Economy
MPC Meeting: Experts Predict Rate Cut to 13%

Modupe Gbadeyanka
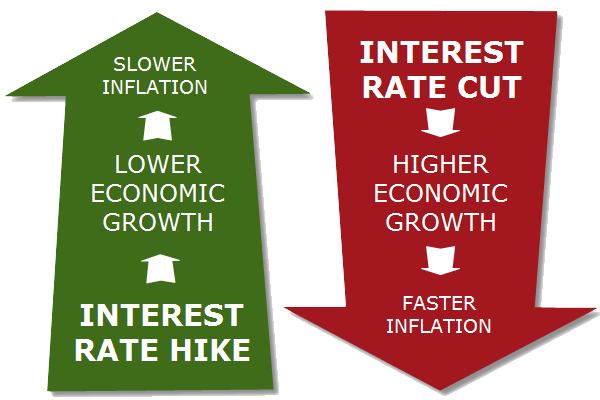
As the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meeting of the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) commences today, experts at FSDH Research are optimistic that the committee will likely support the reduction in the Monetary Policy Rate (MPR) by 50 basis points.
At its last meeting on May 20 and 21, 2019, the MPC retained the benchmark interest rate at 13.50 percent, and retained the asymmetric corridor of +200/-500 basis points around the MPR.
It also left both the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) at 22.5 percent; and the Liquidity Ratio (LR) at 30 percent.
Within the last few weeks, the CBN has issued two important directives to banks within geared towards stimulating lending to the real sector of the economy to boost economic activity.
In its report, FSDH Research said members of the MPC will likely vote to reduce the policy rates because an increase was not an option under the current economic situation in the country.
It said the short-term outlook of the inflation rate (which points to a declining trend, other things being equal), stability in the foreign exchange rate, and the drive of the Federal Government of Nigeria (FGN) and the CBN to stimulate growth in the economy all support a rate cut.
The investment firm said such a cut would add weight to the implementation of the CBN’s 5-year strategic plan.
“FSDH Research anticipates a 50 basis points reduction in the Monetary Policy Rate (MPR), as well as a possible adjustment to the asymmetric rates around the MPR,” the report said.
It noted that developments in the global economy also favour an interest rate cut in the short-term and expects the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) of the US Federal Reserve System to lower the Federal Funds Rate by 0.25 percent at its next meeting later this month.
The firm explained that this would aim to provide additional incentive for the global economy following signs of economic slowdown.
In the June 2019 edition of its Global Economic Prospects (GEP), the World Bank downgraded the global growth forecast for 2019 by 0.3% to 2.6 percent. The downward revision reflects weaker-than-expected international trade and investment during the first half of the year. The growth in sub-Saharan Africa was also significantly lower than expected. The 2019 growth forecast for Nigeria is now 2.1%, lower than the previous forecast of 2.2 percent.
According to FSDH Research, the short-term forecast indicates that the inflation rate in Nigeria may continue to trend downwards until October 2019. This is based on the assumptions that there will be no adjustments to the electricity tariff or the pump price of Premium Motor Spirit (PMS).
“Although we stress that there is a need for these prices to increase, the FGN may not be keen to an adjustment in the short-term.
“Should the increase take place, our projections show that it will shift the inflation curve by 2.5 percent. The impact of the implementation of the new National Minimum Wage on the inflation rate is minimal. Implications of the foregoing are that there may not be pressure on the MPC to raise the policy rate with a view to taming inflationary pressure.
“The CBN is already adopting moral suasion to encourage investment in agriculture to boost production and yields in an attempt to douse a spike in food prices which would place upward pressure on the inflation rate,” it said.
A major pressure point for the FGN at the moment is the high interest expenses relative to FGN revenue. Although the major cause of this problem is government’s low revenue, the low interest rate environment since January 2019 has helped the Debt Management Office (DMO) to raise cheaper debt for the government than before. Unless there is internal or external shock, CBN policies may continue to favour a low interest rate. This may also stimulate lending to non-oil sectors of the economy, provided there are complementary fiscal policies which will improve the business environment.
The negative impact of low growth in the global economy on the price and demand of crude oil may have a negative impact on the exchange rate.
“However, the current external reserve position at over $45billion may provide short-term stability for the exchange rate. In its July 2019 Short-Term Energy Outlook (STEO), the Energy Information Administration (EIA) revised downwards its forecast for Brent crude oil price to $66.51/b in 2019. The data shows that the price of crude oil fell from a peak of $77.06/b in May 2019 to $64.12/b in June.
“We also note that an increase in policy rate may not address the crude oil price. Intervention by the
Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) in the way of a production cut may also provide short-term stability for the crude oil price.
“While FSDH Research notes there are a number of structural challenges in the economy at the moment that can reduce the effectiveness of monetary policy, there are strong indications that the MPC members may vote to reduce the MPR to 13 percent.
“The market should not be surprised if the MPC also announces a reduction in the rate of the Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) of the banks with the CBN. It is possible that the MPC will maintain the Liquidity Ratio and CRR at the current level,” the report said.
Economy
Dangote Cement Assures African Consumers Sufficient Supply With 90MT Yearly

By Aduragbemi Omiyale
Leading cement maker, Dangote Cement Plc, has reaffirmed its commitment to making Africa fully self‑sufficient in cement production by raising its output to 90 million metric tonnes per annum by 2030 from the current 52 million metric tonnes per annum.
The chief executive of the firm, Mr Arvind Pathak, during a strategic briefing on the company’s expansion drive, disclosed that efforts are being made to accelerate investments across African markets to close supply gaps and support the continent’s infrastructural ambitions.
According to him, the organisation is strengthening the continent’s industrial backbone and reducing reliance on imported construction materials, stressing that, “Our vision is clear — to ensure Africa produces enough cement to meet its own needs…Through continuous expansion, operational excellence, and a strong distribution network, we are positioning Dangote Cement to power growth across the continent. We are not just building a business; we are building Africa’s future.”
“Through our collective determination, we have eliminated Nigeria’s dependence on imported cement and transformed the country into a net exporter of cement to several neighbouring nations,” Mr Pathak added.
Dangote Cement currently operates in multiple African countries, with integrated plants, grinding facilities, and distribution hubs strategically located to serve diverse markets.
The company’s ongoing projects include plant upgrades, capacity expansions, and the introduction of advanced energy‑efficient technologies designed to reduce operational costs and carbon footprint.
Reinforcing the company’s long-term vision, its founder, Mr Aliko Dangote, described self-sufficiency as both an economic imperative and a continental responsibility.
“Africa has no reason to depend on cement imports. We have the raw materials, the talent, and the determination. Our goal at Dangote Cement is to unlock Africa’s potential by ensuring that every nation on this continent can access affordable, high‑quality cement produced within Africa. This is how we build prosperity, job opportunities, and sustainable development,” the businessman stated.
Mr Dangote added that the company’s investments reflect its passion for unlocking continental competitiveness and fostering industrialisation across Africa.
With major infrastructural projects rising across African cities — from highways and bridges to housing developments — the demand for cement continues to grow. Dangote Cement’s renewed push toward continental self‑sufficiency is expected to address supply challenges, stabilise prices, and enhance construction reliability in the years ahead.
Economy
NASD OTC Bourse Appreciates Further by 0.46%

By Adedapo Adesanya
The NASD Over-the-Counter (OTC) Securities Exchange appreciated by 0.46 per cent on Friday, February 6, with the market capitalisation expanding by N10.2 billion to N2.207 trillion from the N2.197 trillion quoted in the previous session, while the NASD Unlisted Security Index (NSI) grew by 17.06 points to 3,689.72 points from the previous session’s 3,672.66 points.
The expansion was buoyed by the price appreciation recorded by two securities, which overpowered the declines recorded by four securities.
Central Securities Clearing System (CSCS) increased its value during the session by N4.83 to N53.50 per unit from N48.67 per unit, and IPWA Plc gained 19 Kobo to sell at N2.36 per share versus Thursday’s closing price of N2.17 per share.
On the flip side, Okitipupa Plc lost N10.77 to trade at N220.00 per unit compared with the previous price of N230.77 per unit, FrieslandCampina Wamco Nigeria Plc depreciated by N3.10 to N60.00 per share from N63.10 per share, Geo-Fluids Plc shed 45 Kobo to close at N4.30 per unit versus N4.75 per unit, and Industrial and General Insurance (IGI) weakened by 5 Kobo to 54 Kobo per share from 59 Kobo per share.
A look at the trading data showed that there was a 67.9 per cent drop in the volume of trades to 384,784 units from 1.2 million units, but the value of transactions went up by 33.5 per cent to N16.1 million from N12.0 million, and the number of deals increased by 4.4 per cent to 24 deals from 23 deals.
CSCS Plc ended the day as the most traded stock by value on a year-to-date basis with 16.3 million units exchanged for N667.6 million, followed by FrieslandCampina Wamco Nigeria Plc with 1.8 million units sold for N117.9 million, and Geo-Fluids Plc with 12.4 million units worth N79.5 million.
CSCS Plc also closed the session as the most active stock by volume on a year-to-date basis with 16.3 million units valued at N667.6 million, followed by Mass Telecom Innovation Plc with 13.7 million units worth N5.5 million, and Geo-Fluids Plc with 12.3 million units traded for N79.5 million.
Economy
CAC Deregisters 400,000 Inactive Businesses in 2025

By Adedapo Adesanya
The Corporate Affairs Commission (CAC) has deregistered more than 400,000 inactive companies from the corporate registry in 2025 as part of reforms aimed at strengthening transparency, protecting the economy and restoring investor confidence.
The Registrar-General of the CAC, Mr Hussaini Magaji, disclosed this on Saturday in Abuja during the commission’s monthly fitness walk, which was organised as part of the activities marking its 35th anniversary.
Mr Magaji said the affected entities were largely companies that had failed to file statutory annual returns for years and were no longer operational, warning that such firms posed serious risks to economic integrity.
He said, “In 2025 alone, we deregistered over 400,000 companies from our records. These were largely companies that had become inactive and failed to meet statutory obligations, including filing annual returns.
“Such entities pose threats to economic operations. Cleaning up the register was necessary to build confidence and ensure that Nigeria has a credible and reliable corporate registry,” he stated.
Mr Magaji explained that a transparent and up-to-date register was critical to attracting both local and foreign investment, as well as preventing the misuse of corporate structures for illicit activities.
The CAC boss described the anniversary fitness walk as symbolic, noting that it reflected the commission’s resilience, teamwork and institutional evolution since its establishment in 1991.
He recalled that the commission began operations as a largely manual agency, once confined to a single office in Garki, Abuja, but has since evolved into a fully digital, end-to-end service provider with global reach.
“The CAC has come a long way, from manual operations in one location to a fully digital organisation. Today, our services are available anywhere, anytime, 24/7. We are the only government agency providing end-to-end digital services,” he stated.
According to him, the commission’s digital transformation has significantly supported the Federal Government’s ease-of-doing-business reforms, eliminating the need for physical visits to CAC offices to register or manage businesses.
“You can register and manage your business from your room without stepping into any CAC office. That is what ease of doing business truly means,” he added.
As part of its support for small businesses, Mr Magaji disclosed that the commission partnered with the Small and Medium Enterprises Development Agency of Nigeria to facilitate the free registration of 250,000 MSMEs in 2025.
He explained that the registrations were deliberately channelled through SMEDAN to ensure beneficiaries also received training and capacity-building support, adding that improved welfare, timely payment of entitlements and clear career progression had boosted staff morale and service delivery.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism9 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn