Economy
Despite the Infections, Africa Without Monkeypox Vaccines
By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
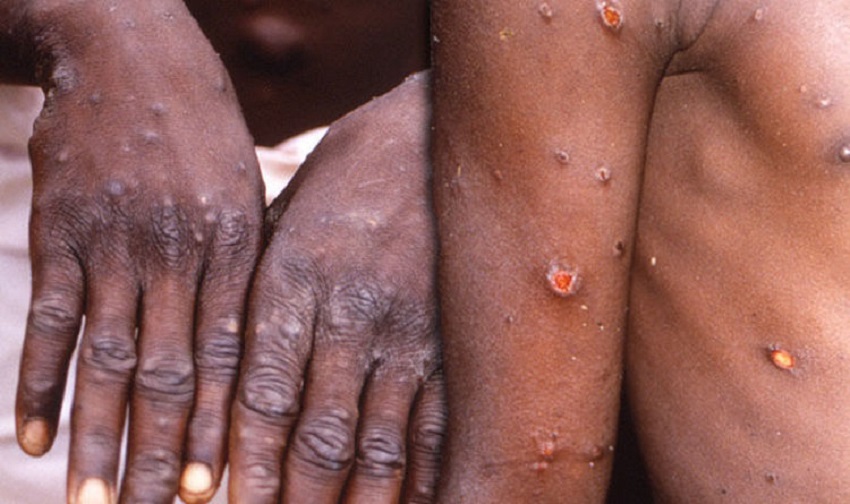
The World Health Organization (WHO) has declared monkeypox a new global health emergency after 20,000 cases were reported in 77 countries. Some 75 people have died in the 11 African countries where the disease was recorded, according to the latest reports in late July. It said monkeypox is an “extraordinary” situation that qualifies as a global health emergency.
Despite these few deaths last month and signs that it would spread further, Africa is fighting monkeypox without vaccine the same as it has been with Covid-19. A surge in monkeypox infections has particularly been reported since early May outside the West and Central African countries where the disease has long been endemic.
The vast majority of deaths due to monkeypox have been registered on the African continent. Africa remains the only part of the world with no doses of the vaccine, according to the Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Let us get vaccines onto the continent,” acting head of the African Centre for Disease Control, ACDC, Ahmed Ogwell, said in a weekly media briefing pointing to another instance of 1.3 billion people on the continent without access to a vaccine, as in the Covid-19 pandemic.
Reports said that monkeypox has been established in parts of central and west Africa for decades, but it was not known to spark large outbreaks beyond the continent or to spread widely among people until May when authorities detected dozens of epidemics in Europe, North America and elsewhere.
Ogwell said the Africa CDC has engaged with international partners in attempts to obtain vaccines, and while he said “good news” is expected in the coming days, “we cannot be able to give you a timeline.”
Even doses of the smallpox vaccine, which has shown effectiveness against monkeypox, are not available in Africa, Ogwell said. “The solutions need to be global in nature,” he said, in a warning to the international community. “If we’re not safe, the rest of the world is not safe.”
The Covid-19 pandemic and the global hoarding of vaccine doses were a jolt to African leaders, who quickly joined together in an unprecedented effort to obtain doses and establish the production of more vaccines on the continent.
WHO’s Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said there were about 16 million doses of approved vaccine available, but only in bulk, so it would take several months to get them into vials. His organization is currently urging countries with stockpiles to share vaccines while supply is constrained. It, however, estimates that between 5 million and 10 million doses of vaccine will be needed to protect all high-risk groups.
It has said it is creating a vaccine-sharing mechanism for protection against monkeypox, but the organization has released few details, so there’s no guarantee that African countries will get priority. No countries have yet agreed to share any vaccines with the health organization.
WHO, however, warned against discrimination. “A failure to act will have grave consequences for global health,” Lawrence Gostin, the director of the WHO Collaborating Center on National and Global Health Law, said on Twitter.
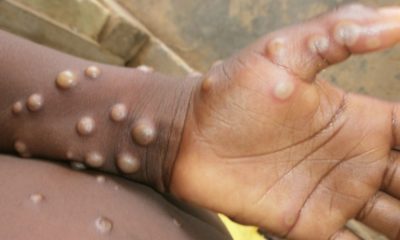
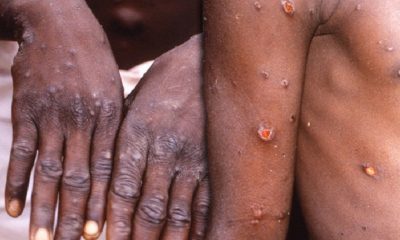
Health officials have emphasized that monkeypox can infect anyone in close contact with a patient or their contaminated clothing or bedsheets. Researchers are still exploring how it spreads but believe it’s mainly through close, skin-to-skin contact and through contact with bedding and clothing that touched an infected person’s rash or body fluids.
Another report also pointed to the fact that monkeypox has been a globally neglected public health problem in parts of Africa for decades, but cases began to be reported outside countries where it is endemic in May. It generally causes mild to moderate symptoms, including fever, fatigue and painful skin lesions that resolve within a few weeks.
In Africa, monkeypox mainly spreads to people by infected wild animals like rodents in limited outbreaks that typically have not crossed borders. In Europe, North America and elsewhere, however, monkeypox is spreading among people with no links to animals or recent travel to Africa. In the U.S. and Europe, the vast majority of infections have happened in men who have sex with men, though health officials have stressed that anyone can contract the virus.
Economy
Naira Retreats to N1,366.19/$1 After 13 Kobo Loss at Official Market

By Adedapo Adesanya
The value of the Naira contracted against the United States Dollar on Friday by 13 Kobo or 0.01 per cent to N1,366.19/$1 in the Nigerian Autonomous Foreign Exchange Market (NAFEX) from the previous day’s value of N1,366.06/$1.
According to data from the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN), the Nigerian currency also depreciated against the Pound Sterling in the same market window yesterday by N2.37 to N1,857.75/£1 from the N1,855.38/£1 it was traded on Thursday, and further depleted against the Euro by 57 Kobo to close at N1,612.52/€1 versus the preceding session’s N1,611.95/€1.
In the same vein, the exchange rate for international transactions on the GTBank Naira card showed that the Naira lost N8 on the greenback yesterday to N1,383/$1 from the previous day’s N1,375/$1 and at the black market, the Nigerian currency maintained stability against the Dollar at N1,450/$1.
FX analysts anticipate this trend to persist, primarily influenced by increasing external reserves, renewed inflows of foreign portfolio investments, and a reduction in speculative demand.
In the short term, stability in the FX market is expected to continue, supported by policy interventions and improving market confidence.
Nigeria’s foreign reserves experienced an upward trajectory, increasing by $632.38 million within the week to $46.91 billion from $46.27 billion in the previous week.
The Dollar appreciation this week appears to be largely technical, serving as a correction to the substantial losses experienced from mid- to late January.
Meanwhile, the cryptocurrency market slightly appreciated, with Bitcoin (BTC) climbing near $68,000, up nearly 5 per cent since hitting $60,000 late on Thursday after investor confidence in crypto’s utility as a store of value, inflation hedge, and digital currency faltered.
The sell-off extended beyond crypto, with silver plunging 15 per cent and gold sliding more than 2 per cent. US stocks also fell.
The latest recoup saw the price of BTC up by 4.7 per cent to $67,978.96, as Ethereum (ETH) appreciated by 6.3 per cent to $2,021.10, and Ripple (XRP) surged by 9.5 per cent to $1.42.
In addition, Solana (SOL) grew by 7.3 per cent to $85.22, Cardano (ADA) added 6.1 per cent to trade at $0.2683, Dogecoin (DOGE) expanded by 5.4 per cent to $0.0958, Litecoin (LTC) rose by 5.2 per cent to $53.50, and Binance Coin (BNB) jumped by 2.3 per cent to $637.79, while the US Dollar Tether (USDT) and the US Dollar Coin (USDC) traded flat at $1.00 each.
Economy
Oil Prices Climb on Worries of Possible Iran-US Conflict

By Adedapo Adesanya
Oil prices settled higher on Friday as traders worried that this week’s talks between the US and Iran had failed to reduce the risk of a military conflict between the two countries.
Brent crude futures traded at $68.05 a barrel after going up by 50 cents or 0.74 per cent, and the US West Texas Intermediate (WTI) crude futures finished at $63.55 a barrel due to the addition of 26 cents or 0.41 per cent.
Iran and the US held negotiations in Muscat, the capital of Oman, on Friday to overcome sharp differences over Iran’s nuclear programme.
It was reported that the talks had ended with Iran’s foreign minister saying negotiators will return to their capitals for consultations and the talks will continue.
Regardless, the meeting kept investors anxious about geopolitical risk, as Iran wanted to stick to nuclear issues while the US wanted to discuss Iran’s ballistic missiles and support for armed groups in the region.
Any escalation of tension between the two nations could disrupt oil flows, since about a fifth of the world’s total consumption passes through the Strait of Hormuz between Oman and Iran.
Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Kuwait and Iraq export most of their crude via the strait, as does Iran, which is a member of the Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC).
According to Reuters, Iran objected to the presence of any US Central Command (CENTCOM) or other regional military officials, saying that would jeopardise the process.
The current confrontation was sparked by more than two weeks of unrest in Iran that saw authorities launch a deadly crackdown that killed thousands of civilians and shocked the world. As reports of the deaths trickled out of Iran, US President Donald Trump threatened to strike Iran if any of the tens of thousands of protesters arrested were executed.
Meanwhile, Kazakhstan’s planned oil exports could fall by as much as 35 per cent this month via its main route through Russia, as the country’s top oil company, Tengiz oilfield, slowly recovers from fires at power facilities in January.
ING analysts have pointed out Iran’s neighbour, Iraq, and a disagreement with the US as another bullish factor for oil prices. It seems Iraqi politicians favour Mr Nouri al-Maliki as the country’s next Prime Minister, but the US thinks Mr al-Maliki is too close to Iran. President Trump has already threatened the oil producer with consequences if he emerges as PM.
Economy
Adedeji Urges Nigeria to Add More Products to Export Basket

By Adedapo Adesanya
The chairman of the Nigeria Revenue Service (NRS), Mr Zacch Adedeji, has urged the country to broaden its export basket beyond raw materials by embracing ideas, innovation and the production of more value-added and complex products
Mr Adedeji said this during the maiden distinguished personality lecture of the Faculty of Administration, Obafemi Awolowo University (OAU), Ile-Ife, Osun State, on Thursday.
The NRS chairman, in the lecture entitled From Potential to Prosperity: Export-led Economy, revealed that Nigeria experienced stagnation in its export drive over three decades, from 1998 to 2023, and added only six new products to its export basket during that period.
He stressed the need to rethink growth through the lens of complexity by not just producing more of the same stuff, lamenting that Nigeria possesses a high-tech oil sector and a low-productivity informal sector, as well as lacking “the vibrant, labour-absorbing industrial base that serves as a bridge to higher complexity,” he said in a statement by his special adviser on Media, Dare Adekanmbi.
Mr Adedeji urged Nigeria to learn from the world by comparative studies of success and failure, such as Vietnam, Bangladesh, Indonesia, South Africa, and Brazil.
“We are not just looking at numbers in a vacuum; we are looking at the strategic choices made by nations like Vietnam, Indonesia, Bangladesh, Brazil, and South Africa over the same twenty-five-year period. While there are many ways to underperform, the path to success is remarkably consistent: it is defined by a clear strategy to build economic complexity.
“When we put these stories together, the divergence is clear. Vietnam used global trade to build a resilient, complex economy, while the others remained dependent on natural resources or a single low-tech niche.
“There are three big lessons here for us in Nigeria as we think about our roadmap. First, avoiding the resource curse is necessary, but it is not enough. You need a proactive strategy to build productive capabilities,” he stated, adding that for Nigeria, which is at an even earlier stage of development and even less diversified than these nations, the warning is stark.
“Relying solely on our natural endowments isn’t just a path to stagnation; it’s a path to regression. The global economy increasingly rewards knowledge and complexity, not just what you can dig out of the ground. If we want to move from potential to prosperity, we must stop being just a source of raw materials and start being a source of ideas, innovation, and complex products,” the taxman stated.
He added that President Bola Tinubu has already begun the difficult work of rebuilding the economy, building collective knowledge to innovate, produce, and build a resilient economy.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism9 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn