Feature/OPED
Alliance of Sahel States Stepping Forward With Common Economic and Security Aspirations
By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
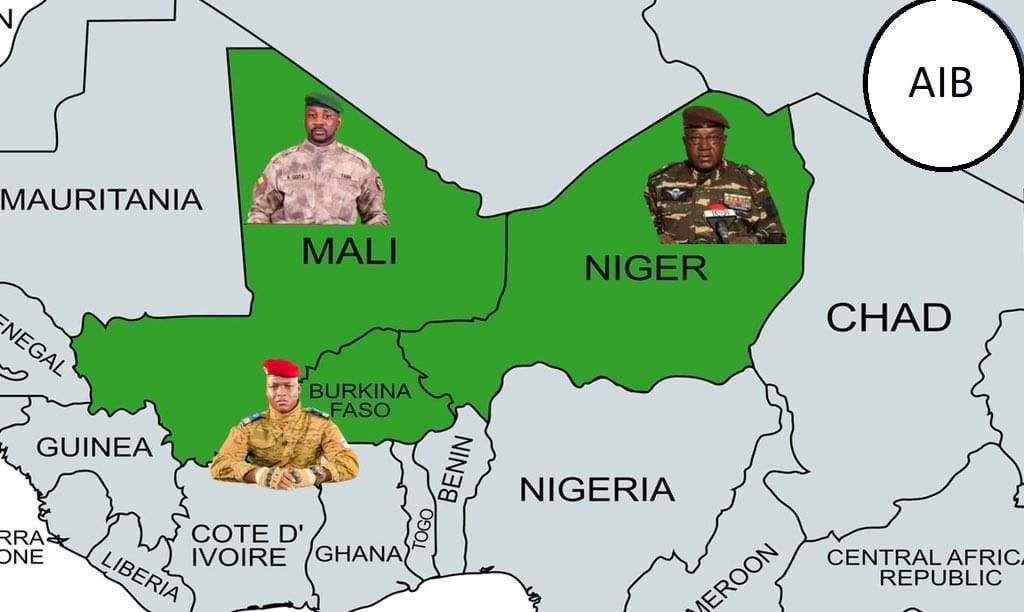
On January 29, 2025, within rapidly geopolitical changes in West African region, three landlocked countries namely Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger, members of the newly created Alliance of Sahel States (AES), declared their withdrawal from the most influential bloc – Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS).
The first implication was that 2025 marks the 50th year of the establishment of ECOWAS. Undoubtedly, it will simultaneously remain in history of the Alliance of Sahel States (AES) as the period of their exit from the 50-year-old regional bloc, established by the Treaty of Lagos in May 1975.
Perhaps, ECOWAS has been fractured with uncertain future. On the other side, the AES will seemingly grow in strength as republics of Côte d’Ivoire, Chad, Ghana and Senegal have shown signs of unswerving support for the newly-created security organisation in the region. Despite broader criticisms and emerging challenges, AES has the capacity to forge expected integration and to tackle existing diverse obstacles while navigating further for strategic external collaboration.
The Alliance of Sahel States (AES) was established on September 16, 2023 with the signing of the Liptako-Gourma Charter by the States of Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger. These three countries share the cross-border region of West Africa and the Sahel called “Liptako-Gourma” from which it derives the symbolic name of the Charter. It is a collective defense bloc aimed at countering any military intervention or any external threat including terrorism and with the ambition of economic integration.
Since last year, the AES has focused on structuring projects in the fields of energy, infrastructure, transport and food security. The trio aims to create an economic and monetary union, as well as its own currency which should be based on the natural resources of the member countries in the Confederation.
The collective initiatives undeniably are at the formative stage, fostering consciousness on structuring operations and functional directions notwithstanding the multiple roadblocks from ECOWAS. That however, worthy to indicate here that particular concern emerging from different regional organisations and the African Union underscores the rising assertiveness of AES.
At a glance, Burkina Faso is a driving force, while Mali and Niger have, in practical sense, shown the pathways for evolutionary influence as well as shaping a codified dynamism to hold the alliance in form towards achieving its primary security objectives and economic development aspirations.
For over a year, their joint effective strategy has been working, and the collective divorce from ECOWAS late January 2025 was an irreversible factor, that was based on the fact that ECOWAS has unprecedented weaknesses, combined with historical record-breaking failure in its mandate to maintain regional security.
In short, the rising insecurity situation has undermined regional cooperation, set the stage for dissatisfaction among the member states. With the sudden withdrawal from the 15-member ECOWAS, it is understandable Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger have attained the collective independence, and prepared to form this new forward-looking regional partnership bloc popularly referred to AES.
ECOWAS and African Union’s Reactions
Reactions from both the ECOWAS and African Union (AU) were ‘business as usual’ characterized by official administrative statements. Late January after the three French-speaking West African States officially exited, the Peacekeeping and Regional Security Commission of ECOWAS said the remaining members tentatively had agreed to ‘keep ECOWAS doors open’ by recognizing national passports and identity bearing the bloc’s logo from the countries, to continue trade under existing regional agreement, and to continue diplomatic cooperation with the countries.
The statement noted that the withdrawal of Burkina Faso, the Republic of Mali and the Republic of Niger from ECOWAS has become effective on 29th January 2025. While the Regional Security Commission has set up a structure to facilitate discussions on these modalities with each of the three countries, its official statement categorically noted the following:
- a) recognize National passports and identity cards bearing ECOWAS logo held by the citizens of Burkina Faso, the Republic of Mali and the Republic of Niger, until further notice.
- b) continue to treat goods and services coming from the three countries in accordance with the ECOWAS Trade Liberalization Scheme (ETLS) and investment policy.
- c) allow citizens of the three affected countries to continue to enjoy the right of visa free movement, residence and establishment in accordance with the ECOWAS protocols until further notice.
- d) provide full support and cooperation to ECOWAS officials from the three countries in the course of their assignments for the Community.
In addition to above-mentioned developments, the Political, Peace and Security Council (PSC) of the African Union (AU) headquartered in Addis Ababa, capital of Ethiopia, has also expressed high-level concern over the deteriorating standing of ECOWAS as a regional bloc and the security situation in West Africa region.
The AU, of course, raised an unequivocal condemnation of the final decision and withdrawal of Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger from ECOWAS. But factually, the AU’s reaction was distinctively similar, in terms of administrative and bureaucratic wording of the official statement, mostly for the sake of filling in the space, under-estimated the long-term repercussions and impact on the developments in the region.
Reaffirming solidarity by the African Union with ECOWAS in enforcing its mandate and high-lightening the importance durable peace, security, and sustainable development as enshrined or stipulated in the documents. The AU employed such phrases as ‘respecting the sovereignty, independence, unity and territorial integrity’ contained their established documents of ECOWAS.
Endowed Natural Resources
In any case, understanding economic potentiality and sustainability is crucial at this stage. The economic potential is huge, as Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger put together holds tremendous untapped resources.
According to various sources, Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger territorially share borders together and are landlocked countries in West Africa, in the Sahel region. They are geographically bio-diverse, which includes plentiful reserves of gold, manganese, copper and limestone, and other invaluable natural resources. The land mass is huge for traditional agriculture, but public infrastructures are poorly developed across the region of their location. Predominantly, the system of state governance combined with gross lack of finance are the main obstacles to sustaining development.
As known in these African countries, the French adopted a form of indirect rule, allowing existing native structures to continue to exist within the colonial framework of governance. But now reawakening to the neo-colonial administration and opaque system of government control have a significant impact on current political development. Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger, to some considerable extent have the human capital.
The 2024 estimates of population have revealed that Burkina Faso has 22.5 million, Mali which is the eighth-largest country in Africa, has approximately 21.9 million people while Niger has 26.5 million. The UN Development Program Report (2024) ranked Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger as the Sahel countries with the lowest category of development index in the world.
The future growth may only be sustained by the exploitation of natural resources and that must necessarily be tied to the development of the economy, building infrastructure and focus on reducing poverty in these French-speaking West African countries.
Future Economic Implications
AES has the capacity and commitment to address development shortfalls. Several development initiatives were already taken in this direction to stimulate the economic sectors, particularly in the priority areas of agriculture, livestock, health, and energy infrastructure.
Burkina Faso currently stepping efforts in agricultural sector, while Mali and Niger restructuring roles of foreign players in exploiting mineral resources suc as gold and uranium. This allows greater economic and political autonomy in order to strengthen their sovereignty. Perhaps, they will further have the opportunity to pursue more economic policies in line with the existing realities dictated by the political environment and to bolster aspirations of maintaining stability across their landlocked region.
Obviously, the AES is getting oriented towards multi-polarity, which is intended to be a more inclusive and concerted approach, where different countries and regions work together to find common solutions. By pursuing the principles of the multipolarity, world, the AES could engage in pragmatic win-win partnerships to advance their interests for the purposes of economic development and growth, and stability.
The AES collective pledge further requires making collaborative efforts and, in a systematic manner, work towards sustainable development, find better chances for practical solutions to existing economic deficiencies. Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger have to adopt strategic positions, first, in West Africa, and generally in Africa.
Feature/OPED
Billions in Nigeria’s Reserves, But Where is the Growth?

By Blaise Udunze
The moment the Governor of the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN), Olayemi Cardoso, recently announced that Nigeria’s foreign reserves had inched to $49 billion as of February 5, 2026, the news was received with understandable enthusiasm.
He described the development as “a very important statistic” when speaking at the 2nd National Economic Council (NEC) Conference in Abuja, while noting a 4.93 per cent increase and emphasising that Nigeria had moved from being a net seller to a net buyer of foreign exchange. He cited improved remittance inflows, a narrowing gap between official and parallel market exchange rates, and greater confidence in the naira as evidence that reforms were working.
On the surface, the numbers are reassuring. The premium between official and parallel market rates has reportedly fallen to under 2 per cent. Remittances have improved following deliberate engagement with the diaspora. Nigerians can increasingly rely on naira cards for international transactions. It can be said that investors are earning positive real returns, banks are recapitalising, equity markets are recovering, and macroeconomic indicators such as GDP growth of 3.98 per cent, a current account surplus of $3.42 billion in the third quarter of 2025, and a reported moderation in inflation to 15.15 per cent are presented as signs of stabilisation.
So far, beyond the celebratory headlines lies a deeper and more consequential question, in the form of, what does the fixation on foreign reserves really tell us about the underlying strength of the Nigerian economy?
History and economic logic suggest that when a central bank repeatedly elevates foreign reserves as a central achievement, it often signals that the true engines of growth are either weak or underdeveloped. Strong reserves are not built through declarations, press conferences, or defensive monetary manoeuvres. They are built through systems that generate value, exports, productivity, and trust. Countries with durable reserve positions did not chase reserves; they built economies that produced them naturally.
This distinction matters greatly for Nigeria.
Foreign reserves are important, but they are not a development strategy. They are a buffer, not a foundation. They are an outcome of economic vitality, not a substitute for it. When reserves become the centrepiece of economic storytelling, there is a risk that policymakers mistake statistical comfort for structural strength.
Even Nigeria’s celebrated $49 billion reserve figure requires closer scrutiny, which appears to be more of sexing up the figures. Gross reserves make headlines, but net usable reserves are what protect a currency in moments of stress. A significant portion of reported reserves is often tied up in swaps, forward commitments, and external obligations. When these are stripped out, the net buffer available to defend the naira is far smaller than the headline figure suggests. The gap between gross and net reserves is too large to justify unqualified confidence about currency stability, especially in an economy that remains import-dependent and structurally fragile.
The danger of over-fixating on reserves is not unique to Nigeria, but it is particularly acute here because of the economy’s narrow production base, which subliminally calls for sexing up the figures. Despite decision-makers prematurely applauding the reserves’ growth, the apex bank must rethink its approach. The reserves are not generated through production-based or stronger export means but rather largely from borrowing (sales of Eurobonds) or through government loans, which come in as dollars to the CBN that temporarily boost dollar inflows. This points to the fact that Nigeria still exports little beyond crude oil, imports most manufactured goods, and relies heavily on volatile capital inflows. In such a context, reserves require constant defence rather than organic replenishment. Tight monetary policy, FX restrictions, and moral persuasion may buy time, but they do not solve the underlying problem of insufficient foreign exchange generation.
By contrast, countries with strong reserve positions followed a very different path. Unlike Nigeria, countries like Saudi Arabia, with foreign reserves of about $410 billion, paired subsidy reforms with visible reinvestment in infrastructure, social welfare, and alternative energy systems. Indonesia, with reserves of roughly $153 billion, combined fiscal reforms with expanded social assistance and a shift toward targeted household support, ensuring that reform pain was offset by tangible benefits. Reserves are mainly meant to grow from productive economic activities like Singapore, whose reserves stood at approximately $397 billion at the end of 2025, as it built its position through decades of disciplined industrial policy, export competitiveness, domestic savings, and institutional credibility. In all these cases, reserves were not the objective; they were the by-product of deliberate economic architecture.
In most successful developmental states, public expenditure plays a catalytic role in growth. Unlike Nigeria’s, most countries’ expenditures It crowds in private investment, expand infrastructure, lower transaction costs, and build productive capacity. Over time, this deepens domestic capital formation, drives industrial productivity, supports export diversification, and strengthens external balances. Nigeria’s recent experience, however, appears to diverge from this model.
Rather than deploying fiscal policy aggressively to stimulate productive capacity, government financing has increasingly leaned on the domestic capital market. While this approach has attracted foreign capital inflows, much of this capital has been short-term portfolio investment into treasury bills, government bonds, and money market instruments. A fact that is well established is that these inflows can temporarily stabilise liquidity and support the exchange rate, but their multiplier effects on the real economy are minimal. In the absence of strong productive investment for a country like Nigeria, the giant of Africa, this pattern resembles constructing a skyscraper on weak foundations, which is impressive in appearance, but structurally fragile.
This fragility is evident in the broader economy. Especially this kind of growth is associated with Nigeria in 2025, which portrays a country that is increasingly survival-led rather than productivity-driven. The underlying challenge today is that households, small businesses and even industrial firms are left with no option but to adapt to rising costs and shrinking real incomes by expanding low-productivity activities. Industrial depth remains shallow. Domestic capital accumulation is weak. Export capability outside oil is limited. Labour productivity continues to lag. These are not the conditions under which reserves become self-sustaining.
This is why the central bank’s strategic focus must extend far beyond reserve accumulation. If the CBN genuinely seeks to grow the economy and build reserves sustainably, it must prioritise the mechanisms that generate foreign exchange organically. The most important of these is productive credit expansion. Central banks around the world are expected to shape economies not only through interest rates but through the direction of credit. Prolonged monetary tightness may suppress inflation at the margins, but it also suppresses investment, output, and employment, as is the case in Nigeria. Contrary to Nigeria’s lived experience, countries that successfully built reserves deliberately channelled affordable, long-term credit to manufacturing, agro-processing, and export-oriented sectors, but the same cannot be said of Nigeria. Nigeria cannot tighten its way into prosperity.
Closely linked to this is the need for a serious export-led industrial strategy. Nigeria’s trade challenge is often framed as an import problem, but it is fundamentally an export deficiency. Banning imports or rationing foreign exchange does not create competitiveness. Export growth does. Sustainable reserves come from selling more to the world than one buys, particularly in manufactured goods and tradable services. Oil exports may still matter, but they are volatile and finite. Value-added exports are repeatable, scalable, and employment-intensive.
Exchange rate stability, too, must be approached through supply rather than fear. Currency pressure reflects insufficient FX supply more than excessive demand. Strengthening real economic fundamentals, which calls for expanding non-oil exports, formalising remittance channels, and attracting long-term productive capital, will do more to stabilise the naira than administrative controls mixed with sexing up figures. Predictability matters, and for this reason, investors may tolerate risk, but they may be forced to withdraw when policies are inconsistent.
Infrastructure financing is another critical missing link. No economy exports competitively without reliable power, efficient transport, and functional logistics. While infrastructure is often treated as a purely fiscal responsibility, central banks in many emerging economies have played catalytic roles in financing industrial infrastructure. Supporting industrial parks, logistics hubs, processing zones, and energy projects would address one of the root causes of Nigeria’s weak export performance and fragile reserves.
Equally important is the mobilisation of domestic savings. Strong reserves are easier to build when a country funds its development internally. One of its domestic savings that has been lying fallow is that Nigeria’s pension and insurance funds remain under-deployed in productive sectors. For a country that is truly angling for growth and with the right regulatory frameworks, these long-term pools of capital can support infrastructure, manufacturing, and export industries, reducing dependence on volatile foreign inflows.
Inflation control must also be re-examined. This is one grey area with Nigeria’s system as its inflation is largely cost-driven, fueled by energy costs, logistics bottlenecks, FX shortages and insecurity. It must be understood that addressing it solely through interest rate hikes risks shrinking output in terms of economic production and growth while prices remain elevated, as is the case today. The policy-makers in Nigeria must understand that supply-side interventions that reduce production costs and stabilise input availability are more likely to deliver durable price stability and stronger reserves than monetary tightening, especially in the case of raising interest rates alone.
The CBN has projected that GDP growth could reach 4.49 per cent, inflation could moderate to 12.9 per cent, and reserves could exceed $50 billion. These projections are presented as evidence of consolidation. Yet many economists caution that macroeconomic stability, while necessary, is not synonymous with sustainable growth. Even if the provided official statistics may suggest that the economy is improving, the reality is that the majority of the populace are not experiencing the benefits, as is the case in Nigeria, where the unemployment rate is high, wages aren’t keeping up with costs, and many households are barely making ends meet.
To further drive the point, Gbenga Olawepo-Hashim has argued that the true measure of economic performance is not headline figures but the living conditions of citizens. This is to say that economic growth is meaningless if it doesn’t create jobs, purchasing power, and opportunity, cannot sustain political or social stability, nor can foreign reserves grow sustainably.
Going forward, it is advisable that the foreign reserves, therefore, should be read for what they are, as a reflection of deeper economic health. When production expands, exports diversify, infrastructure improves, capital deepens, and trust is restored, reserves grow quietly and sustainably. When these foundations are weak, reserves require constant defence and loud celebration.
Today, Nigeria is at a critical point where it must make a major decision, either the choice is between managing reserves endlessly or building an economy that earns them effortlessly. The former offers headlines and is unsustainable. The latter offers prosperity, and it is sustainable in the long term.
Blaise, a journalist and PR professional, writes from Lagos and can be reached via: [email protected]
Feature/OPED
Inside Nigeria’s Telecom Exploitation Crisis Draining Household Budgets

By Blaise Udunze
For about a year now, millions of Nigerians relying on the internet to make a living have been groaning over the manipulation of airtime and data consumption that has turned into a relentless drain on household budgets. Painfully, individuals and businesses buying airtime or data increasingly feel less like paying for a service and more like entering a wager whose odds are permanently stacked against the consumer. Around the nooks and crannies of the country, across cities and rural communities alike, subscribers tell the same weary story of data that evaporates mysteriously, airtime consumed faster than reason allows, and customer care responses that sound rehearsed rather than responsive. The majority will agree that this collective frustration is not a coincidence, nor is it merely the product of careless smartphone use, because others might argue that there are several technical factors inducing rapid mobile data usage. Leave it or take it, it is the outcome of a broken ecosystem where multinational telecom companies wield immense power in an environment marked by weak institutional checks, limited transparency, and a population stretched thin by economic hardship.
The recent 50 per cent upward adjustment of telecom tariffs, later revised in policy conversations to 35 per cent, has intensified this tension, though it is not justifiable as exploitation. For millions of Nigerians already battling inflation, currency volatility, and shrinking purchasing power, the hike landed not as an economic necessity but as an additional burden. When communication costs begin to claim up to 15 per cent or, in some cases, nearly 30 per cent of the national minimum wage, something fundamental has gone wrong. Access to communication is no longer a luxury; it is the infrastructure of modern survival. Yet the price Nigerians are now paying for this access is becoming socially and economically unsustainable.
A published report showed that as of January 2025, statistics from the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC) disclosed that there were 141 million Internet users via the narrowband (GSM), while broadband penetration stood at 45 per cent. Data consumption has increased to 1,000,930.6 terabytes.
A review of the multinational telecom companies indicated that the new tariff for MTN’s revised data prices showed the 1.8GB monthly plan now goes for N1,500, against the previous 1.5GB plan priced at N1,000. The 20GB plan has been adjusted to N7,500, up from N5,500, while the 15GB plan now costs N6,500, rising from N4,500.
Under this new pricing regime, the same would be said of Airtel as it has replaced its cheapest monthly data plan of 1.2GB plan for N1,000 with 2GB plan for N1,500. For 3GB for N2, 000 (from 1.5GB at N1, 200), 4GB for N2, 500, formerly 3GB at N1, 500, and 8GB for N3, 000 (formerly 4.5GB at N2, 000). Other adjustments include 10GB for N4, 000 (formerly 6GB at N2, 500), 13GB for N5, 000 (from 10GB at N3, 000), 18GB for N6, 000 (formerly 15GB at N4, 000) and 25GB for N8, 000 as this replaces 18GB at N5, 000.
Further, the 75GB monthly bundle, which costs N16, 000 has been renamed as plan, costing N20, 000; 100GB for two months, costing N20, 000 have been upgraded to 150GB to cost N40, 000, while 400GB for three months, which cost N50,000 is now upgraded to 480GB to cost N120,000.
The bubble burst was further complicated by a tariff increase, which is the resurgence of widespread complaints about rapid data depletion. The issue is that businesses, students, families, and professionals are now raising alarms that data bundles, which previously lasted weeks, now disappear in days or even hours, which is questionable. Another critical area affected is small and medium-sized enterprises that rely on cloud services, digital marketing, logistics platforms, and online payments, which are finding their operating costs spiralling without any justification. For many, the crux of the matter is that profitability is being quietly eroded, not by poor business decisions, but by the rising cost and unpredictability of connectivity.
The telecom operators, backed by the regulator, have responded with familiar explanations that have always favoured their unscrupulous and illicit activities, with the explanation that data, they say, depletes faster because of background applications, automatic updates, high-definition streaming, malware, faster networks, and users’ failure to manage device settings. Technically, these explanations are not false because modern smartphones are indeed data-hungry, and digital behaviour has evolved. But this defence, repeated endlessly, misses the deeper issue, as the fact is that the problem Nigerians are confronting is not simply that data is consumed; it is that the system governing how data is measured, billed, and explained is not transparent, hard to understand, unaccountable, and tilted entirely in favour of the service providers.
In Nigeria’s telecom market, operators are both the umpires and the players. They measure usage, bill customers, interpret anomalies, and adjudicate complaints, which does not create ground for fair play. Subscribers, on the other hand, are expected to accept consumption figures hook, line, and sinker, which they cannot independently verify. An unacceptable fact is that there are no universally accessible, third-party audited data meters that allow users to confirm what they have truly consumed in real time. Customers and service providers do not have equal access to information; this asymmetry creates fertile ground for silent overbilling, whether intentional or structural, and it erodes trust in a sector that should be built on transparency, not obscurity.
One critical aspect that must be addressed squarely is that the regulatory weakness compounds the problem. While the Nigerian Communications Commission possesses statutory authority, enforcement has often appeared slow, reactive, and insufficiently punitive. Penalties imposed on multinational firms with billion-dollar balance sheets rarely feel consequential. Investigations drag on, public disclosures are limited, and even when infractions are established, consumers seldom receive refunds. In such an environment, corporate restraint becomes optional. Where regulators lack teeth, corporations inevitably test boundaries.
The market structure itself offers little relief, as the market setup does not protect consumers. Nigeria’s telecom sector is effectively oligopolistic, dominated by a few large, powerful players with similar pricing models and limited incentive to compete on fairness. Tariff structures are deliberately complicated and complex, with multiple conditions and layered with bonuses, rollover conditions, expiry clauses, and promotional data that behaves differently from paid data. For the average subscriber, understanding these distinctions is exhausting. Complexity becomes a strategy, not an accident, reducing accountability while increasing revenue certainty for operators.
Though economic pressure on the telecom companies is real, and it must be acknowledged, knowing fully well that exchange rate volatility, energy costs, vandalism, and inflation have hurt profitability. Airtel’s revenue decline and MTN’s reported losses underscore the financial strain facing operators in Nigeria’s macroeconomic climate. It must be understood that corporate hardship does not justify consumer exploitation. The risk arises because multinational firms are subjected to pressure to meet global revenue targets and repatriate profits, adopt aggressive monetisation strategies in markets where regulation is weak, and consumer resistance is fragmented.
From experiences thus far, the human cost of this imbalance is becoming impossible to ignore. From students like Abiodun Yusuf, who spends most of his allowance on data that barely supports his academic needs, and also to small business owners like Cynthia Jude, whose online shop struggles to stay viable, the stories repeat themselves with unsettling consistency and outcomes. Families ration children’s screen time not out of discipline, but out of financial desperation. The adverse part that has continued is the widening of an already dangerous digital divide, as rural communities withdraw from digital platforms altogether because of exploitation.
Perhaps most telling is how quickly exploitation has been normalised in Nigeria. Many Nigerians now shrug and say, “That’s how it is.” This resignation is the greatest victory for an unfair system, and when people stop believing that fairness is possible, for this reason, exploitation becomes invisible, and abuse thrives without resistance.
Consumer advocacy groups like NATCOMS have begun to signal a shift in posture, including the possibility of court action. Labour unions have threatened boycotts. Civil society organisations warn of social and economic repercussions. These responses indicate that public patience is wearing thin. If left unaddressed, subscription apathy, however gradual, could ultimately undermine the very growth the telecom sector seeks to protect.
For a better understanding of what Nigeria faces is not merely a dispute over megabytes and tariffs, for clarity, it is a governance challenge that cuts across corporate ethics, regulatory independence, consumer empowerment and economic justice. A digital economy cannot thrive on distrust. Transparency and easily understandable data billing must become mandatory, not an aspirational goodwill promise. Independent audits should be public, regular, and credible. Complaint resolution mechanisms must be simplified, fast, and binding. Regulators must act not as mediators between equals, but as defenders of the public interest in an asymmetrical power relationship.
Equally important is consumer education, but awareness campaigns alone cannot substitute for structural reform. Digital literacy must go hand in hand with corporate accountability because the better it is understood that teaching users how to conserve data does not absolve operators from the responsibility to bill fairly and transparently.
At its core, the telecom debate reflects a large Nigerian dilemma, if not a broader problem in Nigeria, as corporate power has grown faster than institutional strength. Until regulators are truly independent and totally free from corporate and political influence, transparency is enforced by law, and consumers are recognised and treated not as passive revenue streams but as stakeholders with rights, exploitation will remain systemic rather than accidental or a series of isolated mistakes.
Communication is the bloodstream of modern society. When access to it becomes exploitative, the cost is paid not only in naira but in opportunity, dignity, and trust. Nigeria must decide whether its digital future will be built on fairness that respects consumers or allow it to rest on fatigue, frustration, and exploitation of users. The choice Nigeria makes will make more impact, and the answer will shape not just the telecom sector but the credibility of governance in an increasingly connected nation.
Blaise, a journalist and PR professional, writes from Lagos and can be reached via: [email protected]
Feature/OPED
Making Big Shifts: Why Africa’s Boldest Leaders Are Heading to Lagos

History has a way of rewarding leaders who recognise the moment they are in. There are seasons when refinement is enough, and there are moments when only reinvention will do. Africa’s business and leadership landscape is firmly in the latter. Economic pressures are redefining markets, technology is rewriting industries, and organisations are being forced to confront uncomfortable truths about relevance, resilience, and growth. It is within this context that the SHIFT Conference 2026 returns to Lagos, offering not just conversation, but direction.
Built around the theme Making Big Shifts, the conference speaks directly to leaders who understand that incremental progress is no longer sufficient. Across boardrooms and startups alike, leaders are being challenged to rethink how value is created, how people are led, and how institutions remain competitive in an increasingly complex global environment. SHIFT positions itself as a space for honest reflection and bold reimagination.
Curated by The Global Leadership Consultancy and founded by respected leadership thinker, Dr Sam Adeyemi, the SHIFT Conference has evolved into one of Africa’s most influential platforms for leadership and strategic thinking. Its focus is clear: to help leaders move beyond outdated assumptions and equip them with the mindset and tools required to thrive amid constant change. Dr Adeyemi has long maintained that leadership breakdown often begins not with execution, but with thinking. As he has noted, leaders cannot solve today’s problems with yesterday’s mindset, and meaningful transformation only begins when thinking shifts first.
Lagos, as Africa’s commercial heartbeat, provides a fitting backdrop for this conversation. The city’s pace, energy, and entrepreneurial drive reflect the realities leaders face daily. Following a landmark 2025 edition that attracted thousands and sparked wide-ranging conversations, the 2026 conference is expected to draw more than 4,000 participants from across Africa and the diaspora, spanning business, government, technology, finance, and the creative economy.
The speaker lineup underscores the depth of the gathering. The Chief Executive Officer, Global Leadership Consultancy, Dr Sam Adeyemi; Founder and CEO, Axxess, John Olajide and Founder and President of the Women of Destiny, Dr Nike Adeyemi, will anchor discussions that cut across leadership, enterprise, governance, and personal development. Through keynote addresses and interactive conversations, participants will be challenged to confront critical questions around scale, innovation, sustainability, and influence in a fast-evolving world.
Beyond the ideas shared on stage, the SHIFT Conference is intentionally designed as an immersive and practical experience. Attendees will engage in strategy-driven workshops, panel discussions featuring founders and technologists advancing sustainable innovation, and purposeful networking sessions that prioritise meaningful connections. Special experiences tailored for founders, CEOs, and senior executives further reinforce the conference’s focus on high-level decision-making and real-world application.
The credibility and growing influence of the SHIFT Conference are reinforced by the support of leading corporate and media partners, including Alpha Morgan Bank, BusinessDay, Patton Morgan, Jospong, and other institutional sponsors. Their involvement reflects strong confidence in the conference’s vision and its relevance to Africa’s leadership and business ecosystem.
At its core, SHIFT Conference 2026 responds to a defining question facing leaders today: how do you remain relevant in a world that refuses to stand still? The conference’s answer is clear: leaders must be willing to rethink assumptions, make bold strategic choices, and act with clarity and conviction.
For entrepreneurs seeking scale, executives reimagining strategy, public-sector leaders navigating reform, and professionals searching for direction, SHIFT offers more than inspiration. It offers perspective, practical insight, and a community of peers confronting similar challenges and choosing to lead differently.
As leadership continues to evolve, the decision facing many leaders is no longer whether change is coming, but how they will respond to it. That choice will take centre stage at the SHIFT Conference 2026 on Saturday, February 21, 2026, at Eko Hotels & Suites, Victoria Island, Lagos, where Africa’s next chapter in leadership thinking will be shaped.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn