals from war-torn Ukraine. From basic research for this article, Ukraine has emerged as a choice destination for African students, especially in the fields of medicine and engineering.
According to Ukraine’s Ministry of Education and Science, some 180,000 international students study in Ukraine with the largest number from India, followed by Morocco, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Egypt, Nigeria, South Africa, Tanzania, Zimbabwe and Ghana. The fact is that Africa remains deeply concerned over the escalation of the conflict in Ukraine. Nearly all African foreign ministries have expressed their deepest displeasure over the violation of the territorial integrity of Ukraine and categorically blamed Russia for creating instability in the world.
While looking the future African business to the United States, Europe and Asia, the current Chair of the African Union and President of Senegal, Macky Sall, and the Chairperson of the African Union Commission, Moussa Faki Mahamat, have expressed their extreme concern at the dangerous situation created in Ukraine. They called on the Russian Federation and any other regional or international actor to respect international law, the territorial integrity and the national sovereignty of Ukraine.
The Chair of the African Union and the Chairperson of the African Union Commission urged Russia and Ukraine to establish an immediate ceasefire and to open political negotiations without much delay. It should be under the auspices of the United Nations, in order to preserve the world from the consequences of planetary conflict, and in the interests of peace and stability in international relations in service of all the peoples of the world. Some tough actions are still expected from the Security Council of the United Nations.
Economy
Champion Breweries Concludes Bullet Brand Portfolio Acquisition

By Aduragbemi Omiyale
The acquisition of the Bullet brand portfolio from Sun Mark has been completed by Champion Breweries Plc, a statement from the company confirms.
This marks a transformative milestone in the organisation’s strategic expansion into a diversified, pan-African beverage platform.
With this development, Champion Breweries now owns the Bullet brand assets, trademarks, formulations, and commercial rights globally through an asset carve-out structure.
The assets are held in a newly incorporated entity in the Netherlands, in which Champion Breweries holds a majority interest, while Vinar N.V., the majority shareholder of Sun Mark, retains a minority stake.
Bullet products are currently distributed in 14 African markets, positioning Champion Breweries to scale beyond Nigeria in the high-growth ready-to-drink (RTD) alcoholic and energy drink segments.
This expansion significantly broadens the brewer’s addressable market and strengthens its revenue base with an established, profitable portfolio that already enjoys strong brand recognition and consumer loyalty across multiple markets.
“The successful completion of our public equity raises, together with the formal close of the Bullet acquisition, marks a defining moment for Champion Breweries.
“The support we received from both existing shareholders and new investors reflects strong confidence in our long-term strategy to build a diversified, high-growth beverage platform with pan-African scale.
“Our focus now is on disciplined execution, integration, and delivering sustained value across markets,” the chairman of Champion Breweries, Mr Imo-Abasi Jacob, stated.
Through this transaction, Champion Breweries is expected to achieve enhanced foreign exchange earnings, expanded distribution leverage across African markets, integrated supply chain efficiencies, portfolio diversification into high‑growth consumer beverage categories, and strengthened presence in the RTD and energy drink segments.
The acquisition accelerates Champion Breweries’ transition from a regional brewing business to a multi-category consumer platform with continental reach.
Bullet Black is Nigeria’s leading ready-to-drink alcoholic beverage, while Bullet Blue has built a strong presence in the energy drink category across several African markets.
Economy
M-KOPA Nigeria Plans Expansion to Edo, Others After N231bn Credit Milestone

By Adedapo Adesanya
Emerging market fintech firm, M-KOPA, has announced plans to deepen its reach in Nigeria to the South South and South East regions, starting with Edo this year, after providing N231 billion in credit to over 1 million customers in the country.
The firm released its first Nigeria-focused Impact Report, which showed that Nigeria is M-KOPA’s fastest-growing market and fastest to reach the milestone.
Since its foray into the Nigerian market in 2019, M-KOPA has been working to dismantle barriers to financial inclusion by providing flexible smartphone financing and digital financial tools that align with how people in the informal economy earn and manage their money.
It operates in six states in the country, including Lagos, Ogun, and Oyo, among others.
The report highlights the company’s contribution to income generation, digital inclusion and economic opportunity for Every Day Earners across the country.
The report showed that M-KOPA has enabled 290,000 first-time smartphone users, while 56 per cent of agents accessed their first income opportunity through the platform.
It showed high income and livelihood gains among its users, with about 77 per cent of customers leveraging smartphones or digital loans obtained through the platform to generate income, indicating that access to financed devices is directly supporting micro-entrepreneurial activity and informal sector productivity.
Furthermore, 75 per cent of users report higher earnings since gaining access to M-KOPA’s services, suggesting measurable improvements in personal revenue streams. On the distribution side, 99 per cent of agents disclose increased earnings, reflecting positive spillover effects across the company’s value chain.
In addition, 81 per cent of long-term customers state that their household expenses have improved, pointing to enhanced financial stability and better consumption smoothing over time.
Speaking on the report, Mr Babajide Duroshola, General Manager, M-KOPA Nigeria, said, “Nigeria represents extraordinary potential, and we’re proud that it has become M-KOPA’s fastest-growing market. Our Impact Report shows that when Every Day Earners gain access to the right digital and financial tools, they use them to create stability and long-term progress for their families. This is about access that unlocks opportunity and sustained prosperity.”
On its expansion plans Nigeria-wide, the M-KOPA helmsman said, “Many of the states we are considering are already similar to the ones we are currently in proximity… So, there is proximity and similarity between these states, and that’s what we are going to do, starting with Edo.”
He noted that as M-KOPA Nigeria continues to expand, the focus remains on ensuring more everyday earners gain access to the digital and financial tools they need to build resilient, prosperous futures in Nigeria’s rapidly digitising economy.
Economy
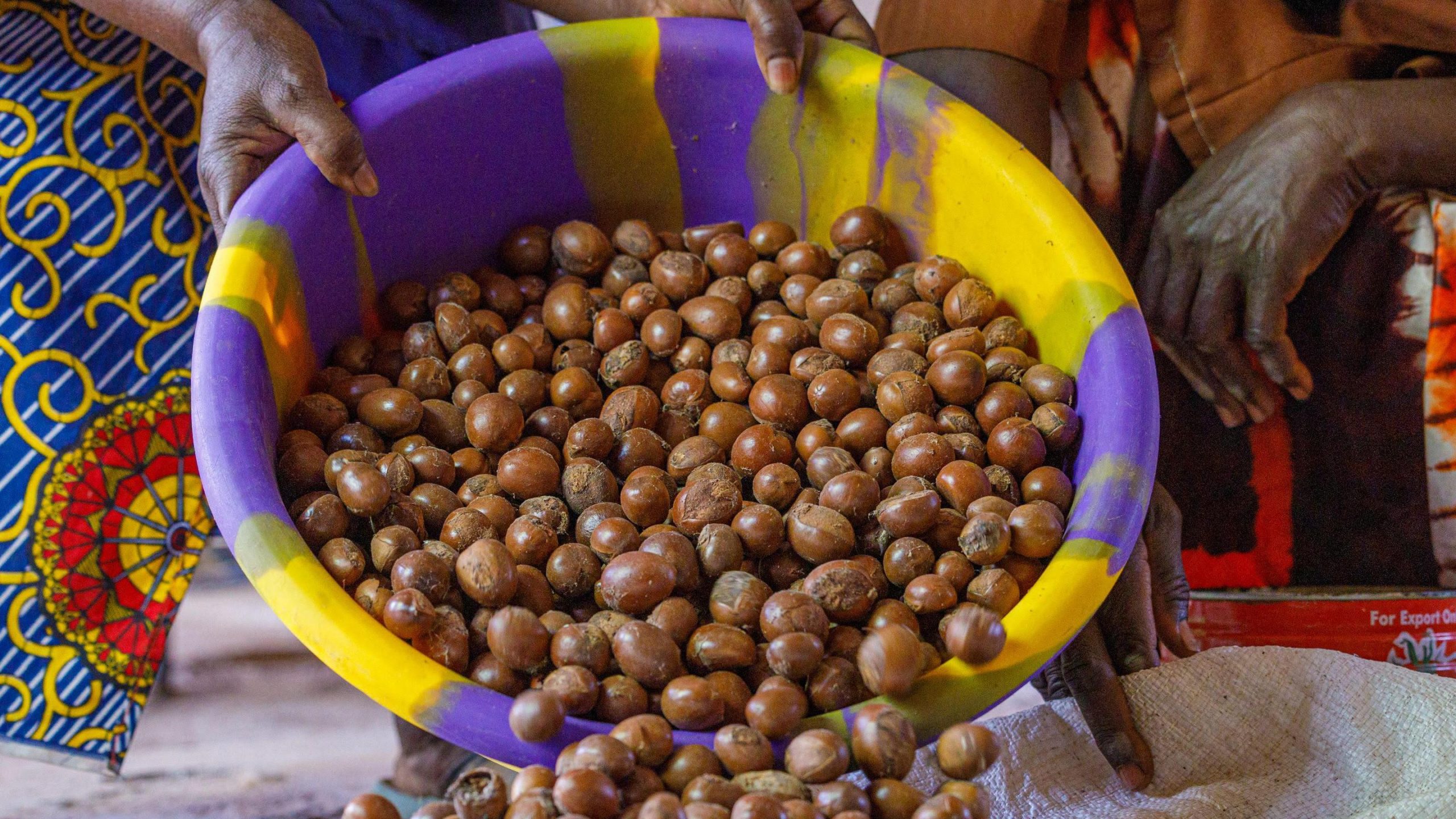
Tinubu Okays Extension of Ban on Raw Shea Nut Export by One Year

By Aduragbemi Omiyale
The ban on the export of raw shea nuts from Nigeria has been extended by one year by President Bola Tinubu.
A statement from the Special Adviser to the President on Information and Strategy, Mr Bayo Onanuga, on Wednesday disclosed that the ban is now till February 25, 2027.
It was emphasised that this decision underscores the administration’s commitment to advancing industrial development, strengthening domestic value addition, and supporting the objectives of the Renewed Hope Agenda.
The ban aims to deepen processing capacity within Nigeria, enhance livelihoods in shea-producing communities, and promote the growth of Nigerian exports anchored on value-added products, the statement noted.
To further these objectives, President Tinubu has authorised the two Ministers of the Federal Ministry of Industry, Trade and Investment, and the Presidential Food Security Coordination Unit (PFSCU), to coordinate the implementation of a unified, evidence-based national framework that aligns industrialisation, trade, and investment priorities across the shea nut value chain.
He also approved the adoption of an export framework established by the Nigerian Commodity Exchange (NCX) and the withdrawal of all waivers allowing the direct export of raw shea nuts.
The President directed that any excess supply of raw shea nuts should be exported exclusively through the NCX framework, in accordance with the approved guidelines.
Additionally, he directed the Federal Ministry of Finance to provide access to a dedicated NESS Support Window to enable the Federal Ministry of Industry, Trade and Investment to pilot a Livelihood Finance Mechanism to strengthen production and processing capacity.
Shea nuts, the oil-rich fruits from the shea tree common in the Savanna belt of Nigeria, are the raw material for shea butter, renowned for its moisturising, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. The extracted butter is a principal ingredient in cosmetics for skin and hair, as well as in edible cooking oil. The Federal Government encourages processing shea nuts into butter locally, as butter fetches between 10 and 20 times the price of the raw nuts.
The federal government said it remains committed to policies that promote inclusive growth, local manufacturing and position Nigeria as a competitive participant in global agricultural value chains.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn

















