Feature/OPED
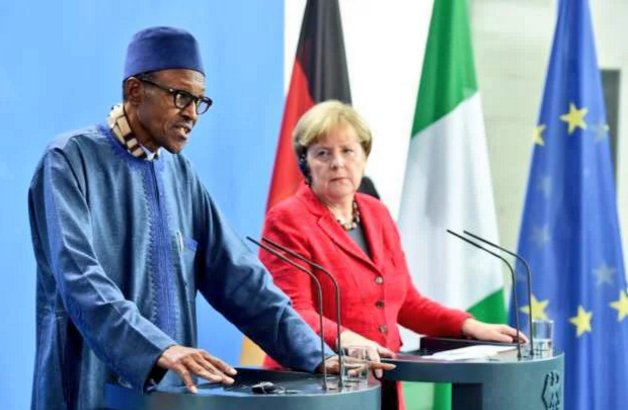
10 Takeaways From President Buhari’s Visit To Germany


By Garba Shehu
President Muhammadu Buhari returned to the country after a three-day intensely busy State Visit to Germany which, as is usual with his foreign engagements, was characterized by punishing schedules.
Unfortunately, an important trip such as this one planned to boost trade and investment, enhance security partnership and pitch the country to eager investors became overshadowed by public outcry over some remarks President Muhammadu Buhari made in Germany, which have sadly been misconstrued by the media and some members of the public.
I can assure you that President Buhari’s sense of humour is one of his most distinguishing characteristics, despite his stern mien.
His comments clearly do not reflect his attitude towards women, a number of whom he has appointed into key positions in his administration, neither do they reflect his attitude towards his wife, Hajiya Aisha, as anyone can see from their history together.
President Buhari has been an invaluable support to his wife, and I know that he has great plans for every Nigerian woman.
Five of his daughters have acquired university degrees. One of them just finished law school and another one undertakes a higher degree program.
I hope that all well-meaning Nigerians will put an end to the unfair insinuations that have been generated by President Buhari’s jocularity. Seeing a well-meaning leader being so misunderstood is painful for me.
Let us hope that God continues to give him the grace and wisdom he requires to steer Nigeria through this difficult time in our country’s history.
In the course of this historic visit, he held formal talks with Chancellor Angela Merkel, a roundtable with the German President Joachim Gauck, a meeting with business leaders and an interactive session with Nigerians resident in Europe. A number of side, but equally important meetings were dotted in-between these.
Three big-ticket items on President Buhari’s Berlin agenda were security, trade and investment, climate change and its consequences for the Nigerian eco-space. A breakthrough was achieved in all areas covered by the discussions.
Bilateral relations:
Chancellor Merkel was the first leader of a major economic power in the world to have foreseen what a Muhammadu Buhari administration would mean to Nigeria, Africa and the world. As Chairperson of the “G 7” group of industrialized nations, she extended a hand of fellowship to him upon his victory in the 2015 elections. She asked him to be ready with his wish list and be present at the G 7 meeting to brief its leaders.
Since that time, there had been a big demand for President Buhari all over the world, a demand that our officials in Foreign Affairs insisted must be cashed on or else we missed the opportunity.
President Gauck came here in February at the head of a business delegation, a visit that pushed the existing relations up by several notches as manifested by the setting up of a one-stop investment centre to facilitate foreign investment and partnerships.
Germany has also proposed a twining of two cities, Lagos and Frankfurt to facilitate the sharing of experience, meeting of businesses, trade and investment as well as exchange of visits by officials.
In the course of the visit by President Gauck, a pledge by the EU to spend fifty million Euro (€50 m.) against terrorism in the Lake Chad basin area was announced.
President Buhari’s state visit brought closer the relationship between Nigeria and Germany in addition to breakthroughs in several areas of negotiations.
Business/Investments:
The other key success area is investment. The President and his team held a highly successful business forum which had in attendance over 100 Nigerian and German business leaders with interests in industries across Manufacturing, Information Technology, Healthcare, Construction, Training, Agro processing, Power, Mining and Consumer businesses
In a speech at the meeting, President Muhammadu Buhari decried the current low level of trade and investment between both countries and Nigeria’s openness for business and long-term investment from Germany. He highlighted the steady work of renewal that has started in the country and the progress that is being recorded in the government’s pillars of security, governance and the economy.
He also presented a strong case on Nigeria’s compelling fundamentals and stated the priority sectors of the government in which investments are being sought as being Agriculture, Industrialization, Solid Minerals, Digital Economy and Infrastructure, especially power generation.
The biggest gypsum producer in the world has already obtained an exploration license for the mineral and is looking to commence local production in Nigeria. A well-known consumer brand with over 50,000 employees worldwide is considering production of its laundry detergent locally. The company has already invested $250 million locally, with 900 employees. The transition to local production will significantly increase the number of Nigerians employed.
A Nigerian-based pharmaceutical company in partnership with a German conglomerate is also to commence a renal testing business in Nigeria before the end of the year
Finance:
The President stated that the Nigerian Development Bank will soon commence operations to help provide additional funding to the Small and Medium-Scale Enterprises (SMEs). As a large contributor to the economy, funding to the SMEs will help spur inclusive economic growth. He thereafter charged government officials and the business community to enhance the process of achieving tangible results that are mutually beneficial to both countries
Economic relations:
A significant takeaway from the Presidential engagement in Germany is the agreement to give vocational skills training to thousands of our youth.
Germany is always known to be a strong developer of apprentice skills. In addition to their reputation for quality education, the distinguishing feature of the German economy is that emphasis on skill development.
What President Buhari got from this trip is a commitment by Germany to share with Nigeria their skills in agriculture, IT, telecommunications, machinery, aviation, vehicles, healthcare, construction and so forth.
As part of the steps towards imparting the vocational skills, there will be collaboration between the German Engineering Federation (VDMA) and a Nigerian conglomerate to build a technical school for artisans. The school will train Nigerians for three years, of which 50percent of the time will be spent in the school and the remaining 50percent of the time spent gaining practical experience. This model will be scaled up for the other parts of the country based on the success of this cooperation.
Agriculture:
Nigeria and Germany had useful discussions on a program of food processing locally, rice and oil milling with the aim of leavening that country’s experience in a new plan by the administration to create wealth in rural communities.
There also plans for a financing fund for agriculture in Nigeria to assist small and medium size entrepreneurs and cooperatives in the agricultural sector.
Energy/Power:
A renewable power company with advanced and affordable solar technologies is going to commence operations in Nigeria. The company is headed by a Nigerian and have commenced the ground-work to commence operations early next year.
Following the MOU at the Bi-national Commission, agreements were also struck for energy partnership in renewable energy. Several states characterized by hot weather, mostly in North have signed for solar Independent Power Project, IPPs. A 30 Megawatt power plant is coming up in Adamawa while Bauchi, Benue, Gombe, Kano, Kaduna, Sokoto, Katsina and some others are on the queue.
Security:
Germany has offered Nigeria support in the war against terrorism with mine detectors, radar equipment and a field hospital.
Chancellor Merkel also pledged increased involvement of Germany in supporting Internally Displaced Persons, IDPs and the reconstruction of their destroyed communities.
Immigration:
Another key area of cooperation is immigration.
There are thousands of illegal immigrants from Nigeria currently in Germany. On their records, 20,000 Nigerians enter their country each year. This is a sore issue for Germany. Of these numbers, only about nine percent of those who enter clandestinely qualify for legal asylum. To deal with the issue, they have indicated to Nigeria their willingness to train all prospective deportees in skills they can use back at home. In addition to this, two other Nigerians will be given free vocational training for every one deported illegal immigrant.
Climate Change:
President Buhari never missed an opportunity to make a pitch for the recharging of the Lake Chad, now only ten percent of its original size, whenever he met the leaders of rich countries.
He has been persuaded a long time ago that the best way to save the lake Chad and the people who inhabit its basin from the corrosive effect of climatic change is to divert water from the Congo Basin to the Lake Chad.
A study financed by Nigeria indicated that USD 15 Billion will be needed to do this but it is the kind of money that neither this country nor its neighbors can muster.
Having successfully established that the climate change has a lot to do with the drastic decline of livelihoods in the area and is at the root cause of the Boko Haram insurgency, the President is convinced that recharging the Lake is no longer the sole business of the Lake Chad Basin countries but that of the wider world.
Given her commitment to saving the environment, Chancellor Merkel had shown keenness in the project and is willing to be a part of the effort.
Her reported earmarking of €18 billion for the project was misconstrued from her speech. After a repeated playback of the speech, the same conclusions were unfortunately drawn. Angela Merkel’s commitment is however to the tune of €18 million on the Nigerian side and the rest €32 million to the rest of the Lake Chad basin countries, with all of the money coming from the European Fund. Nevertheless eighteen Million to support ongoing efforts in the North East is still a mouthwatering amount.
New and Pending Issues:
The Nigerian delegation also had useful discussions on road and rail development, gas exploration, equipment and surveillance for the protection of oil and gas infrastructure in Niger Delta, upgrading of Defense Industries Corporation, DICON, cooperation in rule of law and polio eradication.
Last but not the least, the President used a moment of his time in Germany to act his role a Commander-in-Chief by paying a visit to a recuperating army officer injured in the course of duty in the North East.
Mr Garba Shehu is the Senior Special Assistant to the President on Media and Publicity
Feature/OPED
How Christians Can Stay Connected to Their Faith During This Lenten Period

It’s that time of year again, when Christians come together in fasting and prayer. Whether observing the traditional Lent or entering a focused period of reflection, it’s a chance to connect more deeply with God, and for many, this season even sets the tone for the year ahead.
Of course, staying focused isn’t always easy. Life has a way of throwing distractions your way, a nosy neighbour, a bus driver who refuses to give you your change, or that colleague testing your patience. Keeping your peace takes intention, and turning off the noise and staying on course requires an act of devotion.
Fasting is meant to create a quiet space in your life, but if that space isn’t filled with something meaningful, old habits can creep back in. Sustaining that focus requires reinforcement beyond physical gatherings, and one way to do so is to tune in to faith-based programming to remain spiritually aligned throughout the period and beyond.
On GOtv, Christian channels such as Dove TV channel 113, Faith TV and Trace Gospel provide sermons, worship experiences and teachings that echo what is being practised in churches across the country.
From intentional conversations on Faith TV on GOtv channel 110 to true worship on Trace Gospel on channel 47, these channels provide nurturing content rooted in biblical teaching, worship, and life application. Viewers are met with inspiring sermons, reflections on scripture, and worship sessions that help form a rhythm of devotion. During fasting periods, this kind of consistent spiritual input becomes a source of encouragement, helping believers stay anchored in prayer and mindful of God’s presence throughout their daily routines.
To catch all these channels and more, simply subscribe, upgrade, or reconnect by downloading the MyGOtv App or dialling *288#. You can also stream anytime with the GOtv Stream App.
Plus, with the We Got You offer, available until 28th February 2026, subscribers automatically upgrade to the next package at no extra cost, giving you access to more channels this season.
Feature/OPED
Turning Stolen Hardware into a Data Dead-End

By Apu Pavithran
In Johannesburg, the “city of gold,” the most valuable resource being mined isn’t underground; it’s in the pockets of your employees.
With an average of 189 cellphones reported stolen daily in South Africa, Gauteng province has become the hub of a growing enterprise risk landscape.
For IT leaders across the continent, a “lost phone” is rarely a matter of a misplaced device. It is frequently the result of a coordinated “snatch and grab,” where the hardware is incidental, and corporate data is the true objective.
Industry reports show that 68% of company-owned device breaches stem from lost or stolen hardware. In this context, treating mobile security as a “nice-to-have” insurance policy is no longer an option. It must function as an operational control designed for inevitability.
In the City of Gold, Data Is the Real Prize
When a fintech agent’s device vanishes, the $300 handset cost is a rounding error. The real exposure lies in what that device represents: authorised access to enterprise systems, financial tools, customer data, and internal networks.
Attackers typically pursue one of two outcomes: a quick wipe for resale on the secondary market or, far more dangerously, a deep dive into corporate apps to extract liquid assets or sellable data.
Clearly, many organisations operate under the dangerous assumption that default manufacturer security is sufficient. In reality, a PIN or fingerprint is a flimsy barrier if a device is misconfigured or snatched while unlocked. Once an attacker gets in, they aren’t just holding a phone; they are holding the keys to copy data, reset passwords, or even access admin tools.
The risk intensifies when identity-verification systems are tied directly to the compromised device. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), widely regarded as a gold standard, can become a vulnerability if the authentication factor and the primary access point reside on the same compromised device. In such cases, the attacker may not just have a phone; they now have a valid digital identity.
The exposure does not end at authentication. It expands with the structure of the modern workforce.
65% of African SMEs and startups now operate distributed teams. The Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) culture has left many IT departments blind to the health of their fleet, as personal devices may be outdated or jailbroken without any easy way to know.
Device theft is not new in Africa. High-profile incidents, including stolen government hardware, reinforce a simple truth: physical loss is inevitable. The real measure of resilience is whether that loss has any residual value. You may not stop the theft. But you can eliminate the reward.
Theft Is Inevitable, Exposure is Not
If theft cannot always be prevented, systems must be designed so that stolen devices yield nothing of consequence. This shift requires structured, automated controls designed to contain risk the moment loss occurs.
Develop an Incident Response Plan (IRP)
The moment a device is reported missing, predefined actions should trigger automatically: access revocation, session termination, credential reset and remote lock or wipe.
However, such technical playbooks are only as fast as the people who trigger them. Employees must be trained as the first line of defence —not just in the use of strong PINs and biometrics, but in the critical culture of immediate reporting. In high-risk environments, containment windows are measured in minutes, not hours.
Audit and Monitor the Fleet Regularly
Control begins with visibility. Without a continuous, comprehensive audit, IT teams are left responding to incidents after damage has occurred.
Opting for tools like Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) allows IT teams to spot subtle, suspicious activities or unusual access attempts that signal a compromised device.
Review Device Security Policies
Security controls must be enforced at the management layer, not left to user discretion. Encryption, patch updates and screen-lock policies should be mandatory across corporate devices.
In BYOD environments, ownership-aware policies are essential. Corporate data must remain governed by enterprise controls regardless of device ownership.
Decouple Identity from the Device
Legacy SMS-based authentication models introduce avoidable risk when the authentication channel resides on the compromised handset. Stronger identity models, including hardware tokens, reduce this dependency.
At the same time, native anti-theft features introduced by Apple and Google, such as behavioural theft detection and enforced security delays, add valuable defensive layers. These controls should be embedded into enterprise baselines rather than treated as optional enhancements.
When Stolen Hardware Becomes Worthless
With POPIA penalties now reaching up to R10 million or a decade of imprisonment for serious data loss offences, the Information Regulator has made one thing clear: liability is strict, and the financial fallout is absolute. Yet, a PwC survey reveals a staggering gap: only 28% of South African organisations are prioritising proactive security over reactive firefighting.
At the same time, the continent is battling a massive cybersecurity skills shortage. Enterprises simply do not have the boots on the ground to manually patch every vulnerability or chase every “lost” terminal. In this climate, the only viable path is to automate the defence of your data.
Modern mobile device management (MDM) platforms provide this automation layer.
In field operations, “where” is the first indicator of “what.” If a tablet assigned to a Cape Town district suddenly pings on a highway heading out of the city, you don’t need a notification an hour later—you need an immediate response. An effective MDM system offers geofencing capabilities, automatically triggering a remote lock when devices breach predefined zones.
On Supervised iOS and Android Enterprise devices, enforced Factory Reset Protection (FRP) ensures that even after a forced wipe, the device cannot be reactivated without organisational credentials, eliminating resale value.
For BYOD environments, we cannot ignore the fear that corporate oversight equates to a digital invasion of personal lives. However, containerization through managed Work Profiles creates a secure boundary between corporate and personal data. This enables selective wipe capabilities, removing enterprise assets without intruding on personal privacy.
When integrated with identity providers, device posture and user identity can be evaluated together through multi-condition compliance rules. Access can then be granted, restricted, or revoked based on real-time risk signals.
Platforms built around unified endpoint management and identity integration enable this model of control. At Hexnode, this convergence of device governance and identity enforcement forms the foundation of a proactive security mandate. It transforms mobile fleets from distributed risk points into centrally controlled assets.
In high-risk environments, security cannot be passive. The goal is not recovery. It is irrelevant, ensuring that once a device leaves authorised hands, it holds no data, no identity leverage, and no operational value.
Apu Pavithran is the CEO and founder of Hexnode
Feature/OPED
Daniel Koussou Highlights Self-Awareness as Key to Business Success

By Adedapo Adesanya
At a time when young entrepreneurs are reshaping global industries—including the traditionally capital-intensive oil and gas sector—Ambassador Daniel Koussou has emerged as a compelling example of how resilience, strategic foresight, and disciplined execution can transform modest beginnings into a thriving business conglomerate.
Koussou, who is the chairman of the Nigeria Chapter of the International Human Rights Observatory-Africa (IHRO-Africa), currently heads the Committee on Economic Diplomacy, Trade and Investment for the forum’s Nigeria chapter. He is one of the young entrepreneurs instilling a culture of nation-building and leadership dynamics that are key to the nation’s transformation in the new millennium.
The entrepreneurial landscape in Nigeria is rapidly evolving, with leaders like Koussou paving the way for innovation and growth, and changing the face of the global business climate. Being enthusiastic about entrepreneurship, Koussou notes that “the best thing that can happen to any entrepreneur is to start chasing their dreams as early as possible. One of the first things I realised in life is self-awareness. If you want to connect the dots, you must start early and know your purpose.”
Successful business people are passionate about their business and stubbornly driven to succeed. Koussou stresses the importance of persistence and resilience. He says he realised early that he had a ‘calling’ and pursued it with all his strength, “working long weekends and into the night, giving up all but necessary expenditures, and pressing on through severe setbacks.”
However, he clarifies that what accounted for an early success is not just tenacity but also the ability to adapt, to recognise and respond to rapidly changing markets and unexpected events.
Ambassador Koussou is the CEO of Dau-O GIK Oil and Gas Limited, an indigenous oil and natural gas company with a global outlook, delivering solutions that power industries, strengthen communities, and fuel progress. The firm’s operations span exploration, production, refining, and distribution.
Recognising the value of strategic alliances, Koussou partners with business like-minds, a move that significantly bolsters Dau-O GIK’s credibility and capacity in the oil industry. This partnership exemplifies the importance of building strong networks and collaborations.
The astute businessman, who was recently nominated by the African Union’s Agenda 2063 as AU Special Envoy on Oil and Gas (Continental), admonishes young entrepreneurs to be disciplined and firm in their decision-making, a quality he attributed to his success as a player in the oil and gas sector. By embracing opportunities, building strong partnerships, and maintaining a commitment to excellence, Koussou has not only achieved personal success but has also set a benchmark for future generations of African entrepreneurs.
His journey serves as a powerful reminder that with determination and vision, success is within reach.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn