Feature/OPED
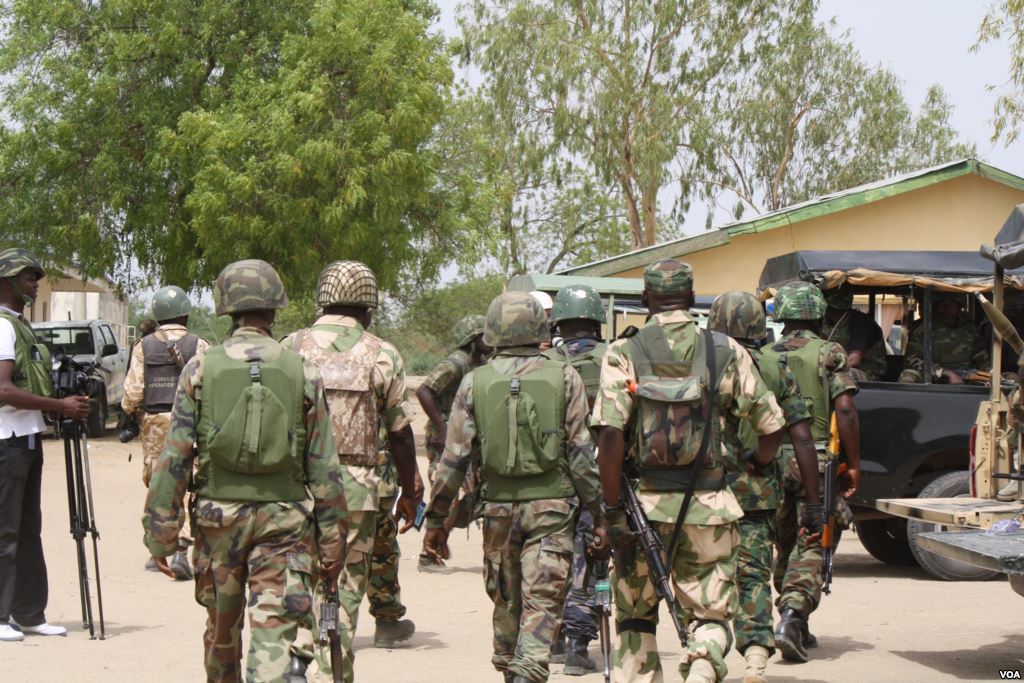
The Nigerian Army, A Journey of Great Strides in Eyes of Observers

By Odeyemi Oladimeji
Celebrating our Gallant Soldiers — While we all are asleep, these Heroes are Awake, making sure we all sleep very soundly.
A critical look at the Nigerian Army and the war against Terror
Many will undoubtedly recall that the Nigerian president, Muhammadu Buhari, upon inauguration, made it clear where his priorities lie — Winning the war against terror and returning the Nigerian Military to the very positive place of total professionalism. That was how it all started from the 29th of May 2015.
Hitherto and before this present administration took over in 2015, of a major hindrance to winning the war against Terror was the very disturbing reports of army mutiny, Indiscipline, various cases of violations of the codes of war.
Such a destabilizing and debilitating situation was what the new administration and the new military heads inherited… And there was a war on Terror that was very far from being won.
Professionalism and Ethics in the Army
Professions create their own standards of performance and codes of ethics to maintain their effectiveness…
And the Nigerian Army is not left out in this venture.
In practice, and in context, this means that not only must Soldiers maintain the Army’s effectiveness, it must do so within the law, and the standards and moral code that make up the professional military ethics…. And in a situation that the Army, prior to May 2015, had been accused of many things, including Human Rights violations, it was a near chaotic situation that was met.
Ethical Contrasts
There are stark contrasts between military ethics and those of other professions, however. For example, whereas conventional ethics may say, “First, do no harm to civilians,” but in an unconventional war in which there are no standard armies but guerrilla-like Terrorists who mingle freely with civilians and wear no uniforms, keeping to professional military ethics become very difficult and will encompass, training and retraining of the army personnel and soldiers to be compliant still with the required ethics of war.
It was therefore a very serious matter for the post-May 2015 Nigerian Army to immediately begin the process that have come to be seen as one of the most important factors, leading to the huge successes recorded so far in the war Against Terror.
Choosing The battles in a War
A battle is a combat in warfare between two or more armed forces, or combatants.
A war sometimes consists of many battles.
Battles generally are well defined in duration, area, and force commitment.
A battle with only limited engagement between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish…
And there lies the difference in this war against Terror in which the battles were very many and diverse.
First and foremost, there was the battle within, in which the soldiers themselves were demoralized — Weapons were in short supply and reinforcements too long on coming. The anger was steadily building and ethics became a huge casualty.
Wars and military campaigns are guided by strategy, whereas battles take place on a level of planning and execution known as operational mobility… It was therefore a different kind of battle that the army now had to face when, these very strategies of the army gets leaked to the enemy as soon as they were made and mobility made redundant as the location of the Nigerian troops were frequently revealed to the enemy.
Any War at all, is fighting and operates in a peculiar element of danger…But not when there were leaks in the lines of command and sabotage among the ranks..!
War is served by many activities quite different from mere conjectures, so that innocent lives and lives of troops will not be lost.
The task therefore was to Retool the Army and rework it from the way of Arbitrariness, all of which concern the maintenance of the fighting forces.
These preparatory activities were quickly incorporated and included into the Army, Post-May 2015.
The meaning of the Training and the Retraining earlier mentioned is this.
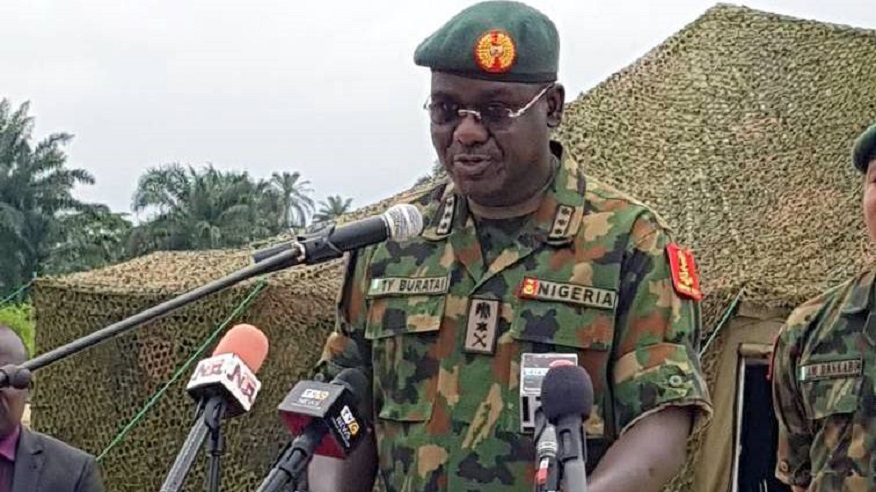
The new Army leadership under , Lieutenant General Tukur Yusufu Buratai clearly understands, The Art-of-Unconventional-war, the actual conduct of this war, because they immediately became concerned with the creation, training, and maintenance of the fighting forces….
The implications of having a new leadership and the rejuvenation of the Army in handling this war on Terror, properly, in the right manner, has by extension brought along with it the use of modern civilian compliant means, by which less and less reports of human rights violations and condemnation by international human rights observers, became considerably, reduced.
The good things about these new models is that, once they have been developed for the purposes of an unconventional war, and they are seen to have succeeded, a new Vista is opened in the annals of warfare in which future engagements can be based.
The Victories of the Nigerian Army over Terror.
The Nigerian Army has recorded a string of victories against the Terrorists as a direct result of the redirection, retraining and repositioning that have happened in the past 30 months…!
In recent times due to efforts being boosted by support from President Buhari
A concerted push by the rejuvenated Nigeria’s military, has regained considerable ground in the fight against the Boko Haram Terror Group.
As at this very day, the Nigerian Army has repelled Boko Haram from all local government districts in the Northeast….
What remains are a few skirmishes, ambushes and isolated suicide bomb attacks, aimed at soft targets and not at a whole local governments, districts, villages, towns and cities.
And, as they inch closer to total victory, the military men and officers fighting the war against the Boko Haram sect in the Northeast are in high spirit!
A few weeks ago the Nigerian Army killed about 15 Boko Haram terrorists in Gwoza, Borno state, and the people, took to the street to celebrate the military victory over the insurgency.
The Nigerian troops attached to “Operation LAFIYA DOLE” under the ongoing Operation Deep Punch in the North-east region have cleared all the Boko Haram Terrorists’ camps in various confrontations in the in the past 30 months whilst suffering minimal casualties in the process, capturing high calibre arms and ammunition, particularly in the Lake Chad region.
The Terrorists, have been cleared out, from their hideouts in Metele village, Tumbun Gini and Tumbun Ndjamena in Borno State.
During the clearance operations, Boko Haram terrorists abandoned the area in disarray, leaving behind livestock, large quantity of foodstuff, motorcycles and donkeys.
Also in Metele, and other place, the terrorists have been completely destroyed and their gun trucks and and other equipment, captured.
The Intelligence War on Terror.
The Gallant Nigerian troops also have made many discoveries of Terrorists’ logistics base at Tumbu Ndjamena which held stocks of fish, foodstuffs, fuel and motorcycles. All these items were promptly destroyed.
In all of these Intelligence work truly paid off as information gathering and effective civilian collaboration and handling have led the army to many of these victories… Sadly, some Nigerian troops paid the supreme price for securing the great peace and relief we all are enjoying today. Specifically, the high spirit among the troops that continues to define the cohesion and camaraderie that have led to these strings of successes.
The Human Rights Abuse allegation against the Nigerian Army.
Despite these strings of successes and the high morale, professionalism and ethics, restored into the Nigerian Army, there were not to be unexpectedly, a few allegations of human rights abuses against the Nigerian Army in her conduct of war against Terror.
And a responsive government of President Muhammadu Buhari rose to the task by the then Acting President, Prof. Yemi Osinbajo, releasing a statement to the effect that it is the responsibility of the Federal Government and the Armed Forces to ensure that the military conform with the international best practices on human issues.
Vice president Yemi Osinbajo as the Acting President then, stated this while inaugurating a nine-man presidential panel to review allegations of human right abuses by the military charged the panel to find out whether they carried out their duty diligently, impartially and with all sense of professionalism, in August of 2017.
He said, “It is the responsibility of the armed forces and those of us in government to ensure that we interrogate our own activities and ensure that those activities meet up to human rights norms and basic rules of decency observed across the world.”
The panel was given the mandate to review compliance of Armed Forces with human rights obligations and rules of engagement.
You may recall that in June, 2015, President Muhammadu Buhari directed the military to conduct an internal inquiry into allegations of rights abuses by its personnel.
The then Acting President also praised the Nigerian military saying “it is also a well – known fact that the conduct of the country’s defence and security forces during insurgency in the North East and militancy in the Niger Delta has in recent times attracted significant commendations.”
The members of the Panel were Hon. Justice Biobele Geogrewill who is appointed to serve as Chairman Maj. Gen. Patrick Akem, Olawale Fapohunda, Mrs. Hauwa, Jibrin Ibrahim, Mr. Abba A. Ibrahim, Mrs Ifeoma Nwakama, Dr. Fatima Alkali, Counsel to the Panel, while Mr. S. Halliru is the Secretary (OSGF)
Responding on behalf of other members of the panel the Chairman, Justice Biobele Georgewill assured they will put in their best in order to uphold the confidence reposed on them by the government.
The panel sat in the geopolitical zones and cases even as far back as 2007 were brought to the fore.
The one good and interesting thing is the openness under which the whole exercise was conducted.
No one was barred, including notable human rights lawyers were also made submissions.
Boko Haram suspects were also allowed to make their inputs, that altogether, a very thorough job was done by the panel on the laudable platform of determining the credible claims from the spurious ones… The task was completed without a hitch with no glitch in November of 2017.
Though the report is yet to be released, the report citing Army/Nigerian relations in the last two years will no doubt be favourable.
Improved Army/Civilian Relations.
It is pertinent to make a reference to the period of Nigeria’s independence to date, in determining how far the nation has gotten with managing the Military/Army/Civilian relations.
After independence, the Nigerian Military, especially the Army, gave a good account of itself by rescuing the country from the precipice. And this happened not just once but several times because we had internal security problems in Nigeria, some of which are as a result of the deficiencies of other security agencies in the country. So, it has always been the Nigerian military that rises to the occasion. We must give it to them. They did a lot during the Civil War; we should commend them for that. Again we had situations of insurgency and they have done wonderfully well.
However, the situation started to change, when the military became active in politics….
Military involvement in politics has somewhat since then, made them antagonistic to the civil population.
This perception has waned only a little since the beginning of the 4th Republic in 1999.
In recent years, the Army/Civilian relations has been somewhat low-keyed, especially during the years the Boko Haram Terror held sway.
Undoubtedly also, the clear and detailed army victories against Terror have brought a new resurgence in the otherwise low-tide of checkered relations in which the people’s confidence and empathy have started to rise again.
Nigerians now celebrate great victories and also deeply mourn their fallen heroes wherever and whenever our Gallant Soldiers pay the Supreme price of service to fatherland with their lives.
And lately, we are seeing a lot of modest changes within the military from 2015 to date.
They have done a lot to improve the Army/Civilian relations to ensure that their professional calling is done within the ambit of the law, with respect to human rights, due process and professionalism.
In this regard the military is becoming professional, is maturing, becoming much more advanced and is fixing itself very well.
Lately also, the Nigerian Army is doing some programmes to ensure that the common man is made to appreciate the activities of the military….
Civilian Schools are incorporated into the Civil/military Healthcare delivery system. And also in tackling crimes of kidnappings and armed robberies.
In Truth Army/Military/Civilian conflicts happen everywhere in the world. Therefore, bridging the gap between the common man and the military is desirable even though it will take some time.
Worthy of note also in the rescue of nearly 50% of all the kidnapped Chibok girls, by the Nigerian Army.
First, it was 21 girls out of the 240 kidnapped. Then 81 girls at a go.
And random numbers in twos and threes and the 107th Chibok Girl, Salomi Pagu just rescue only a few days back.
A conclusion
Concluding this article, must rest on the commitment of the Army, to service, which anchors on safely International Core Values of the military.
The core values of all the military services, including the army, reflect honour, courage, integrity and a commitment to the ideals upon which the nation’s core values are based.
The Nigerian Army presents these values as loyalty, duty, respect selfless service, honour, integrity and personal courage. The other services too, consolidate these same ideals.
The responsibility of carrying these ideals into the battlefield and exercising same among civilians is a function of Leadership. And this is where leading from the front has become the watchword of the rejuvenated Nigerian Army.
A war is not a fair exercise, it is neither fun or always necessary…. But it happens, in order to defend a Nation and secure its peace.
Military ethics require war to be just, however. The philosophical theory of the just war requires war to be the last result. These are the very words and attitude displayed by the present Nigerian Army leadership. It is only then a war is deemed a just war, and it is then fought to correct a wrong, just as the Nigerian Army is doing fighting the war on terror.
The goals of The Nigerian Army, is to establish peace, not continue violence unnecessarily. Excessive violence is unacceptable and civilians must not be the deliberate targets of violence — That is the message from the Chief of Army Staff, Lieutenant General Tukur Yusufu Buratai.
Comrade Oladimeji Odeyemi, A Counter terrorist analyst and a Security Expert, is the Convener of the Coalition of Civil Society Groups against Terrorism in Nigeria sent this piece from Ibadan, Oyo State.
Feature/OPED
Piracy in Nigeria: Who Really Pays the Price?

Ever noticed how easy it is to get a movie in Nigeria, sometimes before or right after it hits cinemas? For decades, films, music, and series have circulated in ways that felt almost natural; roadside DVDs, download sites, and streaming hacks became part of how we consumed entertainment. It became the default way people experienced content.
But what many don’t realise is that what feels normal for audiences has real consequences for the people behind the screen. As Nigeria’s creative industry grows into a serious economic force, piracy isn’t just a “shortcut” anymore; it’s a drain on the very lifeblood of creativity.
The conversation hit the headlines again with the alleged arrest of the CEO of NetNaija, a platform widely known for downloadable entertainment content. Beyond the courtrooms, the story reopened an important question: how did piracy become so normalised, and why should we care now?
Filmmaker Jade Osiberu put it into perspective in a post that resonated across social media: for many Nigerians, pirated CDs and downloads were simply the most accessible way to watch films. Piracy didn’t just appear from nowhere. It grew because legal options were limited, streaming platforms scarce, and affordability a challenge. In other words, piracy is as much a story about opportunity and access as it is about legality.
The cost of this convenience is real. Every illegally downloaded or shared film chips away at revenue that sustains the people who create it. Producers risk their own capital to tell stories, actors and crew rely on fair compensation, and distributors and cinemas lose income when pirated copies hit screens first. Over time, this doesn’t just hurt profits; it erodes confidence in investing in new projects and threatens the ecosystem that allows Nigerian creativity to flourish.
Piracy is also about culture and necessity. Many audiences never intended harm; they simply wanted stories in a system that didn’t always make legal access easy. Streaming services were limited or expensive, internet access was spotty, and distribution was weak outside major cities. Piracy became the default, and generations grew up seeing it as normal. But what was once a practical workaround has now become a barrier to sustainable growth.
This is where enforcement comes in. Legal action, like the NCC’s intervention against NetNaija, isn’t about pointing fingers at audiences; it’s a reminder that creative work has value and that infringement carries consequences. It’s about sending the message that the people who write, produce, act, and edit these stories deserve protection. Enforcement alone isn’t enough, though. Without accessible, affordable legal alternatives, audiences will naturally gravitate back to piracy.
The bigger picture is this: Nollywood is no longer just a local industry. It’s a global player, employing thousands, creating cultural influence, and generating revenue across multiple sectors. Its growth depends not just on talent, but on a system that rewards creators, protects their work, and builds a sustainable ecosystem.
Piracy may have been normalised in the past, but its consequences today are impossible to ignore. It threatens livelihoods, investment, and the future of stories that define Nigeria culturally and economically. Understanding its impact isn’t about shaming audiences or vilifying platforms; it’s about valuing the people behind the content, the stories themselves, and the industry’s potential.
The real question isn’t just whether piracy is illegal. It’s whether Nigeria is willing to build an entertainment ecosystem where creators thrive, stories get told properly, and audiences can enjoy them without undermining the very people who made them possible. Until that happens, the cost of convenience will keep being paid by someone else, and it’s the people who create the magic.
Feature/OPED
The Economics of Middle East Tension and Impact on Livelihoods

By Timi Olubiyi, PhD
The ongoing tensions in the Middle East may seem geographically distant from Nigeria, but the economic effects are already being felt in very real and personal ways across many countries, including Nigeria, even though light at the moment. For ordinary Nigerians, the impact shows up in rising fuel prices, which are already happening. So, we may be experiencing increased transportation fares, higher food costs, and a volatile naira if the unrest continues. Remember, the electioneering and campaign season is almost here politicians may face a far more complex environment than in previous cycles. With the current reality, voters may have less patience, interest and may be more economically stressed, and more focused on immediate survival than long-term projections, which the elections stand for.
The first and most immediate effect of global tension anywhere is usually a spike in crude oil prices due to fears of supply disruption. Ordinarily, this should appear like a positive impact for Nigeria as an oil-exporting country because higher oil prices should increase government revenue, but the benefit is often limited by our production challenges, oil theft, pipeline vandalism, and largely the pegged Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) output quotas. In reality, Nigeria may not produce enough oil to fully take advantage of the high prices that may arise. At the same time, higher global oil prices generally increase the cost of imported refined fuel, shipping, insurance, and manufactured goods. Since Nigeria still imports a dominant and significant portion of what we consume from abroad, these higher global costs may quickly translate into domestic inflation if the trend continues, and this can happen because it is an external force beyond control. The result will be painful, though small businesses will struggle even more with operating expenses, transport costs, and transaction costs will climb further. Already, many households are battling many challenges,s but the current reality will have their purchasing power shrinking even more. Inflation in Nigeria is not just a statistic; it is the daily reality of families and businesses who must continue to spend even more for the same needs and services. In an economy where food inflation is already high, any additional imported inflation would worsen hardship and deepen poverty levels.
Another major effect is on foreign exchange stability, and campaign financing itself could also be affected in the coming elections if the global tension is not tamed early enough. Whenever global tensions rise, investors move their funds to safer markets, and this often weakens emerging market currencies, and the Naira is not immune. A weaker naira makes imports even more expensive, which could further fuel inflation. It may also increase the cost of servicing Nigeria’s external debt, putting more pressure on government finances. The global uncertainty that we will experience in the coming weeks to months may likely reduce foreign portfolio investment in Nigerian equities and bonds. Investors may prefer to wait and see how things unfold. This cautious sentiment would slow capital inflows to the capital market and into our economy, and the outcome is better imagined. Companies that rely heavily on imported raw materials are especially vulnerable to exchange rate volatility that will come with the current reality.
If tensions in the Middle East escalate further, for instance, through a broader regional conflict involving major oil producers or a prolonged disruption of key shipping routes, oil prices may even surge further sharply, global inflation could intensify, and financial markets could become more volatile. In such a scenario, Nigeria might see temporary revenue gain,s but inflation could accelerate faster than income growth in my opinion. The naira could face renewed pressure, and interest rates might remain high as monetary authorities attempt to control inflation. Poverty levels could worsen in real time because, as real wages fail to keep pace with rising prices, the number of people living below the poverty line increases. Youth unemployment, already a concern, may increase if businesses cut back on hiring due to uncertainty or think of reducing staff numbers. In extreme cases, prolonged global instability could even disrupt remittance flows and compound domestic economic stress when expectations are not met.
However, within this difficult environment lies an opportunity. Global instability reinforces an important lesson: Nigeria must reduce its vulnerability to external shocks. Overdependence on crude oil exports leaves the country exposed to geopolitical events thousands of kilometres away. True resilience will come from diversification of the revenue base. The government must accelerate investment in local refining capacity to reduce dependence on imported petroleum products. Strengthening domestic agriculture is critical to reducing food imports and improving food security, but most important ensure security. Supporting small and medium enterprises as well, through access to credit, low-interest loans and infrastructure can stimulate local production and job creation. Fiscal discipline is also essential; any windfall gains from higher oil prices should be saved in stabilisation funds, invested in infrastructure, education, healthcare, and technology, rather than consumed through recurrent expenditure. Strengthening foreign exchange management through improved export diversification, including non-oil exports such as agro-processing, solid minerals, and services, will help stabilise the naira over time.
For businesses, the path forward requires adaptation and sourcing all required resources locally where possible, hedging against currency risks, investing in energy efficiency, and building financial buffers. The era of predictable global markets is over; volatility is becoming the norm rather than the exception.
Ultimately, the unfolding tensions in the Middle East serve as both a warning and a call to action for Nigeria. The warning is clear: as long as the economy remains heavily tied to crude oil exports and imports of essential goods, distant conflicts will continue to shape domestic hardship. The call to action is equally clear: build a more diversified, production-driven, and self-reliant economy. If tensions escalate, Nigeria will feel the shockwaves through higher inflation, higher cost of fuel pump price, currency pressure, and deeper poverty. But if reforms are sustained and strategic investments prioritised, Nigeria can transform global uncertainty into a catalyst for structural change. The future will depend not on whether oil prices rise or fall, but on whether Nigeria uses each episode of global tension as an opportunity to strengthen economic resilience, protect vulnerable citizens, and build a stable foundation for long-term growth and prosperity. Good luck!
How may you obtain advice or further information on the article?
Dr Timi Olubiyi is an expert in Entrepreneurship and Business Management, holding a PhD in Business Administration from Babcock University in Nigeria. He is a prolific investment coach, author, columnist, and seasoned scholar. Additionally, he is a Chartered Member of the Chartered Institute for Securities and Investment (CISI) and a registered capital market operator with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). He can be reached through his Twitter handle @drtimiolubiyi and via email at dr***********@***il.com for any questions, feedback, or comments. The opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the author, Dr Timi Olubiyi, and do not necessarily reflect the views of others.
Feature/OPED
Another Oil Boom: Will Nigeria’s Government Turn Windfall into Growth or Squander it?

By Blaise Udunze
The past recurring conflicts on other continents and the current developments in the Middle East are a clear reminder to the world that energy markets are deeply linked to conflict and uncertainty, as experienced across the globe today. The rise in geopolitical tensions with Iran, Israel, and the United States has led to a sudden increase in global crude oil prices. Some individuals may question what business the war has with Nigeria. Economically, yes, as one of Africa’s major oil producers, Nigeria finds itself in a delicate position amid the current global situation. Since it can gain financially when global crude oil prices skyrocket and this is so because the same increase can create economic challenges locally. The price of Brent crude has jumped to $109.18 per barrel, crossing the $100 mark for the first time in more than five years.
The country is getting a temporary fiscal boost, knowing fully well that prices now surpass the benchmark used in the 2026 national budget. The high oil prices gain is further amplified by two major domestic policy shifts, as the first is the removal of fuel subsidy projected to free nearly $10 billion annually for public investment, and a new Executive Order by President Bola Tinubu aimed at boosting oil and gas revenues flowing into the Federation Account by eliminating wasteful deductions allowed under the Petroleum Industry Act. The combination of these developments could significantly increase government revenue over the next few years, but history shows that such windfalls, if not well managed, often go toward short-term spending rather than creating lasting national wealth.
Moreover, our lingering concern today is that Nigeria as a country has experienced this pattern before, and it often brings instability. One of such examples is the 2022 Ukraine conflict, when oil prices spiked above $100 per barrel.
Obviously, during such a period, countries that export oil will suddenly receive a large and sudden increase in revenue from the sale of crude oil. The truth is that if such a windfall is managed well, it can be used to build stronger and diversify their economies beyond oil. Unfortunately, Nigeria has always told a different story as these opportunities were frequently lost to weak fiscal discipline, rising recurrent expenditure, and limited investment in productive assets. The global conflict, in its real sense, could become an opportunity, even though there are risks inherent. Just like any prudent country, Nigeria can use any short-term benefits (like higher oil revenues) to strengthen its economy for the future.
At the heart of this opportunity lies the need for disciplined fiscal management, if the government will tread in line with this call. It is now time for the policymakers to understand that extra money from oil prices should not be wasted, as it has become a tradition to spend through the regular government expenditures. It is high time the government saved and invested the extra funds it gained wisely rather than spending them all immediately. Nigeria’s fiscal vulnerability has often been exposed whenever oil prices fall or global demand weakens. Establishing strong buffers through sovereign savings mechanisms can protect against such volatility. A significant portion of the windfall should therefore be directed into strengthening the country’s sovereign wealth structures and stabilisation funds. This resonates with our subject matter: Can Nigeria convert Oil Windfall into Economic Strength? This rhetorical question is directed to those at the helm of affairs because, by saving during periods of high prices, Nigeria can build reserves that help sustain public spending during downturns without excessive borrowing.
Closely linked to fiscal buffers is the issue of public debt. Nigeria’s debt servicing obligations have continued to rise in recent years, and the current development might be the answer. The debt has continued to place pressure on government revenues and limit fiscal flexibility. Alarming is the fact that the public debt is projected to have surpassed N177.14 trillion by the end of 2026, which is driven by the budget deficit in the 2026 Appropriation Bill.
The truth is that one sensible response to the current situation would be to use some of the unexpected revenue from higher oil prices to pay off loans (debts), especially those with high interest costs. This would reduce future financial burdens on the government and help it spend on development later. The fact is that debt reduction, if the government can quickly address it, also signals fiscal credibility to investors and international financial institutions, thereby strengthening the country’s macroeconomic reputation.
Beyond fiscal stability, Nigeria must recognise that oil windfalls provide a rare opportunity to accelerate strategic infrastructure investment. In today’s world, infrastructure remains one of the most critical constraints on Nigeria’s economic growth. The cost of doing business in Nigeria has been a serious palaver, and it has continued to discourage and scare investment. This is informed by various structural deficiencies, such as inadequate electricity supply and congested transport corridors, as well as weak logistics networks. The question again, can Nigeria convert Oil Windfall into Economic Strength? This is because the truth is not unknown to leaders, but they have continued to deliberately stay away from the fact that channelling windfall revenues into transformative infrastructure projects can therefore yield long-term economic dividends.
Power sector development should be a top priority. Reliable electricity remains the backbone of industrial productivity and economic expansion. Over the years, a well-known fact is that despite various reforms, Nigeria continues to struggle with an epileptic power supply that forces businesses to rely heavily on expensive diesel generators and has posed a double challenge that comes with noise and atmospheric pollution. The nation is tired of the regular audio investment, but strategic investment in power generation, transmission, and distribution infrastructure would significantly reduce operating costs for businesses that translate into manufacturing and encourage new investment across multiple sectors in the country.
Transportation infrastructure also deserves sustained attention, and if nothing is done, the mass commuters will reap nothing but pain. Nigeria’s highways, rail networks, and ports require large-scale modernisation to support efficient trade and mobility. The unexpected extra income from high oil prices, if used carefully for long-term national benefit, can be used to build transport networks that move food and goods from farms and factories to markets and ports. Businesses today are very much dependent on transportation; hence, improved logistics not only facilitates domestic commerce but also strengthens Nigeria’s position as a regional economic hub in West Africa.
Another critical area for deploying oil windfalls is economic diversification. The over-emphasised dependence of Nigeria on crude oil exports has long exposed the economy to external shocks.
Any rise or fall in global oil prices has an immediate impact on Nigeria’s government revenue since oil exports are a major source of government income, foreign exchange availability, and macroeconomic stability follow suit. To break this cycle, Nigeria must invest aggressively in sectors capable of generating sustainable non-oil income and abstain from the unyielding roundtable discussion of diversification without implementation.
With vast arable land and a large labour force, Nigeria has the capacity to become a global agricultural powerhouse; hence, this is to say that agriculture offers enormous potential in this regard. However, productivity remains constrained by limited mechanisation, inadequate irrigation, and poor storage facilities. If the government intentionally invests in modern agriculture and the systems that support it, the country can produce more food, create jobs via agricultural value chains (from production to processing, storage, transportation, and marketing), while earning more from agricultural exporting.
Manufacturing and industrial development represent another pathway to long-term economic resilience, but this sector has been starved of any tangible investment. Unlike Nigeria, countries that successfully convert natural resource wealth into sustainable prosperity typically invest heavily in industrial capacity. The government should be deliberate in using the extra revenues from the high oil prices to invest in building industrial zones, strengthening hubs, and encouraging the transfer of technologies that will fast-track the production of goods within Nigeria, instead of relying on imports. The unarguable point is that the moment Nigeria invests in industries and production of goods locally instead of buying them from other countries, it becomes better able to manufacture and export products that have higher economic value.
One critical aspect that calls for concern is that strengthening Nigeria’s foreign exchange reserves represents another important avenue for deploying excess oil revenues. The truth, which applies to every economy, is that adequate reserves enhance the country’s ability to stabilise its currency during external shocks and support the operations of the Central Bank of Nigeria in maintaining monetary stability, and this part must not be treated with kid gloves. Given Nigeria’s history of foreign exchange volatility, this is another opportunity to know that building strong reserves can significantly improve investor confidence and macroeconomic resilience.
Human capital development must also remain central to any long-term strategy for managing oil windfalls. A country’s greatest asset is not merely its natural resources but the productivity and innovation of its people, and in Nigeria, more attention has been placed on the former. For so long, Nigeria’s budget allocation has told this story, as the government has been glaringly complacent in investing in quality education, healthcare systems, technical training, and research institutions, which can unlock enormous economic potential. If the government aligns with the necessities, Nigeria’s youthful population represents a demographic advantage that can only be realised through sustained investment in human development.
Investment from the higher oil prices should be channelled to the educational sector, and more emphasis should be placed on science, technology, engineering, and vocational skills that align with the demands of a modern economy. Strengthening universities, technical institutes, and research centres can foster innovation, entrepreneurship, and technological advancement. Similarly, improving healthcare infrastructure enhances workforce productivity and reduces the economic burden of disease. Will the government ever shift reasonable investment to these sectors?
Another strategic use of all the categorised oil windfalls is the expansion of social protection systems that shield vulnerable populations during economic shocks. What is unbeknownst to the government is that while infrastructure and industrial investments drive long-term growth, social protection programs help ensure that economic gains are broadly shared. Helping the poor, creating jobs for young people, and supporting small businesses can make society more stable and grow the economy from the ground up.
Lack of transparency and accountability has been anathema that has hindered the progress of growth in Nigeria. The right implementation will ultimately determine whether Nigeria successfully transforms this oil windfall into lasting prosperity. Public trust in government fiscal management has often been undermined by corruption, waste, and non-transparent financial practices. Once there are clear frameworks for managing windfall revenues, this becomes essential. Also, if it is monitored by neutral institutions that are not controlled by politicians, while information about spending is made available to the populace, the media, and the National Assembly supervises how the funds are spent, it will translate to what benefits the country instead of short-term political interest.
A section of the economy that calls for action is the need to improve the efficiency of government institution capacity within agencies responsible for revenue management, budgeting, and project execution. It is a well-known fact that when government institutions are strong and effective, public money is less likely to be wasted, stolen, or misused, and investments produce measurable economic outcomes. This institutional strengthening should include digital financial systems, procurement transparency, and improved project monitoring mechanisms.
Nigeria’s policymakers must immediately put in place clear fiscal rules governing the use of oil windfalls. This will help define how excess revenues are distributed between savings, infrastructure investment, debt reduction, and social programs, and this will also help Nigeria prevent the politically driven spending patterns that have historically undermined effective resource management.
Another question confronting Nigeria is not whether oil prices will rise again in the future, but whether the country will finally break the cycle of squandered windfalls. It is to the country’s advantage that the current crisis has pushed oil prices above the budget benchmark, creating a temporary revenue advantage, but it must be noted that temporary advantages become transformative only when they are guided by deliberate policy choices and long-term vision.
Nigeria possesses immense economic potential. With a large domestic market, abundant natural resources, and a vibrant entrepreneurial population, the country is well-positioned to achieve sustained growth. This potential requires disciplined management of national wealth, particularly during periods of resource windfalls.
The common saying that a word is enough for the wise is directed to policymakers to understand that, if managed wisely, the current surge in oil revenues could strengthen fiscal buffers, modernise infrastructure, diversify the economy, and invest in human capital. The obvious here is that the investments would not only protect Nigeria against future oil price volatility but also lay the foundation for a more resilient and prosperous economy.
The lesson from global experience, as it has always been, is that resource windfalls do not automatically translate into national prosperity. Nigeria’s leaders must understand that, without exception, countries that succeed are those that convert temporary commodity gains into permanent economic assets. Nigeria now stands at such an intersection, which requires turning crisis-driven oil gains into strategic investments; the nation can transform a moment of geopolitical turbulence into an opportunity for lasting economic resilience and national wealth.
Blaise, a journalist and PR professional, writes from Lagos and can be reached via: bl***********@***il.com
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn