World
Prospect of Wagner’s Growing Influence in Africa Worries Western Powers

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
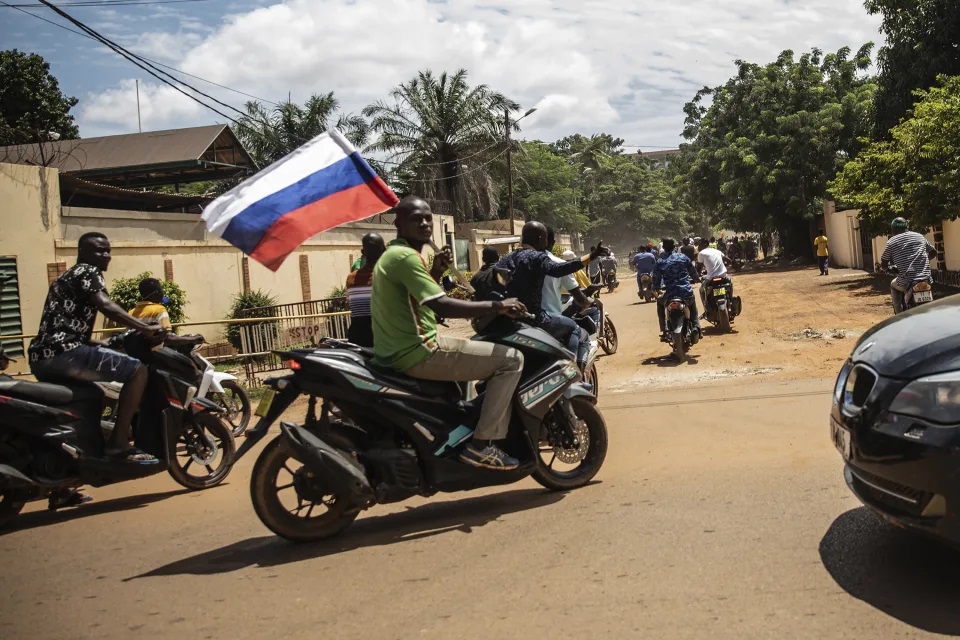
Some Western powers, including France, have expressed serious concerns over the prospect of a private military contractor with close ties to the Kremlin, the Wagner group, cementing its influence in Africa.
At the recently-concluded US-Africa Leaders’ Summit in Washington, DC, the President of Ghana, Mr Nana Akufo-Addo, made a genuine claim about neighbouring Burkina Faso during the panel discussions on Peace, Security and Governance in Washington.
Speaking about the growing violence linked to al-Qaida and the Islamic State group in the west African region, Mr Akufo-Addo alleged that Burkina Faso allocated a mine to the Wagner Group as a form of payment for its deployment of fighters in the country.
“To have (Wagner) operating on our northern border is particularly distressing for us in Ghana,” a former Chairman of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) and Ghanaian leader Nana Akufo-Addo informed at the summit.
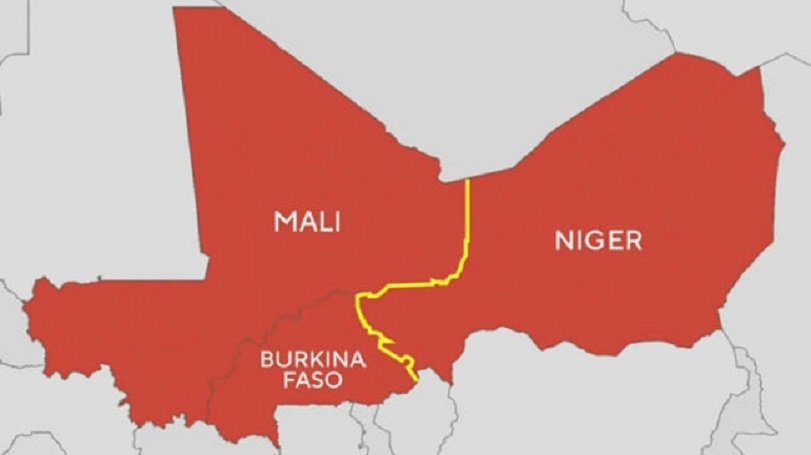
“Today, Russian mercenaries are on our northern border. Burkina Faso has now entered into an arrangement to go along with Mali in employing the Wagner forces there,” he said, adding that Burkina Faso had ceded a mine, reportedly with gold reserves, near the border with Ghana in exchange for the group’s services to deal with the militant insurgency that began in 2015. In recent weeks, hundreds of people fleeing militants attacks in Burkina Faso have crossed the border into northern Ghana.
Burkina Faso has summoned the Ghanaian ambassador for ‘explanations’ after Ghana’s president alleged that Burkina Faso had hired the Russian mercenary group, Wagner, according to reports from Burkina’s Foreign Ministry. Burkina Faso has further recalled its ambassador from Ghana for a meeting, a spokesperson at the ministry told Reuters.
Nana Akufo-Addo’s comments came on the heels of a trip to Moscow by Burkina Faso’s Prime Minister, Apollinaire Joachim Kyelem de Tambela, to further strengthen Russia-Burkina relations.
The visit was planned to “consolidate the international community’s efforts in combating the terrorist threat” in the region, said a statement made available on the official website by Russia’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
Earlier this month, a new mining concession was given to Nordgold, a Russian mining company which has been operating in Burkina Faso for more than a decade. A permit for industrial exploration was granted to the Nordgold Yimiougou SA company in Sanmatenga province, said a statement from Burkina Faso’s Council of Ministers.
The four-year agreement is estimated to contribute some $8 billion (£6.5bn) to the state budget. Burkina Faso is one of the largest gold producers on the continent. Nordgold and the Wagner Group are Russian companies, although there is no known connection between them.
For several years Burkina Faso has been struggling to stem jihadi violence that has killed thousands, displaced nearly two million people and made swaths of land inaccessible. Lack of faith in the Burkina Faso government’s ability to contain the jihadi insurgency has led to two coups this 2022.
After the latest coup in September, the Wagner Group was among the first to congratulate the new junta leader, Ibrahim Traore, raising questions about his relationship with Russia and how big a role it played in catapulting him to power. People with close ties to Burkina Faso’s ruling junta said pressure had been mounting on the leader of the first coup, Lieutenant Colonel Paul Henri Sandaogo Damiba, for months to work more closely with Russia, but he had refused.
Reacting to this issue, Foreign Ministry spokesperson, Anne-Claire Legendre, told a news conference that Paris and its European partners continued to be available to cooperate with Burkinabe authorities if they wished and without ambiguity in what she described as a worsening security and humanitarian situation.
“With regard to Wagner, our message is well known; Wagner has distinguished itself in Africa by a policy of plundering, which harms the sovereignty of states,” she said, Reuters reported from Paris. “The Wagner militia has distinguished itself, particularly in Mozambique, the Central African Republic, and Mali; this is obviously known to the Burkinabè authorities.”
The Western nations believe that the presence of Wagner in Africa was harmful as the group exploits mineral resources and commits human rights abuses in countries where it operates.
The pace of Islamic extremist violence is increasing in Burkina Faso and getting closer to the capital, Ouagadougou, which could make the desperate junta welcome support from the Russian mercenaries, said Laith Alkhouri, CEO of Intelonyx Intelligence Advisory. “This could have significant negative implications for Burkina Faso and the region,” he said. “Wagner mercenaries have operated with impunity, and they are unlikely to be held accountable for any human rights violations.”
Most leading global media, including Associated Press (AP), Cable News Network (CNN), Agence France-Presse (AFP), British Broadcasting (BBC), Voice of America (VOA), Reuters, Al Jazeera and many others, well-noted for their comprehensive and verified coverage of geopolitical changes and developments shaping or affecting daily lives in the world, have also informed the public about Wagner Group being hired or deployed in Burkina Faso.
In all the reports, the main message concerns the indelible fact Burkina Faso contracts shadowy Russian mercenaries to fight against jihadist insurgency. Across the Sahel region, neighbours feared the jihadist insurgency might spread further down from Burkina Faso to coastal neighbours, including Ivory Coast, Ghana, Togo and Benin. Nigeria is already consistently fighting Boko Haram and other militant groups.
Associated Press reporter Sam Mednick from Dakar, Senegal, with his colleague Elise Morton from London, wrote in their joint news report that Burkina Faso residents expressed scepticism at the Ghanaian president’s comments and said the junta was trying to diversify partnerships.
“We have the capacity to defend ourselves without outside help if we have the required equipment. Burkina Faso collaborates with states, not with mercenaries,” said Mamadou Drabo, Executive Secretary for Save Burkina, a civil society group that supports the junta.
Edward Lozansky, President of the American University in Moscow and professor of World Politics at Moscow State University, wrote in an email interview that “there has not been too much information about Russia’s activities in Africa, but the Western media is saturated with the scary stories about Russia’s efforts to bolster its presence in at least 14 countries across Africa by building relations with existing rulers, striking military deals, and grooming a new generation of leaders and undercover agents.”
Further to the narratives, Russia has now embarked on fighting “neo-colonialism,” which it considers a stumbling block on its way to regaining a part of the Soviet-era multifaceted influence in Africa. Russia has sought to convince Africans over the past years of the likely dangers of neo-colonial tendencies perpetrated by the former colonial countries and the scramble for resources on the continent. But all such warnings largely seem to fall on deaf ears as African leaders choose development partners with funds to invest in the economy.
Vedomosti, a Russian daily Financial and Business newspaper, reported that Russia is interested in offering Sahel countries military equipment in exchange for exploiting the untapped minerals resources. Worth noting here that Russia, in its strategy on Africa, is reported to be looking into building military bases on the continent.
In late October, President Vladimir Putin participated in the final plenary session of the 19th meeting of the Valdai Discussion Club, the focus was on matters related to the changing geopolitics, the new world order and its future developments. He discussed, at considerable length, so many controversial questions.
According to him, Russia still has friends around the world and mentioned that in central America and Africa, the ‘Russian flags’ are flying everywhere. Putin, along the line, argued that the support for multipolar order largely exists in the Global South, appreciated Africa’s struggle for independence and now rising against growing neo-colonialism. Russia has good relations with African countries, these absolutely unique relations were forged during the years when the Soviet Union and Russia supported African countries in their fight for freedom.
Despite these widely published allegations about Burkina Faso, Russia has demonstrated wide interest in making drastic steps toward penetrating the G5 Sahel in West Africa. The G5 Sahel are Burkina Faso, Chad, Mali, Mauritania and Niger. Russia is broadening its geography of military diplomacy covering poor African countries and especially fragile States that need Russia’s military assistance.
Russian Foreign Ministry has oftentimes explained in statements released on its website that Russia’s military-technical cooperation with African countries is primarily directed at settling regional conflicts and preventing the spread of terrorist threats, and fighting the growing terrorism in the continent.
Over the past several years, strengthening military-technical cooperation has been a key part of the foreign policy of the Russian Federation. Russia has signed a bilateral military-technical cooperation agreement with nearly 14 African countries.
The South African Journal of International Affairs has published a special report on Russia-Africa. It said, in part, heading into the 2023 Russia-Africa Summit in St Petersburg (unless the proposed date and venue change, again), Russia looks more like a ‘virtual great power’ than a genuine challenger to European, American and Chinese influence.
The report titled – Russia’s Private Military Diplomacy in Africa: High Risk, Low Reward, Limited Impact – says that Russia’s renewed interest in Africa is driven by its quest for global power status. Few expect Russia’s security engagement to bring peace and development to countries with which it has security partnerships.
While Moscow’s opportunistic use of private military diplomacy has allowed it to gain a strategic foothold in partner countries successfully, the lack of transparency in interactions, the limited scope of impact and the high financial and diplomatic costs exposes the limitations of the partnership in addressing the peace and development challenges of African host countries, the report says.
The report authored by Ovigwe Eguegu, a Beijing-based Nigerian Researcher on Politics and International Affairs, focused on the use of private military companies to carry out ‘military diplomacy’ in African states, and the main research questions were: What impact is Russia’s private military diplomacy in Africa having on host countries’ peace and development? Why has Russia chosen military diplomacy as the preferred means to gain a foothold on the continent?
His report was based on more than 80 media publications dealing with Russia’s military-technical cooperation in Africa. It interrogates whether fragile African states advance their security, diplomatic and economic interests through a relationship with Russia.
Overcoming the multidimensional problems facing Libya, Sudan, Somali, Mali, and the Central African Republic will require comprehensive peace and development strategies that include conflict resolution and peacebuilding, state-building, security sector reform, and profound political reforms to improve governance and the rule of law – not to mention sound economic planning critical for attracting foreign direct investment needed to spur economic growth.
The United Nations (UN), The African Union (AU), the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) and the entire international community have expressed collective concerns about any use of private mercenary forces instead of well-constituted regional forces approved by regional blocs, as a means to address conflicts in Africa.
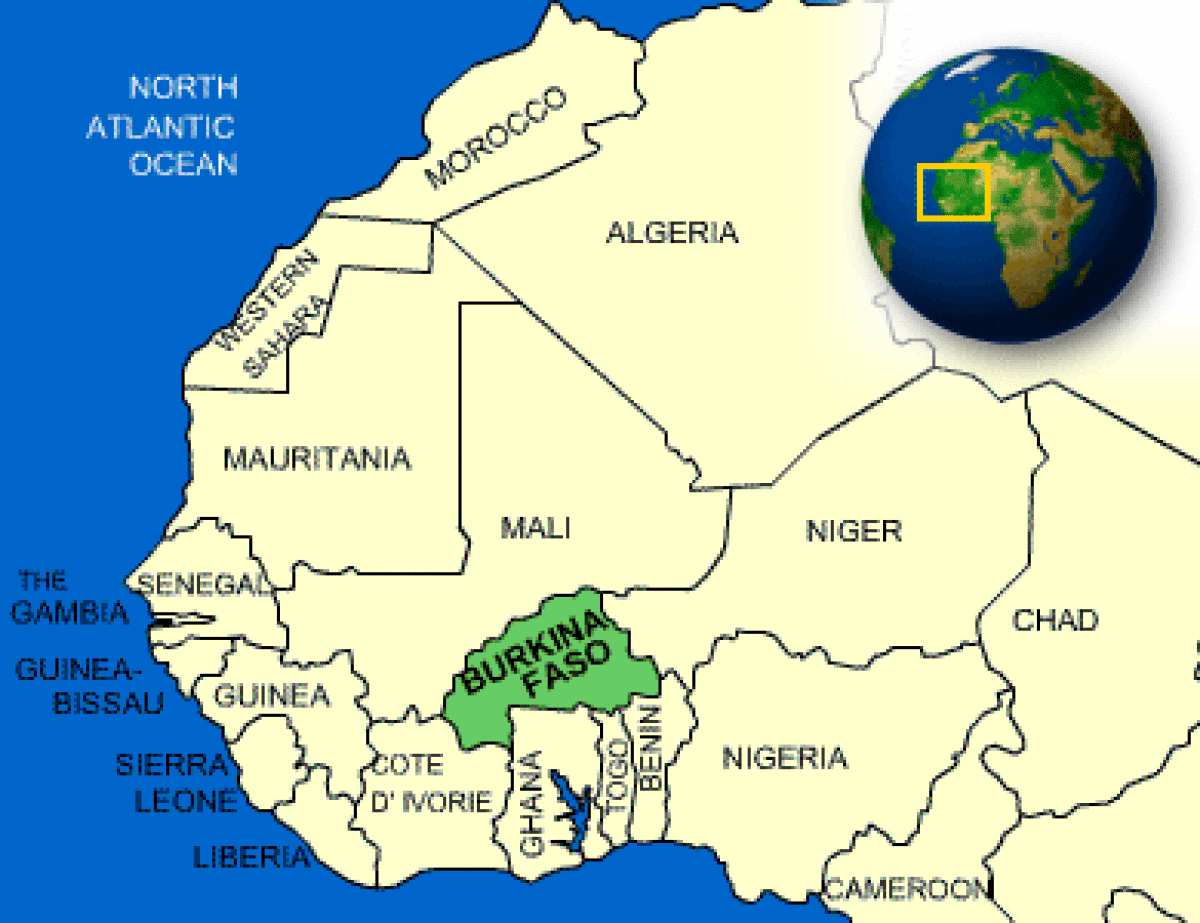
The G5 Sahel are Burkina Faso, Chad, Mali, Mauritania and Niger. And Burkina Faso, per well-known geographical description, is a landlocked country in West Africa with an area of 274,200 km2, bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Ivory Coast to the southwest.
World
Russia Expands Military-Technical Cooperation With African Partners

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
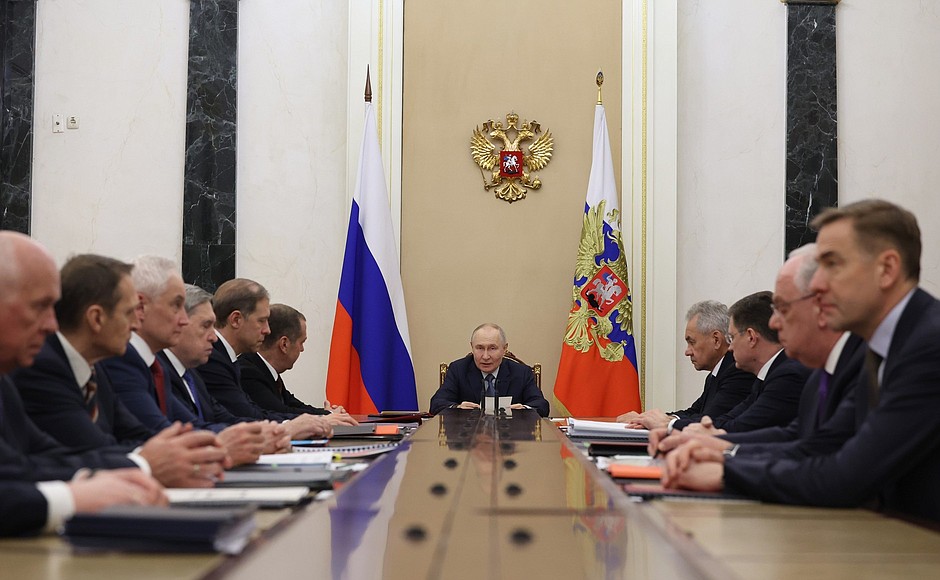
Despite geopolitical complexities, tensions and pressure, Russia’s military arms and weaponry sales earned approximately $15 billion at the closure of 2025, according to Kremlin report. At the regular session, chaired by Russian President Vladimir Putin on Jan. 30, the Commission on Military and Technical Cooperation with Foreign Countries analyzed the results of its work for 2025, and defined plans for the future.
It was noted that the system of military-technical cooperation continued to operate in difficult conditions, and with increased pressure from the Western countries to block business relations with Russia. The meeting, however, admitted that export contracts have generally performed sustainably. Russian military products were exported to more than 30 countries last year, and the amount of foreign exchange exceeded $15 billion.
Such results provide an additional opportunity to direct funds to the modernization of OPC enterprises, to the expansion of their production capacities, and to advanced research. It is also important that at these enterprises a significant volume of products is civilian products.
The Russian system of military-technical cooperation has not only demonstrated effectiveness and high resilience, but has created fundamental structures, which allow to significantly expand the “geography” of supplies of products of military purpose and, thus strengthen the position of Russia’s leader and employer advanced weapons systems – proven, tested in real combat conditions.
Thanks to the employees of the Federal Service for Military Technical Cooperation and Rosoboronexport, the staff of OPC enterprises for their good faith. Within the framework of the new federal project “Development of military-technical cooperation of Russia with foreign countries” for the period 2026-2028, additional measures of support are introduced. Further effective use of existing financial and other support mechanisms and instruments is extremely important because the volumes of military exports in accordance with the 2026 plan.
Special attention would be paid to the expansion of military-technological cooperation and partnerships, with 14 states already implementing or in development more than 340 such projects.
Future plans will allow to improve the characteristics of existing weapons and equipment and to develop new promising models, including those in demand on global markets, among other issues – the development of strategic areas of military-technical cooperation, and above all, with partners on the CIS and the CSTO. This is one of the priority tasks to strengthen both bilateral and multilateral relations, ensuring stability and security in Eurasia.
From January 2026, Russia chairs the CSTO, and this requires working systematically with partners, including comprehensive approaches to expanding military-technical relations. New prospects open up for deepening military-technical cooperation and with countries in other regions, including with states on the African continent. Russia has been historically strong and trusting relationships with African countries. In different years even the USSR, and then Russia supplied African countries with a significant amount of weapons and military equipment, trained specialists on their production, operation, repair, as well as military personnel.
Today, despite pressure from the West, African partners express readiness to expand relations with Russia in the military and military-technical fields. It is not only about increasing supplies of Russian military exports, but also about the purchase of other weapons, other materials and products. Russia has undertaken comprehensive maintenance of previously delivered equipment, organization of licensed production of Russian military products and some other important issues. In general, African countries are sufficient for consideration today.
World
Trump Picks Kevin Warsh to Succeed Jerome Powell as Federal Reserve Chair

By Adedapo Adesanya
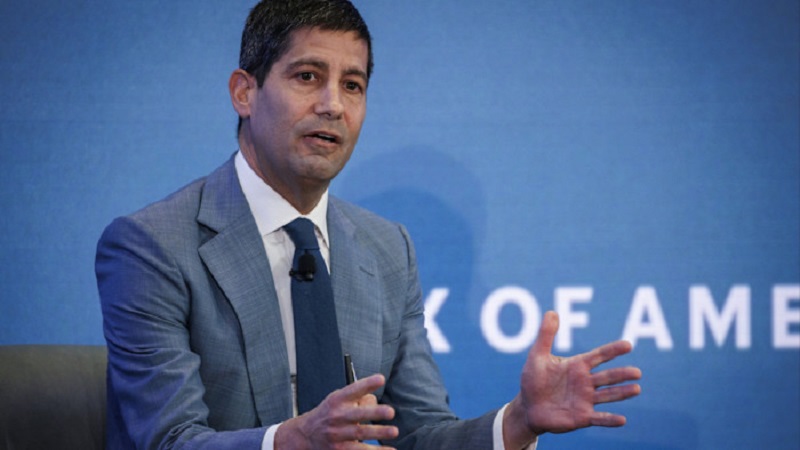
President Donald Trump has named Mr Kevin Warsh as the successor to Mr Jerome Powell as the Federal Reserve chair, ending a prolonged odyssey that has seen unprecedented turmoil around the central bank.
The decision culminates a process that officially began last summer but started much earlier than that, with President Trump launching a criticism against the Powell-led US central bank almost since he took the job in 2018.
“I have known Kevin for a long period of time, and have no doubt that he will go down as one of the GREAT Fed Chairmen, maybe the best,” Mr Trump said in a Truth Social post announcing the selection.
US analysts noted that the 55-year old appear not to ripple market because of his previous experience at the apex bank as Governor, with others saying he wouldn’t always do the bidding of the American president.
If approved by the US Senate, Mr Warsh will take over the position in May, when Mr Powell’s term expires.
Despite having argued for reductions recently, “Warsh has a long hawkish history that markets have not forgotten,” one analyst told Bloomberg.
President Trump has castigated Mr Powell for not lowering interest rates more quickly. His administration also launched a criminal investigation of Powell and the Federal Reserve earlier this month, which led Mr Powell to issue an extraordinary rebuke of President Trump’s efforts to politicize the independent central bank.
World
BRICS Agenda, United States Global Dominance and Africa’s Development Priorities

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
Donald Trump has been leading the United States as its president since January 2025. Washington’s priority is to Make America Great Again (MAGA). Trump’s tariffs have rippled many economies from Latin America through Asian region to the continent of Africa. Trump’s Davos speech has explicitly revealed building a ‘new world order’ based on dominance rather than trust. He has also initiated whirlwind steps to annex Greenland, while further created the Board of Peace, aimed at helping end the two-year war between Israel and Hamas in Gaza and to oversee reconstruction. Trump is handling the three-year old Russia-Ukraine crisis, and other deep-seated religious and ethnic conflicts in Africa.
These emerging trends, at least in a considerable short term, are influencing BRICS which has increased its geopolitical importance, and focusing on uniting the countries in the Global East and Global South. From historical records, BRICS, described as non-western organization, and is loosing its coherence primarily due to differences in geopolitical interests and multinational alignments, and of course, a number of members face threats from the United States while there are variations of approach to the emerging worldwide perceptions.
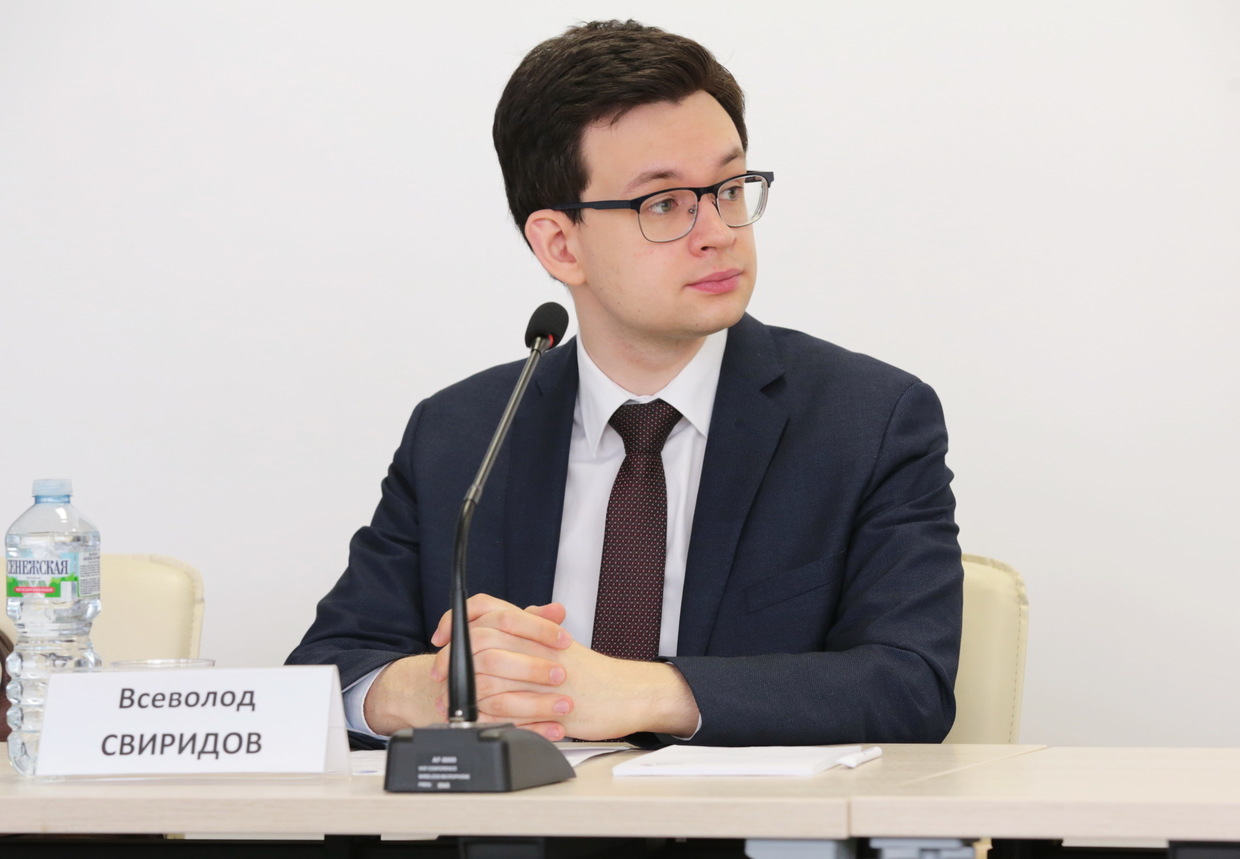
In this conversation, deputy director of the Center for African Studies at Moscow’s National Research University High School of Economics (HSE), Vsevolod Sviridov, expresses his opinions focusing on BRICS agenda under India’s presidency, South Africa’s G20 chairmanship in 2024, and genegrally putting Africa’s development priorities within the context of emerging trends. Here are the interview excerpts:
What is the likely impact of Washington’s geopolitics and its foreign policy on BRICS?
From my perspective, the current Venezuela-U.S. confrontation, especially Washington’s tightened leverage over Venezuelan oil revenue flows and the knock-on effects for Chinese interests, will be read inside BRICS as a reminder that sovereign resources can still be constrained by financial chokepoints and sanctions politics. This does not automatically translate into BRICS taking Venezuela’s side, but it does strengthen the bloc’s long-running argument for more resilient South-South trade settlement, diversified energy chains, and financing instruments that reduce exposure to coercive measures, because many African and other developing economies face similar vulnerabilities around commodities, shipping, insurance, and correspondent banking. At the same time, BRICS’ expansion makes consensus harder: several members maintain significant ties with the U.S., so the most likely impact is a technocratic push rather than a loud political campaign.
And highlighting, specifically, the position of BRICS members (South Africa, Ethiopia and Egypt, as well as its partnering African States (Nigeria and Uganda)?
Venezuela crisis urges African members to demand that BRICS deliver usable financial and trade tools. For South Africa, Ethiopia, and Egypt, the Venezuela case is more about the precedent: how quickly external pressure can reshape a country’s fiscal room, debt dynamics, and even investor perceptions when energy revenues and sanctions compliance collide. South Africa will likely argue that BRICS should prioritize investment, industrialization, and trade facilitation. Ethiopia and Egypt, both debt-sensitive and searching for FDI, will be especially attentive to anything that helps de-risk financing, while avoiding steps that could trigger secondary-sanctions anxieties or scare off diversified investors.
Would the latest geopolitical developments ultimately shape the agenda for BRICS 2026 under India’s presidency?
India’s 2026 chairmanship is already framed around “Resilience, Innovation, Cooperation and Sustainability,” and Venezuela’s shock (paired with broader sanction/market-volatility lessons) will likely sharpen the resilience part. From an African perspective, that is an opportunity: South Africa, Ethiopia, and Egypt can press India to translate the theme into deliverables that matter on the ground: food and fertilizer stability, affordable energy access, infrastructure funding. India, in turn, has incentives to keep BRICS focused on economic problem-solving rather than becoming hostage to any single flashpoint. So the Venezuela episode may function as a cautionary case study that accelerates practical cooperation where African members have the most to gain. And I would add: the BRICS agenda will become increasingly Africa-centered simply because Africa’s weight globally is rising, and recent summit discussions have repeatedly highlighted African participation as a core Global South vector. South Africa’s G20 chairmanship last year explicitly framed around putting Africa’s development priorities high on the agenda, further proves this point.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism9 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn