Travel/Tourism
Global Airline Profits To Hit $29.8m in 2017—IATA


By Modupe Gbadeyanka
The International Air Transport Association (IATA) has declared that it expects the global airline industry to make a net profit in 2017 of $29.8 billion.
On forecast total revenues of $736 billion, that represents a 4.1 percent net profit margin.
This will be the third consecutive year (and the third year in the industry’s history) in which airlines will make a return on invested capital (7.9%) which is above the weighted average cost of capital (6.9%).
IATA revised slightly downward its outlook for 2016 airline industry profitability to $35.6 billion (from the June projection of $39.4 billion) owing to slower global GDP growth and rising costs. This will still be the highest absolute profit generated by the airline industry and the highest net profit margin (5.1%).
“Airlines continue to deliver strong results. This year we expect a record net profit of $35.6 billion. Even though conditions in 2017 will be more difficult with rising oil prices, we see the industry earning $29.8 billion. That’s a very soft landing and safely in profitable territory. These three years are the best performance in the industry’s history—irrespective of the many uncertainties we face. Indeed, risks are abundant— political, economic and security among them. And controlling costs is still a constant battle in our hyper-competitive industry,” said Alexandre de Juniac, IATA’s Director General and CEO.
“We need to put this into perspective. Record profits for airlines means earning more than our cost of capital. For most other businesses that would be considered a normal level of return to investors. But three years of sustainable profits is a first for the airline industry. And after many years of hard work in restructuring and re-engineering the business the industry is also more resilient. We should also recognize that profits are not evenly spread with the strongest performance concentrated in North America,” said de Juniac.
2017
While airline industry profits are expected to have reached a cyclical peak in 2016 of $35.6 billion, a soft landing in profitable territory is expected in 2017 with a net profit of $29.8 billion. 2017 is expected to be the eighth year in a row of aggregate airline profitability, illustrating the resilience to shocks that have been built into the industry structure. On average, airlines will retain $7.54 for every passenger carried.
Expected higher oil prices will have the biggest impact on the outlook for 2017. In 2016 oil prices averaged $44.6/barrel (Brent) and this is forecast to increase to $55.0 in 2017. This will push jet fuel prices from $52.1/barrel (2016) to $64.9/barrel (2017). Fuel is expected to account for 18.7% of the industry’s cost structure in 2017, which is significantly below the recent peak of 33.2% in 2012-2013.
The demand stimulus from lower oil prices will taper off in 2017, slowing traffic growth to 5.1% (from 5.9% in 2016). Industry capacity expansion is also expected to slow to 5.6% (down from 6.2% in 2016). Capacity growth will still outstrip the increase in demand, thus lowering the global passenger load factor to 79.8% (from 80.2% in 2016).
The negative impact of a lower load factor is expected to be offset somewhat by a strengthening of global economic growth. World GDP is projected to expand by 2.5% in 2017 (up from 2.2% in 2016). Along with structural changes in the industry, this is expected to help stabilize yields for both the cargo and passenger businesses. This is a welcome development as yields (calculated in dollar terms) have fallen each year since 2012.
There is some optimism over the prospects for the cargo business in 2017. The break in falling yields and a moderate uptick in demand (3.5%) will see cargo industry volumes reach a record high of 55.7 million tonnes (up from 53.9 million tonnes in 2016). Industry revenues are expected to rise slightly to $49.4 billion (still well below the $60 billion level of annual revenues experienced in 2010-2014). Trading conditions remain challenging.
“Connectivity continues to set new records. We expect nearly 4 billion travelers and 55.7 million tonnes of cargo in the coming year. And almost 1% of global GDP is spent on air transport—some $769 billion. Air transport has made the world more accessible than ever and it is a critical enabler of the global economy,” said de Juniac.
“Governments, however, do not make aviation’s work easy. The global tax bill has ballooned to $123 billion. Over 60% of countries put visa barriers in the way of travel. And the total number of ticket taxes exceeds 230. Billions of dollars are wasted in direct costs and lost productivity as a result of inefficient infrastructure. These are only some of the hurdles which confront airlines. Our aim is to work in partnership to help governments better understand and fully maximize the social and economic benefits of efficient global air links,” said de Juniac.
2017 Regional Analysis
North American carriers: The strongest financial performance is being delivered by airlines in North America. Net post-tax profits will be the highest at $18.1 billion next year, although down slightly from the $20.3 billion expected in 2016. The net margin for the region’s carriers is also expected to be the strongest at 8.5% with an average profit of $19.58/passenger. In 2017 capacity offered by the region’s carriers is expected to grow by 2.6%, slightly outpacing expected demand growth of 2.5%. Recent consolidation continues to underpin the region’s strong profitability, even as the region faces upwards cost pressures which include the price of fuel.
European carriers: Airlines based in Europe are expected to post an aggregate net profit of $5.6 billion in 2017 which is below the $7.5 billion for 2016. Nonetheless, carriers there are forecast to generate a 2.9% net profit margin and a per passenger profit of $5.65. There remains a significant gap between the performance of the region’s carriers and the performance of North American ones. Capacity in 2017 is expected to grow by 4.3%, ahead of demand growth which is forecast at 4.0%. The region is subject to intense competition and hampered by high costs, onerous regulation and high taxes. And terrorist threats remain a real risk, even if confidence is starting to return after the tragic incidents in recent times.
Asia-Pacific carriers: Airlines in the Asia-Pacific region are expected to generate a net profit of $6.3 billion in 2017 (down from $7.3 billion in 2016) for a net margin of 2.9%. On a per passenger basis average profits are anticipated to be $4.44. Capacity offered by the region’s carriers is forecast to grow by 7.6%, ahead of a forecast growth in demand of 7.0%. Improved cargo performance is expected to offset rising fuel prices for many of the region’s airlines. The expansion of new model airlines and progressive liberalization in the region is intensifying already strong competition. In addition profitability varies widely across the region.
Middle Eastern carriers: Middle Eastern airlines are forecast to generate a net profit of $0.3 billion for a net margin of 0.5% and an average profit per passenger of $1.56. This is below the $900 million profit expected in 2016. Average yields for the region’s carriers are low but unit costs are even lower, partly driven by the strong capacity expansion, forecast at 10.1% this year, ahead of expected demand growth of 9.0%. Threats are emerging to the success story of the Gulf carriers, including increases in airport charges across the Gulf States and growing air traffic management delays.
Latin American carriers: Latin American airlines are expected to post a net profit of $200 million, which is slightly lower than the $300 million forecast for 2016. Profit per passenger is expected to be $0.76 with a net profit margin of 0.7%. Capacity offered by the region’s carriers is forecast to grow by 4.8% which is ahead of expected demand growth of 4.0%. Despite some signs of improvement in the region’s currencies and economic prospects, operating conditions remain challenging, with infrastructure deficiencies, high taxes, and a growing regulatory burden across the continent. Venezuela continues to block the repatriation of some $3.8 billion of industry funds in contravention of international obligations.
African carriers: Carriers in Africa are expected to deliver the weakest financial performance with a net loss of $800 million (broadly unchanged from 2016). For each passenger flown this amounts to an average loss of $9.97. Capacity in 2017 is expected to grow by 4.7%, ahead of 4.5% demand growth. The region’s weak performance is being driven by regional conflict and the impact of low commodity prices.
2016
2016 will be a record year for industry profitability. The expected net profit of $35.6 billion is slightly ahead of the $35.3 billion recorded in 2015, as is the 5.1% net profit margin (slightly ahead of the 4.9% recorded for 2015).
The modest revision from previous expectations largely is owing to two factors: slower global GDP growth: 2.2%, which was below mid-year expectations of 2.3% growth and non-fuel unit costs increased by 2.0% in 2016.
The Business of Freedom
“Air transport is the business of freedom. The safe and efficient global movement of goods and people is a positive force in our world. Aviation’s success betters peoples’ lives by creating economic opportunity and supporting global understanding. We must stand firm in the face of any rhetoric that would put limits on aviation’s future success,” said de Juniac.
Some key indicators of the strength of global connectivity include:
The average return airfare in 2017 is expected to be $351 (2015 dollars), which is 63% below 1995 levels.
Average air freight rates in 2017 are expected to be $1.48/kg (2015 dollars) which is a 68% fall on 1995 levels.
The number of unique city pairs served by aviation grew to 18,429 in 2016, a 92% increase on 1995.
The value of trade carried by air transport in 2017 is expected to be $5.7 trillion, a 4.9% increase on 2015. Air cargo accounts for around 35% of the total value of goods traded globally.
The global spend on tourism enabled by air transport is expected to grow by 5.1% in 2017 to $681 billion.
Supply chain jobs supported by aviation are expected to grow by 3.4% in 2017 to some 69.7 million worldwide.
Airlines are expected to take delivery of some 1,700 new aircraft in 2017, around half of which will replace older and less fuel-efficient aircraft. This will expand the global commercial fleet by 3.6% to 28,700.
Airlines are expected to operate 38.4 million flights in 2017, up 4.9%.
Travel/Tourism
FAAN Traces Source of Lagos Airport Fire to Server Room
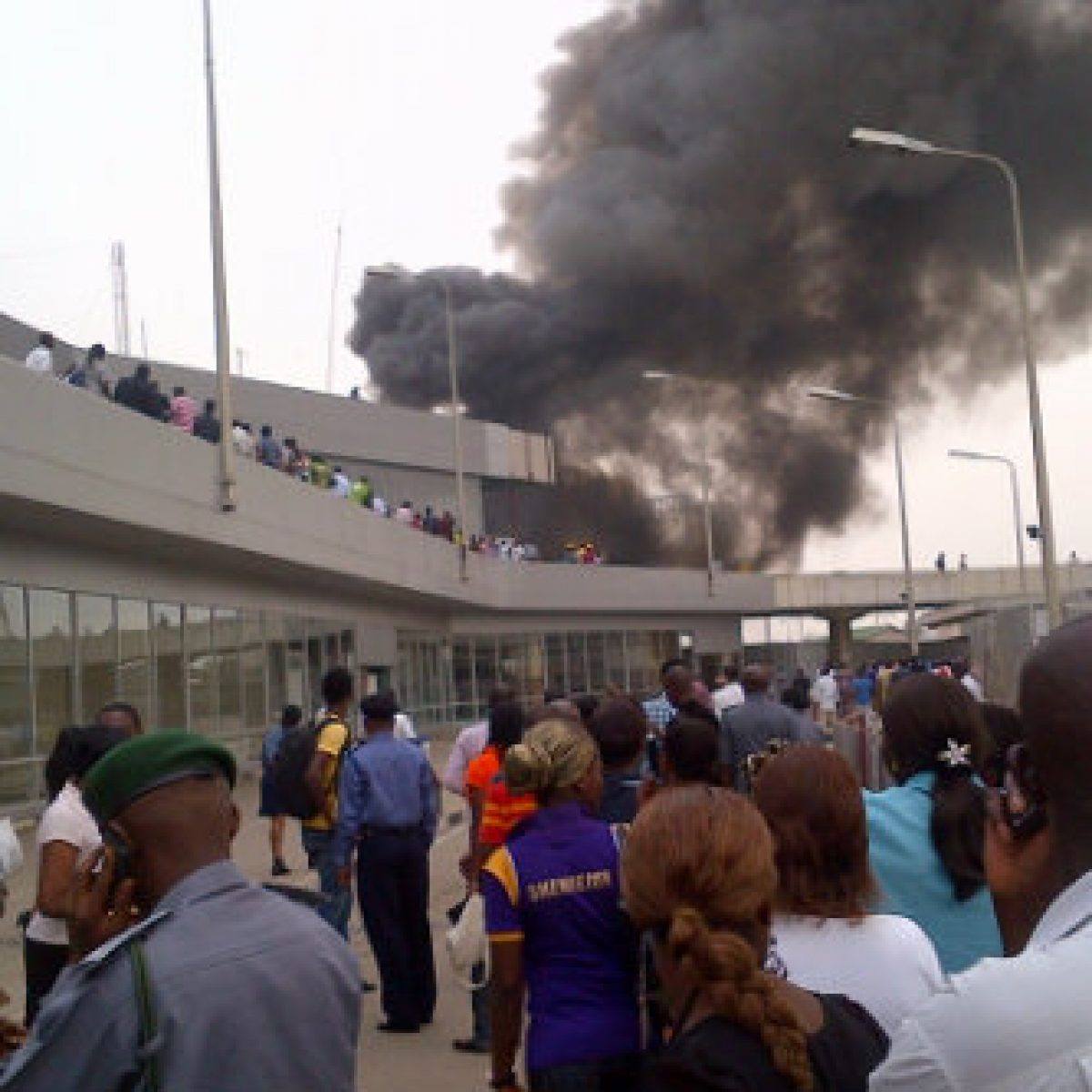

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
The Federal Airports Authority of Nigeria (FAAN) has disclosed that the fire incident at Terminal 1 of the Murtala Muhammed International Airport (MMIA), Lagos, on Monday originated from the server room on the first floor of Terminal 1.
In a statement in the wee hours of Tuesday, the agency confirmed that six casualties were recorded, involving three males and three females.
“A total of six casualties, comprising three males and three females, were recorded, all of whom are in stable condition. One affected individual has been transferred to the FAAN Headquarters Hospital for further medical evaluation and remains stable,” a part of the statement said.
FAAN noted that emergency response operations remain active, with coordinated firefighting, rescue, and safety teams continuing containment and recovery efforts.
A crane was successfully deployed to support rescue operations at the Control Tower, and all 14 persons initially trapped have been safely rescued and fully evacuated from the facility, it added.
The organisation disclosed that as an additional safety precaution, the sixth floor of the affected facility has been completely evacuated to support ongoing emergency operations and risk mitigation, adding that the fire within the departure hall is now largely under control, while responders continue close monitoring to prevent any spread to adjoining sections of the terminal.
“In line with established safety protocols, the airspace remains temporarily closed,” it stated, confirming that all emergency procedures were promptly activated and continue to collaborate with relevant emergency and support agencies to safeguard lives, infrastructure, and operational integrity.
Also, the statement revealed that the Nigerian Airspace Management Agency (NAMA) is actively working to establish a temporary Control Tower to enable the safe and timely restoration of airport operations as soon as practicable.
Travel/Tourism
UK to Issue Digital Visas to Nigerian Travellers from February 25

By Adedapo Adesanya
The United Kingdom says all Nigerian visitors to the country, who need a visa, will only get a digital visa from February 25, 2026.
In a statement, the UK Visas & Immigration said that from the scheduled date, all Nigerian nationals applying for a UK Visit visa will receive an eVisa, rather than a vignette (sticker) in their passport.
The shift also indicates that travellers will access their visa electronically through their UK Visas and Immigration (UKVI) account, marking a significant step in modernising the UK’s visa process.
For Nigerian applicants, the visa application requirements remain unchanged. Travellers will still apply as usual, attend a Visa Application Centre to provide biometric information, and meet all existing eligibility criteria. The only difference is how the visa is issued: instead of a physical sticker, applicants will receive a secure digital record of their immigration status.
According to a statement, the British government clarified that Nigerians currently holding a valid vignette sticker do not need to take any action. Their physical visa remains valid until it expires or requires replacement.
It added that the move to eVisas brings a number of benefits for Nigerian travellers, including passports being returned more quickly and travellers being able to manage their immigration status online at any time, from any location. The digital format offers stronger security as eVisas cannot be lost, stolen, or tampered with.
Welcoming the transition, British Deputy High Commissioner in Abuja, Mrs Gill Lever, said, “We are committed to making it easier for Nigerians to travel to the UK. This move to digital visas will streamline a key part of the visa process, making it more secure while reducing dependence on paper documents. We look forward to continuing to welcome Nigerian visitors, students, and workers to the UK.”
Once a visa is approved, applicants will need to create a free UKVI account to access the eVisa.
Travel/Tourism
Russia Facilitates Travel, Tourism for Africans

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
Russian Foreign Minister, Sergey Lavrov, has reiterated the official statement on expanding visa-free travel between Russia and Africa, signaling Kremlin’s earlier position on facilitating people-to-people movement and raising cultural interaction. The question of ‘visa-free’ travel and tourism dominated discussions during the first and second Russia-Africa summits, as a step to embrace new bilateral relations and soft-power diplomacy with Africa.
While ‘visa-free’ travel could be interpreted as a potential driver for boosting tourism business, Sergey Lavrov’s definition limited this policy only to ‘Africans holding diplomatic passports’ and largely excludes political elites and business executives looking to develop entrepreneurial connectivity to Russia. The broader ambition is to focus on Africa’s middle class, estimated at 380 million envision as the constituting a huge tourism market, which is twice Russia’s population.
The Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs has further underlined the fact that the implementation of a ‘visa-free regime’ with all African countries aims at strengthening cultural relations with the continent. That announcement filled the local Russian media from Moscow to Vladivostok. Later, the Ministry clarified that the ‘visa-free regime’ for African countries was still under serious review. Diplomatic talks with various countries on the drafts of visa-free travel agreements were underway at different stages, as each had its specific requirements. There was a need to categorise African countries into groups.
This initiative is within the framework of the Joint Action Plan (2023-2026) adopted at the second summit in St. Petersburg. From investigations, Russia has ‘visa-free agreements’ with only six African countries. The visa-free regime only applied to African countries that signed agreements with the Foreign Ministry. Within the agreements, only holders of diplomatic passports are permitted under this consular agreement. According to sources monitored, agreements would be signed after successful negotiations with Russian authorities.
The Head of the Russian Foreign Ministry’s Consular Department, Alexey Klimov, explained in an interview with local Russian media: “Russia is currently working out travel agreements on abolishing visa requirements and providing visa-free entry for short-term trips, usually up to 90 days, with several friendly states, nine of them being the countries of Africa and the Middle East.”
“As always, we will immediately inform the public about the concrete results achieved and embodied in documented bilateral agreements,” Klimov concluded, the full transcript posted on the official ministry’s website.
With the changing times, Russia has been pursuing an integrative, multipolar approach in its relations with friendly countries around the world, including those in Africa. During these past few years, Asian countries, such as China and India, have been granted such short-term visa-free privileges. In practical terms, this policy boosts tourism. It is noticeable that Russia remains a holiday destination for Africa’s political elite, corporate business leaders, and the middle class. But undoubtedly, African politicians and corporate business leaders highly prefer to spend their vacation in the United States and Europe. Some Asian destinations are becoming increasingly popular as a preferred choice for recreation. That trend is unlikely to change; it will remain as such for the next few decades.
Tourism topic at Russia-Africa summits
Following the Russia-Africa summits, both Russia and Africa adopted joint declarations—in fact, comprehensive documents that outline various parameters for elevating cooperation to a new qualitative stage.
Tourism is one of the most highly praised spheres during discussions. Brilliant speeches called for the frequent exchange of cultural groups and the taking of comprehensive measures to promote a broad scope of cultural and tourism collaboration between Russia and Africa.
Ultimately, to boost compelling economic interests and foster cooperation, frequent interactions are necessary. The frequency of interaction should not be limited to summits and conferences alone. Some basic strategic steps and measures are also required to encourage simple holiday travels to both regions.
These are significantly missing in the current relations between Russia and Africa. Critics often argue that Russia is contributing considerably to its so-called isolation by closing its doors, especially when there are considerable opportunities to develop high-quality tourism. The African elite could visit Moscow, St. Petersburg, and coastal cities, including Sochi, as well as along the Volga River.
Indeed, playing with flexible visa regimes will not only promote tourism and strengthen cultural ties, but also, in practical terms, will build positive perceptions and further help to neutralise a high level of Western media disinformation across the continent. There is a need to adopt a pragmatic approach to these crucial questions and carefully examine social aspects to enhance people-to-people interactions.
Notably, Russian officials consider visits by heads of African states and ministers to be an essential pillar of their version of building relations in the anticipated multipolar world.
With the current geopolitical situation, Africa’s middle class, estimated at 380 million (twice the population of Russia), has suitable alternative holiday destinations. For now, Moscow and St. Petersburg are not their desired priority for spending vacations. Russian tour operators acknowledge, in a media query with this article’s author, that there is no bilateral entrepreneurial activity between Russia and the African tourism sector. However, on the other hand, African destinations such as Egypt, Morocco, the Maldives, Seychelles, South Africa, and Zanzibar are popular among Russian vacationers.
Most often, Russian and African experts have been discussing how best to promote exchanges of delegations, explore untapped resources, and explore the possibilities of boosting cooperation in the field of tourism, as well as the dissemination of information on tourism opportunities in the Russian Federation and African States.
Over the past few years, the summit declarations have remained tacitly as declarations. In practical terms, the visa-free regime for African countries has mainly remained as official declarations. The fundamental question often asked is for what purposes the summit declarations are made.
Current Tourism Challenges
Russian experts say Chinese, Indians and many Asians are the real potentials, taking advantage of the emerging opportunity to travel to Russia, more than Africa’s middle class and entrepreneurs. In addition, Africa is currently assessed as “reawakening to geopolitical changes” and less capable of taking their own development initiatives based on the huge resources on the continent.
The continent’s challenges still existed. Notwithstanding that, Africa is seemingly moving from the periphery toward the negotiating table. With tourism, engagement remains weak and fragmented. In comparison, in African and Asian tourism, that distinction matters. Africa has a demographic advantage, but the dynamics of tourism perceptions are low.
In the sense of uplifting bilateral partnerships, especially during this time at the heightening of geopolitics, Africa is not simply a reliable partner but has to be treated as such for operating at the tourism development scale. The future of the relationship can be an extremely positive lever, and to take important steps for mapping out diverse ways for its sustainability and expansion. Less arguably, Africa’s political leadership and business executives have explicitly understood the criticality of Russia’s ‘visa-free’ regime, as one of the most geopolitical rhetoric in the contemporary era.
Multifaceted relations with Russia
Russia is ready to build multifaceted relations with Africa. “If Russia Wins, Africa Wins!” remarked Azali Assoumani, President of Comoros, during the late July St. Petersburg summit plenary session in 2023.
With hopes for an enduring collaboration on long-term programs, the Secretariat of the Russia-Africa Partnership Forum was created. And it has since been networking, intending to promote Russia’s economic interests in Africa and to foster mutually beneficial cooperation with African countries.
The Director of the Department of Partnership with Africa of the Russian Foreign Ministry, Tatiana Dovgalenko, in an interview with the TV BRICS channel on July 9, 2025, emphasised that the importance of her new department is its functionality—focus on the comprehensive, integrated development of relations between Russia and the entire African continent, which are experiencing a genuine revival today. It implies that the main task is to implement the decisions which cover a wide range of cooperation areas, including culture and tourism.
While Russian officials focus on their work aimed at increasing Russian presence in Africa, the role of Africa in the Russian Federation is vastly underestimated. At these changing times, officials have to necessarily note with mutual interest the economic presence of Africa, beyond just training students, in the Russian Federation. And, of course, promoting African tourism is not only a promising niche but also a unique pathway for sustaining bilateral cooperation.
Still on the topic of bilateral tourism, Tatiana Dovgalenko rightly pointed out that more active participation by representatives of the African tourism industry in various events in Russia, along with the introduction of visa-free travel to African countries, would help increase the tourist appeal of Africa. Within the Action Plan of the Russia-Africa Partnership Forum for the period 2023-2026, it is anticipated that both Russia and Africa will hold constructive positions on mutual bilateral ties in this emerging multipolar world.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn